Viscous saliva in the mouth can occur due to many reasons. The phenomenon is associated with both natural and pathological processes in the body and can be temporary or permanent. To find out what exactly influenced the degree of viscosity of salivary fluid, you should pay attention to the accompanying symptoms.
Record content:
- 1 Composition and function of saliva
- 2 What should be normal saliva
- 3 What should be alarming
-
4 Causes of viscous saliva
- 4.1 In adults
- 4.2 In pregnant women
- 4.3 In children
- 5 Why saliva thickens and turns white
- 6 Why does saliva foaming
- 7 Why saliva sticks in your throat
- 8 The appearance of thick saliva and dryness in sleep
-
9 What diseases does the character of saliva change?
- 9.1 Disorders of the salivary glands
- 9.2 Smoking
- 9.3 Seasonal allergies
- 9.4 Gastroenteritis
- 9.5 GERD
- 9.6 Sinusitis
- 9.7 Fungal candidiasis
- 9.8 Periodontal disease and periodontitis
- 9.9 Acute infections
- 10 How to relieve the condition when saliva is viscous and viscous?
- 11 When and which doctor should I contact?
- 12 Diagnostics
- 13 Treatment
- 14 Ayurvedic remedies for sticky saliva
- 15 Folk remedies
- 16 Saliva video
Composition and function of saliva
The composition and consistency of saliva are rather unstable indicators that change during the day in depending on food intake, state of sleep or wakefulness, as well as individual characteristics organism.
Saliva is 98% water, and the remaining 2% is dry residue, which includes organic and mineral substances.
| Organic matter | Minerals |
|
|
The salivary secretion performs the following functions:
-
Digestive. Saliva participates in the digestion process by softening food and breaking it down. In the oral cavity, thanks to saliva, the initial stage of the breakdown of carbohydrates occurs.

- Protective. Calcium, proteins, glycoproteins and peptides that make up saliva form a protective film on the tooth enamel, which reduces the negative effects of organic acids.
- Bactericidal. Lysozyme and leukins, which are part of saliva, perform a bactericidal function.
- Immune. The salivary glands synthesize immunoglobulins A, C, D.
- Mineralizing. Salivary secretion maintains oral homeostasis, as it is a solution saturated with calcium and phosphorus compounds.
- Hormonal. Saliva contains the hormone parotin, which mineralizes hard dental tissues.
What should be normal saliva
The saliva of a healthy person has a liquid transparent consistency with a slightly turbid shade without a pronounced odor. Normally, the amount of salivary secretion should be sufficient in order not to feel constant discomfort when eating or swallowing. The normal volume of saliva produced in the oral cavity during the day reaches 1.5-2 liters.
What should be alarming
Any discomfort associated with a disruption in the production of salivary fluid or a change in its consistency does not go unnoticed. Against this background, concomitant symptoms arise that indicate possible diseases.
Viscous saliva in the mouth (causes can be associated with both natural and pathological processes) often accompanied by other complaints that should alert:
- decreased sensitivity of taste buds;
- feeling of dryness in the mouth;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- burning sensation in the area of the tongue;
- difficulty swallowing;
- foci of inflammatory processes on the oral mucosa.
Any of these symptoms may be due to changes in the composition and volume of saliva produced.
Causes of viscous saliva
The appearance of viscous saliva in most cases is due to the presence of various disorders that relate not only to the oral cavity, but also to the functioning of the body as a whole.
In adults
The main reasons provoking changes in the consistency of saliva in adults:
- taking medications - hormonal, antihistamines and antidepressants;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- dehydration;
- diseases of the salivary glands - mumps, Mikulich's disease, sialostasis, sialoadenitis;
- acute infectious diseases;
- xerostomia.
In pregnant women
A change in the consistency of saliva during pregnancy is associated with a change in hormonal levels. The active production of estrogen affects the oral epithelium and the secretion of salivary fluid.
Other possible causes of excessive saliva viscosity in pregnant women include:
- a change in the acidity of the stomach;
- toxicosis;
- eating a lot of salty foods and, as a result, an increase in fluid requirements;
- frequent bouts of heartburn.
In children
Viscous saliva in the mouth (the reasons may be associated with an increased need for fluid) can occur not only in adults, but also in children. Often, a change in the consistency of salivary secretion is associated with diseases of the upper respiratory tract and pathologies of the oral cavity.
The main reasons for the viscosity of saliva in a child include:
- difficulty in nasal breathing due to rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis;
- an increase in body temperature against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or an infectious process, in connection with which dehydration occurs;
- diseases of the oral cavity: candidiasis, stomatitis, cheilitis.
Why saliva thickens and turns white
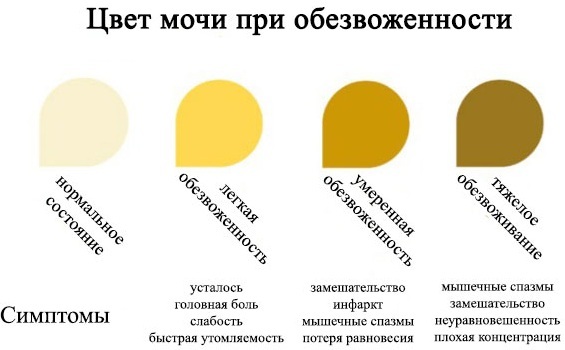
Saliva viscosity and discoloration can be associated with many reasons. The consistency of saliva changes with dehydration. Since the salivary secretion is 98% water, the abrupt cessation of its entry into the body leads to a decrease in the volume of reproduced saliva and its excessive density.
The thick salivary fluid has a high density and therefore its color changes from transparent to white.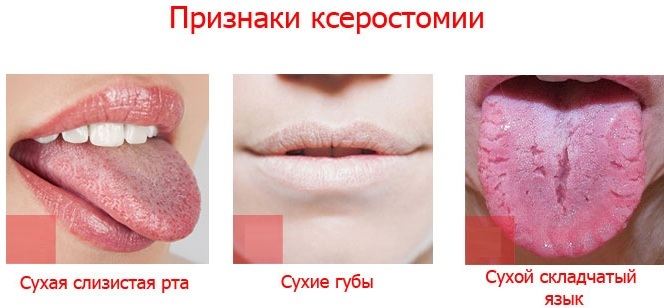
Saliva turns white and thickens also due to the presence of xerostomia - excessive dryness in the mouth, which has arisen against the background of a decrease in salivation.
Why does saliva foaming
The formation of thick, frothy saliva is due to the action of mucin, a special substance that contributes to the formation of a food lump when chewing and swallowing food. When a malfunction of the salivary glands occurs, the amount of mucin in the salivary secretion decreases and leads to the appearance of its foamy structure.
Why saliva sticks in your throat
Throat diseases - pharyngitis, laryngitis or tonsillitis - lead to the appearance of thick saliva. The defeat of the tonsils by infection leads to the formation of abscesses, which contribute to the spread of purulent exudate into the oral cavity. This causes the formation of thick mucus mixed with saliva.
Non-pathological reasons include exposure to dry air. In a warm room with a low percentage of humidity, the mucous membrane of the respiratory system quickly dries up and provokes a decrease in salivary fluid.
The appearance of thick saliva and dryness in sleep
The appearance of thick saliva at night or immediately after waking up can be associated with several reasons:
- eating a large amount of spicy or salty food on the eve provokes temporary dehydration;
- excessively dry air in the bedroom affects the nasopharyngeal mucosa and dries it out;
- difficulty breathing through the nose against the background of respiratory diseases leads to breathing through the oral cavity;
- snoring while sleeping leads to breathing through the mouth.
What diseases does the character of saliva change?
Viscous saliva in the mouth, the causes of which lie in pathological processes, can occur against the background of diseases. In this case, the phenomenon is accompanied by other characteristic symptoms associated with the work of certain organs.
Disorders of the salivary glands
Changes in the work of the salivary glands, expressed in a decrease in the produced salivary secretion, is called "hyposalivation".
This process is associated with the destruction of the parenchyma of the salivary glands and their ducts due to such diseases:
- sialoadenitis;
- sialolithiasis;
- Mishulin's disease;
- Sjogren's disease.
Due to the fact that the volume of reproduced saliva decreases, its consistency changes.
Smoking
Cigarette smoke irritates the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract and provokes an increase in the volume of mucus, which mixes with saliva and makes it viscous. In addition, tobacco smoke, interacting with saliva, changes its composition and causes an increase in the amount of organic acids. It also affects the consistency of salivary secretions.

The smoking process also affects the volume of the reproduced saliva fluid, significantly reducing it.
Seasonal allergies
The appearance of viscous saliva systematically at certain periods, especially in the spring and summer, may indicate the development of seasonal allergic reactions to pollen of flowering plants.
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is an inflammatory process in the stomach and small intestine caused by a bacterial or viral infection. The main symptoms of the acute course of the pathology are severe vomiting and diarrhea, leading to the development of dehydration. a lack of
fluid in the body provokes a decrease in the production of saliva and a change in its consistency.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is an inflammation of the walls of the lower esophagus. Pathology is accompanied by a constant release of gastric contents into the esophagus, which causes the development of heartburn. 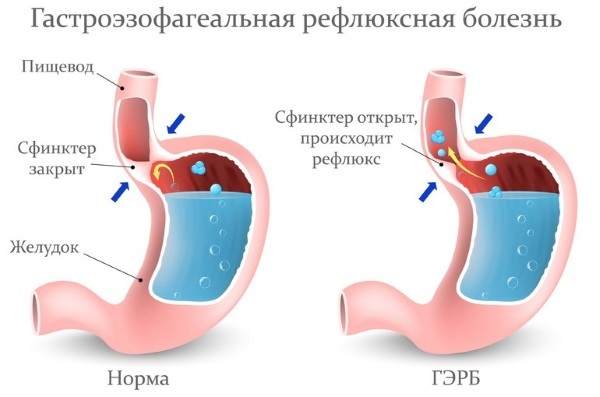 In order to neutralize the aggressive effect of gastric juice on the esophagus, more saliva is secreted, and it becomes viscous.
In order to neutralize the aggressive effect of gastric juice on the esophagus, more saliva is secreted, and it becomes viscous.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is a chronic lesion of the paranasal sinuses. Sero-purulent discharge from the nose, produced by an infectious or bacterial process, also enters the mucous membrane of the back of the throat. A large accumulation of mucus facilitates its penetration into the oral cavity.
Fungal candidiasis
Oral candidiasis is manifested by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane, the formation of white plaques, a burning sensation in the tongue, and excessive dry mouth. In this regard, the volume of saliva produced decreases and its consistency changes.
Periodontal disease and periodontitis
In inflammatory processes of the gums, particles of epithelial tissue separated during the destruction of periodontal tissues penetrate into the salivary secretion and make it viscous.
Acute infections
Acute infections affecting other organs cause fever, diarrhea, or vomiting. These symptoms can lead to dehydration.

Acute infections include: salmonellosis, typhoid fever, dysentery, cholera.
How to relieve the condition when saliva is viscous and viscous?
If viscous saliva causes discomfort, complicates the process of chewing food and swallowing, urgent measures must be taken to eliminate the unpleasant sensations. The main task is to stabilize the moisture level of the mucous membrane.
To do this, you can use the following guidelines:
- increase the amount of fluid consumed;
- rinse the mouth with a water-saline solution;
- use artificial saliva in the form of drugs;
- apply special moisturizing sprays for the oral cavity;
- use sugar-free gum or lozenges to increase salivation.
When and which doctor should I contact?
If the change in the consistency of saliva is associated with exposure to temporary factors and arose as a result of dehydration, hormonal changes, smoking or taking medications, then there is no reason to seek medical help, since the phenomenon is periodic character.
You should consult a dentist in cases where the formation of viscous saliva will be accompanied by other symptoms:
- a burning sensation on the tongue;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- small white plaques on the mucous membrane;
- constant feeling of thirst and dry mouth.
If the problem is related to complaints of a systemic nature: fever, signs of intoxication, pain and discomfort in the throat, cough or runny nose, you should visit a physician.
Diagnostics
Viscous saliva in the mouth, caused by various pathological processes, is a reason for diagnostics. To assess the general condition of the patient and identify a provoking disease, the doctor conducts a visual examination to collect an anamnesis.
Based on this, other diagnostic methods are prescribed in the form of instrumental and laboratory studies:
- General and biochemical blood test. A blood test is performed to assess the state of the body, identify infectious and inflammatory processes. The method allows you to determine the number of platelets and leukocytes, indicators of hemoglobin and ESR.
- Pharyngoscopy. The method is used for visual examination of the condition of the pharynx. The study is used for infections of the throat or inflammatory processes in the tonsils.
- Laryngoscopy. Method for visual examination of the larynx. The study is used if the cause of the viscosity of saliva is diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
- X-ray of the sinuses. Diagnostics used for acute and chronic forms of sinusitis. X-rays of the sinuses are performed to assess the condition of the paranasal regions and bony walls.
-
Ultrasound of the salivary glands. The study allows you to identify the presence of pathological processes, determine the size and location of the glands, assess the state of the excretory ducts.
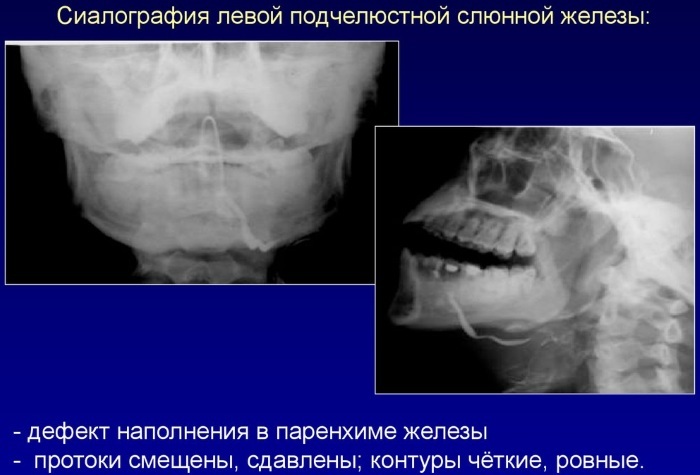
- Sialography of the salivary glands. The method is an X-ray imaging of the salivary gland using a contrast agent injected into its ducts.
Treatment
Treatment with increased viscosity of saliva should be aimed at increasing the activity of secretion production and its liquefaction, as well as to eliminate the underlying disease, which caused the development of an unpleasant phenomena.
Symptomatic therapy includes the use of the following groups of drugs:
- agents that stimulate the work of the salivary glands;
- artificial saliva substitutes;
- antifungal;
To stimulate salivation, in case of diseases of the salivary glands, use:
- Pilocarpine - a drug in the form of drops, which, when used systemically, increases the secretion of the salivary glands. The tool is used in the form of a 1% solution, 5-10 drops 3 times a day before meals. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
Artificial saliva substitutes come in the form of gels, sprays and solutions. They are analogous to human natural saliva and replace it in cases of insufficient production. The drugs in this group include:
- Hyposalix - a solution in the form of a spray used to moisturize the oral cavity. The drug is used 6-8 times a day, irrigating the oral mucosa if necessary.
- Oralgin - an agent in the form of a spray, designed to moisturize the mucous membranes and eliminate pathogens of infectious processes in the oral cavity. The drug is used 2-3 times a day between meals, evenly distributing the substance over the surface of the oral mucosa.
Antifungal drugs are used in cases where the cause of the viscosity of saliva is fungal candidiasis of the oral cavity. Among them are:
-
Diflucan - a triazole antifungal agent in powder form for preparation of a suspension. The drug is taken at 50-100 mg 1 time per day for 7-14 days.
- Levorin - an antifungal drug that affects the membranes of fungal cells and destroys them. Adults need to take 2-4 tablets per day for 10-12 days.
Ayurvedic remedies for sticky saliva
Viscous saliva in the mouth, the causes of which are associated with inflammatory processes in the gums, can change the consistency under the influence of Ayurvedic drugs.
Daily Ayurvedic oral care should consist of:
- brushing teeth;
- cleansing the tongue;
- gum massage;
- rinses.
To clean your teeth, you must use toothpastes based on astringent and bitter herbs.
Among them are:
-
Nambudiri - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory paste based on ginger, black pepper.

- Meswak - anise fruit based toothpaste with astringent and antibacterial properties.
Gum massage improves blood circulation in soft tissues and is carried out using cold sesame or coconut oil.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can be used as an auxiliary method of treatment as part of complex drug therapy.
Folk recipes involve the use of medicinal herbs, the action of which is aimed at alleviating the condition and liquefying viscous saliva:
- A decoction of pine bark and needles. Take 2 tbsp. l. chopped bark and pine needles and mix in a separate bowl. 1 tbsp. l. dry mixture should be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and boiled over low heat for about 5-7 minutes. The resulting solution must be infused for 1 hour and filtered. The drink is taken 2 times a day for 2 tbsp. l.
- A mixture of honey and scarlet. Grind 1 scarlet leaf into a gruel and squeeze the juice out of it. Freshly squeezed juice should be mixed with 1 tbsp. l. honey. Take the prepared mixture in 1 tbsp. l. 2 times a day.
- A mixture of propolis tincture and peach oil. 1 tbsp. l. propolis tinctures must be mixed with 2 tbsp. l. peach oil. The prepared mixture is used as a medicinal solution used to lubricate the oral mucosa 2 times a day.
- Sage tea. 2 tbsp. l. sage leaves should be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and insisted for 1 hour. The prepared solution must be filtered and consumed as a drink throughout the day.
Viscous saliva in the mouth causes discomfort and makes it difficult for food to move through the esophagus, regardless of the reasons that provoked this phenomenon. To get rid of discomfort and affect the quality of the salivary fluid produced, you should drink more fluids, quit smoking and undergo treatment in case of pathological processes.
Saliva video
What saliva can tell you about you: