INR and PTI are important indicators of the hemostatic system in women and men. Their norms differ by age. This data can be found in tables. The importance of these indicators is difficult to overestimate.
They are necessary for diagnosis conditions accompanied by a tendency to thrombus formation. They play an important role in the constant intake of anticoagulants by persons with rhythm disturbances, as well as during pregnancy.
Record content:
- 1 General information about prothrombin
- 2 Distinguishing features of female analysis
- 3 When is the analysis scheduled?
- 4 Preparation and delivery of analysis
- 5 Rules for taking a blood test for PTI
- 6 Decoding the results
- 7 The norm in women by age
-
8 Deviations of PTI from the norm in the blood test
- 8.1 Why the index might be downgraded
-
9 Elevated prothrombin levels
- 9.1 Prothrombin index in a woman during pregnancy
- 10 In what cases should the test be taken regularly?
- 11 Video about coagulogram
General information about prothrombin
The coagulation system and the factors that are antagonists in relation to it are always in a state of dynamic equilibrium. That is, the second should respond friendlyly to changes in one system. This is a biological law that maintains the stability of the body in a constantly changing environment.
The blood coagulation system is a collection of enzymes. These are protein structures for the most part. All of them are sequentially involved in a chain of chemical reactions, starting and activating the subsequent ones. One of the main clotting factors is prothrombin. This protein is otherwise called factor 2 or FII.
It is synthesized, like many other proteins, in liver cells. The process takes place with the help of vitamin K. Prothrombin contains about 18 amino acid residues, but belongs to mixed proteins - glycoproteins.
The role of prothrombin is key in the process of coagulation. It acts as an activator of the main protein that forms the "plug" - fibrinogen. This inactive precursor is converted by prothrombin into a functioning thrombin. Thus, the stop of bleeding is started.
The prothrombin index is one of the most important indicators of hemostasis, which is included in the examination standards at almost every hospitalization. Like INR, it allows you to assess the so-called external coagulation pathway, which is implemented when the integrity of the vascular wall is violated.
PTI, the norm in women by age (the table clearly indicates its dynamics throughout life) is determined as follows. For the calculation, it is necessary to determine the time during which the patient's plasma coagulates.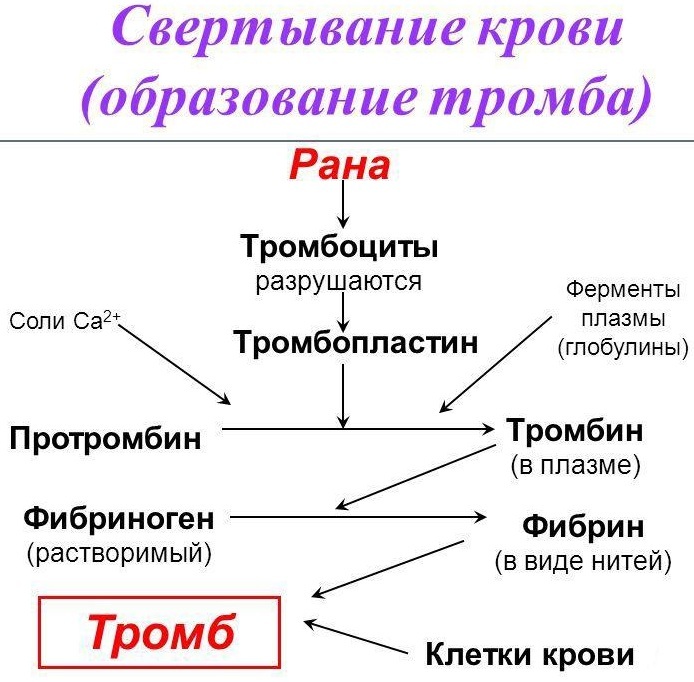
The second indicator is the plasma clotting time in the control tube. The ratio of the second indicator to the first in the form of a quotient (divided by one another) will show the value of the index.
The International Normalized Ratio is calculated somewhat in reverse. The dividend is the patient's prothrombin time, determined by analysis.
The divisor is the time during which the control plasma coagulates. This number is multiplied by a special index called MIR. Otherwise, they are referred to as the international sensitivity index. This is a constant value for certain reactive systems.
Distinguishing features of female analysis
As in men, the norms of PTI and INR in the female half of the population depend on age. But there is one important point. Determination of these indicators in the first phase of the menstrual cycle can significantly distort the results of the study.
It is for this reason that the analysis is recommended to be carried out from 14-20 days after the first day of the onset of menstruation. The second feature is the change in the norms during pregnancy, since this condition is very significantly reflected in the hemostatic system.
When is the analysis scheduled?
PTI, the norm in women by age (the table exists for the possibility of comparing the research results with it) is compared with the actual data obtained as a result of the prescribed examination.
Method for determining PTI and INR in combination with the study of activated partial thromboplastic time, as well as the concentration of blood fibrinogen is screening to detect hemostasis disorders. And yet, there are situations when the values of these coefficients make it possible to diagnose other pathologies.
Considering that prothrombin, like other coagulation factors, is synthesized in the liver, it is clear that its content in the bloodstream will be determined by the functional reserves of the organ. In other words, if there is a pathology, then this will invariably be reflected at the level of PTI and INR.
If liver cirrhosis is suspected, a blood test is required to determine the prothrombin index and the international normalized ratio. In addition, these indices can be taken into account to assess the stage of the disease, when there is compensation or decompensation of the organ. Not only with cirrhosis, IPT and INR change.
This phenomenon can be detected in hepatitis within the cytolytic syndrome (massive cell death due to an aggressive inflammatory process).
The next important indication for the analysis is the upcoming surgery. For the operating surgeon, and even more so for the anesthesiologist, who will decide on the type of pain relief, blood coagulation parameters will be extremely important.
Therefore, in addition to the INR and PTI, the following studies are prescribed:
- APTT;
- fibrinogen of the blood;
- PV;
- blood clotting time.
Thus, doctors have a complete understanding of the state of the coagulation / antiocagulation system in order to be alert and prepared for what may happen during surgical treatment.
Vascular diseases associated with the formation of blood clots in various segments of the arterial or venous bed are also on the list of indications for the study of IPT and INR.
This can be thrombosis of veins, pulmonary artery (life-threatening disease - PE), as well as cerebral arteries with the formation of a stroke and heart vessels with the development of a heart attack. IPT and INR in these conditions are important for dynamic control of the state of the hemostasis system.
Violations of the rhythm of cardiac activity are considered separately. This is not only atrial fibrillation, but also high-grade extrasystoles, paroxysmal tachycardia. All of these syndromes are thrombogenic situations.
Before and after the restoration of the rhythm, it is necessary to determine the described parameters of the coagulation system. With a constant form of atrial fibrillation, when Warfarin and its analogs are prescribed, it is imperative to determine the INR indicator at regular intervals.
Abundant bleeding occurs in the practice of a surgeon, gynecologist, ENT doctor. After them, it is imperative to check the hemostasis system for the presence of pathology. INR and PTI are included in the required analyzes.
Often, with diseases such as jaundice or intestinal dysbiosis, manifestations of a lack of vitamin K are found. As you know, it is he who is a cofactor in the synthesis of prothrombin. Therefore, vitamin K deficiency will affect the PTI values.
With a clinically pronounced deficiency of ascorbic acid, it is also indicative to conduct a blood test for the prothrombin index and the international normalized ratio.
Preparation and delivery of analysis
PTI and INR is determined and compared with the norm in men and women by age with the data in the table. Properly organized training allows you to get the most accurate result. This is the key to a successful study. Particular attention is paid to food intake and medication intake.
Rules for taking a blood test for PTI
- The last meal should be taken no later than 12 hours before the planned analysis.

- Attention is drawn to the qualitative composition of food: less fat-containing products, preference for durum wheat, light drinks.
- Patients taking Warfarin should keep their own dietary recommendations in mind so that the INR is not overestimated or underestimated.
- All drugs that the patient takes, he must write out separately, indicating the dose, number of tablets, frequency and time of administration, as well as the approximate duration of their use.
- Most laboratories collect blood in the early morning hours; donation at a later time can skew the results due to physiological reasons.
- It is not recommended to smoke before the procedure, and at least a week before the tests, you should completely refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages.
The implementation of these rules - recommendations will allow you to determine the necessary indicators of the blood coagulation system as accurately as possible.
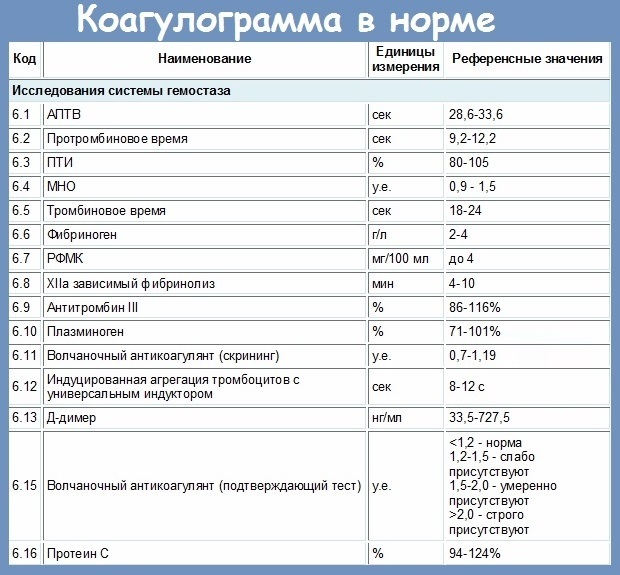
Decoding the results
The assessment is carried out in a laboratory environment. To begin with, the time interval is determined in seconds. Further, the indices are automatically calculated: INR and PTI. International Normalized Ratio has no unit of measurement, it is usually an integer, greater than 0. At the same time, the prothrombin index is expressed as a percentage. Contrary to the laws of arithmetic, this figure can be more than 100%.
The following factors influence the rate in each specific case:
- floor;
- age;
- growth and complexion;
- nutritional features;
- taking medications;
- pregnancy and lactation for women.
The index obtained in the study, like the INR, is compared with the conditional norm.
The norm in women by age
PTI, the norm in women by age (the table gives a visual comparison), differs from the norm in men. Different age categories among the fairer sex also have features presented in the table.
| Age period | PTI rate, percent (%) | INR indicator rate |
| 0-1 month | 70-120% | 0.8-1.28 |
| 1 year | 50-100% | 0.8-1.28 |
| Preschool age | 70-140% | 0.8-1.28 |
| Prepubertal | 60-140% | 0.8-1.28 |
| Puberty | 60-150% | 0.8-1.28 |
| Adult women | 70-140% | 0.8-1.28 |
The international normalized ratio is less variable. It depends on the use of anticoagulants, pregnancy and certain dietary habits.
For doctors, there are also a number of clinical situations that often affect the results of research on IPT and INR. Change in hematocrit, for example. This is the percentage of blood formed elements to the total volume. MNO and PTI can change at an overestimated and at a decreased value of the indicator.
You should also pay attention to the possibility of such a disease as systemic lupus erythematosus, or antiphospholipid syndrome. When a lupus anticoagulant is detected, the INR, PTI and other values of the coagulogram change, as a rule.
Deviations of PTI from the norm in the blood test
PTI is the norm in women by age (the table is not very informative), or otherwise - the prothrombin index and the normalized ratio are inversely proportional. If one of them is increased, then you should think about the fact that the second is reduced, and vice versa.
Why the index might be downgraded
Reduced PTI means that the INR will be increased. The situation as a whole suggests that there is a tendency to bleeding. That is, a state of hypercoagulability. In such a situation, the most likely deficiency of the factors involved in the external coagulation pathway.

A condition in which 2, 5 and 7 factors of hemostasis are lacking is usually congenital. But more often this situation arises due to a deficiency of vitamin K. After all, it is with his participation that the synthesis of these proteins occurs.
There are clinical conditions accompanied by a reduced content of only 10 factors. One of the reasons is amyloidosis. In the analysis, this will affect the PTI (it will decrease) and the INR (this indicator will be higher than the norm).
Liver diseases affect the entire coagulation system. Therefore, with cirrhosis, hepatitis of a high degree of activity and alcoholic damage to the organ, the INR and PTI change, since the production of proteins in principle and coagulation factors in particular decreases. More often, you can identify the lack of 1 factor.
This condition is called hypofibrinogenemia. Normally, there should be 4 g / l of fibrinogen in the venous blood. Dysfibrinogenemia also occurs. Protein is produced, but it cannot perform its function. This is due to the fact that it is defective due to a violation of the sequence of amino acid residues in the primary structure.
Among the conditions in which the protein composition of the blood changes, kidney disease occupies a strong position. This is especially true for situations involving nephrotic syndrome. Its essence is the loss of protein through a failed glomerular filter. There is less protein in the blood.
Not only its quantity is changing, but also its qualitative composition. Indeed, through the altered pores, the 5th and 7th factors of hemostasis are removed faster. This is reflected in the INR (it is growing) and PTI (the indicator is reduced). Nephrotic syndrome is confirmed by a general analysis of urine, blood, lipid profile. For further examination, ultrasound of the kidneys, spectral analysis of blood proteins are prescribed.
Among other somatic diseases, in which the PTi may fall and the INR may increase, there may be cardiac decompensation. Clinically, this is an increase in shortness of breath, edema and a decrease in exercise tolerance in the usual volume.
Sometimes acute leukemia with a bright debut is reflected in the coagulogram data. Another group of pathologies is diseases of the hepatobiliary-pancreatoduodenal zone. This includes diseases of the pancreas (pancreatitis, adenoma, malignant neoplasm), liver, duodenum, gallbladder.
There are other factors contributing to the described changes in the prothrombin index and the international normalized ratio. This can be the use of fatty foods, alcohol.
There is also a whole list of drugs that lower IPT and increase INR:
- NSAIDs (indomethacin);
- corticosteroids;
- anabolics (retabolil);
- uricozostatics (allopurinol);
- antibiotics (tetracycline and representatives of this group, kanamycin, nalidixic acid);
- L-thyroxine;
- antidepressants from the group of MAO reuptake inhibitors;
- antiparkinsonian drugs.
A special place is occupied by funds acting on individual links of hemostasis. These are Warfarin and Heparin.
Elevated prothrombin levels
Many factors can increase IPT and the amount of prothrombin in general. Among them, food is not the least important place. Eating too much vitamin K-rich foods will definitely increase your PTI and lower your INR.
These include:
- cabbage;
- green tea;
- turnip and radish;
- pork and beef liver;
- gooseberry;
- light green leaves;
- soy;
- broccoli.

The spectrum of diseases, accompanied by the described changes in the coagulogram, is not wide. First of all, it is erythrocytosis or polycythemia. We are talking about an increase in the content of red blood cells in the blood. This also includes venous thrombosis. A more formidable situation is the DIC syndrome, which complicates childbirth, difficult operations, accompanied by blood loss.
Another important group of causes is dehydration. This condition is caused by the loss of fluid from the body. It is accompanied by vomiting, frequent loose stools. The condition is dangerous for children.
Among the drugs that increase PTI, vitamin K analogues are in the first place. This is Vikasol, which is used to stop bleeding. The same changes in the coagulogram will cause diuretics.
For women, taking oral contraceptives is more common as a possible cause. Antacids, antihistamines, and cardiac glycosides can reduce INR and increase prothrombin.
Prothrombin index in a woman during pregnancy
During this period, all systems and organs of the mother's body are rebuilt. Therefore, pregnancy affects the parameters of hemostasis. There is a clear tendency to thrombophilia, that is, the coagulation factors are slightly higher than the anticoagulants.
After all, the body must be ready for childbirth. And they, as you know, are often complicated by massive bleeding. The hypercoagulable state aims to prevent these situations.
The norms of the coagulogram differ for these reasons. PTI must exceed 100%. At lower rates, it is necessary to search for the cause and adequately correct it.
In what cases should the test be taken regularly?
Monitoring INR is necessary in the case of taking Warfarin, Fenilin and other representatives of this group of anticoagulants. The INR rate when taking these funds is in the range of 2.0-3.5. It must be maintained to adequately maintain a balance between the coagulation and anticoagulant system.
When the INR exceeds 3.5, one should think about hypocoagulation and the danger of bleeding. When the INR falls below the recommended level, the dose of the drug should be increased. At first, the frequency of the study should be about once a week. But when the target INR values are reached, an analysis can be carried out once a month.
PTI is needed for observation when using Heparin. This is done under stationary conditions.
INR and PTI are necessary for screening for disorders in the hemostasis system, as well as for dynamic control when taking Warfarin and Heparin. The rate in women is different from that of men, and there are some peculiarities in pregnant women. Within this group, there are differences in age. There are tables for ease of assessment.
Video about coagulogram
What is the analysis of the coagulogram:



