Status epilepticus is a common neurological disorder associated with seizures and other disorders.
Relief of symptoms requires the use of special medications and adherence to certain rules. Means for eliminating manifestations can be taken in short and long courses, depending on the condition, the presence of concomitant deviations.
Record content:
- 1 Classification
- 2 Status epilepticus: clinical picture
- 3 Complications of status epilepticus
-
4 Emergency care for an epileptic seizure
- 4.1 Before the attack
- 4.2 During an attack
- 4.3 After an attack
- 5 Drugs for treatment and remedies for relief
- 6 Prognosis and clinical guidelines
- 7 Status epilepticus videos
Classification
Status epilepticus is a severe neurological disorder with frequent seizures as epilepsy progresses. The condition can provoke disorders from the internal organs, as well as systems.
Diagnosis of the status is carried out only in the case when for a short period of time in patients several convulsive seizures develop, while the beginning of the next one is noted without recovery of the state after the previous one.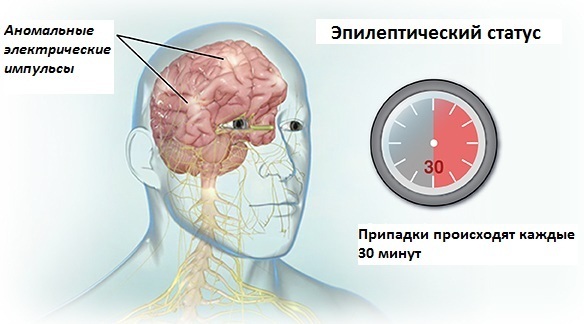
This means that after the initial seizure, the patient loses consciousness, his condition worsens for a certain time. The second attack develops almost immediately, and the patient's consciousness is not restored. That is why experts talk about status epilepticus.
On average, patients with epilepsy experience from 1 to 10 seizures during the year, which depends on the medications taken and the characteristics of the condition. With frequent recurrence of seizures, patients develop status epilepticus, which can be of different forms and stages. Experts identify several types of pathological conditions.
| Name | Peculiarities |
| Generalized status | With this disorder, patients lose consciousness during an attack. In this case, the appearance of extensive seizures is noted, which affect the limbs, trunk. With this type of disease, the patient's condition deteriorates significantly, the development of concomitant abnormalities from the side of the brain and internal organs is possible. |
| Not fully generalized status | With this type of disease, convulsive seizures are atypical, the patient completely loses consciousness, there is a deterioration in respiratory function, which can provoke death. Often, this form of the disease affects children. |
| Focal paroxysms | This form is considered one of the lungs, since it is accompanied by convulsions of certain muscle groups, for example, on the face, one side of the body or one limb. With such a disorder, the patient does not always lose consciousness, only a temporary disturbance is possible. |
| Non-convulsive status | This type of disease proceeds without the development of a convulsive attack. The patient loses consciousness during an attack, but any muscle contractions are absent. |
| Partial status | A mixed form of the disease, in which loss of consciousness may be partial or complete, but convulsions are always present. |
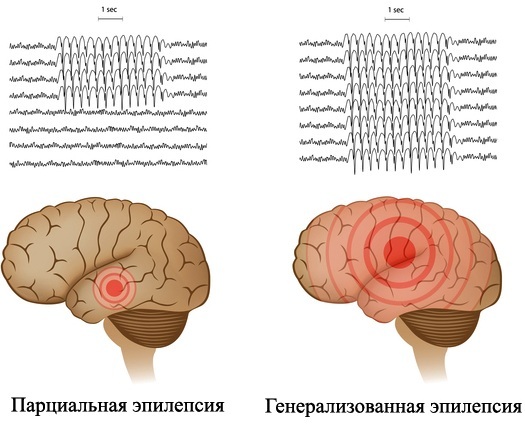
Depending on the type of disease, the patient's symptoms differ, as well as accompanying deviations.
The relief of status epilepticus (funds can prevent the development of complications with such a violation) is recommended to be carried out at the initial stage, when there are no acute manifestations.
Experts distinguish several stages of the pathological condition, accompanied by various disorders:
- The stage of precursors usually lasts several minutes and is accompanied by typical signs in the form of worsening of the condition, headache.
- The initial stage in most cases lasts no more than 30 minutes. At this stage, more pronounced disorders appear, the symptoms of concomitant diseases are aggravated.
- The advanced stage is considered the most severe, lasts about 60 minutes, accompanied by acute and subacute manifestations.
- The refractory stage proceeds with different manifestations, usually lasts several hours. After its completion, the patient's condition gradually returns to normal.
The patient can receive help at any stage of the attack, but when the first symptoms appear, it brings more pronounced results and significantly reduces the risk of developing severe complications.
Status epilepticus: clinical picture
Epilepsy is considered a fairly common neurological disorder. Therefore, most patients can distinguish the manifestations of the disease. At the initial stage, the large becomes detached and apathetic. He refuses food, takes a horizontal position. Many people talk about the appearance of a severe headache.
If the patient has a history of cardiac and vascular pathologies, it is possible to develop tachycardia, arrhythmias and fluctuations in blood pressure indicators. In this case, there is a deterioration in the work of the respiratory system. Patients notice shortness of breath, they have shortness of breath, which is not associated with physical activity.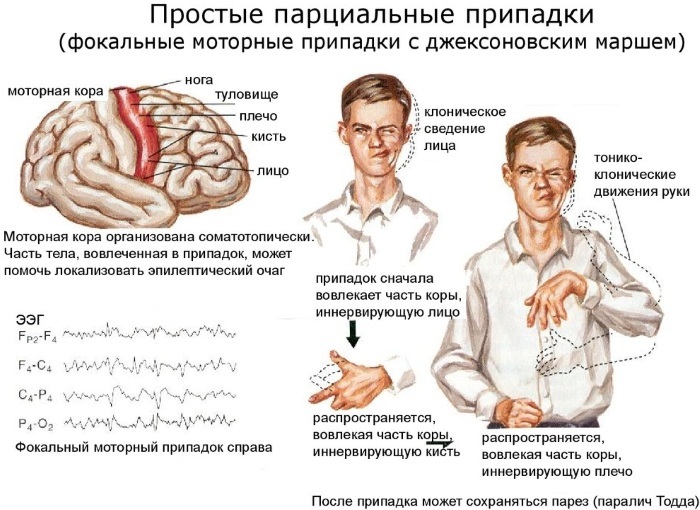
After the transition of pathology to the initial stage, the following symptoms may join:
- Changes in the size of the pupils to one side or the other, which is associated with fluctuations in blood pressure indicators.
- The patient's unconscious gaze. Even when referring to him, the doctor cannot achieve attention, the patient simply does not understand the words and does not react to them, which significantly complicates the diagnosis and definition of concomitant deviations.
- For several minutes, convulsions join. At the initial stage, they are clonic, somewhat later they become tonic. The patient's body bends in one line, the head is thrown back.
- With such cramps, the emphasis is on the head and feet only. For a long period, the patient can be in this state. Such manifestations are dangerous and can provoke other complications.
- Often the condition is accompanied by indigestion, pain in the abdomen. Patients, while retaining consciousness, refuse to eat, but often suffer from thirst, accompanied by dry mouth.
When symptoms worsen, patients report repeated vomiting over a short period of time. Often, during an attack, involuntary emptying of the intestines and bladder occurs. Patients often have foam in the mouth, and seizures lead to biting of the tongue.
In severe cases, blood appears on the tongue and lips. If the pathology is mild, psychosis may develop. In this case, the patient is conscious, but his condition is significantly aggravated.
Respiratory dysfunction often leads to discoloration of the skin. In the initial stages, it becomes pale, but as the symptoms worsen, the face becomes cyanotic or purple, depending on the blood pressure indicators.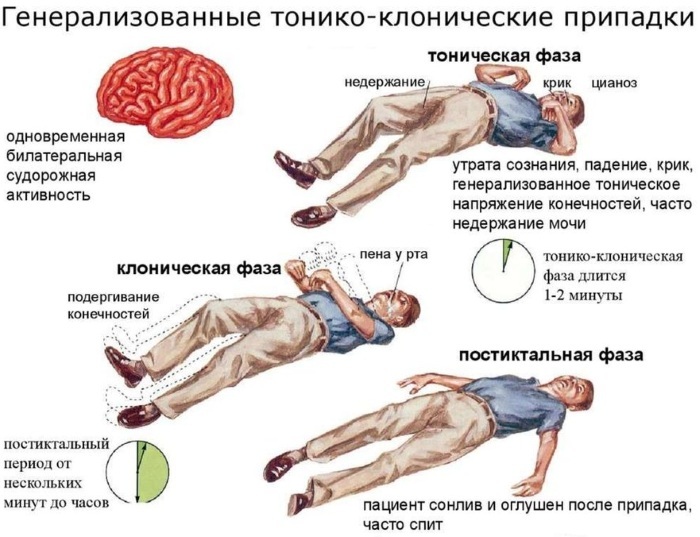
Relief of various types of status epilepticus in mild and severe course can be carried out with the help of different drugs. The remedies are usually selected depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Complications of status epilepticus
With the progression of the pathological condition, patients often develop various complications. Many of them can lead to irreparable consequences.
The most common disorders are:
- Pulmonary artery thrombosis.
- Severe oxygen starvation of tissues, which can provoke cerebral edema.
- A critical increase or decrease in blood pressure indicators, which can lead to the development of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, and other disorders.
- Damage to muscle fibers, which occurs as a result of the accumulation of excessive amounts of lactic acid in them.
- Violation of the psycho-emotional state, the progression of chronic mental disorders.
The most dangerous complication is death as a result of acute cerebral edema or respiratory arrest on the background of seizures. Experts note that the non-convulsive form of the pathological condition is not so dangerous and less likely to provoke complications.
Emergency care for an epileptic seizure
Depending on the stage of development of the pathological condition, the methods of first aid may differ. In each case, the specialist determines the need to use one or another means, method.
Before the attack
Until the onset of an attack, therapeutic measures are usually not taken. If the patient has a history of any form of epilepsy, they usually take anticonvulsants. The main method of assistance is considered to be adherence to dosages prescribed by a specialist, as well as regular visits to a doctor.
A specialist assessment of the patient's condition helps prevent complications. At the reception, the dosage is also adjusted if the patient or doctor notes a decrease in the effectiveness of therapy. Methods for preventing the development of an attack include the exclusion of psychoemotional stress, stressful conditions.
During an attack
Relief of status epilepticus (funds are selected in each case individually) is usually required immediately when its symptoms appear. The main goal of people who are near the patient at the time of the attack should be to prevent his injury before the arrival of an ambulance.
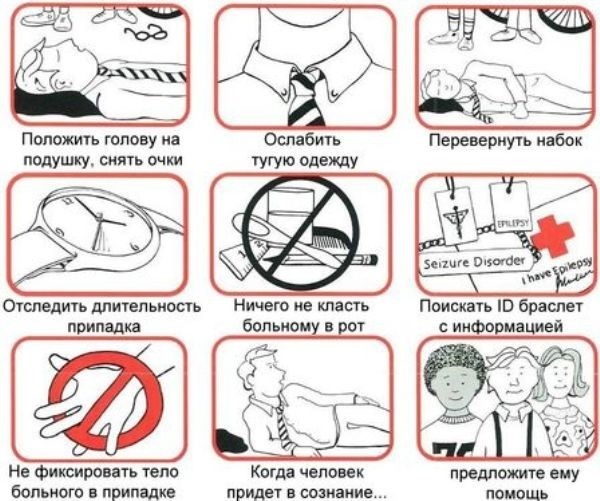
The sequence of actions when providing assistance:
- Provide fresh air to the patient.
- Unbutton tight clothing that can cause injury if symptoms worsen.
- Place the patient on a flat surface and, if possible, put a handkerchief or a piece of clean cloth in the oral cavity, which will help prevent injury to the teeth and tongue.
- If the patient's teeth are compressed, they must be unclenched with care. Some experts recommend not doing this at all, but the standard treatment regimen involves unclenching, which will help prevent the tongue from blocking the airways.
- When a large amount of saliva appears in the mouth, it is necessary to turn the patient's head on its side to eliminate the likelihood of it entering the respiratory tract.
- If there are sharp, hard objects nearby, they should be removed so that during convulsions the patient does not harm himself and others.
When providing assistance, do not overly fix the patient's body. This can lead to limb fractures. It is strictly forbidden to give the patient any medications in any form during an attack.
After an attack
When the first signs of an attack appear, people who provide assistance on the spot are advised to fix the time of its beginning and end. Emergency physicians may need this information.
After the patient returns to consciousness, he should be offered help. Usually, by this time, his condition is normalized, and an ambulance is in place. If necessary, the patient is injected with solutions to restore water balance and placed in a hospital. There the patient undergoes treatment, he is prescribed appropriate drugs to improve his condition.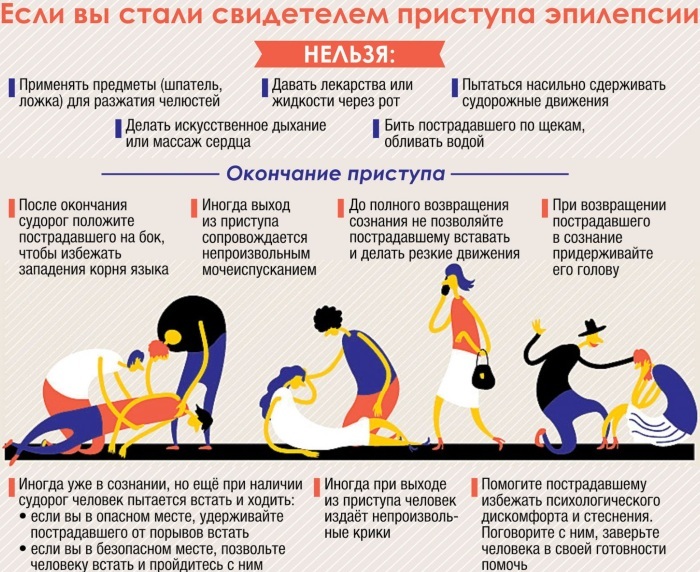
If the doctor does not come before the end of the attack, the patient should not be given any medication on the spot. It is allowed to drink water, do not suddenly take an upright position. If the seizures persist, it is worth staying in a horizontal position.
Drugs for treatment and remedies for relief
Relief of status epilepticus (drugs are usually used to prevent such complications) is carried out at the initial stage. This means that the patient is prescribed drugs that are used to treat pathology and help prevent or significantly reduce the number of attacks within a short period of time.
Most often, patients are prescribed the following medications:
- Diazepam has a pronounced sedative and muscle relaxant effect on skeletal muscles. The drug is used in various forms of epilepsy in order to prevent the development of status epilepticus. The tablets are used for several weeks or even months, depending on the severity of the condition. The daily dosage ranges from 5-20 mg, it can be divided by 2 times during the day. The drug can also be administered intramuscularly or intravenously in severe disease. Such treatment is carried out in a hospital and the dose is determined in each case individually.
- Relanium used in severe disease, injected intramuscularly at 2 ml per day for 1-2 weeks, depending on the condition. After relief of acute symptoms, the patient takes pills. The remedy has pronounced sedative properties, relaxes muscles and leads to an improvement in the condition, prevents the development of complications.
-
Phenobarbital refers to drugs from the group of barbiturates and has pronounced antiepileptic properties. In addition, the medication has a hypnotic effect, improves the patient's sleep and reduces the number of attacks within a short period of time. Tablets are taken in 1-2 pieces, depending on the severity of the symptoms. The duration of the course in each case is determined individually, but usually it is used in short courses of 7-10 days, since prolonged use leads to the development of addiction.

- Dexamethasone injected intravenously or intramuscularly in the acute course of the condition. It helps prevent the development of cerebral edema and somewhat improves the patient's well-being. The dosage is also determined individually, but usually from 8 to 16 mg is administered. The treatment lasts up to 10 days.
- Furosemide used simultaneously with Dexamethasone, as it has diuretic properties and helps prevent the development of cerebral edema. The patient is injected intravenously or intramuscularly with 2-4 ml of solution. Such treatment lasts no more than 5 days. When diagnosing severe renal failure, no medication is prescribed.
- Magnesium sulfate injected intravenously at 5 ml per day with the preliminary addition of 15 ml of sodium chloride 0.95. The agent must be poured in slowly, as it leads to the appearance of intense heat. Treatment lasts from 10 to 20 days, depending on the degree of neglect of symptoms. It helps lower blood pressure and improves brain nutrition. If the patient is diagnosed with persistent hypotension, the drug is not prescribed.
In each case, the specialist individually decides on the appointment of a particular agent. The duration of treatment is also determined individually. The patient takes many funds on an ongoing basis, but regular visits to the doctor are required.
Other means may be included in the course of treatment, depending on the presence of concomitant complications and diseases of internal organs.
Prognosis and clinical guidelines
Subject to the doctor's recommendations and taking special medications, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. You can control the condition and reduce the number of attacks. In the absence of timely treatment, the prognosis is unfavorable, the development of mental and neurological abnormalities, severe complications from the vessels, brain, heart is possible.
Patients with such disorders are advised to regularly visit a doctor and take medications that improve the condition. If necessary, the dosage is adjusted by a specialist depending on the condition. Doctors also recommend avoiding stress, balancing the diet, and ensuring regular physical activity.
An important recommendation is the rejection of alcoholic beverages, cigarettes, drugs. If any deterioration occurs, the patient should consult a doctor. It is strictly forbidden to independently change the dosage of the drug or take medications without a doctor's prescription.
Status epilepticus is considered a common neurological disorder, which can be difficult to control when the manifestations worsen. The means for therapy are selected individually. They cannot completely eliminate the symptoms, but they significantly improve the condition, prevent various disorders.
Status epilepticus videos
Status epilepticus A to Z:



