Coprogram is laboratory research feces, prescribed in order to identify diseases of the digestive system.
Record content:
- 1 What the scatological analysis shows
- 2 Indications for appointment
-
3 How to prepare for stool delivery?
- 3.1 Pevzner diet
- 3.2 Diet according to Schmidt
- 3.3 What is prohibited before testing?
-
4 How to collect feces for coprogram correctly?
- 4.1 Adults
- 4.2 Children
- 4.3 Babies
- 5 Where to do the analysis and how long to wait for the results?
-
6 Decoding the coprogram of an adult
- 6.1 Table of norms of physical examination of the coprogram
- 6.2 Color deviations
- 6.3 Deviations in consistency, density, quantity
- 6.4 Odor deviations
- 6.5 The presence of impurities in feces
- 6.6 Table of norms for chemical research of feces
- 6.7 Acid-alkaline environment
- 6.8 Gregerson occult blood test
- 6.9 Protein content
- 6.10 Bilirubin
- 6.11 Stercobilin
- 6.12 Table of normal and pathological microscopic examination of feces
- 7 Features of decoding coprograms in children
- 8 Scatological study video
What the scatological analysis shows
A coprological study allows you to assess the composition of feces, detect hidden bleeding and inflammatory areas in the digestive tract, and find the cause of digestive disorders. Also, using the analysis, you can identify parasites (in particular, helminths and ascaris).
Indications for appointment
Almost any doctor can prescribe a coprogram: a therapist (in children - a pediatrician), an allergist, a gastroenterologist, an infectious disease specialist.
The analysis is carried out at:
- inflammatory processes in the digestive tract;
- pathologies of the small, large and rectum;
- violations of the biliary system;
- anemia (since with latent bleeding in the organs of the digestive tract, there is a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood);
- damage and cracks in the mucous membrane of the large intestine;
- tumors of a different nature in the digestive tract;
- poisoning;
- infections;
- parasitoses and allergic reactions caused by them.
Also, a scatological examination can be prescribed to confirm a certain diagnosis (for example, a doctor suspects constipation in a patient - laboratory diagnostics will help to refute or confirm the diagnosis and find out its causes), assessing the results of treatment, before surgery or instrumental diagnostics. Sometimes the analysis is carried out before prescribing physiotherapy for the gastrointestinal tract.
How to prepare for stool delivery?
Scatological research requires simple preparation so that its results are as reliable and undistorted as possible. 4-5 days before the analysis, one of the dietary regimens suggested below must be observed.
4-5 days before the analysis, one of the dietary regimens suggested below must be observed.
Pevzner diet
Pevzner's diet implies a strong food load.
With this diet, the following foods should be included in the daily diet:
- rice and buckwheat groats (in water or milk - about 200 g each);
- 200 g of wheat bread;
- 200 g of black bread;
- 250 g of fried meat;
- fried or baked potatoes;
- vegetable salads;
- sauerkraut;
- 100 g of any oil;
- 40 g sugar;
- fruit or berry compote;
- any fresh fruit.
The calorie content of this diet should be 3000-3250 Kcal. Compliance with the described diet allows you to identify violations of the digestive and evacuation functions of the digestive tract, subject to their enhanced work.
Diet according to Schmidt
The Schmidt diet is sparing - if this diet is followed, undigested food particles should not be found in the feces.
The daily diet of the diet contains:
- 100 g of wheat bread (can be replaced with breadcrumbs);
- 50 g of any oil;
- 2-3 soft-boiled eggs;
- 125 g medium-rare minced meat;
- 200 g mashed potatoes;
- 1-1.5 liters of milk;
- oat broth;
The daily calorie content should be 2000-2200 Kcal.
What is prohibited before testing?
4-5 days before collecting the material, you need to stop using:
- laxatives, rectal suppositories;
- lubricants and petroleum jelly;
- preparations containing salts of iron, barium and bismuth, as well as activated carbon;
- enzyme preparations;
- probiotics.
The coprogram cannot be taken earlier than 2 days after the administration of the enema, colonoscopy, X-ray and other endoscopic studies of the intestine and stomach.
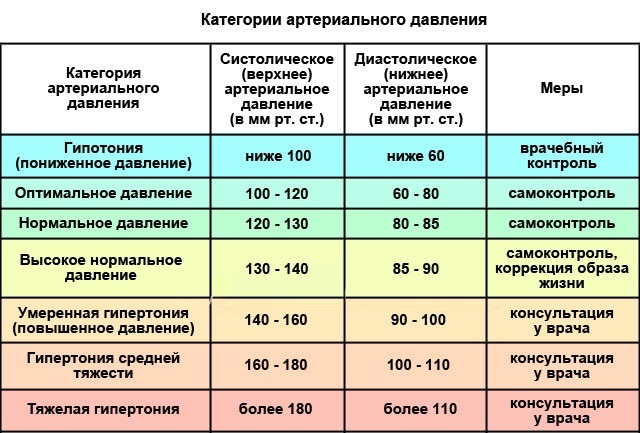
How to collect feces for coprogram correctly?
The research result depends on the conditions under which the material was collected (how accurate it will be).
Adults
Preparation for the delivery of feces in adults is carried out as follows:
- First, you need to empty the bladder so that no drops of urine get into the feces, as this distorts the test results.
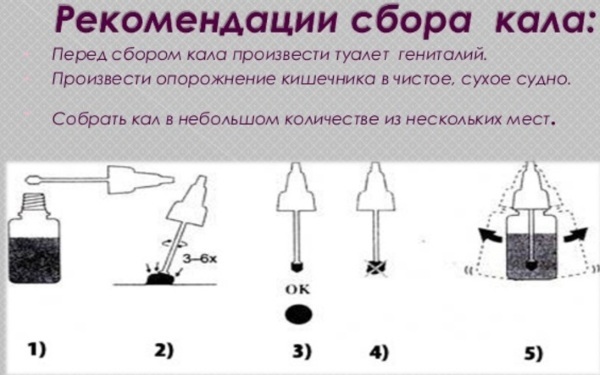
- Then you need to rinse the external genitals and anus with warm running water without using soap and intimate hygiene products.
- Next, you need to perform the act of defecation in the toilet, covered with a film or dry, clean container (for example, a baby pot). It is not recommended to empty the toilet at the bottom of the toilet, as other substances will get into the material that can distort the analysis result.
- It is necessary to collect feces in a special plastic container with a spatula (if there is no such container, then you can collect the material with a plastic spoon in a glass jar, having previously sterilized tools). The material must be taken from different parts of the feces in a volume of about 0.5 tsp. l. For research, 3-4 servings are enough.
- After sampling the material, it is necessary to tightly close the container with a lid and attach a doctor's referral to it.
It is important that the process of emptying the intestines before collecting feces is natural - it is forbidden to use laxatives, enemas.
It is advisable to deliver the feces to the laboratory on the day of collection (since all analyzes are carried out in the morning, you will also have to visit the toilet in the morning). But if this is not possible, then you can collect feces in the evening and store it in the refrigerator at a temperature of +4 to +8 ° C for 12 hours.
Women should not be tested for stool during menstruation. If blood gets into the feces, then the laboratory technician conducting the diagnosis may mistake it for hidden bleeding.
Children
Fecal sampling in children is carried out in the same way as in adults. If the child is still going to the potty, then the container should first be washed with soap and rinsed thoroughly.
Babies
In infants, feces can be taken from a diaper or diaper, provided that they are not soaked in urine. If the stool is liquid, it can be carefully poured into a container. For research, 1 tsp is enough. l. feces in any form. You can store the material in the refrigerator for no more than 8 hours.
Where to do the analysis and how long to wait for the results?
You can get a referral to a coprogram in a regular polyclinic from a general practitioner or any other specialist when you apply and there are reasons for an analysis. The collected material must be brought to the laboratory, which is attached to the clinic or hospital.
You can also make a coprogram in private clinics and laboratories (the cost of the analysis is 200-600 rubles, depending on the region). You can get the finished test result the next day - either in the laboratory or from the doctor who ordered the study.
Decoding the coprogram of an adult
Scatological examination includes the determination of physical (macroscopic, visual), chemical (various reagents are used to identify certain substances and environments) and microscopic properties feces.
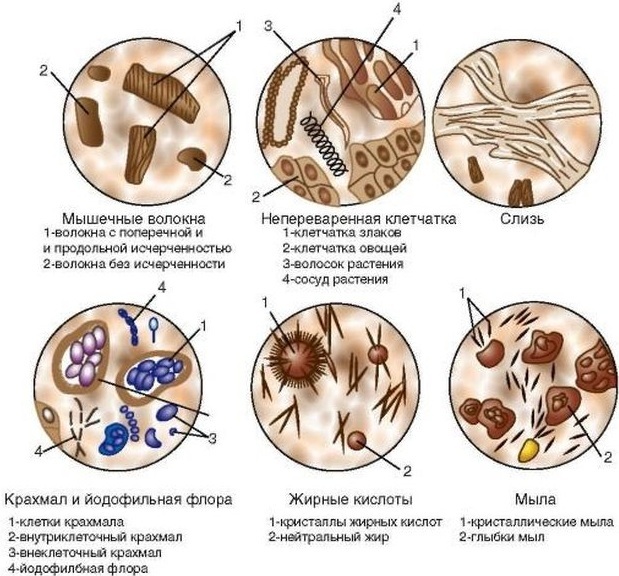
Table of norms of physical examination of the coprogram
| Index | Norm values |
| Colour | Brown |
| Consistency and shape | Dense, soft and shaped |
| Smell | The characteristic odor of feces of moderate severity |
| Slime | Missing or too little. |
| Blood | Missing |
| Pus | Missing |
| Leftover undigested food | Absent or available in too small quantities. |
Color deviations
Abnormal stool color can be from black to white:
- Dark brown color can be a consequence of colitis, constipation, increased intestinal secretory function.
- Too dark (almost black) color indicates bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, a red tint indicates bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract.
- Light brown: too fast evacuation of stool from the colon.
- Yellow or yellow-green color: fermentative dyspepsia (including diarrhea); too light yellow shade of feces indicates a small amount of bile in it due to pathologies of the gallbladder and the pathways of bile excretion.
- A gray or white stool indicates that no bile is reaching the intestines.
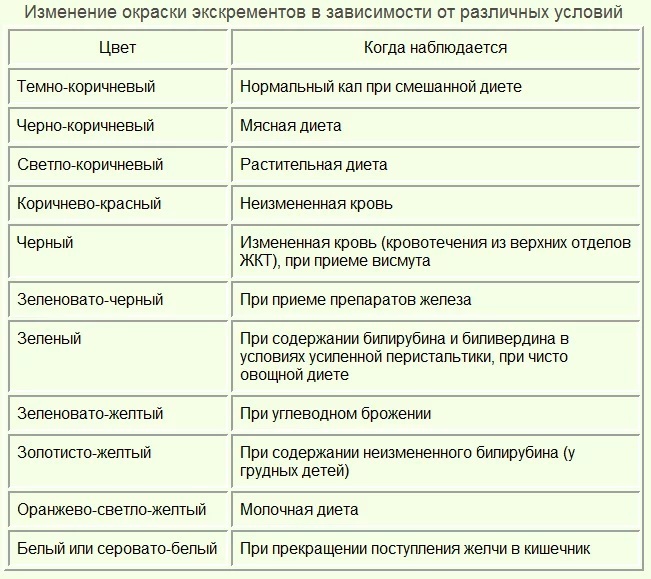
The normal color of feces can also vary depending on the food consumed - the predominance of meat products in the diet makes the color of the feces darker; if a person eats a lot of vegetable and dairy products, then the color of his feces becomes light.
Deviations in consistency, density, quantity
The consistency of the stool depends on the percentage of water content in it - the optimal level is 75%. In this case, the stool is shaped and has a moderately dense texture. When the moisture level rises to 85%, diarrhea is diagnosed (the stool becomes liquid), with a decrease to 50-60% - constipation (stool moves too slowly through the intestines, as a result of which dehydrated).
Deviations in density and quantity indicate the following pathologies:
| Feces type | Decoding |
| Greasy | Characterized by insufficient secretion of bile into the intestines |
| Liquid | Diarrhea, putrid dyspepsia, colitis |
| Mushy | Fermentative dyspepsia, colitis with diarrhea, accelerated flow of feces into the rectum |
| Foamy (liquid with a lot of air bubbles) | Fermentative dyspepsia |
| “Sheep” (too dense, almost hard, standing out in separate small fragments) | Colitis, constipation |
The normal amount of excreted feces per day should be 100-300 g. In this case, it turns out to collect the required amount of material for analysis - with constipation, this is difficult.
Odor deviations
The course of the processes of putrefaction in the intestines is accompanied by a strong fetid odor of excreted feces. Also, such a smell indicates colitis with chronic constipation, lack of bile flow from the pancreas, or increased secretory function of the colon.
The sour smell is a symptom of improper breakdown and assimilation of carbohydrate molecules, due to which the fermentation process of the food bolus intensifies in the intestine. Also, a sour smell can be due to an intestinal infection.
Too little odor indicates a tendency to constipation; faint odor - ulcerative colitis.
The presence of impurities in feces
Visible blood in the stool is a sign of open bleeding in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Since the intestines are covered with a mucous membrane from the inside, a small amount of traces of mucus is permissible in the feces. An increased amount indicates that an active inflammatory process is taking place in the intestinal walls.
A large number of undigested food particles indicates a reduced synthesis of digestive juice and enzymes, as well as accelerated intestinal motility.
Table of norms for chemical research of feces
| Index | Norm values |
| PH level | 6-8 (neutral) |
| Hidden blood | Missing |
| protein | Missing |
| Bilirubin | Missing |
| Stercobilin | Present |
Acid-alkaline environment
A neutral (less often slightly alkaline) environment is the norm. An increase in pH to an alkaline environment indicates incomplete digestion of proteins, as well as constipation, colitis, and impaired pancreatic secretion. A sharply alkaline environment indicates putrefactive dyspepsia.
The lowered pH level is caused by the fermentation of the food lump in the intestine or the presence of fatty acids in the stool. Because of this, an acidic environment is found during the reaction.
Gregerson occult blood test
This analysis is carried out with the aim of detecting hidden (invisible) blood in the material and diagnosing diseases that cause bleeding.
When analyzing, a special reagent is added to the preparation of feces, which has the property of oxidizing hemoglobin. If there is even the smallest amount of hemoglobin molecules in the feces (hemoglobin is carried by erythrocytes, which are formed elements of blood), then under the influence of the reagent the feces become blue-green shade. Normally, the feces do not change color.
Protein content
In the process of digesting food, proteins are broken down and absorbed, so they should not be in the feces. To identify proteins, a chemical reaction is used, the essence of which is the addition of reagents to the feces that precipitate proteins and their particles. As a result of this, flakes are formed, which settle to the bottom, and a clarified liquid remains on the surface.
Bleeding, colitis and inflammation cause protein to be found in the feces.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin (a component of bile) is completely absent in healthy feces. Its presence is due to strong intestinal peristalsis. Also, bilirubin in feces is present in people who have been using sulfonamide preparations or antibiotics for a long time.
Stercobilin
Stercobilin is also a component of bile - it gives the stool a brown tint. Per day, together with feces, from 40 to 280 mg of stercobilin are excreted.
Changes in the level of stercobilin indicate the following pathologies:
- An increased level is about violations of the breakdown of erythrocytes (since stercobilin is formed as a result of the destruction of erythrocyte components).
- A lowered level - about acute pancreatitis.
- The complete absence of stercobilin (due to which the feces become gray or white) is a consequence of the blockage of the biliary tract.
Table of normal and pathological microscopic examination of feces
| Index | Norm | With pathology | The cause of the pathology |
| Stretched muscle fibers | Absent | Present | Incomplete digestion of the food lump in the stomach; dysfunction of the pancreas; fermentation dyspepsia, ulcerative colitis. |
| Unstated muscle fibers | Single or absent | Present in large numbers | |
| Connective tissue | Missing | Present | Decreased gastric digestion. |
| Fat neutral | Missing | Present even in small quantities | Incomplete digestion of fats due to dysfunctions of the pancreas (less often - the liver), pathologies of the biliary tract. |
| Fatty acid | Absent | Are present even in small quantities | Violation of the absorption function of the small intestine due to inflammation of its walls. |
| Soap | Single or absent | Present in large numbers | Incomplete breakdown of fats due to enzymatic deficiency. |
| Digested fiber | In a small amount | Abundant | Incomplete digestion of plant foods in the stomach, putrefaction processes in the intestines, pathology of the biliary tract. |
| Undigested fiber | In a small amount | Abundant | Putrid dyspepsia, impaired secretion of the pancreas, colitis with manifestations, increased contraction of the intestinal walls. |
| Intracellular starch | Missing | Present | Insufficient fermentation of starchy foods, increased putrefactive and fermentative processes in the intestine. |
| Extracellular starch | Missing | Present | Lack of amylase, an enzyme responsible for the digestion of starch; increased contraction of the intestinal walls. |
| Iodophilic flora (a group of bacteria that cause fermentation processes) | Missing | Present (bacteria are stained with iodine solution) | Fermentative dyspepsia. |
| Crystals | Absent | Present |
In feces, it is possible to detect:
|
| Epithelial cells | Absent | Present in large numbers | Inflammation in the intestines. |
| Leukocytes | Absent | Present | Inflammatory and infectious process in the intestine. |
| Erythrocytes | Absent | Present | Intestinal bleeding caused by cracks in the mucous membrane, hemorrhoids, polyps, ulcerative colitis. |
| Clostridia | Absent | Present | Insufficient fermentation of food, which leads to fermentation processes in the colon. |
| Yeast mushrooms | Absent | Present | Intestinal dysbiosis due to prolonged use of antibiotics, reduced immunity, infection or unhealthy diet, in which carbohydrate and starchy foods predominate in the diet. |
| Worm eggs and protozoa | Absent | Present | Helminthiasis and parasitosis. |
Features of decoding coprograms in children
Scatological examination in children is the same as in adults, but has a slightly different interpretation.
In infants, feces normally have a liquid or slightly liquid consistency and a yellow tint, due to the fact that their gastrointestinal tract is not yet functioning sufficiently and is just beginning develop. The smell may be sour (but not putrid).
Also, in the feces of babies, a very small content of the following substances is allowed:
- bilirubin;
- fatty acids and their salts;
- neutral fat;
- starch;
- unchanged muscle fibers (if the child receives meat meals);
- crystals;
- mucus;
- leukocytes.
Parasites, clostridia, yeasts should normally be absent. In older children, the results of the coprogram do not normally differ from adult values.
Coprogram is a voluminous and informative analysis that helps to identify many diseases of the digestive tract. For the study to be as accurate as possible, preparation and adherence to the rules for the collection of material is necessary.
Scatological study video
Doctor about coprogram: