Catatonic stupor is considered a psychopathological syndrome. This is the condition is characterized by various movement disordersarising against the background of schizophrenia, organic brain lesions, depression and severe poisoning. The symptom complex is quite pronounced.
Record content:
- 1 Catatonia - what is it?
- 2 What is human stupor?
- 3 The reasons for the development of catatonic syndrome
- 4 Pathogenesis of the development of catatonic stupor
-
5 Varieties
- 5.1 Empty catatonia
- 5.2 Lucid and oneiroid catatonia
-
6 Symptoms of catatonia
- 6.1 Specific symptoms
- 6.2 Symptoms of catatonic agitation
- 6.3 How does catatonic schizophrenia manifest?
- 7 How can catatonic syndrome be complicated?
- 8 Diagnostics
- 9 Treatment of catatonic syndrome with drugs
- 10 Side effects of drug therapy
- 11 Forecast
- 12 Video about catatonic stupor
Catatonia - what is it?
Catatonic stupor is a disease, the development of which is accompanied by autonomic and psychomotor disorders. The pathology was first described in 1874. doctor Karl Ludwig Kalbaum.
He is considered the author of the doctrine of the catatonic syndrome. For several years, pathology was considered an independent nosological unit, until psychiatrists Bleuler and Kraepelin proved that the disease is a subspecies of schizophrenia.
The syndrome is diagnosed in people regardless of age and gender. In children, catatonic stupor is manifested by chaotic, monotonous twitching of the arms and legs.
The child walks on tiptoe, tries to lick and sniff the objects around him. The maximum intensity of the symptom complex is noticeable at the age of 30. If catatonic stupor strikes a woman, then its manifestation vaguely resembles hysteria.
The syndrome can be conditionally divided into 3 types:
- malignant - serotonin intoxication, neuroleptic syndrome;
- delirium - panic, manic syndrome;
- non-malignant is a typical disorder.
Pathology manifests itself not only in stupor. Sometimes movement disorders are accompanied by impulsive behavior or arousal. The patient is tormented by hallucinations, he is often in a state of delirium. If untreated, the disease leads to social degradation.
What is human stupor?
Catatonic stupor is a "synonym" for stupor in psychiatry. The syndrome is considered one of the disorders of motor activity. The person is usually immobilized.
In this state, there can be an absolute refusal to interact with others, dumbness or lack of response to various stimuli. A person suffering from stupor does not have reactions to what is happening: he is not interested in events, does not contact with loved ones. The patient does not pay attention to cold, noise and pain.
For a long period, he is unable to eat and talk. Stupor can occur with fear, stress, depression, and other mental disorders. The patient stands, sits or lies without changing position for several days. Psychological disorders are characterized by suppression of speech, mental activity, and motor skills.
The person is motionless. In some cases, he answers questions with short sentences, words or interjections.
In addition to movement disorders, symptoms of stupor include:
- affect;
- clouding of consciousness;
- hallucinations;
- rave.
The reasons for the development of pathology are quite numerous.
The reasons for the development of catatonic syndrome
The causes of catatonic stupor have not yet been clarified. Psychiatrists have put forward several hypotheses to help explain the etiology of the disease.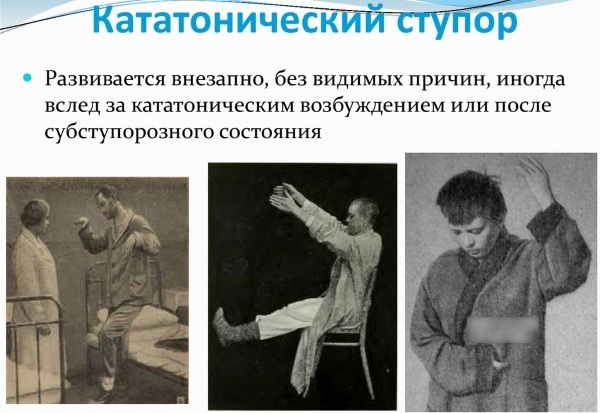
Catatonia can be provoked by:
- deficiency of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the brain;
- lack of dopamine;
- violation of metabolic processes occurring inside the organ.
The theory associated with primitivism has a right to exist. Some scientists argue that catatonia is a subjective reaction of a person who feels imminent death. The syndrome occurs against the background of psychoses (somatic, withdrawal symptoms, intoxication, infectious, viral, organic) and schizophrenia. Stupor is diagnosed in autistic patients.
At risk are people who have had a tumor growth in the brain.
There is a high risk of developing pathology with:
- drug addiction (including addiction to cocaine);
- vascular lesions of the brain;
- benign thrombocytopenia;
- mental disorders after delivery;
- epilepsy.
Catatonic stupor also develops against the background of severe diseases of infectious etiology.
Pathogenesis of the development of catatonic stupor
The pathogenesis of the development of catatonic stupor is practically unknown. In the course of research conducted by psychiatrists and neurologists, several mechanisms have been identified that contribute to the formation of pathology.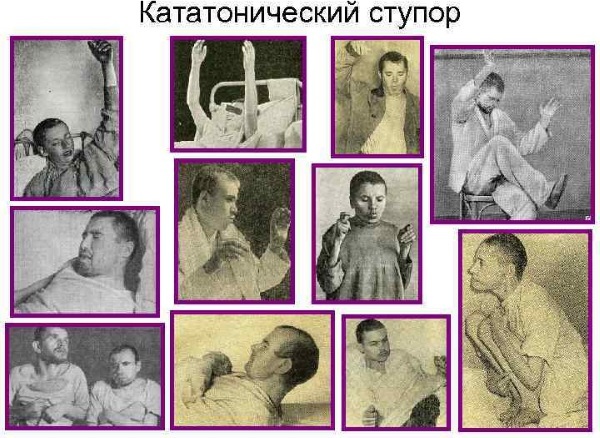
These include:
- violation of metabolic processes occurring in the thalamus and frontal lobes (characteristic of chronic catatonic stupor);
- activation of the serotonergic and cholinergic systems, which has arisen against the background of a sharp discontinuation of Clozapine;
- massive rapid blockade of the pituitary hormone;
- an increase in the activity of an amino acid that excites neurons;
- violation of metabolic processes occurring in the tissues of the brain.
Stupor often develops against the background of a deficiency of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In this case, medications that accelerate the synthesis of GABA are effective. It is strictly forbidden to take antipsychotic drugs that selectively inhibit dopamine during catatonic stupor. This will lead to a deterioration in the patient's condition.
Varieties
Catatonic stupor is a pathology that includes several main forms of stupor:
- Numbness. This form is characterized by pronounced lethargy. Muscle tone is increased, patients lie motionless in the fetal position.
- Negativistic. The form is accompanied by motor retardation, the patient resists when people around him try to change his posture.
-
Catalytic. The patient freezes in an uncomfortable position for him, does not react to loud speech. Sometimes the patient responds to a whisper or whistle. The stupor may subside at night.
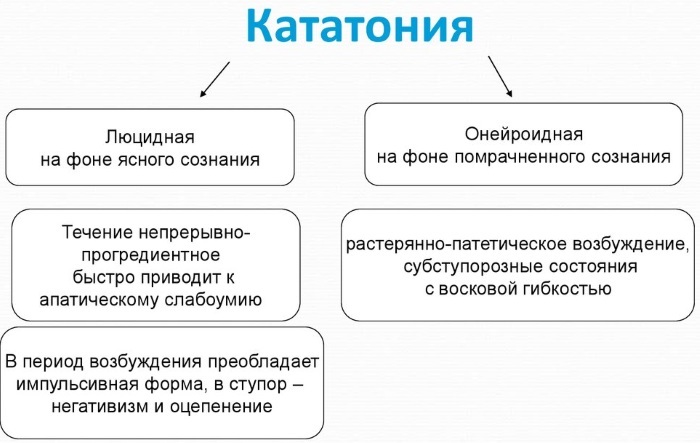

Also, there are 3 main types of pathology according to the type of manifestation: oneiric, lucid and empty.
Empty catatonia
Empty catatonia is inherent in:
- Negativism. The patient may take other actions instead of those proposed or ignore requests.
- Echosymptoms. The patient reproduces the sounds and movements of another person.
- Verbigeration. The patient repeats the same word or sentence.
- Stereotypy. The patient repeats the same movements or postures after another person.
Empty catatonia can be accompanied by delusional, affective, or hallucinatory disorders.
Lucid and oneiroid catatonia
With the lucid form of catatonia, the patient retains memory, spatial, personal and temporal orientation. The exact reasons for the development of pathology have not been identified.
Psychiatrists suggest that the onset of the disease is triggered by an imbalance in neurotransmitters, which are responsible for the process of inhibition and transmission of excitation along the fibers of the nervous system. Catatonia most often develops against the background of schizophrenia, brain pathologies, psychoses of organic and infectious etiology.
There is no productive symptomatology. People do not suffer from hallucinations, obsessions and delusions. They do not have seizures.
The characteristic symptoms of the disease include:
- numbness and immobility;
- ignoring words and requests;
- strong excitement.
The patient is fully aware of what is happening. During stupor, tension is observed. This position is maintained for a long time.
Oneiric catatonia is considered a type of recurrent (periodic) schizophrenia. The deterioration increases gradually. It is characterized by somatogenic reactions. The apogee comes in a couple of hours: the patient may have an expression of horror on his face, which after a few minutes will be replaced by laughter.
Foolishness, pretentiousness, spitefulness, rudeness are not characteristic of this form. There is speech disruption, the patient cannot clearly formulate thoughts. Pathology is characterized by clouding of consciousness, the patient experiences negative emotions.
Symptoms of catatonia
Catatonic stupor is a disease accompanied by impaired motor activity. Strengthening character traits is considered the first manifestation of pathology. The prodromal period is accompanied by isolation: a person tries to remain alone as often as possible.
He shows aggression at attempts of others to establish contact. The patient does not sleep well, complains of weakness and headache. As the disorder progresses, delusional ideas and thoughts, anxiety, and panic attacks appear. A person's perception of reality is distorted, he becomes irritable and refuses food.
The severe stage is characterized by negativism, real estate and mutism. Speech disorders gradually increase, muscle rigidity becomes more prolonged.
For catatonic stupor, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- violation of vascular innervation (hyperemia);
- weight loss;
- sleep disorders;
- excessive sweating;
- salivation;
- dilated pupils;
- shallow breathing.
Children have regressive catatonia, the child tries to copy the behavior of the pet.
Specific symptoms
During the period of catatonic stupor, the following specific symptoms are observed:
- sudden stop of movement or speech;
- incoherent, continuous, monotonous muttering;
- demonstration of ambition;
- automatic submission (the patient fulfills any request);
- catalepsy (the patient is disgusted with the people around him).
The patient has wide eyes and dilated pupils. They do not tolerate touching their body. The transition from stupor to arousal, and vice versa, is usually instantaneous.
Symptoms of catatonic agitation
The disease is classified according to the degree of arousal:
- Not mine. The patient with this form of arousal is rather aggressive. He, without uttering a word, damages others or himself. Psychiatrists consider this type of pathology to be the most dangerous.
- Impulsive. The condition develops rapidly and is characterized by the destructiveness, determination and cruelty of the patient. A person repeats the same actions, phrases or words many times. He is dangerous to others and himself.
- Pathetic. This form of arousal is characterized by gradual development. The patient is in a good mood, slightly exalted, and speaks pompously. Consciousness is preserved. As it develops, the behavior becomes more silly.
The transition from one state to another is quite abrupt.
How does catatonic schizophrenia manifest?
Motor dysfunction is a characteristic symptom of catatonic schizophrenia. The patient becomes agitated or stupor, the condition may suddenly change.
With catatonic schizophrenia, there is:
-
Pillow Syndrome. Even if a person is lying on a perfectly flat surface, he keeps his head slightly raised. The position does not change: the patient is awake and asleep in this position.
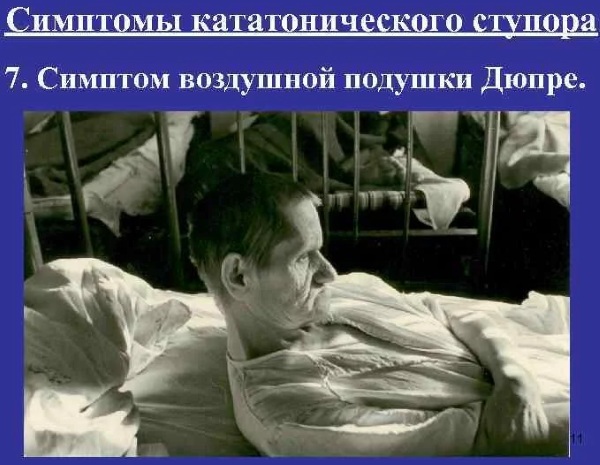
- Hood syndrome. The patient tries to hide his head by covering it with various items of clothing, a blanket, a sheet or a blanket.
- Trunk Syndrome. The behavior is dominated by sucking, grasping reflexes.
- Mutism. During an attack, the patient remains silent, not responding to someone else's speech and actions. He is fully aware of what is happening.
- Echolalia. The patient begins to copy the behavior of others, right down to the words of facial expressions and actions.
Catatonic schizophrenia is manifested by several syndromes at the same time. The patient feels depressed, may be aggressive during an attack. Pathology is characterized by redness and hallucinations.
How can catatonic syndrome be complicated?
If not properly cared for, the patient can die of hunger and dehydration. With catatonic stupor, patients develop pressure sores. Against the background of a decrease in immunity, the risk of developing diseases of an infectious etiology is high.
In a Catholic stupor, the internal systems of the body do not work properly. Possible problems with bowel movements and emptying the bladder. Complications include intestinal obstruction and urinary retention. The patient often walks under himself. Complications from the muscular and nervous systems are manifested in the form of paralysis or contracture.
Diagnostics
Substupor or stupor is diagnosed due to clinical manifestations and other specific symptoms (impaired motor activity, speech, behavioral disorders). The psychiatrist, in addition to confirming the fact that the patient is in a stupor, must determine the exact cause and identify the diseases that led to the development of pathology.
The specialist examines the patient, interviews his relatives and prescribes a number of apparatus examinations and analyzes. Patients suspected of having catatonic stupor should have EEG testing.
Screening can detect other neurological conditions. The results are usually satisfactory, provided that there are no associated conditions that cause the development of the disease.
Various neurological conditions can provoke catatonia, so the patient is prescribed an MRI. Imaging of the brain can detect circulatory disorders or other organic damage.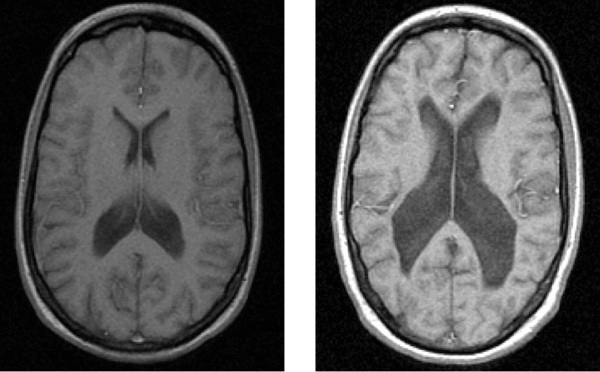
Diagnostic tests include:
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- examination of the endocrine system;
- Ultrasound of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland;
- angiography of the vessels of the neck and brain;
- analysis for the human immunodeficiency virus;
- blood clotting test;
- bacterial culture of blood and urine for pathogenic microflora.
Differential diagnosis allows you to identify a disease, the symptoms of which are similar to catatonia.
These include:
- selective mutism;
- conversion disorder;
- stiffness syndrome;
- malignant hyperthermia;
- Parkinson's disease.
During the examination, a specialist must differentiate all possible causes that can provoke a stupor.
Treatment of catatonic syndrome with drugs
A patient with suspected catatonic stupor should be hospitalized. In some cases, they are transferred to the intensive care unit for constant care and monitoring of the functioning of internal systems. The composition of drug therapy includes drugs of the benzodiazepine series. Their principle of action is based on the stimulation of aminobutyric acid neurotransmitters.
The active ingredients reduce its activity. Medications have a hypnotic, sedative effect, reducing arousal and relaxing muscle tissue. These drugs are characterized by a moderate anticonvulsant effect. Organic catatonia lends itself to therapy with benzodiazepine drugs.
Some patients have drug resistance. They are prescribed electroconvulsive therapy. The method is actively used to treat various mental illnesses, including schizophrenia, hysterical and idiopathic catatonia, depression. The method is considered quite radical - it helps to increase the concentration of dopamine.
Drugs effective for catatonia: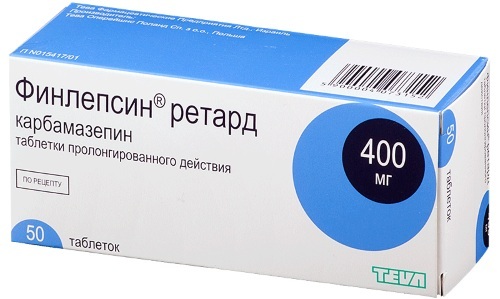
| Name | Release form and composition | pharmachologic effect | Contraindications | Instructions |
| Finlepsin | It is marketed in pill form. The main component is carbazepam (no more than 200 mg). | Analgesic, antidiuretic, antipsychotic, antidepressant. | Simultaneous reception with MAO inhibitors, atrioventricular block, intermittent acute porphyria, blood diseases, intolerance. | The initial dose is 400 mg. with the permission of the doctor, it is increased to 1200 mg. |
| Risperidone | Release form - tablets. The main component is the substance of the same name (1, 2 or 4 mg). | Sedative, antiemetic, antipsychotic. | Glaucoma, seizures, pregnancy, heart failure, childhood, Parkinson's disease, prostatitis. | The therapeutic norm is 4-6 mg, which is equivalent to 1, 2, 3 or 6 tablets. |
| Amantadine | It is marketed in pill form. The active ingredient is amantadine (10 mg). | Antiparkinsonian, antiviral. | Lactation, gestation period, prostatic hyperplasia, glaucoma, thyrotoxicosis, epilepsy. | The initial dose is 10 mg. the maximum daily allowance is 40 mg. |
| Dantrolene | Release form - solution, capsules. The main component is the substance of the same name. | Antiepileptic, antidepressant, anti-sclerotic. | Pregnancy, childhood, heart, kidney or liver failure, intolerance. | Solution - 1 mg / kg, capsules - 5-8 mg / kg. |
| Diazepam | It is marketed in the form of a solution and dragee. The active ingredient is diazepam (5-10 mg). | Anxiolytic, hypnosedative, muscle relaxant, tranquilizing. | Pregnancy, angle-closure glaucoma, chronic hypercapnia, myasthenia gravis, hepatic / renal failure, hypersensitivity. | Solution (w / m, w / w), pills - up to 15 mg / day. |
| Lorazepam | Release form - solution, tablets. The main component is lorazepam. | Anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, sedative, hypnotic. | Lactation, sleep apnea, pregnancy, respiratory failure, myasthenia gravis, glaucoma, hypoproteinemia. | The daily rate is 5 mg. |

Catatonic stupor is treated with muscle relaxants. In this condition, the patient is prescribed drugs that support the work of the digestive tract. Psychotropic medications are available by prescription.
Side effects of drug therapy
Medicines prescribed to patients with Catholic stupor are not always well tolerated. With prolonged use, the risk of side effects is quite high.
Malaise occurs from the side:
- urinary and genital area: incontinence, delayed outflow of urine, false urge to empty the bladder, impotence, menstrual irregularities;
- digestive tract: loss of appetite, diarrhea, dry mouth, instant jaundice:
- circulatory systems: anemia, leukopenia:
- organs of vision and hearing: tinnitus, loss of visual acuity, diplopia;
- nervous system: outbursts of fear, aggression, suicidal tendencies, muscle spasms, hallucinations, delirium, mood swings, catalepsy, drowsiness, fatigue, lethargy, ataxia.
Drugs cannot be abruptly canceled. In this case, the risk of tremor and dysphagia increases.
Forecast
In the absence of proper care, the prognosis is rather disappointing. If the patient was placed in a state institution, where it is technically impossible to provide him with proper treatment and examination, then there is a high probability of his death. If the disease is deeply rooted in behavioral aspects, then it is quite difficult to get a person out of the stupor. The prognosis is poor in the presence of complications.
Catatonic stupor at the initial stage, characterized by movement disorders, is treatable with medication. This condition leads to personal degradation, so it is important to seek qualified medical help when the first signs of the development of pathology appear.
Video about catatonic stupor
How a doctor brought a schizophrenic out of a catatonic stupor: