Hematocrit value determine the proportional relationship in the blood plasma of the formed elements - platelets, leukocytes and erythrocytes. The norm of this laboratory indicator in women changes slightly with age and is 36-46%. Such an analysis makes it possible to diagnose pathologies at an early stage of development.
Record content:
- 1 Functions in the body
- 2 How and under what conditions is it produced
- 3 Indicator table is normal
- 4 Symptoms of the rise and fall
- 5 Reasons for promotion and demotion
- 6 Indications for research
- 7 How is it determined
- 8 Preparation and analysis
- 9 Decoding the results
- 10 When to see a doctor
-
11 How to bounce back
- 11.1 Medications
- 11.2 Folk methods
- 11.3 Other methods
- 12 Possible complications
- 13 Video about hematocrit
Functions in the body
The hematocrit number is a specific laboratory feature that characterizes the ratio of blood cells to the total volume of biological fluid.
A source of decrease or increase in the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets are various factors of age, physiological, pathological nature:
- dysfunction of internal organs;
- inflammatory processes;
- malignant or benign neoplasms;
- pregnancy;
- hormonal changes;
- various diseases of the endocrine system;
- trauma;
- bacterial and viral infections, much more.
Each indicator taken separately does not have significant diagnostic value. To assess the entire clinical picture in the aggregate, a hematocrit value has been developed.
This laboratory sign allows you to identify pathological abnormalities at the initial stage of their development and formation. It provides a basis for a more detailed diagnosis.
This is the main function of hematocrit in the body. This number is a kind of marker of diseases and pathological disorders. The level of the plasma state and active agents is determined by the percentage of the liquid fraction of blood and the uniform components.
How and under what conditions is it produced
Red blood cells, called red blood cells, are special cells that deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This laboratory indicator determines their content relative to other shaped elements.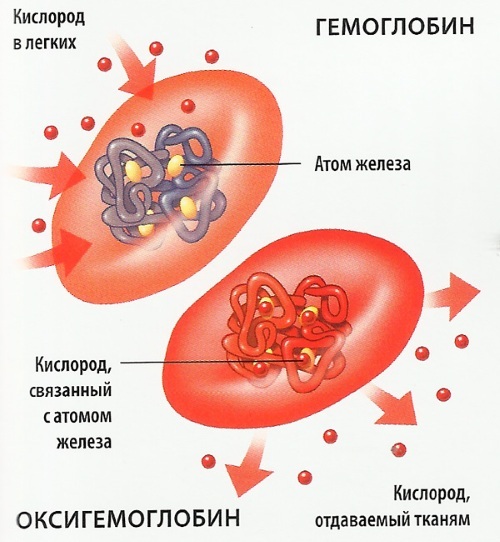
Red blood cells are made up of hemoglobin, a specific protein that captures oxygen atoms and transports them into cells, simultaneously removing carbon dioxide. As a standard, the blood formula of a healthy person is 60% composed of the plasma (liquid) fraction and 40% of the corpuscles.
Hematocrit (the norm in women by age changes under certain physiological conditions) characterizes their ratio with leukocytes and platelets, the total content of which does not exceed 1%. Indirectly, this laboratory parameter is an indicator of cell respiration.
The hematocrit value is used for:
- diagnosing anemia and evaluating the effectiveness of its treatment;
- determining the level of tissue dehydration;
- making a decision on the feasibility of carrying out hemosorption;
- obtaining data on the results of transfusion.
This specific laboratory sign acts as a component of the biochemical blood test and is not evaluated separately. The hematocrit number is always directly related to the volume of red blood cells, given the standard size of the latter.
The relationship between the factors influencing the synthesis of intracellular hemoglobin and the level of their content in blood plasma is not observed. The deviation of this laboratory indicator from the standard value does not necessarily indicate the presence of pathology, but serves as the basis for additional examination.
Indicator table is normal
The hematocrit is correlated with age and sex. The permissible deviation from the norm is no more than 5%.
The reference values are summarized in the table:
| Age | Women, % | Men, % |
| Newborn | 42-52 | 42-52 |
| Babies 6 months old | 34-44 | 34-44 |
| From 6 months to a year | 32,5-41 | 27,5-41 |
| 1-3 years | 30-40 | 28-40 |
| 3-6 years old | 31-40 | 31-39 |
| 6-12 | 32-41 | 32-41 |
| 12-16 | 33-43 | 34-47 |
| 16-19 | 32-43 | 35-48 |
| 19-30 | 33-44 | 38-49 |
| 30-40 | 33-44 | 38-49 |
| 40-50 | 33-45 | 38-49 |
| 50-65 | 34-46 | 37-48 |
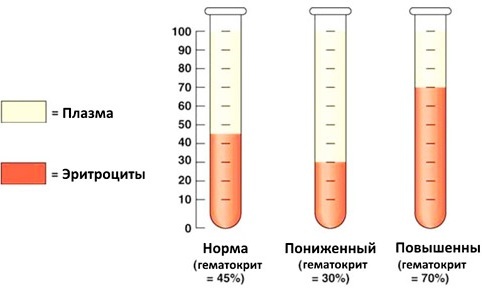
Hematocrit (the norm in women by age is indicated in the table) decreases in the presence of iron deficiency anemia. This is due to a decrease in the size of red blood cells. Critically dangerous is the hematocrit number below 30% and above 55%.
With such indicators, the rheological properties of blood are violated, in particular, coagulability. Leukocytes, which perform a barrier function, cease to cope with their task.
This leads to the vulnerability of the body to bacterial and viral invasion. At different ages, hematocrit values change, which is associated with an increase in blood volume and, accordingly, the uniform elements of its formula.
Symptoms of the rise and fall
Signs of a violation of the proportions of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets are manifested in various conditions.
Common symptoms with low hematocrit:
- apathy;
- prostration;
- chronic fatigue;
- constant sleepiness;
- dyspnea.

The signs are due to the course of the pathology or physiological state that caused the change in the hematocrit number.
With an increase in this specific laboratory indicator, pain occurs:
- in the joints;
- the spinal column;
- ribs;
- chest;
- in the limbs.
A common sign of an increase in hematocrit is unreasonable swelling of soft tissues. Pain syndrome in each case has a different intensity and duration.
Violation of the hematocrit may be accompanied by an increase or decrease in body temperature, suppression of appetite, and a yellowish tint of the facial skin. Often the mucous membrane dries up, ulcerative destruction appears in the oral cavity.
In especially severe cases, tactile sensitivity decreases, visual function is partially inhibited. When such alarming symptoms occur, there is every reason to suspect the development of a dangerous pathological process.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
The etiology of hematocrit disorders is numerous and varied. A decrease or increase in this specific blood parameter is caused by both natural causes, which eventually disappear on their own, and pathologies that require immediate medical intervention.
Type 1 etiological factors include:
- profuse blood loss due to trauma or surgery;
- a wasting diet and an unbalanced vegetarian diet low in iron;
- sedentary life (hypodynamia);
- dehydration of the body;
- taking diuretic medications and a course of treatment with shock doses of corticosteroid drugs;
- oxygen starvation, which the body is trying to compensate for with increased hemoglobin synthesis.
The latter reason may be caused by the region of residence (mountainous areas located high above the world ocean level) or the abuse of nicotine, which constricts blood vessels.
Pathological factors of hematocrit disturbance and deviations from the norm in the table in women by age include:
- leukemia and other blood diseases;
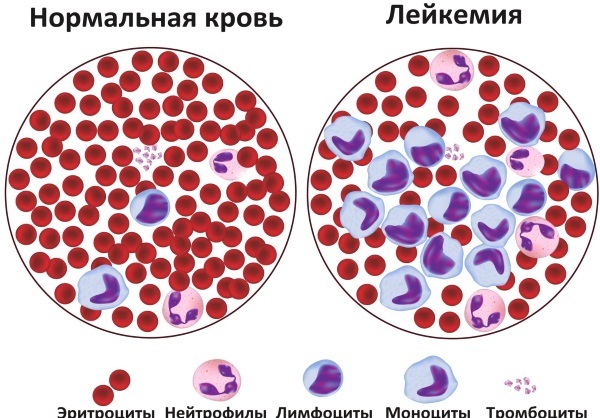
- erythremia - erythrocyte proliferation;
- secondary erythrocytosis;
- tumor neoplasms in the renal organ, causing increased synthesis of erythropoietin;
- hydronephrosis and polycystic pathologies;
- Congenital heart defect;
- hemoglobinopathy;
- dysfunction of the lungs and other respiratory organs;
- sickle anemia.
Hodgkin's lymphoma, a malignant destruction associated with the proliferation of cells of lymphoid tissues, leads to a violation of the hematocrit number. Erythrocytes destroy some pathogenic agents and intoxication of the body with synthetic or organic poisons inhibits.
Indications for research
A blood test to determine the hematocrit number is prescribed if the patient has a history of genetic mutations, hereditary diseases, and renal failure.
Common provocateurs for violations of the proportions of blood corpuscles:
- oncology of any localization;
- abnormally low content of protein compounds in plasma and serum;
- thalassemia - inhibition of the secretion of polypeptide chains that are part of the structure of hemoglobin;
- myeloma;
- peritonitis;
- dynamic injuries of internal organs;
- fractures;
- hemoblastosis - a tumor of the hematopoietic and lymphatic tissue;
- renal vascular stenosis;
- dysbiosis;
- cirrhosis;
- malaria;
A laboratory analysis to determine the Ht index is prescribed by a hematologist or family doctor for varicose veins. expansion of the veins of the esophagus, damage to the spinal cord of any genesis, poisoning with hemolytic poisons and heavy salts metals.
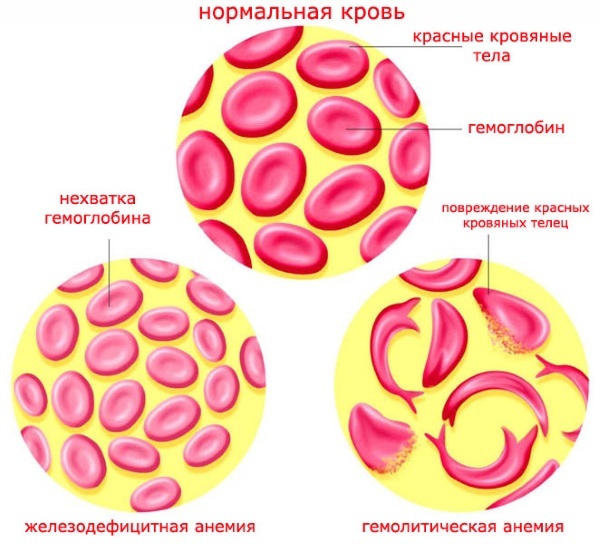
In 20-25% of cases, hematocrit disorder is provoked by anemic pathologies.
The risk group includes people with certain physiological conditions:
- consuming a large daily volume of fluids;
- 4th month and later period of bearing a child;
- active stage of the menstrual cycle;
- excessive absorption of table salt;
- postpartum period.
Women and children are more likely to experience a decrease in Ht, while men are more likely to increase.
How is it determined
Venous blood is taken for analysis. It is filled with special medical test tubes made of transparent graduated glass or plastic. The biological fluid is processed by centrifugation to separate blood into fractions.
Hematocrit (the norm in women by age depends on the physiological state to a greater extent than in men) is calculated by the micro- or macroscopic method. The latter is considered to be more accurate.
The blood is mixed with an anticoagulant laboratory reagent that prevents the biological fluid from clotting. A test tube from the compositions is installed in a centrifuge. The blood processing process takes about 1.5 hours.
During this time, the tube is unwound to the maximum speed for the technical characteristics of the model laboratory centrifuge. All components of the blood formula differ in specific gravity and density. Therefore, they are easily separated into layers.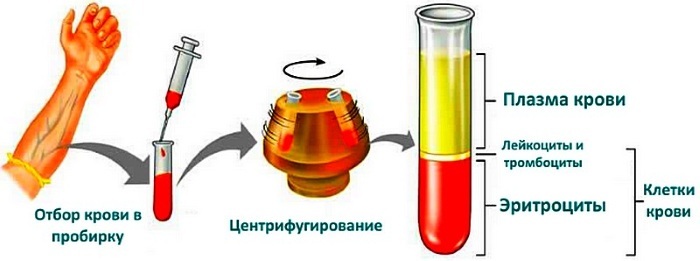
After the completion of the centrifugation process, the laboratory assistant, using a high-precision scale applied to the test tube, determines the percentage of each fraction. Since red blood cells are the heaviest blood cells, they settle to the bottom of the flask.
Leukocytes and platelets are placed sequentially above them. The uppermost layer is occupied by plasma cleared of functional cells. For maximum analysis accuracy, the test tube is marked from 0.01 to 100.00%.
All biological material placed in a laboratory vessel is taken as 100%. Further definition of complexity does not constitute. The resulting indicator is considered the hematocrit number. If the analysis is done after blood loss, including menstruation or surgery, it may be distorted.
Preparation and analysis
The established rules for preparing for blood donation for laboratory research also apply to the determination of the hematocrit number:
- The sampling of biomaterial is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach.
- The last meal should be at least 8 hours in advance. before taking the analysis.
- Taking blood will make it easier to drink plenty of clean water without gas and sugar, which dilutes the biological fluid.
- The analysis is not carried out against the background of drug therapy with diuretic, anticoagulant and corticosteroid drugs.
- It is better not to take any medications at all before the procedure.
The concentration of blood corpuscles is significantly influenced by physical activity and psychoemotional stress. Therefore, during the procedure, it is advisable to be in a state of rest and balance.
The puncture site is pretreated with antiseptic compounds. Blood is drawn into a regular 20-cc syringe or into a special vacuum container with a medical needle. From there it is poured into a graduated laboratory tube.
The analysis result is distorted by:
- helminthic invasions;
- colds;
- influenza strain;
- food poisoning;
- any intoxication of the body;
- avitaminosis;
- changes in hormonal levels.
In the presence of such conditions, it is advisable to refrain from taking tests.
Decoding the results
The analysis is interpreted by the doctor. However, the research results are not difficult to figure out on their own. The balanced blood formula has a 6: 4 ratio between plasma and total blood cell count.
Depending on the fluctuation in one direction or the other, the Ht indicator is considered to be increased or decreased. The average (reference) value is in strict correlation with age and gender. Additional physiological factors are usually at work.
Hematocrit (the norm in women by age should not go beyond 30-45%). For men, this indicator varies in the range of 35-49%. A 5 percent deviation is acceptable. If it is greater, the hematocrit number is considered to be understated or overestimated.
Such a result may be caused by temporary natural causes and not be of diagnostic value. But in any case, medical advice and additional examination are highly recommended.
Disturbances in the balance of blood cells are often associated with dangerous pathologies - oncological, endocrine, cardiovascular.
When to see a doctor
A hematologist, cardiologist or family doctor will refer you to a blood test to determine the hematocrit number. He also interprets the results of the analysis and, if necessary, directs them to a specialist with a narrow profile.
As a rule, first, additional tests are prescribed and hardware diagnostics are performed, and only then it is time for medical consultations, depending on the pathology detected.
How to bounce back
The success of therapy and the restoration of the Ht indicator consists in the elimination of the imbalance of the blood formula. In frequent cases, special clinical measures are not required. It is enough to change the way of life, give up addictions to alcohol and nicotine, and correct the diet.
They will help to quickly normalize the hematocrit value:
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- airing the room and everyday wet cleaning;
- drinking a lot of water;

- refusal from uncontrolled intake of drugs - Analgin, Aspirin and others, which are in every home medicine cabinet;
- doing sports or morning exercises;
Alcohol and caffeine are diuretics that lead to an imbalance in red blood cells. You must stop using them. These drinks dehydrate the body and stimulate urinary function.
Soda water and sweet juices belong to the same category. Antioxidants protect the body from free radicals, which contribute to the saturation of cells with oxygen. For sports activities, morning jogging and leisurely cycling are recommended.
Medications
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the imbalance of the blood cells. A universal technique has not been developed. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor only after a complete examination and identification of the cause of the hematological disorder.
In case of peptic ulcer disease, which often leads to a violation of the Ht index, a gastroenterologist develops therapeutic tactics. Usually it includes a complex intake of symptom suppressants - anabolic steroids, antiemetic medications, antispasmodics.
Additionally, analgesics are prescribed. To maintain the body's defenses, vitamin complexes and immunostimulants are prescribed.
Inflammation and dysfunction of the renal organ is treated:
- antibiotics;
- sulfa drugs;
- uroseptic agents;
- antibacterial medicines of the nitrofuran group.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used. Therapy for anemic syndrome, which leads to a violation of the blood count, is developed depending on the severity of the pathology. With an increased hematocrit, a course of medications is often prescribed to dilute the biological fluid.
In severe cases, a replacement solution is infused, which reduces the viscosity of the blood and improves its rheological properties.
Traditional medicines for hematocrit disorders:
- Interferon;
- Hydroxyurea;
- Anagrelide;
- Mielosan;
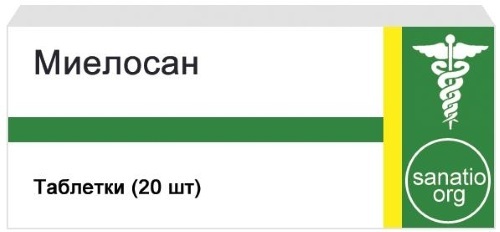
- radioactive phosphorus.
The duration of the course of treatment, dosage and combination of drugs, the doctor prescribes individually based on the clinical picture and the patient's history.
Folk methods
If a hematocrit disorder occurs, dietary correction is necessary.
Folk recipes provide for the use of iron-containing and protein-rich foods:
- chicken eggs;
- beef and pork;
- seaweed;
- legumes;
- sturgeon caviar.

It is advisable to include apples, dried apricots, raisins in your own diet. If the cause of the imbalance in the blood formula is iron deficiency anemia, you can make a special nutritious cocktail from carrots, beets and radishes.
They are passed through a coarse grater, squeezed and the juice is poured into a saucepan. It is placed in the oven and 3 tsp. torment at the smallest flame. Take the resulting broth 3 times a day after meals. The full course of alternative therapy is 3 months.
Other methods
If a decrease in the hematocrit number is associated with a breakdown and chronic fatigue syndrome, you can take 1 tbsp before meals. garlic pomace with honey, simmered 5 min.
150 ml of aloe extract mixed with 200 g of natural honey and a glass of Cahors wine helps well in this state. This remedy will increase the hemoglobin content in the blood. They drink it in 1 tbsp. 3 times a day before meals.
For the treatment of home methods of hematocrit disorders, garlic tincture with 96% alcohol is used. The vegetable is crushed and poured with a flammable liquid. It is necessary to withstand the solution for 2-3 weeks in a hermetically sealed bottle. Take 20 drops three times a day in a glass of fresh cow's milk.
Possible complications
Imbalance in the blood formula leads to acid-base imbalance in the body, dysfunctions of internal organs, creates favorable conditions for the invasion of pathogenic pathogens. This is fraught with numerous complications and the formation of severe pathologies.
With increased blood viscosity, it is difficult to remove toxins and toxins from the body, the protective abilities of the immune system are suppressed.
Life-threatening pathologies arising from hematocrit disorders:
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- airway spasm;
- gangrene of the extremities, requiring surgical amputation.
A change in the rheological properties of blood in a pregnant woman's body leads to severely complicated childbirth and fetal hypoxia. A child may be born with severe disorders of the central nervous system, destruction of bones and muscle fibers.
In such a responsible physiological state, a woman needs to carefully monitor that the hematocrit is normal. By age, such a deviation is more typical for pregnant women after 35 years than for young girls. If the Ht value is too high, the risk of thrombosis and vein blockage increases sharply.
Video about hematocrit
What is hematocrit:



