After physical activity, each person feels a feeling of tightness in the chest, the frequency and depth of breathing increases. A similar condition in medical terminology is called shortness of breath (dyspnea). Its occurrence after any physical activity is considered a physiological norm. However, if the feeling appears at rest, it is necessary to find out the reason.
Shortness of breath is an alarming symptom., in which the rhythm and frequency of breathing are disturbed, a feeling of tightness in the chest appears, the breaths become deeper and heavier. A symptom may indicate a number of diseases (for example, pathology of the heart and blood vessels, pneumonia, asthma, tuberculosis).
Record content:
- 1 Symptoms
-
2 Reasons for the appearance
- 2.1 Cardiovascular pathology
- 2.2 Pulmonary dyspnea
- 2.3 Anemia
- 2.4 Other reasons
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 When to see a doctor
-
5 Treatment methods
- 5.1 Medications
- 5.2 Traditional methods
- 5.3 Other methods
- 6 Possible complications
- 7 Shortness of breath video
Symptoms
The clinical picture of shortness of breath is varied, but, nevertheless, it is associated with impaired respiratory function.
In this state:
- the frequency of respiratory movements (RR) changes significantly;
- feeling of an acute lack of oxygen;
- attempts to take a deep breath or, conversely, try to breathe shallowly.
If shortness of breath appears against the background of physical activity (for example, when running or climbing to a high floor), this is considered a physiological norm.
Resting breathlessness (the causes may be the most dangerous) should force a person to see a doctor. The etiology of the condition is determined according to the classification used in medical practice according to the types of dyspnea.
Types of shortness of breath:
| Shortness of breath | Description of sensations |
| Inspiratory | It is difficult to inhale due to the narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, trachea and bronchi. In this case, the inhalation is accompanied by a noise. Often appears against the background of respiratory infections, laryngeal diphtheria, inflammation of the pleura, or injuries in which the bronchi are compressed. |
| Expiratory | Exhalation becomes difficult. The provoking factor is the narrowing of the lumen of the small bronchi. The symptom is typical for the development of emphysema, chronic obstruction of the lungs. |
| Mixed | In this case, difficulty in inhaling and exhaling alternates, sometimes leading to an absolute cessation of breathing. It is often diagnosed with advanced stages of heart failure and pulmonary pathologies. |
Dyspnea classification by intensity of manifestation:
| Degree | Manifestation |
| The first | Shortness of breath appears for physiological reasons (climbing stairs, running, doing exercises). |
| The second | The onset of shortness of breath makes a person slow down the usual pace of walking. |
| Third | Shortness of breath forces the person to constantly stop to catch their breath. |
| Fourth | Shortness of breath appears at rest and indicates a complex pathological process. |
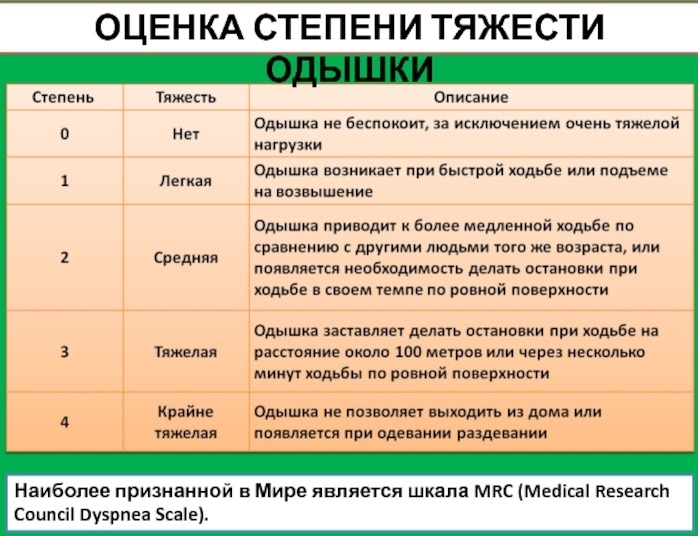
If the difficulty in breathing occurs only after physical activity, doctors speak of zero severity. In addition to shortness of breath, symptoms characteristic of the pathology that triggered the appearance of an alarming symptom are added.
Reasons for the appearance
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a violation of the frequency and depth of breathing. At rest, it occurs for pathological reasons, and is often a response to oxygen deficiency.
Taking into account the etiology, the causes of dyspnea can be divided into groups:
- cardiovascular pathology;
- pulmonary dyspnea;
- anemia.
Depending on the type of shortness of breath and the stage of its course, treatment tactics are selected.
Cardiovascular pathology
Dyspnea at rest (causes of heart pathologies, as a rule, occurring in a chronic form), depending on the type, its duration, physical activity, after which it appears, may indicate the stage of cardiac diseases. As a rule, with cardiac dyspnea, an inspiratory appearance and frequent paroxysmal attacks at night are noted.
There are many reasons why cardiac dyspnea can occur:
- heart failure;
- heart defects;
- myocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy;
- acute phase coronary syndrome;
- pericarditis;
- cardiac tamponade.
Heart pathologies that provoke the appearance of dyspnea.
| Definition of disease | Reasons for development | Symptoms |
Heart failure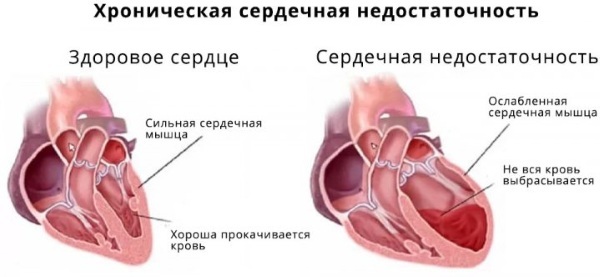 | ||
| A disease in which the heart, for some reason, is not able to pump enough blood, which disrupts natural metabolic processes and provokes dysfunction of various organs and systems. |
|
|
| Acute coronary syndrome | ||
| A group of symptoms that define myocardial infarction and angina pectoris. With myocardial infarction, oxygen supply to the myocardium is disrupted, which leads to cell necrosis. Unstable angina is an exacerbation of coronary artery disease, which provokes myocardial infarction. |
|
|
| Heart defects | ||
Pathological changes in the structure of the heart, provoking circulatory disorders in the large and small circle. Defects can affect the following structures of the heart:
|
Congenital malformations appear due to various genetic abnormalities of intrauterine development or infection of the fetus. The acquired forms develop against the background:
|
General symptoms of defects:
|
Cardiomyopathy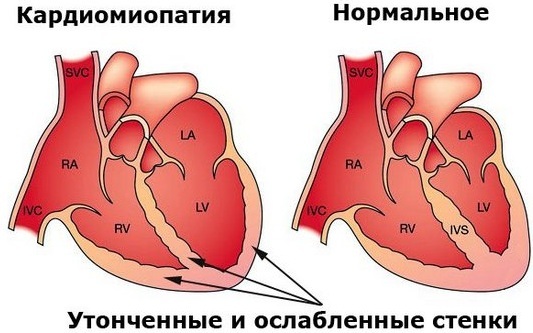 | ||
| Damage to the heart, which is manifested by hypertrophy or dilatation. | There are two types of pathology:
|
The signs of the disease are not specific, however, they can indicate possible disorders with the heart:
|
| Myocarditis | ||
| Damage to the heart muscle (myocardium), as a rule, by an inflammatory process. |
|
|
| Pericarditis | ||
| Inflammatory process of the pericardium (pericardium). | The causes of pericarditis are identical to those of myocarditis. |
|
Tamponade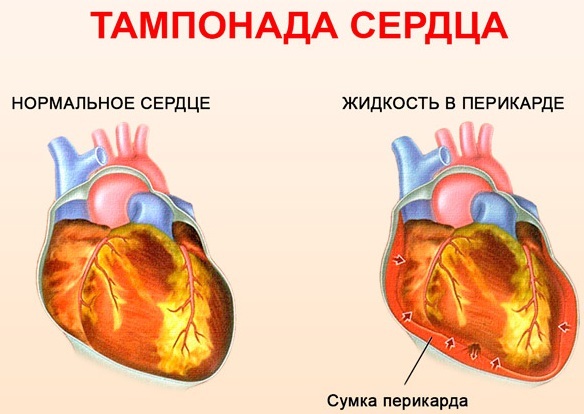 | ||
| The accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity, which disrupts the movement of blood through the vessels. The fluid accumulated in the pericardial sac restricts the contractions of the heart, squeezes it. |
|
|
Pulmonary dyspnea
Dyspnea at rest (causes may be in pulmonary pathologies characterized by a change in the frequency and depth of contractions of the diaphragm) may appear with pulmonary diseases, when an obstacle to the passage of air is created in the alveoli, which causes insufficient plasma oxygenation blood.
A number of reasons contribute to the appearance of pulmonary dyspnea, as a rule, these are inflammatory processes in the parenchyma, the presence of foreign bodies in the respiratory tract.
The most common diseases that provoke the appearance of pulmonary dyspnea:
- chronic pulmonary obstruction (COPD);
- emphysema of the lung tissue;
- bronchial asthma;
- pneumonia;
- pneumothorax;
- pulmonary embolism;
- hemothorax;
- aspiration.
Diseases of the lungs accompanied by shortness of breath:
| Definition of disease | Reasons for development | Symptoms |
Chronic pulmonary obstruction (COPD)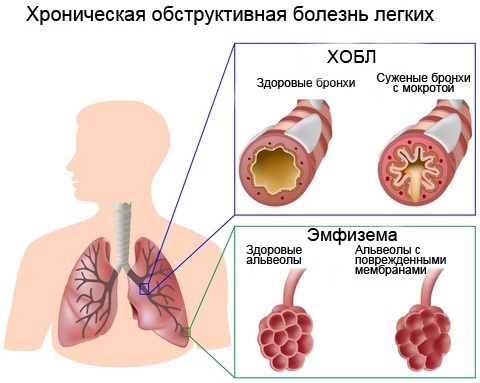 | ||
| An inflammatory process in which there is a progressive or partially reversible obstruction of air flow into the respiratory tract. Often, COPD causes the development of cor pulmonale and respiratory failure. |
|
|
| Bronchial asthma | ||
| Inflammation of the respiratory tract, in particular the bronchi. As a result of a negative impact from the outside, the mucous membrane of the bronchial tree is irritated, in which a large volume of sputum is produced and smooth muscles spasm. All this provokes an attack of suffocation, shortness of breath and severe coughing. Dyspnea occurs on expiration, the obstruction increases, and a large volume of air remains in the lungs. This leads to stretching of the tissues of the organ. |
|
|
| Emphysema | ||
| Pathological expansion of the space of the distal bronchioles, resulting from destructive changes in the walls of the alveoli. The process is irreversible. The affected area of the lung is not able to perform its direct functions, which affects the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. The complicated form leads to pneumothorax and heart failure. |
|
|
Pneumonia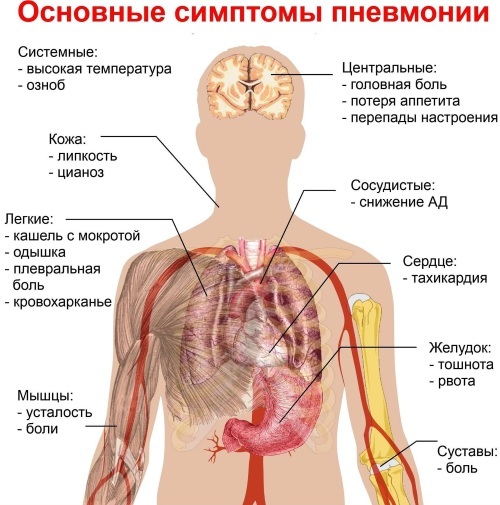 | ||
| Inflammation of the lung tissue of an acute or chronic nature. The process involves the alveoli and interstitial tissue of the organ. | The causative agents of the inflammatory process are such microorganisms:
|
|
| Pneumothorax | ||
| Filling the pleural cavity with air. |
|
|
| Hemothorax | ||
| The accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity, which creates pressure on the lungs, and makes it difficult for the diaphragm to move. |
|
|
Anemia
A critical decrease in the level of hemoglobin, erythrocytes or hematocrit (anemia) can occur as an independent disease or be a separate sign of any pathology.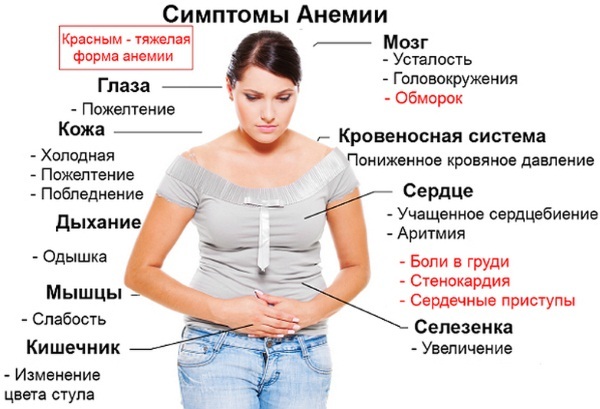
Numerous factors can influence the development of the condition:
- deficiency of certain nutrients (folic acid, iron, cyanocobalamin);
- impaired reabsorption function (absorption of useful elements);
- loss of blood with leiomyoma or peptic ulcer;
- the use of certain dosage forms;
- parasitic diseases (necatorosis, ankylostomiasis, ascariasis);
- malignant neoplasms, blood cancer;
- intoxication;
- heredity, developmental anomalies (violation of the structure of hemoglobin, impaired function of enzyme substances);
- severe infectious or somatic diseases.
Shortness of breath at rest (the reasons may be in the formation disorders, destruction or loss of red blood cells, hemoglobin or hematocrit) occurs as a result of impaired oxygen transport in the body, which leads to hypoxia.
Together with shortness of breath, the patient has the following symptoms:
- general weakness, severe fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- sleep disturbance;
- headache, dizziness;
- decreased concentration, memory problems.
Anemia can be recognized by the color of the skin. In such patients, the skin becomes pale, sometimes with a pronounced yellow tint.
Other reasons
There are several more reasons due to which shortness of breath appears.
This is:
- With nervous disorders. In patients with nervous disorders, there is an acute shortage of air, while they are worried about the fear of death from suffocation. As a rule, persons suffering from such disorders, with an unstable mental state, prone to hypochondria. In such situations, one feature is noted, shortness of breath in patients is accompanied by "noisy design" (oohs, oohs, loud and frequent groans).
- Endocrine pathologies. Shortness of breath is an indirect sign of thyroid dysfunction. For example, with thyrotoxicosis, the level of thyroid hormones increases, which speeds up the metabolism. As a result, tissues and organs need a lot of oxygen consumption, the heart does not always cope with the increased load, which provokes an attack of compensatory shortness of breath.
- Shortness of breath during pregnancy. During the gestational period, the volume of circulating blood increases, the respiratory system works in an enhanced mode, as it supplies oxygen not only to the mother's body, but also to the fetus. The enlarged uterus presses on the diaphragm, reducing the respiratory function, the respiratory rate increases to 24 movements per minute, in addition there is an increase in breathing rate during any physical exertion and emotional shocks.
Diagnostics
Since dyspnea at rest is only a sign of pathological disorders, and not an independent disease, to differentiate possible problems, a number of diagnostic measures are carried out:
- echocardiogram;
- ECG during exercise and at rest (daily monitoring - Holter);
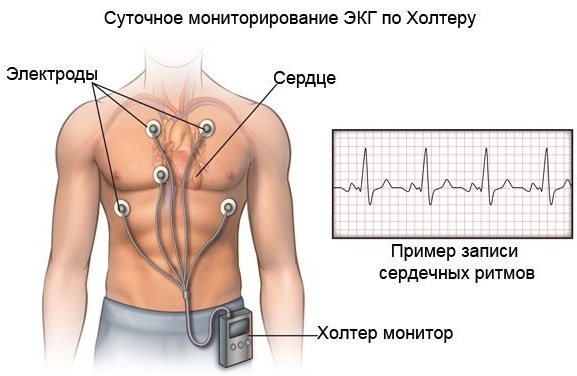
Ischemic heart disease is diagnosed by Holter monitoring - x-ray;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- blood sugar test;
- MRI, CT of the chest organs;
- Ultrasound;
- load tests.
When to see a doctor
Shortness of breath at rest is an alarming symptom indicating the development of a complex pathological process. Therefore, this condition requires a medical examination, especially if chest pain, general weakness, and dizziness appear along with shortness of breath.
If dyspnea rarely bothers, but is noted at rest, you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible. Shortness of breath has an unexpected and increasing character, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. It may indicate a ruptured lung tissue, heart attack, or vascular embolism.
The initial examination is carried out by a therapist, he prescribes a comprehensive examination, on the basis of which further treatment and possible consultation are determined narrow-profile specialists:
- pulmonologist;
- cardiologist;
- hematologist;
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist;
- psychiatrist.
Treatment methods
Treatment for shortness of breath depends on the underlying cause of this alarming symptom. The tactics of therapy are determined only after receiving the results of a comprehensive examination.
Medications
Symptomatic treatment of dyspnea gives only a temporary effect, relieves the condition. Therefore, the main task of conservative therapy is to eliminate the root cause.
If the cause of shortness of breath is cardiac pathology, patients are prescribed:
- beta blockers (Atenolol, Metoprolol);
- suspension dilators (Nitroglycerin);
- ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril);
- diuretic drugs (Furosemide, Spironolactone);
- anticoagulants (warfarin);
- statins (atorvastatin).
With pathologies of the respiratory system, the following are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- phlegm thinning agents;
- bronchodilators;
- xanthines;
- breathing exercises.
For nervous disorders, the doctor prescribes sedatives and antidepressants. If the cause of dyspnea is anemia, patients need to adjust their diet along with medications. Acute respiratory failure requires treatment in an intensive care unit.
Traditional methods
If dyspnea is of a short-term nature, traditional medicine will help to relieve this symptom:
- Wild rosemary decoction. 1 tbsp. l. dry plant, pour 200 ml of water and put on the stove. Let the broth boil for 10 minutes. Cool and drain. Take the broth 3 times a day, each time brewing a new medicine.
- Infusion of birch leaves. 2 tbsp. l. pour raw materials with 1 glass of hot water. Let it brew for half an hour. Strain. Take 0.5 cups of medication 4-5 times a day.
- Elixir of garlic and lemon. For cooking, you need 300 g of garlic and 3-4 lemons. Pass the garlic through a meat grinder, and squeeze the juice from the lemons. Mix all components, transfer to a jar and cover with gauze. Leave in a dark place for a day. Take 1 tsp. l. medicines with water. The course is 14 days.
Traditional medicine should be used only in cases where dyspnea appears rarely and does not have a pronounced character. In other situations, the condition requires qualified medical attention.
Other methods
You can relieve an attack of dyspnea by carrying out some simple procedures:
- Pursed-Lipped Breathing. Such an exercise reduces the respiratory rate, it is recommended to carry it out in patients in whom the manifestations of shortness of breath are associated with nervous disorders. To do the exercise, sit in a comfortable position and relax. The lips are compressed, leaving a small gap between them. Then a noisy breath is taken, and an exhalation is made in 4 counts, while the lips remain compressed. The exercise should be done for 10 minutes.
- Fan application. Turn on the fan and direct the air stream to your face. This will give the body extra air and relax.
- Steam treatments. Pour hot water into a container and add a few drops of peppermint or eucalyptus oil. Lower your face over the steam and cover with a towel. Take deep breaths while inhaling the oil vapor. The procedure is performed for 5-7 minutes.
It is important to carry out these measures in simple situations when rare and weak attacks of shortness of breath are noted.
Possible complications
Shortness of breath, which occurs for physiological reasons, has no consequences, it is eliminated after the elimination of the provoking factor (stress, physical activity).
If dyspnea is a symptom of any pathology, it cannot be ignored. A timely visit to a doctor will avoid the further development of serious disorders inside the body (cardiovascular pathologies, endocrine diseases, neurological disorders).
The neglect of the condition will gradually worsen the general state of health, the attacks of dyspnea will begin to increase in frequency and become more severe. It is very dangerous when shortness of breath appears at rest or during sleep. The reasons in such situations can be the most dangerous, they require urgent medical attention.
Shortness of breath video
Malysheva about shortness of breath:



