Often, in a laboratory study of urine in it detect altered erythrocytes.
Record content:
- 1 What does it mean?
- 2 Determination of red blood cells by type
- 3 Allowed Values Table
-
4 The main reasons for the excretion of red blood cells in the urine
- 4.1 Modified cells
- 4.2 Unchanged cells
- 4.3 In men
- 4.4 Among women
- 4.5 In pregnant women
- 4.6 The child has
- 5 External causes
- 6 Indicator in the analysis according to Nechiporenko
-
7 What to do with altered red blood cells
- 7.1 With increased
- 7.2 At reduced
- 8 Video about red blood cells in urine
What does it mean?
Red blood cells are non-nuclear blood cells whose main function is to carry oxygen to tissues.. They are detected by examining the urine sediment using a microscope.
The altered red blood cells in the urine are interpreted by various researchers ambiguously, and sometimes even contradictory. It is assumed that damage to the cell membrane occurs when they move across the basement membrane of the kidney glomeruli.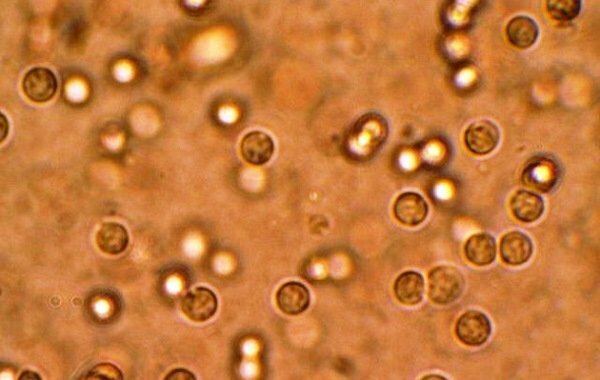
Then the injured red blood cells lose hemoglobin when passing through the distal tubules in a hypotonic environment of primary urine. If there are any changes in the structure of red blood cells, nephrological pathology should be suspected. For quite a long time, it was believed that altered erythrocytes appear in the urine exclusively with renal diseases.
Now, as a result of clinical, laboratory and instrumental studies, it has been established that the appearance of altered erythrocytes is affected by the prolonged presence of these cells in the urine before microscopic examination, as well as the osmolarity index urine.
Therefore, a very important point for the reliability of the test results is the correct collection of material and its prompt delivery to the diagnostic laboratory.
Determination of red blood cells by type
Altered and standard erythrocytes can be found in the urine. The latter appear under a microscope in the form of small yellowish round cells without granularity.
Altered (leached) erythrocytes, due to the loss of hemoglobin, appear in the urine of an alkaline reaction as colorless one- or double-circuit rings, in neutral urine - grayish discs with uneven edges, in acidic urine they have stellate, wrinkled shape.
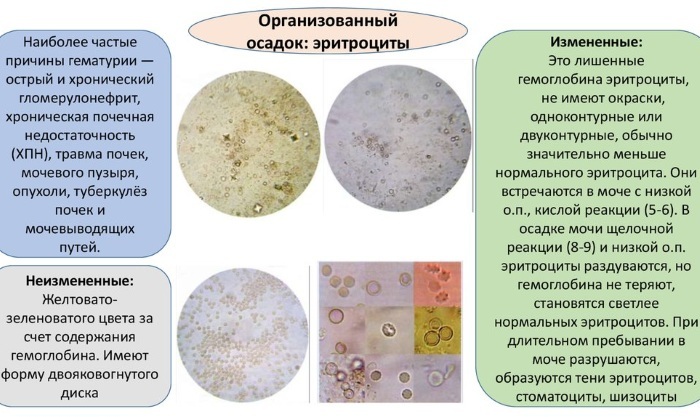
Laboratory research of the sediment is carried out according to a unified method. The urine delivered to the laboratory is shaken, 10 ml is poured and centrifuged for 10 minutes. at a speed of 1500 rpm. Then a precipitate is obtained by removing the supernatant.
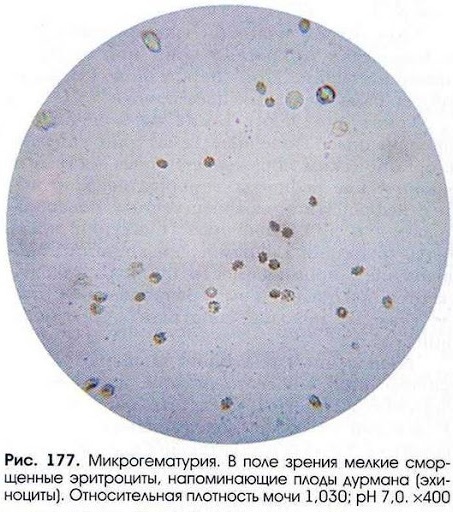
A small drop of sediment is examined under a microscope, first visually with a magnification of 80-100 times, and then in detail with a magnification of 400 times. In this case, there is a layer-by-layer examination of the material. It is considered normal if the number of erythrocytes in urine should not be more than 2 in the field of view at a standard magnification of 400 times. In cases of detection of 3 or more cells, we should talk about hematuria.
At the present stage, most laboratories analyze urine using automatic analyzers. Modern devices use the flow cytometry method. The analyzer determines the total number of red blood cells, detects altered red blood cells in the urine, differentiates destroyed (lysed) red blood cells.
The result is given in terms of 1 ml of urine. In complex urinary stations, sediment examination is carried out using a large number of micrographs. In a number of devices, red blood cell analysis is performed on test strips.
If such a study of urine reveals a positive result for erythrocytes or hemoglobin, it is imperative that the urine sediment be examined visually under a microscope. Only microscopy is a reliable method for determining red blood cells.
Differentiation of altered and unchanged forms of erythrocytes is carried out using the methods of phase contrast microscopy.
With glomerular hematuria, from 50% to 80% of erythrocytes, passing through the basement membrane of the glomeruli, change:
- contours become uneven;
- the shape looks wrong;
- the integrity of the membrane is violated;
- there is no hemoglobin.
A reliable sign of glomerulonephritis is the presence of acanthocytes as a result of urine analysis, which are erythrocytes with one, and possibly several outgrowths (resembling maple leaves).
The presence of more than 5% of acanthocytes is evidence in favor of glomerular hematuria. Acanthocytes are not formed during the differentiation of acidity and osmolarity of urine or long-term storage (up to a day) of urinary sediment. They are also not detected in healthy people.
Allowed Values Table
The excretion of red blood cells in the urine does not depend on gender and age. Acceptable indicators of the presence of cells in the sediment are universal for all groups of the population, except for children:
| Categories | The content of erythrocytes in the sediment |
| Men | 0-2 |
| Women | 0-2 |
| Children | 0-4 |
The main reasons for the excretion of red blood cells in the urine
When detecting red blood cells, it is necessary to determine the cause of this process. It is customary to distinguish hematuria into: extrarenal, renal, postrenal.
Modified cells
Altered red blood cells in the urine appear with extrarenal and renal hematuria.
Extrarenal hematuria is not associated with kidney disease, it is observed when:
- systemic blood diseases (erythremia);
- connective tissue pathologies;
- thrombocytopathies;
- hemophilia;
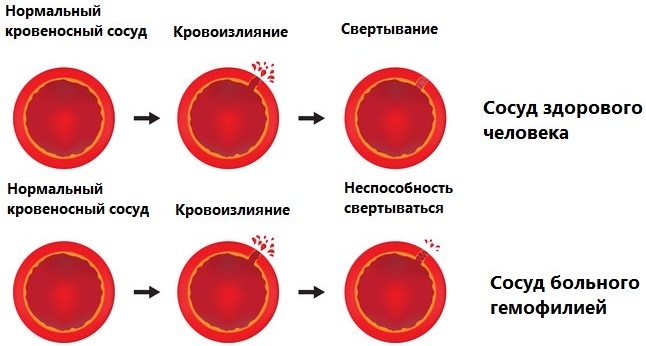
- hemolytic disease of the newborn.
In addition, red blood cells are found in urine in acute pathologies accompanied by fever, especially in pediatric practice.
In practically healthy people, they can be found when:
- overheating;
- heat and sunstroke;
- with significant physical overload;
- eating a lot of alcohol or spicy food.
Renal hematuria is:
- glomerular, caused by pathological processes of an immune or inflammatory nature in basement membrane of the glomeruli of the kidneys (glomerulonephritis, nephropathy, systemic lupus erythematosus, medicinal nephritis);
- tubular, with inflammatory or toxic damage to the renal tubules;
- with activation of intravascular blood coagulation (disseminated intravascular coagulation, antiphospholipid syndrome);
- in cases of seizure of the kidney parenchyma by inflammation (interstitial nephritis, tumors, myeloma, polycystic disease, hydronephrosis, tuberculosis);
- with pathologies of the renal vessels (heart attack, venous thrombosis);
- with metabolic disorders (hypercalciuria, hyperoxaluria, hyperuricosuria, cystinuria) with gout, oxalosis, uric acid diathesis, diabetes mellitus;
- with kidney injuries (crush injury, contusion);
- with congenital and hereditary kidney defects;
- with bacterial and viral infectious diseases as a result of the action of toxins (scarlet fever, mumps, influenza, dysentery, viral hepatitis).
Unchanged cells
Unchanged erythrocytes are found in urine in urological diseases with lesions of the calyces, renal pelvis, ureters and urethra, when the pathological focus is located below the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Postrenal hematuria is associated with inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract:
- stones of the ureters or bladder;
- benign or malignant tumors in the ureters, bladder, urethra;
- inflammatory processes: cystitis, urethritis;
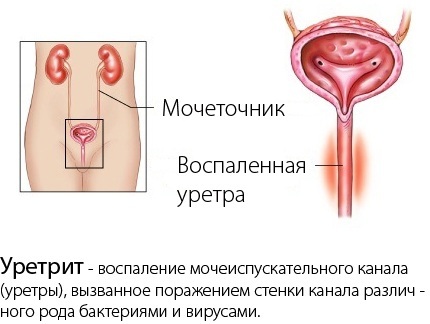
- parasitic diseases: schistosomiasis, filariasis, bilharziasis;
- injuries: bruises, prolonged walking, foreign body; taking certain medications: warfarin, heparin, cyclophosphamide;
- the appearance of large crystals of oxalates, uric acid, sharp edges injuring the mucous membrane of the urinary tract.
In men
Erythrocytes in the urine of men are present with inflammatory or malignant changes in the prostate gland (prostatitis, adenoma, cancer) or seminal vesicles.
Among women
In women, red blood cells can appear in the urine with inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs (vulvitis, vaginitis, endometritis), in diseases accompanied by bloody discharge (fibroids, endometriosis, cancer uterus).
In pregnant women
Hematuria occurs in 20% of cases in pregnant women, half of this amount is recorded for periods up to 32 weeks. According to statistics provided by various systems, from 6% to 12.2% of women during pregnancy suffer from pyelonephritis, accompanied by microhematuria, along with leukocyturia and bacteriuria.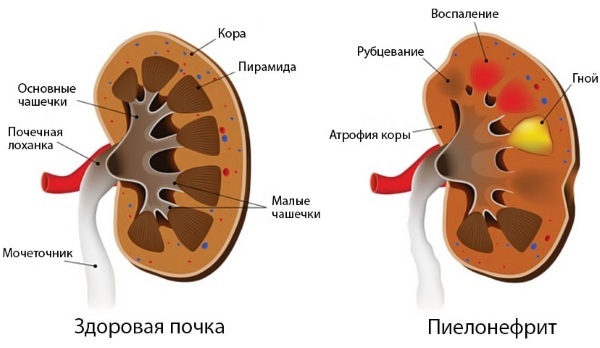
Gestational pyelonephritis negatively affects the further course of pregnancy, contributing to the development of preeclampsia, placental insufficiency, and fetal malnutrition.
Hematuria in pregnant women can be a symptom of the threat of spontaneous abortion, premature placental abruption. Hematuria during pregnancy is considered a risk factor for complications during childbirth. Pregnant women should be regularly examined and monitored by a doctor for the timely detection of pregnancy pathologies and treatment.
The child has
Changed erythrocytes in the urine of a child indicate the need for a comprehensive examination of the patient. Among pediatricians, there is no consensus on the quantitative criteria for hematuria in children.
According to the latest clinical recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia (2016), hematuria should be discussed if 3 or more cells were found in the field of view of non-centrifuged urine, or 5 or more cells in the urine sediment (with standard increase).
According to statistics, these phenomena are detected in 0.5-4% of children.
A detailed family history is of great importance in determining the cause of abnormalities in children in order to identify hereditary and congenital factors.
One of the main ones seems to be the age when the episode of hematuria was first noted. If this happened at an early age, then there is a high probability of genetic or congenital pathology. It is necessary to establish whether hematuria is chronic or appears in episodes against the background of hypothermia, physical overload, colds and other traumatic factors.
When examining a child, an additional examination of the genitals for inflammatory diseases should be carried out, smears for infection, scraping for enterobiasis should be taken.
If an inflammatory reaction is found, it is necessary to establish its etiology. With the predominance of lymphocytes in the smear and the appearance of eosinophils, one should think about the allergic process, with the predominance of neutrophils, one can assume the presence of an infection of a bacterial nature.
External causes
Due to the anatomical structure, red blood cells can enter the urine from the genital tract. Their sources in women are uterine bleeding, erosion and tumors of the cervix, sexually transmitted diseases, trauma. In the urine of men, red blood cells can be found in prostatitis, prostate cancer.
Diseases of the rectum, accompanied by rectal bleeding, can become a source of red blood cells in the urine. These are bleeding hemorrhoids, ulcers, polyps or rectal cancer, ulcerative colitis, anal fissures.
Indicator in the analysis according to Nechiporenko
Method A is used for the quantitative determination of red blood cells in urine. Z. Nechiporenko, proposed in 1961. According to a special unified technique, the number of erythrocytes in 1 ml of urine is determined.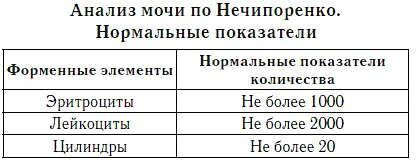 This indicator does not depend on gender and age and should not be higher than 1000.
This indicator does not depend on gender and age and should not be higher than 1000.
What to do with altered red blood cells
Altered red blood cells in the urine are a reason for urgent action. If they are found, it is necessary to establish the reasons for their appearance. If in a patient with already established kidney disease, altered cells appear in the urine, this indicates an exacerbation or progression of the pathological process.
In order to determine the nature of the process, clarify the diagnosis and timely prescribe adequate treatment, it is advisable to urgently seek qualified medical help.
With increased
To identify metabolic disorders, the daily excretion of calcium, phosphorus, and uric acid salts is determined. To exclude anemia and thrombocytopenia, a complete blood count is performed. In order to assess the filtration capacity of the kidneys, creatinine, urea, and electrolytes in the blood are determined.
To identify the pathology of the coagulation system, the main indicators of hemostasis are examined. In order to exclude the autoimmune process, an analysis is performed for serological markers of autoimmune pathology.
To identify defects in the development of the kidneys and urinary tract, tumors, stones, blockages, inflammation X-ray, ultrasound, computer or magnetic resonance imaging are performed tomography.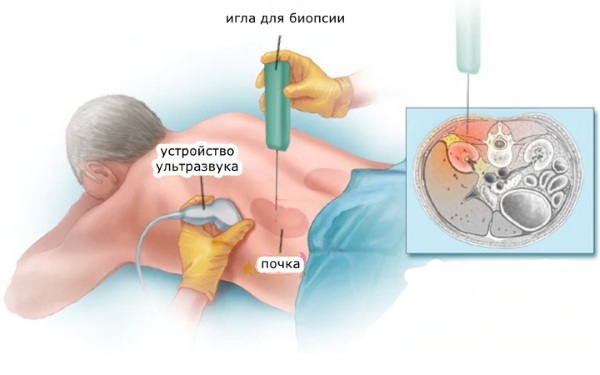
In difficult cases, to verify the diagnosis, a morphological examination of the renal tissue (biopsy) is performed.
At reduced
If red blood cells are not detected in the urine, you should not worry about this, since this is a variant of the norm.
If the urine analysis reveals the appearance of altered erythrocytes in it, it should be understood that this factor is a sign of severe kidney disease. Patients with such an analysis must undergo a serious examination and treatment in a hospital setting. In the future, they are subject to dispensary observation with a systematic annual analysis of urine.
Video about red blood cells in urine
What to do if erythrocytes are found in urine:



