Each segment on the ECG has its own purpose. The first wave of small amplitude is called the P wave, and reflects depolarization and arousal of the atria.
Record content:
- 1 Types and significance of ECG waves
- 2 Where and how to find the P wave on the ECG
- 3 Normal duration (width) and amplitude (height) of the wave
- 4 Causes of P wave deviations
-
5 What can be confused with the P wave
- 5.1 If the polarity of the P waves is not what it should be
- 5.2 If 2, 3 or more prongs, similar to P, follow each other
- 5.3 If you see something similar to the P waves, but they are very fuzzy and not alike
-
6 Negative P in lead I
- 6.1 Dextrocardia
- 6.2 Electrodes applied incorrectly
- 7 Deep negative P in lead V1
- 8 Negative P wave in lead II
-
9 PQ interval
- 9.1 PQ interval lengthening
- 9.2 Shortening the PQ interval
- 9.3 PQ segment depression
-
10 QRS Complex Width
- 10.1 Blockade of the anterior branch of the left bundle branch
- 10.2 Blockade of the posterior branch of the left bundle branch
- 10.3 Incomplete left bundle branch block
- 10.4 Incomplete right bundle branch block
- 11 What are the false noises on the cardiogram that are not associated with heart pathologies?
- 12 What to do with deviations in the P wave on the ECG?
- 13 P wave video
Types and significance of ECG waves
Shortly before each stage of the heartbeat, electrical excitement accumulates in the muscle, which, like a wave, propagates through various areas of the organ, causing muscle fibers to contract. This phenomenon is known as excitation conductivity.
Weak currents can be measured with electrodes attached at 12 locations to the upper body, arms and legs. These are standard abduction sites. A normal ECG is a defined pattern of 3 recognizable waves in the cardiac cycle.
The P wave on the ECG reflects the first wave that occurs at the beginning of the heartbeat. And also on the curve the QRS wave and T wave, PR interval, ST segment are indicated.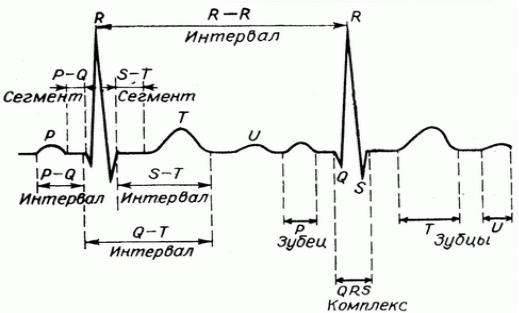
| P wave | A small upward wave that appears first. Indicates depolarization of the atria (systole), during which excitation spreads from the SA node to the entire atrium. |
| QRS wave | The second wave is represented as a small downward wave, continues as a large vertical triangle wave and ends with a downward wave. Immediately after the onset of the QRS segment, the ventricles begin to contract. Hence, the QRS wave represents ventricular systole. |
| T wave | This is the third small wave in the form of a domed upward deflection. Indicates repolarization of the ventricles (diastole). |
| PR interval | This is the time it takes for a pulse to travel through the atria, AV node and bundle before reaching the ventricles. |
| ST segment | Measured from the end of the S to the beginning of the T wave. This is the time when the fibers of the ventricles are completely depolarized. |
| PQ interval | Shows the propagation of impulses along the right and left atria. |

The electrocardiograph captures the electric currents produced by the heart muscle during the cycle of contraction and relaxation, It displays them in the form of lines, waves and peaks, the so-called ECG curve.
Where and how to find the P wave on the ECG
The P wave on the ECG reflects atrial excitation. Interpretation of the screening begins with an assessment of this wave. With a normal ECG, in leads II or VI, the P wave is seen in front of the QRS segment. It's a small bump above the baseline. The P wave is usually smooth and rounded.
The initial part of the wave corresponds to the excitation of the right atrium, and the final part - to the left.
Normal duration (width) and amplitude (height) of the wave
A normal P wave is best seen and studied in lead II because the axis of the P wave is toward the positive pole of the lead. The P wave has a somewhat pyramidal shape with a rounded apex. Its limbs are smooth, without irregularities.

The duration of the P wave is 0.08-0.10 s, but does not exceed 0.11 s.
The maximum normal amplitude is 2.5 mm, but a normal P wave is usually less than 2 mm.
Causes of P wave deviations
Abnormal or missing P waves indicate problems in the atria.
P wave deviations include:
- bifurcated P waves, which is characteristic of an enlarged left atrium;
- pointed P wave with an enlarged right atrium;
- inversion of the P wave, observed with ectopic atrial and junctional rhythms;
- different P wave morphology observed with multifocal atrial rhythms.
What can be confused with the P wave
In some cases, a sinus P wave can be confused with a junctional rhythm. With a nodal rhythm, the P wave in leads aVF, II is negative (normally it should be positive). Therefore, this is not a sinus P wave, but one of the varieties of the supraventricular rhythm (a type of arrhythmia).
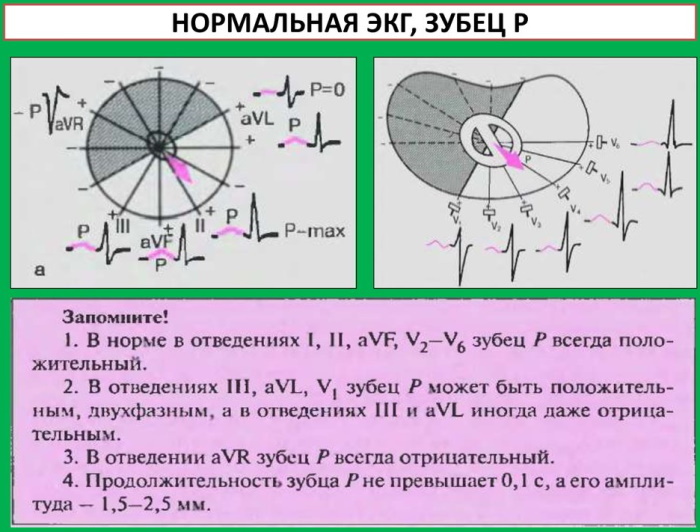
If the polarity of the P waves is not what it should be
The polarity of the P waves in leads I-III is an important electrocardiographic sign. It reflects depolarization (activation) of the atria. This is a small positive and smooth wave.
The tooth is small because the atria make up a relatively small muscle mass. If the rhythm is sinus (at normal), the P wave vector is directed to the left and down the frontal plane, which gives a positive P wave in lead II.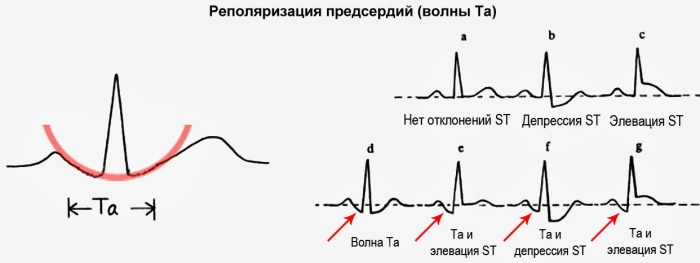
The P wave on the ECG always reflects a positive result in II and aVF leads with sinus rhythm. But this same tooth will be negative in lead aVR.
The P-wave vector is slightly curved in the horizontal plane. It points forward at first, but then turns to the left to activate the left atrium. Therefore, a 2-phase P wave may appear in lead VI. This means that most of it is positive, and the final part is slightly negative.
Thus, the first half of the P-wave reflects depolarization of the right atrium, and the second half reflects depolarization of the left atrium.
If 2, 3 or more prongs, similar to P, follow each other
2 or more waves similar to the P wave may appear on the cardiogram. In this case, there is a sign of atrial flutter, because this wave is called - wave F.
In another case, the appearance of a series of successive P waves indicates AV block. This occurs when the P wave is not conducted through the AB node.
If you see something similar to the P waves, but they are very fuzzy and not alike
On the cardiac picture, you can see waves that outwardly resemble the P wave. But upon closer inspection, it becomes noticeable that the waves are not identical. If it is impossible to find two identical waves in successive QRS cycles, then these are not P waves. This picture indicates a violation of the atrial rhythm (atrial fibrillation).
Negative P in lead I
In some cases, there are features of the cardiogram graphics, expressed by negative P waves in lead I. This is due to errors in the placement of electrodes, congenital or acquired anomalies of the myocardium.
Dextrocardia
When the heart is located on the right side, doctors diagnose an anomaly - dextrocardia.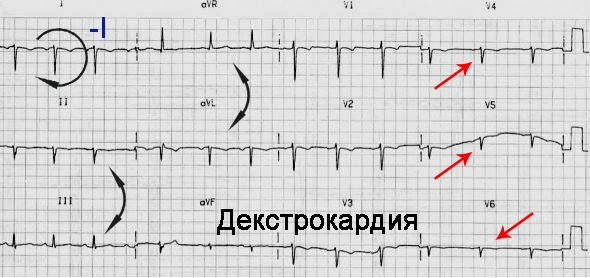
ECG results show:
- Predominantly negative P wave, QRS segment and T wave in lead I.
- Low voltage in the V3-V6 leads (as these leads are located on the left side of the chest).
Electrodes applied incorrectly
Changing the direction of the right and left hand electrodes is the most frequent change in the direction of abduction. This error will result in a negative P wave and a QRS segment in lead I. Negative P and QRS waves are rare and even less common in heart disease.
Deep negative P in lead V1
A negative P wave in lead VI shows an abnormality of the left atrium. The ascending apex of the tooth is widened to ›0.04 s, the amplitude is› 1 mm. The anomaly reflects aortic defect, heart failure. In the case of premature atrial contractions in the P waves on the ECG, there may be no negative component.
Negative P wave in lead II
With an increase in the mass of the left ventricle, an increase in the time and amplitude of the associated component of the P wave occurs. This is manifested by the appearance of a widened and two-humped P wave in leads I and II.
PQ interval
For the diagnosis of heart disease, such an ECG indicator as the rate of passage of excitation along the right and left atria to the muscle tissue of the ventricles of the heart is of paramount importance. 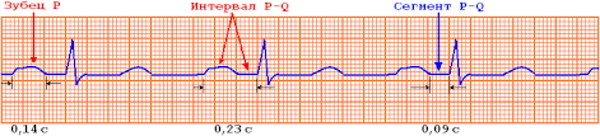 This is the PQ interval, the general time norm of which is considered to be the range from 120 to 200 ms.
This is the PQ interval, the general time norm of which is considered to be the range from 120 to 200 ms.
PQ interval lengthening
Extended PQ interval means impulse conduction delay, full or partial AB (violation conduction between the atria and ventricles, resulting from anatomical or functional obstacles).
Shortening the PQ interval
The interval size is <0.12 s. This suggests that the pulse is traveling too quickly from the atrium to the ventricle. The PQ segment on the ECG in such cases is measured from the starting point of the P wave to the Q wave, since there is a connection between a rapid rhythm and a short interval.
The short interval may be asymptomatic or indicate episodes of a previous heart attack or paroxysmal tachycardia (heart palpitations lasting 10-20 seconds).
PQ segment depression
With atrial infarction, there is a depression of the PQ segment. It can be oblique in the case of right atrial hypertrophy, horizontal in the case of acute pericarditis. The interval represents the time it takes for the impulse to pass through the right atrium - 0.12-0.20 s. This is indicated by the PQ segment in leads aVF, II, III.
QRS Complex Width
The QRS complex is the largest component of the ECG, it is recorded during the excitation of the ventricles. The expansion of the complex is possible with a bundle branch block.
Blockade of the anterior branch of the left bundle branch
Left bundle branch block is more often associated with structural heart disease than right bundle branch block.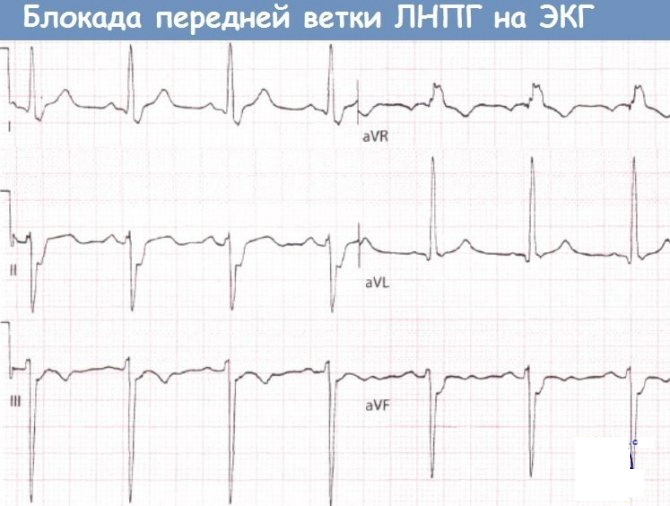
An electrical impulse is delivered to the anterior wall of the left ventricle through the anterior branch.
ECG criteria for left anterior beam block:
- Electric axle from -45˚ to -90˚. If the range is less, from 30˚ to -45˚, then an anterior branch block is diagnosed.
- QRS duration <0.12 sec.
- Lead aVL shows a qR complex. Leads V5 - V6 usually show qR complexes as well.
- Leads II, III, aVF display rS complexes.
Pathology is associated with diseases:
- coronary heart disease;
- hyperkalemia;
- myocarditis;
- left ventricular hypertrophy.
Blockade of the posterior branch of the left bundle branch
Posterior block is much less common because the posterior bundle is larger and has a greater arterial blood supply.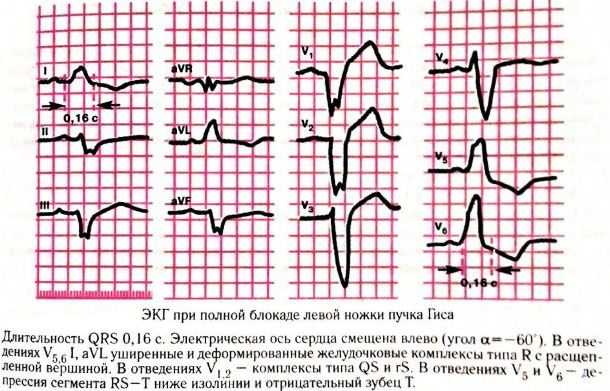
ECG criteria:
- Axis deviation to the right (> +90 degrees).
- Small R-waves with deep S-waves. in I and aVL leads.
- Small Q waves with tall R waves in leads II, III, and aVF.
- The QRS duration is normal or slightly increased (80-110 ms).
- Increased QRS tension in limb leads.
Deviations cause pathologies: acute or chronic myocardial damage, myocardial inflammation, the development of pulmonary embolism (pulmonary heart).
Incomplete left bundle branch block
When you change the supply of an electrical impulse along the leg or bundle of His, pathologies are detected in some people.
ECG criteria for this:
- Presence of a scheme, as in left ventricular hypertrophy, with missing Q waves in I and V5 / 6.
- Broadening of the QRS segment from 110 to 119 ms.
The electrocardiographic picture of incomplete blockade expresses chronic stress of the left ventricle (in the case of prolonged arterial hypertension or aortic stenosis).
Incomplete right bundle branch block
In this case, cardiac conduction is impaired. Deviation also occurs in a healthy heart. In this case, the QRS segment expands, it is 110 - 119 ms.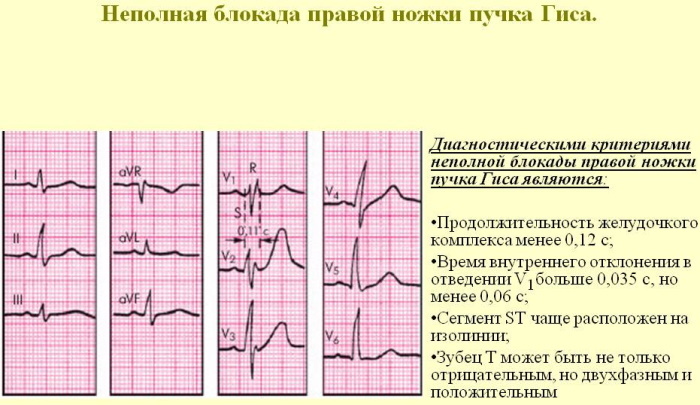
Incomplete blockade may occur for the first time or temporarily in connection with acute stress of the right ventricle (for example, in the case of sudden blockage of the branches or trunk of the pulmonary artery by a thrombus).
What are the false noises on the cardiogram that are not associated with heart pathologies?
Lead switching is a common ECG error that can lead to misdiagnosis.
The most common errors are associated with arrhythmias, conduction abnormalities and pacemakers.
The P wave on the ECG reflects in some cases an erroneous value, as well as other segments.
This is due to external factors:
- Resistance of the skin to electrical signals passing through it.
- Patient movement can create deviations in the ECG waveform.
- An incompletely inserted cable or wire may prevent the ECG signal from reaching the monitor.
- Broken cable, poor quality electrodes prevent the ECG signal from reaching the monitor.
- Unwanted ECG interference from nearby sources such as power cords, infusion pumps, and ventilators.
What to do with deviations in the P wave on the ECG?
When treating heart disease, the underlying disease is considered, not the ECG measurement. Abnormal P waves in ECG testing can result from a variety of conditions. After evaluating the characteristics of the P wave in relation to other factors, treatment for the cause of the abnormal wave may be proposed.
- Each contraction begins with an electrical charge from the atria, which then travels down to the ventricles and creates other waves. Thus, the P wave in its most direct interpretation represents the electrical characteristics of the right and left atrium. If the electrical conduction takes longer than usual and is an abnormally large P wave, this may indicate an enlarged left atrium. Cardiac supportive therapy is used to treat atrial flutter and fibrillation.
- Arterial pressure. Although enlarged atria are a common cause of abnormal P waves, many other conditions affect this part of the ECG measurement. Cor pulmonale (a form of hypertension) can display an abnormal P wave when an imbalance occurs between the right and left heart. Treatment for this condition often consists of drugs, anticoagulants, and supplemental oxygen. In extreme cases, a heart defect can be the cause of the problem, so surgery or even a heart transplant is necessary.
- Violation of conductivity. Abnormal P-waves are often a symptom of poor electrical circulation in one area of the heart, which only affects testing and does not necessarily mean a real heart problem. These conduction defects can be easily recorded on the ECG, since electrical conduction is the only source of data in these tests. But such defects in electrical measurements are not always due to impaired cardiac function.
EKG studies should be done if there are risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, palpitations, or chest pain.
The P wave is the first wave that occurs at the beginning of the heartbeat. Waves shorter than 2 mm or more than 3 mm are considered to reflect abnormal amplitude on the ECG. The causes of this disorder are widespread and treatment varies depending on the source of the problem.
P wave video
The P wave is normal and with pathologies:



