Oligophrenia is characterized by mental retardation (speech, motor skills, emotions). Symptoms and signs in children vary depending on the cause of the development of the pathology. It is difficult for a child with personality integrity disorders to adapt in society.
Record content:
- 1 Classification of mental retardation in children by severity, generalized table
-
2 The degrees of mental retardation and their symptoms in children
- 2.1 Easy
- 2.2 Moderate
- 2.3 Heavy
- 2.4 Deep
- 3 Epidemiology of oligophrenia
-
4 General etiology of the disease
- 4.1 Genetic causes of mental retardation
- 5 Clinical picture
- 6 Diagnostics and its criteria
- 7 Differential diagnosis
- 8 Testing
- 9 Treatment
-
10 Diet therapy
- 10.1 Sulfonamides with Chloridine (Daraprim)
- 10.2 Hormone therapy
- 10.3 Correction of emotional lability and suppression of perverse drives
- 11 Social adaptation
- 12 Features of interpersonal relationships
-
13 The connection between mental retardation and schizophrenia
- 13.1 Pfropfschizophrenia
- 13.2 Distinguishing mental retardation from schizophrenia
- 14 Video about oligophrenia
Classification of mental retardation in children by severity, generalized table
Oligophrenia (symptoms and signs in children are described later in the article) can be acquired or congenital.
Pathology is classified depending on the severity:
| Degree | Description | Manifestations |
| Moronity | The lightest degree. The child is not able to think abstractly, to build complex inferences. They are easily suggestible. Volitional and moral qualities are poorly developed. | Visual-figurative thinking, speech underdevelopment (FFN, ONR), bradilalia, sluggishness, agrammatism, inability to generalize, underdevelopment of moral and aesthetic qualities. |
| Imbecility | Moderate mental retardation. Pathology can develop in utero. Outwardly, the deviations are almost invisible. The emotional background is varied. | Double behavioral reactions, reduced blinking, rough skull structure, defective bite, sloppy appearance. |
| Idiocy | Severe oligophrenia. Pathology is characterized by a sharp lag in development. Children are not able to contact others, they do not master primitive skills. | Weakly expressed reactions to what is happening, lack of addiction to loved ones (the baby does not recognize the parents), unstable attention, of course, reflex. |
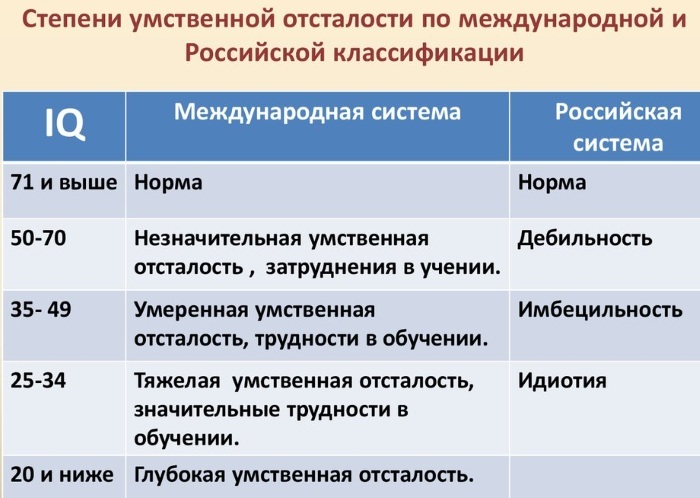
 The ICD-10 classification implies a test of the child's intelligence level through an IQ test. Depending on the results, there are deep, severe, moderate and mild degrees.
The ICD-10 classification implies a test of the child's intelligence level through an IQ test. Depending on the results, there are deep, severe, moderate and mild degrees.
The degrees of mental retardation and their symptoms in children
Oligophrenia (symptoms and signs in children appear as they grow older) are virtually untreatable. There are several basic degrees. To diagnose pathology (in addition to identifying characteristic signs through conversation and examination), Wechsler's methods, non-verbal or verbal scales are used. These methods help determine the level of development in a child.
Easy
Oligophrenia (symptoms and signs in children appear at 3-5 years old) mild accompanied by minor mental disorders. It is almost impossible to detect the disease in infants. As they grow up, the child begins to experience difficulties in adapting in society, it is difficult for him to find a common language with his peers, to observe the daily routine and master skills.
Most often, children with mental underdevelopment are hyperactive and inattentive.
Early symptoms of mild mental retardation:
- Lack of abstract thinking. The child's creative, mathematical and logical abilities are not developed.
- Lack of interest in new toys and entertainment. The child is closed, does not take part in games.
- Emotional poverty. The child has almost no interest in what is happening.
- Delay in speech. With oligophrenia, children begin to speak late. There is no coherent speech.
- Unbalanced processes of inhibition and excitation. The child is either too impulsive or slow and lethargic.
For oligophrenia, mild motor developmental disorders are characteristic. The child tries to get up late, sit down, walk and hold his head. The grasp reflex is most often impaired.
Moderate
Oligophrenia (symptoms and signs in children may differ depending on the degree of development of the pathology) in a moderate form can be acquired or congenital. Children with this diagnosis feel affection, are able to distinguish the tone of the speaker (praise, censure).
With moderate mental retardation, the child is able to learn the simplest self-care skills. Mastering elementary counting, reading and writing is possible.
The main symptoms include:
- violation of the volitional and emotional sphere;
- lack of interest in knowledge;
- poor memory;
- underdeveloped abstract thinking;
- impaired attention and perception;
- decrease in intellectual development.
Children suffering from moderate mental retardation need qualified support. They are rarely independent, but they are quite mobile and physically developed.
Heavy
Idiocy or severe mental retardation is characterized by mental, emotional and mental retardation. It is difficult for children to master speech and basic self-care skills. Their vocabulary is meager, limited to 15-20 words.
With their help, the child informs the parents about his needs. Chaotic, unsystematic thinking is characteristic of pathology. The child does not pay attention to unfamiliar objects. He reacts to toys that are in front of his eyes for a long time.
Physical manifestations of idiocy include:
- chaotic movements of legs, arms;
- clumsiness;
- unstable gait.
Children with idiocy do not show interest in those around them. It is difficult for them to find a common language with their peers. They can behave aggressively towards strangers.
Deep
With deep mental retardation, not only the brain is affected, but also most of the internal systems. The child's speech functions are completely impaired, he does not understand what the people around him are talking about and does not distinguish between parents and strangers.
Deep mental retardation manifests itself in 2-3 years. The child begins to sit and hold his head late, his movements are awkward, there is no balance of legs and arms. With oligophrenia, children are usually inactive and completely non-contact.
Epidemiology of oligophrenia
Oligophrenia is considered a common disease. Its symptoms and signs are found in 25-30% of children. Of these, up to 50% face learning difficulties. 60-80% have intellectual disability. In industrialized countries, the frequency of birth of children with mental retardation is 5-6 cases per 1000 people. In severe form, pathology is quite rare - 2-3 children per 1000 people.
General etiology of the disease
According to the results of the studies, a number of pathologies can provoke the development of oligophrenia in a child in the womb.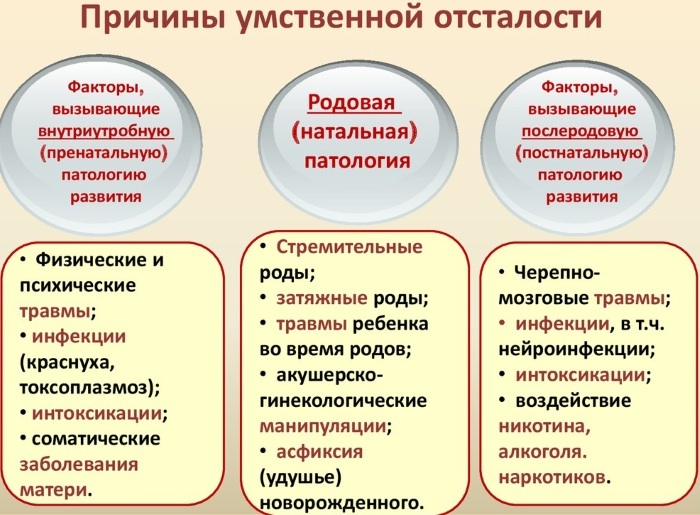
These include:
- syphilis;
- listeriosis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- infectious type hepatitis;
- measles rubella;
- flu.
An infection affecting the fetus in the embryogenesis stage provokes the development of anencephaly or organic brain damage. The bacteria trigger inflammation inside the membranes and tissues. The etiological factors include drug poisoning. Barbituratic acid is able to accumulate in the placenta. The substance provokes fetal intoxication.
If a woman during pregnancy takes sulfonamides, antipsychotics and antibiotics that can have a teratogenic effect, then the risk of having a child with oligophrenia is quite high.
Genetic causes of mental retardation
Almost 70% of cases of birth of children with moderate and mild oligophrenia have a hereditary etiology. Pathology develops due to chromosomal abnormalities.
They are associated with a rearrangement of the structure or a change in the number of chromosomes. Anomalies also affect autosomes. If during the formation of the fetus the number of sex chromosomes has changed, then the child is more likely to be born mentally retarded.
Severe mental retardation develops against the background of hereditary pathologies associated with improper metabolism. Phenylketonuria is considered the most common. It is a monogenic autosomal recessive disorder in which phenylalanine (amino acid) metabolism is impaired.
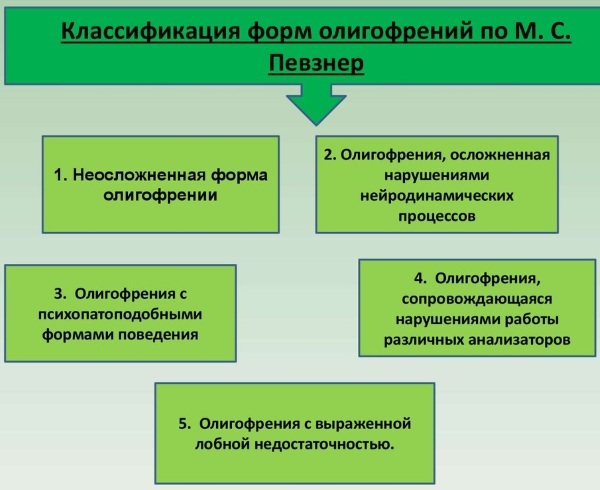
Clinical picture
Against the background of dementia, the personality of the child suffers. Underdevelopment concerns not only thinking and intelligence, but also a number of mental functions: will, emotions, speech, attention, memory, motor skills. With oligophrenia of any type, violations of pathogenetic functions are observed.
The child is unable to think abstractly and generalize the information received. Memory, attention and self-criticism are undeveloped. Oligophrenia is accompanied by a delay in mental and physical development. Children suffering from this disease (especially in severe form) are usually inactive.
Diagnostics and its criteria
Factors that doctors rely on when diagnosing pathology:
- A. With incomplete or delayed development, special, motor, speech and cognitive abilities are impaired.
- B. Oligophrenia develops with or without other somatic or mental disorders.
- C. Oligophrenia is accompanied by adaptive disorders. When providing support to children with a mild degree of retardation, they do not appear.
- D. Cross-cultural assessment helps to measure the level of mental development.
- E. Determination of the severity of behavioral disorders in the absence of mental disorders.
Indicators for behavioral disorders:
- 9 - behavioral disorders are not indicated;
- 8 - a set of violations;
- 1 - violations requiring care;
- 0 - behavioral disorders are mild.
The specialist is obliged to identify the cause of the development of oligophrenia.
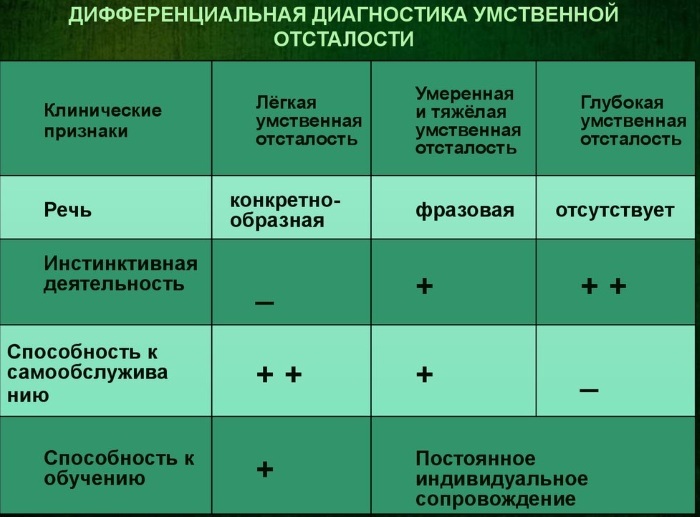
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis allows you to distinguish between oligophrenia and schizophrenia. In patients with mental disorders, mental retardation becomes dissociated or partial.
In the clinical picture, there is a number of manifestations that are characteristic only of the endogenous process:
- catatonic signs;
- pathological daydreaming;
- autism.

Mental retardation must be distinguished from dementia. This is acquired dementia, in which the vocabulary is completely preserved. The patient retains abstract thinking and part of the knowledge acquired earlier. Dementia is characterized by a wide range of emotions.
Testing
In order to assess the level of intelligence in children with developmental delay, the Wechsler and Stanford-Binet tests are used. The techniques have been criticized for their unreliable results and lack of sensitivity to creative and personalized responses. With the help of Bender and Benton's gestalt tests, organic brain lesions are detected. The child must copy 9 figures from the map and describe each of them in detail.
If organic brain lesions are present, then the patient makes typical mistakes. To assess the level of social fitness, use the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale or the Vineland Maturity Scale. They conduct a conversation with guardians or parents and, on its basis, identify the level of socialization, the presence or absence of skills necessary in everyday life.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the specific causes of the development of oligophrenia (toxoplasmosis, congenital syphilis). If mental retardation is provoked by phenylketonuria, then the child is prescribed a diet. With oligophrenia caused by toxoplasmosis, it is required to take sulfonamides, which contain daraprim.
Hormonal treatment is indicated for endocrinopathy (cretinism, myxedema). Medicines will help to correct emotional lability. Sonapax, Phenazepam or Neuleptil. The oligophrenic defect of developmental delay is compensated by vocational training and labor education. The child can be sent to a specialized vocational school or boarding school.
Diet therapy
Children suffering from oligophrenia (regardless of the form), provoked by phenylketonuria, are advised to adhere to a diet. The basic principle is the consumption of foods that are low in protein. For children under one year old, it is recommended to give a dry mixture that does not contain phenylalanine.
Prohibited Products:
- cereals (rice, pearl barley, millet groats);
- bitter, milk, white chocolate;
- seafood, fish;
- eggs;
- nuts;
- dairy products (cottage cheese, cheese);
- smoked, boiled sausages;
- poultry meat (chicken, turkey);
- beef, lamb, veal, pork.
The diet should be dominated by fresh fruits, vegetables, berries. It is permissible to use honey, jam, preserves, canned vegetables and vegetable oils.
Sulfonamides with Chloridine (Daraprim)
For drugs in this category, an extensive antimicrobial effect is characteristic. They are prescribed for children suffering from oligophrenia, provoked by toxoplasmosis.
The most effective medicines:
- Metakelfin. The drug is marketed in pill form. Children with mild to moderate oligophrenia can be given pills from 5 years of age. The therapeutic norm is no more than 500 mg, which is equivalent to 1 tablet. Adolescents, whose body weight does not exceed 40 kg, are given 2 tablets per day.
- Fansidar. Release form - tablets. Children under 2 years of age are given ½ tablets per day. For adolescents, the therapeutic norm is 1 g, which is equivalent to 2 tablets.
- Pyrimethamine. The drug is not prescribed for children under 6 years of age. The initial dose (from 6 years old) is 10 mg. The maximum allowable therapeutic rate is 50 mg.
The course of treatment is selected by a specialist individually, depending on the degree of mental retardation.
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy is indicated for children suffering from oligophrenia, provoked by pathologies of the thyroid gland. Drugs in this category will help eliminate the root cause of the development of the disease. Medications do not affect the functioning of the brain in any way and are not able to restore the mental activity of the child.
Correction of emotional lability and suppression of perverse drives
Emotional lability is understood as affective reactions in response to moderate or weak stimuli. Children with mental retardation are usually shy, whiny, openly showing joy and embarrassment. Outbursts of irritation are replaced by aggression.
With strong feelings, self-control decreases, the child is not able to objectively assess what is happening. Before starting procedures aimed at correcting the emotional-volitional sphere, a specialist must first identify the cause of the development of oligophrenia. Etiotropic therapy is carried out not only by a psychiatrist, but also by an endocrinologist, therapist, neurologist or venereologist.
Specific treatments for emotional lability and suppression of perverse drives include:
- Medication correction. The child is prescribed drugs that can relieve tension, eliminate anxiety and restore the psycho-emotional background. These can be antidepressants, sedatives, or tranquilizers. If behavioral disorders are pronounced, then you need to take antipsychotics.
- Group therapy. The child can be taken to trainings. This allows him to improve his social adaptation and motivate him to primitive activities. In a group, the child learns to interact with others and peacefully resolve conflicts.
- Individual therapy. A psychotherapy session is carried out in order to identify the child's fears. The specialist tries to help him establish control over his own reactions.
It is the responsibility of the therapist to talk to the parents. The specialist will help you develop a daily routine for the child.
Social adaptation
Educational and educational work with children suffering from mild, moderate or severe oligophrenia is carried out in special institutions of health care and education.  If a child's central nervous system is deeply affected, then he is placed in social welfare homes, where specialists work with him according to a special program.
If a child's central nervous system is deeply affected, then he is placed in social welfare homes, where specialists work with him according to a special program.
Features of interpersonal relationships
A child who is lagging behind in development needs support and communication help. Often he does not understand what is happening around him. In terms of communications, this is a weak partner. The child may fall into negativity or aggression. Behavioral problems trigger anxiety and fear.
The quality of interpersonal relationships is of fundamental importance for children with underdeveloped intellectual, emotional and volitional spheres. It is important for a child to know that he is not indifferent to others.
He needs to maintain contact with his parents and close relatives. A family of trust should be built. Communication with peers plays an important role in the formation of personality - this allows the child to become aware of his “own self”.
The connection between mental retardation and schizophrenia
The terms "mental retardation" and "schizophrenia" are sometimes closely related to each other.  If you suspect mental retardation, it is recommended to conduct a series of differential studies in order to identify the exact cause of the pathology.
If you suspect mental retardation, it is recommended to conduct a series of differential studies in order to identify the exact cause of the pathology.
Pfropfschizophrenia
Mental disorders that occur against the background of mental retardation are called olegoschizophrenia or pfropfschizophrenia.
There are 2 main types of pathology:
- In addition to oligophrenia, the child has hebephrenic features in childhood. As they grow older (14-17, 20-30 years), the patient develops a hebephrenic fur coat (acute attack).
- Schizophrenia in combination with oligophrenia. This condition is characterized by a meager symptom complex (hallucinations, panic attacks, delirium) and a catastrophic course.
Schizophrenia, which appears in early childhood, entails a delay in intellectual and emotional development.
Distinguishing mental retardation from schizophrenia
A diagnosis can only be made by a specialist who is able to distinguish the symptoms of schizophrenia from the signs of oligophrenia. Mental retardation is considered mental defects, formed against the background of a number of factors that interfere with the normal formation of the fetal brain in the womb. Schizophrenia is an ongoing process characterized by procedural phenomena.
If a mental disorder was formed in childhood, then its symptom complex is devoid of brightness and is completely rudimentary. Signs can appear gradually, as in cases of oligophrenia.
A form of mental retardation is often confused with schizophrenia, whose clinical presentation includes:
- instability;
- affective immaturity;
- lack of interest in the events taking place around.
In children with mental underdevelopment, instincts are poorly expressed. They rarely show strong emotions, so pathology is often confused with schizophrenia with autism. With oligophrenia, a violation of psychomotor development is noticeable. Children have poor memory and almost no desire to make contact with others.
Oligophrenia is a serious disease characterized by developmental delay, emotional lability and impairments to the volitional sphere. In children, symptoms and signs develop as they get older. Pathology is considered incurable.
Video about oligophrenia
Diagnosis - mental retardation:



