General blood analysis is a widely used type of laboratory research. Since blood is the internal environment of the body, its parameters are sensitive to changes in various organs.
The color indicator is one of the leading research standards, based on which one can judge the work of the hematopoietic system as a whole, and its erythroid germ in particular.
Record content:
- 1 What is a color index?
- 2 The relationship of the CPU with the size of red blood cells
- 3 Who should I contact to check the CPU?
- 4 How the examination is carried out: blood test and decoding
- 5 CPU rate by age
- 6 Calculation formula
-
7 Reasons for deviations from the norm
- 7.1 Downgraded
- 7.2 Promoted
- 8 How does it manifest
- 9 Video about color blood counts
What is a color index?
In pathological conditions, changes in the parameters of red blood are often detected: the concentration of hemoglobin and the content of erythrocytes. In most cases, these fluctuations do not occur in parallel. Conditions are more common when a decrease in hemoglobin is more pronounced than a decrease in the level of red blood cells.
In a number of diseases, on the contrary, a decrease in the number of erythrocytes comes to the fore. For a qualitative assessment of the erythrocyte germ, an index was proposed that reflects the correlation between the concentration of hemoglobin and the content of erythrocytes.
The color indicator (the norm is determined on the basis of the standard index) is a calculated value that characterizes the fullness of red cells with hemoglobin. The change in this parameter is influenced by fluctuations in the level of hemoglobin and the number of erythrocytes.
The coefficient is relevant when performing the analysis by a routine method without the use of hematological analyzers. Since most laboratories examine blood by automated methods, the use of this value is gradually becoming a thing of the past. In hematological analyzers, it is replaced by similar, but more accurate calculated indices. These include MCH and MCHC.
However, the importance of this ratio cannot be overemphasized. The plan for further examination and treatment of the patient depends on its value. It can be normal, low or high. With its decrease, they speak of hypochromia of erythrocytes, with an increase - about hyperchromia, if this indicator remains within the normal range, this indicates normochromia of erythrocytes.
The relationship of the CPU with the size of red blood cells
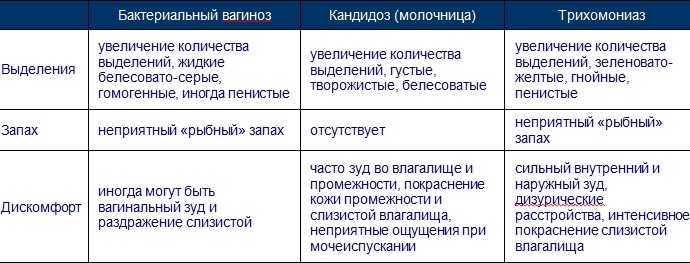
Since the size of the erythrocyte is directly related to the content of hemoglobin in it, there is a direct relationship between the value of the indicator and the size of the cell. The higher it is, the more hemoglobin in the erythrocyte and the larger its size.
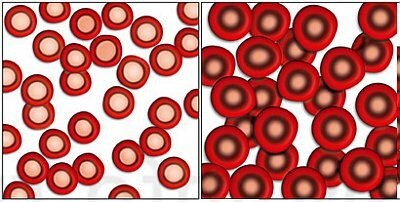
Therefore, hyperchromic red blood cells, as a rule, are macrocytes (large red blood cells) and even megalocytes (giant red blood cells). Conversely, if this index is low, there is little hemoglobin in the erythrocyte, it is a hypochromic microcyte and has a size less than normal.
Who should I contact to check the CPU?
The color indicator (the norm is established for assessing the hematopoietic system) refers to the necessary hematological parameters. Therefore, if a blood test is prescribed by a doctor, then the laboratory assistant is obliged to calculate it.
Except for automated blood tests, where the hematology analyzer determines MCH and MCHC in all samples. Thus, in order to find out your CP, you need to contact your doctor for a referral for analysis.
How the examination is carried out: blood test and decoding
A general analysis is usually taken in the morning, since hematological parameters, obeying general laws biological rhythms, subject to fluctuations within 10% with a maximum in the time interval from 7-00 until 10-00. Ideally, the patient should be on an empty stomach.
If this is not possible, a light breakfast is allowed. For example, for small children, for patients with diabetes mellitus. During blood sampling, the patient must sit, his position also affects the hematological parameters. The exception is bedridden patients.
Capillary or venous blood is taken for analysis. Capillary blood is taken by a laboratory assistant from the pulp of the extreme phalanx of the ring finger into a 1 ml plastic disposable microtube with EDTA K anticoagulant2 or EDTA K3. Venous blood is taken in the treatment room from the cubital vein into a 5 ml or 10 ml plastic disposable tube with an anticoagulant.
If the analysis is performed by manual unified methods, then hemoglobin is determined by the hemiglobin cyanide method on a hemoglobinometer or spectrophotometer. Erythrocyte counting is performed in the Goryaev chamber under a microscope. The study on hematological analyzers is considered more accurate, since errors associated with the human factor are excluded here.
It is very important not only the qualitative performance of the study, but also its competent interpretation. The plan for further examination of the patient and the appointment of treatment depend on how correct the conclusions on this analysis will be.
Assessment of the red sprout begins with the interpretation of hemoglobin. The reference figures for adult men are 130-160 g / l, for women - 120-155 g / l. As for pregnant women and children aged 2 weeks to 5 years, due to physiological characteristics, the lower limit of the norm is lower for them, it is noted at the level of 110 g / l.
A decrease in this parameter in most cases indicates the presence of anemia. To determine the type of anemia, it is necessary to assess the variations in the indicator relative to the norm. If it is reduced, they talk about hypochromic anemia, if within the normal range, about normochromic anemia, if higher, about hyperchromic anemia.
As for the number of red blood cells, it can be reduced, or it can remain normal for a long time, for example, in the regenerative stage of iron deficiency anemia. If this index is within the normal range, this indicates that both hemoglobin and the number of erythrocytes are reduced to the same extent.
For differential diagnosis, it is also advisable to inquire about the number of reticulocytes.
CPU rate by age
Starting from adolescence and throughout adulthood, the normal values of this coefficient do not change. They also do not have sex differences. And only in newborn children, due to the persisting, to some extent, embryonic hematopoiesis and physiological macrocytosis, does it have higher values.

The values of the color indicator depending on gender and age:
| Category | Cpu |
| Women | 0,85-1,05 |
| Men | 0,85-1,05 |
| Newborn | 0,9-1,3 |
| Children from 5 days to 15 years old | 0,85-1,0 |
| Adolescents 15 to 18 years old | 0,85-1,05 |
Calculation formula
CPU = 3 × Нв: Er, the result is rounded to hundredths (up to the second decimal place).
Where, Нв - concentration of hemoglobin in g / l,
Er - the first three digits of the content of erythrocytes.
For example, hemoglobin 115 g / l, erythrocytes 3.85 T / l.
CPU = 3 × 115: 385 = 0.8961 ≈ 0.90.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
The established index is not a dogma, and fluctuations in the results relative to it are quite acceptable.
Downgraded
The norm is a control indicator and a decrease in the color indicator relative to it is evidence of a violation of the processes of hemoglobin formation or a consequence of blood loss. This occurs when the decrease in hemoglobin is more pronounced than the decrease in the number of red blood cells.
It is known that hemoglobin is composed of the iron-containing heme and the protein globin. Violation of hemoglobin synthesis is most often caused by a decrease in iron intake, impaired absorption, increased consumption or loss.
Thus, the following reasons can lead to the development of iron deficiency anemia:
- Lack of iron in food.
- An insufficient supply of iron from the mother to the fetus is a common cause of anemia in children under 3 years of age.
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines, accompanied by impaired absorption of the mucous membrane.
- Increased iron requirements due to pregnancy, childbirth and lactation, especially if the second pregnancy occurs soon after childbirth.
- Chronic blood loss (uterine, nasal, hemorrhoidal).
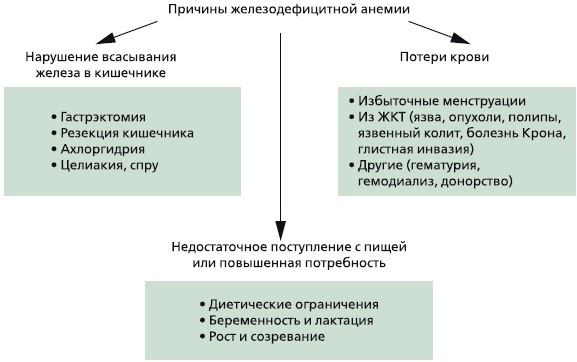
There are situations when there is enough iron, but due to a decrease in the activity of enzymes that catalyze synthesis of heme, it does not go to the needs of erythrocyte formation, but is deposited in the tissues of parenchymal organs. As a result, their hemosiderosis and sideroachrestic hypochromic anemia develop.
Causes:
- Congenital fermentopathies.
- Lead intoxication.
- Chronic alcoholism.
Confirmation of sideroachrestic anemia is an increase in the content of ferritin. In the treatment of this group of anemias, in no case should iron preparations be used, this will aggravate the condition patients and will lead to failure of the parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys, pancreas, testicles in men).
A pronounced decrease in the coefficient is observed in patients with thalassemia - congenital hemolytic anemia. This is a hereditary disease characterized by a violation of the formation of hemoglobin due to a genetic defect in the synthesis of protein chains of globin.
It is common in the Mediterranean, the Middle East, the Transcaucasus, and India. Patients develop severe hypochromic anemia. The color indicator (the norm of hemoglobin corresponds to the established one) will be reduced in the presence of an increased number of red blood cells.
This is observed when:
- erythremia (blood disease of tumor etiology);
- reactive erythrocytosis, for example, at high altitude;
- with kidney disease, accompanied by an increase in the production of erythropoietin.
Promoted
If the decrease in the number of red blood cells prevails over the decrease in the hemoglobin level, the CP will be increased. This process is typical for megaloblastic anemias. This is a group of anemias caused by a violation of eryropoiesis due to a defect in DNA synthesis. These anemias develop against the background of a lack of vitamin B12 or folate (vitamin B9).
Causes:
- Not enough in food. This is especially true for folate, as liver stores are low. Folate (vitamin B9) are found in liver, legumes, spinach, asparagus, broccoli,12 - in eggs, seafood, beef liver, dairy products.
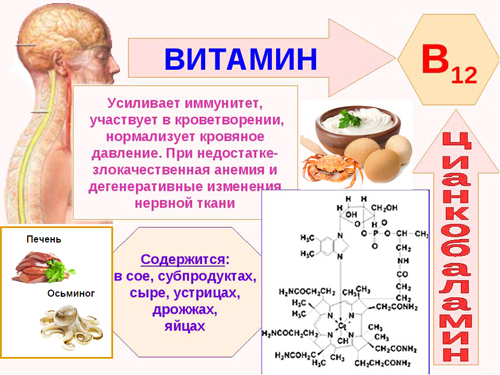
- Not absorbed due to the pathology of the stomach and intestines.
- Competitive expenditure in case of helminthic invasions. This occurs when infected with a broad tapeworm, which absorbs vitamin B in large quantities12 in the small intestine.
- Increased intake of vitamin B12 intestinal microflora with intestinal diverticulosis.
- Pathology of the liver, which is the keeper of the reserves of these elements.
How does it manifest
All manifestations of the dynamics of indicators are quite textbook and are easily diagnosed.
The color indicator (the norm is much higher than the test results) is accompanied by the appearance in blood smears hypochromic microcytes - small, insufficiently filled with hemoglobin erythrocytes, with an increased central enlightenment.
In the symptoms of iron deficiency anemia, tissue hypoxia comes to the fore, manifested by general pallor, brittle nails, hair loss, weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, dizziness. A detailed study of the blood reveals a sharp decrease in iron and ferritin.
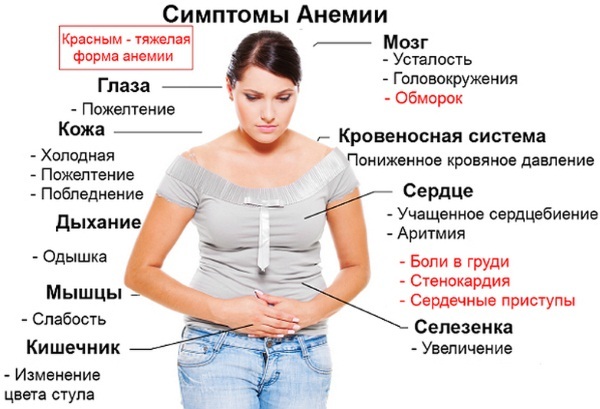
With sideroachrestic anemias, symptoms of damage to parenchymal organs join the manifestations of hypoxia:
- exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, manifested by unstable stools, flatulence, nausea;
- the development of diabetes mellitus;
- liver failure with impaired liver detoxifying function, jaundice, enlarged liver;
- impaired renal function;
- insufficient function of the genital glands in men with the development of eunuchoidism.
With lead intoxication, in addition to anemia, there is a pathology of the digestive tract - cramping pains (lead colic), flatulence, constipation, liver pathology. In addition, the nervous system suffers - there is a violation of sleep, taste, hearing and vision, encephalopathy, paresis.
In patients with thalassemia, target erythrocytes, bone disorders, osteoporosis, hepatomegaly, and enlargement of the spleen appear.
Increased CP is usually accompanied by the appearance of macrocytes and megalocytes.
Clinically, folic acid deficiency is manifested by anemic syndrome. Patients have irritability, unstable stools, ulcers on the mucous membranes of the mouth, poor appetite.
Lack of vitamin B12 manifested by changes in the hematopoietic, digestive and nervous systems. In patients, along with hyperchromic macrocytic anemia, changes in the tongue with atrophy of the papillae are revealed, stomatitis, atrophic gastritis, enterocolitis, funicular myelosis (paresthesias, unsteadiness of gait, numbness limbs).
Confirmation of the cause of anemia is a decrease in blood levels of folate or vitamin B12.
Thus, the color indicator is an integral standard of hematological research, which is necessary for the correct diagnosis of many blood diseases.
Video about color blood counts
About the color indicator of blood: