The multitasking and holistic functioning of each organ is ensured by the ubiquitous presence of nerve plexuses. The diagram of their structure in humans clearly shows the beginning of the peripheral nerves along the spinal column. Further, the branching of nerve endings reaches each edge of the entire skin - from head to feet, from one little finger to another little finger.
This structure allows you to feel minimal irritation and transmit a signal to the brain for processing. Availability only correctly functioning nerve periphery defines concepts such as pain, pleasure, sight, perception of sounds and movement of the entire human body.
Record content:
- 1 How the human nervous system works
-
2 Diagram of nerve endings on the human body
- 2.1 Back
- 2.2 Ribs
- 2.3 Leg
- 2.4 Arm
- 2.5 Head
- 2.6 Face
-
3 Symptoms of inflammation of the nerve endings
- 3.1 Spinal nerve disorders
- 3.2 Intercostal neuralgia
- 3.3 Lesions of the nerves of the legs
- 3.4 Damage to the nerves of the hands
- 3.5 Disorders in the nerves of the head and face
- 4 Treatment
- 5 Video about the human nervous system
How the human nervous system works
The nervous system is branched into the central (CNS) and peripheral (PNS). The brain and spinal cord are structural units of the central nervous system. Their tasks include collecting, processing and transmitting signals to each other or PNS. In the periphery, all other organs of the nervous system work - nerves, their endings and nodal plexuses.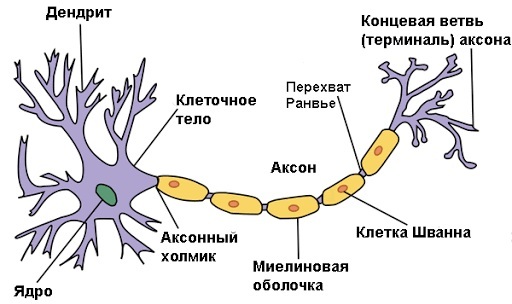
Nerve endings of a person (the scheme repeats the structure of all organs of the body) form the nervous tissue that accompanies each element of the body. The tissue consists of nerve cells - neurons and neuroglia. The latter have a supportive and protective effect, and also have a secretory function.
Each component of a neuron is responsible for a specific task - processing, encoding, transmitting information to the brain through communication with other neurons.
For this, its structure provides for terminal formations in the form of an axon (transmits an impulse from a nerve cell to cells of other tissues) and a dendrite (receives an impulse from cells). A special end of the cell - the synapse - is responsible for the transmission of electrical signals from one neuron to another.
The work of the nervous system consists in the constant communication of nerve cells with each other. Some perform a receptor function and transmit electrical impulses from the site of irritation.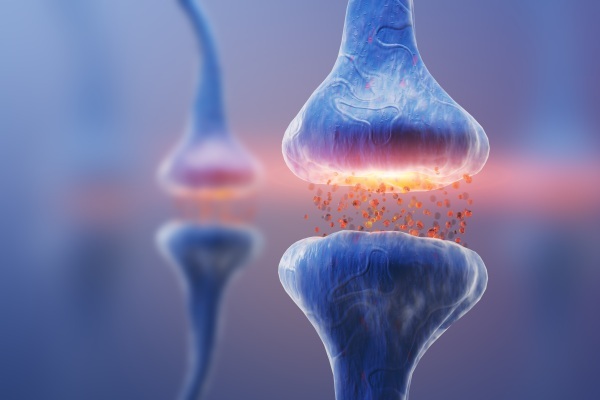
Others receive signals from receptors and transmit them to neighboring cells and tissues. Some of them process and convert signals by generating different types of neurotransmitters in accordance with a specific response. For example, histamine is produced by allergic irritation.
Diagram of nerve endings on the human body
Each major section of the human body has a distinct nerve-building system.
Back
The main role in the formation of peripheral nerves is played by the formation of the sensory roots of the neural tube. With the fusion of which at the 6th week of embryonic development, the formation of spinal nerves occurs. They are 31 pairs of innervating formations that connect the spinal cord with certain parts of the body.
Of these, cervical - 8 pairs, chest - 12 pairs, lumbar and sacral - 5 pairs and a pair of coccygeal. The size of the nerves depends on the metameric region, for the innervation of which a particular block of spinal nerves is responsible. Due to the high concentration of receptors and muscle fibers in the limbs, they are connected to the PNS by the lower cervical, lumbar and sacral nerve branches.
When leaving the intervertebral foramen, each nerve of the spinal cord is divided into 4 branches: anterior, posterior, meningeal and connecting branches. The latter connects the nerve process to the sympathetic trunk.
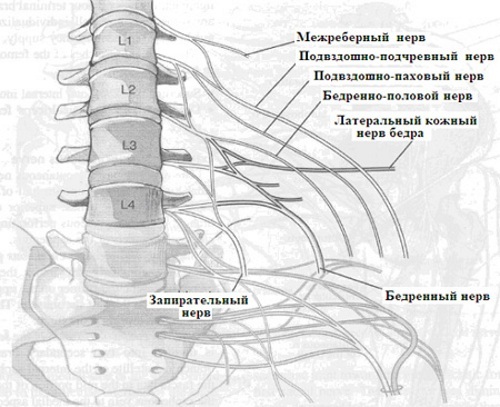 The meningeal, or meningeal, returns to the spinal cord trunk and supplies it with nerve conduction. The remaining branches metamerically extend to the dorsal muscle groups, limbs, and skin. The anterior branch forms an intercostal group of nerves.
The meningeal, or meningeal, returns to the spinal cord trunk and supplies it with nerve conduction. The remaining branches metamerically extend to the dorsal muscle groups, limbs, and skin. The anterior branch forms an intercostal group of nerves.
Ribs
Each of the 12 pairs of human ribs is surrounded by muscles of the same name. The nerve supply continues from the anterior branch of the spinal nerves. Intercostal nerves penetrate the outer and inner sides of muscle tissue. Moreover, 11 pairs of nerves pass between the ribs, the last pair is called the hypochondrium. They occupy a concomitant position with the artery and vein.
The top 6 pairs represent the cutaneous branch and end in the cutaneous layer of the chest wall. Their task is to innervate the intercostal muscles, muscle fibers of the sternum, abdomen, and also the lower back. The lower 5 pairs reach the level of the oblique and transverse abdominal muscles and end in the anterior wall of the peritoneum. The intercostal muscles are responsible for the nerve conduction of the segments of the thoracic region and the abdomen.
Leg
The lumbar plexus of the spinal nerves passes into the main nerve of the lower limb - the femoral nerve. It innervates the lumbar muscles, as well as the muscles of the thigh and the articular part of the knee. The femoral nerve in a long saphenous branch reaches the foot and ends in the skin of the big toe.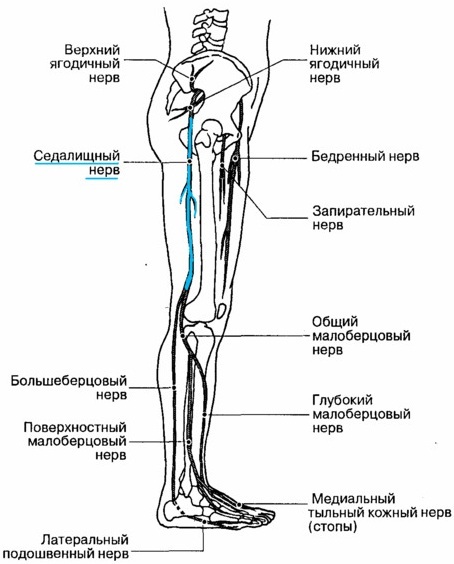
Along the way, it branches out to the anterior cutaneous part of the thigh, then to both surfaces of the lower leg. Along the way, the peroneal nerve follows, dividing into a common, deep and superficial branches.
The posterior surface of the leg is supplied with a continuation of the sacral roots - the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve ending in terms of the branching area. It extends to the entire gluteal region, thigh muscles and hip joint.
Arm
The human nerve endings, the scheme of which, according to the anatomical atlas, is concentrated in the hands, originate in the complex brachial plexus. The nerve trunks are responsible for the innervation of the shoulder girdle and the free part of the upper limbs. The brachial nerve extends down to the skin of each finger, passing through the grooves of muscles and tendons.
It is accompanied by branches of the radial nerve, which innervates the triceps and ulnar muscles. The nerve conductor of the flexor muscle group is the median nerve, which extends from the brachial plexus and descends along the artery, simultaneously bending around it.
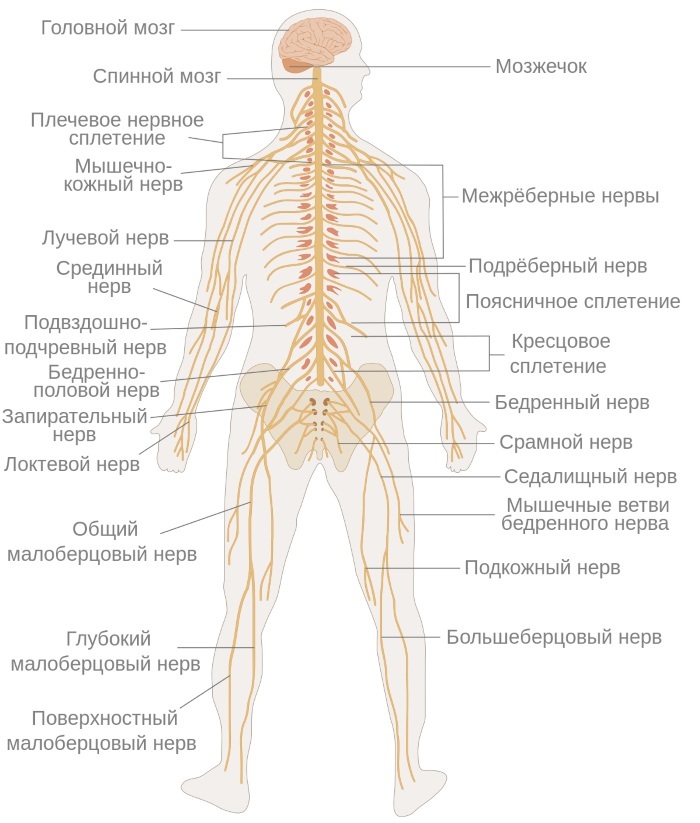
The ulnar nerve is responsible for the coordination of the hand and the precise regulation of impulses when the hand moves. In the sensory and motor functions of the thumb, 3 nerves are involved at once: radial, ulnar and median. The area in the brain that processes the thumb is much larger than the areas that regulate the rest of the fingers.
Head
The peripheral nerve system of the head is represented by the cervical plexus, which branches into 3 types: muscular, sensory and phrenic nerves. The muscular branch supplies the muscles of the neck and head.
The special significance of this branch lies in the accompaniment of the motor function of the cervical muscles. The phrenic nerve does not rise to the head, but descends to the chest and participates in the nerve conduction of the diaphragm.
The scalp is equipped with two sensitive nerve branches. The first - the large ear - innervates the auricle, earlobe and external auditory canal. The second, the small occipital nerve, provides conduction to the occipital region and part of the auricle.
Face
The facial area is connected to the PNS through the trigeminal nerve. The first of its three branches conducts impulses in the frontal zone, the upper eyelid of the eye and the nasal mucosa. The second plexus works in the infraorbital area of the face and provides nervous regulation of the lower eyelid, sinuses, upper lip, mucous tissue of the cheeks, as well as the gums of the upper teeth and the teeth themselves.
The third branch of the trigeminal nerve is the chin nerve. It provides innervation to the lower corners of the mouth, lower teeth and gums, chewing muscles, salivary glands, and the front of the tongue.
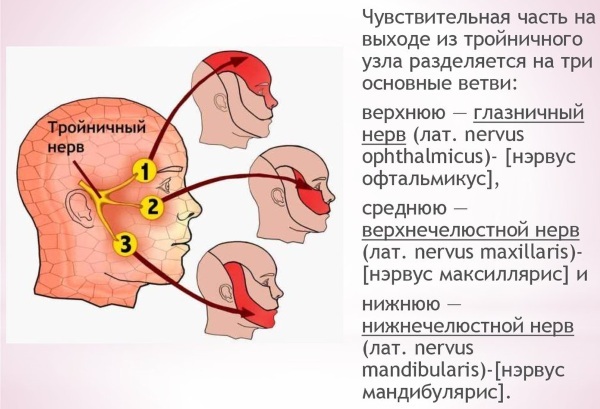
The facial function of the facial muscle tissue supplies the facial nerve with nerve endings. It is divided into 5 main groups of nerves: temporal, maxillary, buccal, mandibular, and cervical. The motor innervation of the lower lip is regulated by the mandibular ramus.
The muscles that lift the edges of the sinuses and the upper lip are innervated by the zygomatic branch of the facial nerve. For the nerve conduction of the lacrimal gland and taste areas of the tongue, the intermediate nerve is responsible, which adds a sensitive character to the motor facial nerve.
Symptoms of inflammation of the nerve endings
In a neurological clinic, half of the diseases are related to the pathology of the peripheral nervous system. Moreover, in most cases, they do not threaten human life, but become the main prerequisites for disability.
This is due to structural changes in the nerve fiber, which disrupt not only motor and autonomic functions, but also affect sensory conduction. The main symptom of such manifestations is severe pain syndrome and is collectively called neuritis, or neuropathy.
Nerve endings are schematically similar to the branches of the circulatory system, therefore, the localization of their pathological changes occurs in any segment of the human body. However, the symptomatology is characteristic of a specific site of nerve damage.
Spinal nerve disorders
The most common (especially in old age) are diseases of the neurological profile in the back: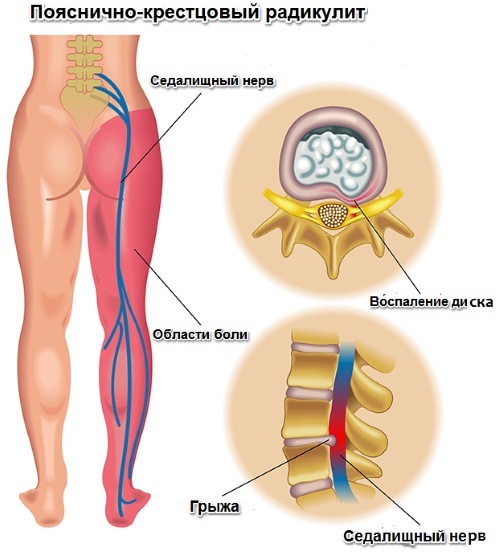
| Name | Brief description of pathology |
| Inflammation of the sciatic nerve | The disease is characterized by aching, stabbing, sharp or dull pains starting from the lower back. The sensation of a lumbago extends down the lower extremity down to the toes. May be accompanied by numbness, edema, redness of the skin. At the site of nerve damage, the temperature may rise or fall relative to the rest of the body. The defeat of the nerve accompanied by a feeling of cooling and "goose bumps" is called sciatica. |
| Radiculitis | Changes in the roots of the spinal cord cause pain in the lumbosacral region. Probably a lingering burning pain from the buttock to the foot. A feature of radiculitis is that sensations increase with sudden movements: it is difficult for a person to sit down, stand up, bend the body of the body. Radiculitis of the cervicobrachial region is distinguished, which spreads the pain syndrome to the neck, scapula and shoulder. Makes itself felt when coughing and raising hands. In severe cases, completely immobilizes the neck and head. |
| Radiculopathy | In a different way, radicular syndrome, which occurs due to compression of the roots of the spinal nerves, but manifests itself mainly not in the back. Sharp tingling of internal organs, in the arms and legs, neck and head - symptoms of radicular disorders. As a rule, it has an increasing character over time. |
Intercostal neuralgia
It is accompanied by girdle pain from the back to the chest. When moving, shooting spasms, both lingering and pinpoint, are felt. When breathing and coughing, stiffness and stitching pains are noted. Intercostal nerve neuralgia is often accompanied by involuntary muscle contraction, sweating, and numbness of the skin around the chest.
Lesions of the nerves of the legs
Serious consequences are brought about by disorders of nervous activity in the lower extremities: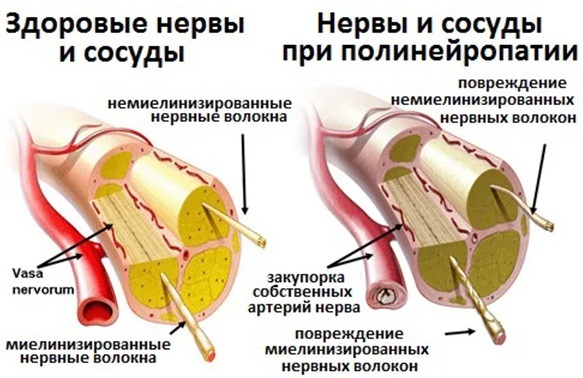
| Diseases | Symptoms |
| Polyneuropathy | Toxic damage to the nerves of the lower extremities is accompanied by a violation of the sensitivity of the feet. Itching and tingling sensations, convulsive manifestations occur. The gradual spread of the affected areas of the nervous tissue leads to muscle atrophy, up to necrosis. Feelings of hypothermia or sweating are accompanied, sometimes together. |
| Tibial neuritis | Extinction of motor processes in the foot is noted, the function of flexion of the fingers decreases and, as a result, the patient loses the ability to stand on his toes. Atrophy of the posterior surface of the lower leg and the lower surface of the foot is observed. There is a pulling pain in the hamstring and heel tendon |
| Peroneal nerve neuropathy | The main symptom is the inability to stand on the heel. The foot hangs down, the function of extension of the toes and ankle joint does not work. Feelings of numbness of the muscles of the anterior surface of the leg and the back of the foot prevail. Pain syndrome is observed during walking, increases with an increase in dynamics. |
Damage to the nerves of the hands
No less serious troubles are caused by pathologies in the nervous activity of the upper extremities:
-
Median nerve neuritis. The defeat leads to the impossibility of flexing the hand and dysfunction of the interphalangeal joints of 1-4 fingers. The sensitivity of the palm decreases with its gradual flattening. The muscles of the forearm atrophy, as well as the skin of the lower arm. It is accompanied by vegetative-vascular disorders in the form of sweating of the palm, cyanotic skin and destruction of the nail plates.
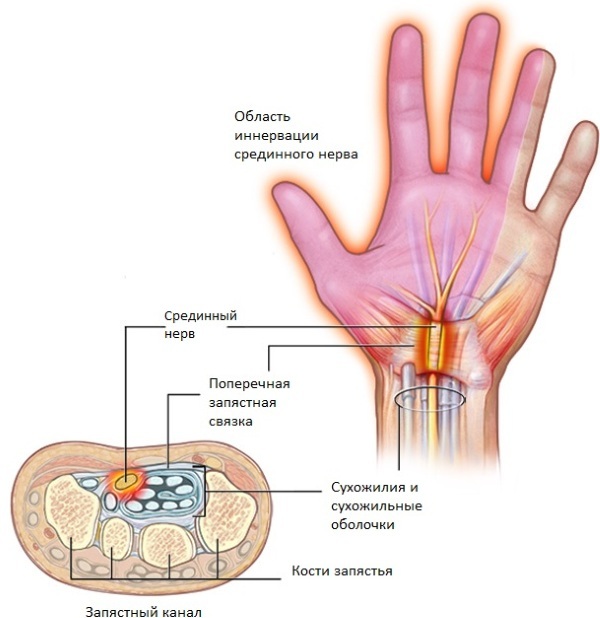
- Radial nerve neuropathy. It is characterized by deformation of the hand due to the depletion of small muscles. There are aching pains with decreased sensitivity in the 4th and 5th fingers. The patient does not have the ability to bend his thumb and lean on it with his whole palm. There is a functional disorder of the elbow and wrist joints. The neuritis of the radial nerve is also called the "drooping hand" syndrome.
Disorders in the nerves of the head and face
The lesions of the nerves of the head are quite numerous:
-
Trigeminal neuralgia. It spreads over the entire area of the head and face. It is accompanied by a burning sharp pain with attacks from several seconds to a couple of minutes. What is characteristic is the removal of the pain signal from the site of the nerve injury. When the symptom occurs, psychological stiffness, fear of making any movement, is likely to hold the breath until the nerve relaxes. Outwardly, it is expressed in profuse lacrimation and discharge of mucous secretions from the nose. Convulsive contractions of facial muscles are often observed.
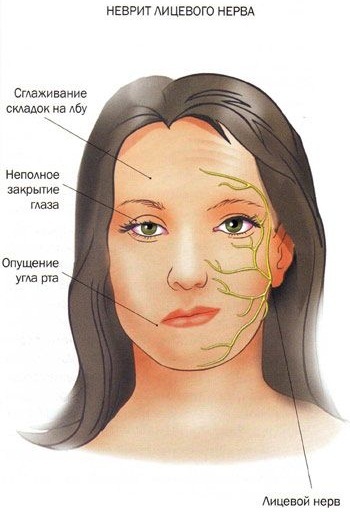
- Neuritis of the facial nerve.The most pronounced symptom is facial asymmetry, moreover, the curvature occurs in the healthy direction. The characteristic peripheral paralysis is accompanied by changes in the skin folds, the inability to close the eye - the eyeball rolls up. When chewing, food remains behind the cheek, the motor functions of the tongue are weakened. Disorders of taste and hearing are associated with increased or decreased lacrimation and salivation, often dry mouth.
- Occipital neuralgia. Pain syndrome affects one half of the occiput in accordance with the affected branch of the nerve. Shots are localized in the ear, neck, scapula. They intensify with movements of any dynamics, coughing and sneezing. The patient is forced to fix the position of the head and avoid sharp turns. There may be a feeling of numbness in the occipital region. A chronicle of twitching headaches gradually develops.
- Slader's Syndrome. Pterygopalatine neuritis causes a sharp spasm in the eye, jaw, and nasal septum. The main symptom is oppressive pain in the palate and tongue with profuse salivation. It spreads to the ear, neck and half of the head. The development of dizziness with sensations of noise and ringing in the ears is characteristic. There is a high likelihood of reddening of the corresponding side of the face with an increase in the volume of lacrimation. It takes at least an hour before the nerve begins to relax.
This is the most common part of the neurological disorders of the peripheral system. The causes of occurrence can be trauma, infection, intoxication, compression and many other disorders. All prerequisites can be acute or chronic, and pain sensitivity depends on the time of the course of the disease.
Treatment
Human nerve endings, the recovery scheme of which corresponds to the treatment of inflammatory processes, respond to all types of therapy: drug, physiotherapy procedures, surgery and some folk remedies:
-
Medication - first of all, analgesic agents are prescribed to relieve pain symptoms. With neuritis of infectious genesis, antibiotics and topical antiviral drugs are prescribed. A frequent effect is exerted by a glucocorticoid drug, which is capable of removing fermentation in the area of inflammation everywhere. A sharp attack of sciatica is temporarily removed from drugs based on diclofenac. Applied vasodilator and decongestant drug groups. Complexes of vitamins B and C, nicotinic acid are often added to the course of treatment. To improve neuromuscular conduction, the appropriate pharmacological group is used: for enhancing contractile function - cholinomimetic drugs, for muscle relaxation - muscle relaxants. The latter give a positive effect in the fight against intercostal neuralgia. For the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy, the correct external insulin dosing system is calculated. Anticonvulsants are used to restore the nerves of the extremities.
- Physiotherapy - for the treatment of neuralgia, the entire procedural range of physiotherapeutic treatment is suitable. When restoring the nerve fibers of the face and head, ultra-high-frequency therapy is used, which has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected area of the nerve. Along the way, it increases blood circulation and lymph flow, which gradually restores nerve conduction. Ultraviolet radiation is used to relieve acute inflammations. Diadynamic currents, in other words "Bernard currents", are prescribed as an impulse therapy for neuralgia of different localization. Laser therapy has a positive effect in the treatment of nervous disorders, which acts at a depth of up to 3 cm from the skin. This allows the nerve plexuses that are close to the surface of the body to be affected. Laser physiotherapy is actively used in the restoration of the trigeminal and facial nerves, lumbosacral plexus, cervical and brachial nerve branches.
- Exercise therapy and massage. Physiotherapy exercises and massage have both a therapeutic and a prophylactic effect in the event of neuritis. The main task is to strengthen the spinal nerve branches by exerting stress on the spine.
Human nerve endings (the PNS scheme allows you to act on the nerve endings through muscle tone) respond well to massage. In the treatment of neuralgias of the face and head, special massage schemes are used with point and vibration techniques.
When massaging the occipital region, sharp chopped movements and beating are excluded. A course of mimic gymnastics is prescribed. Exercise therapy and massage techniques are the safest for humans because of the natural approach to health improvement, as opposed to the medication method.
-
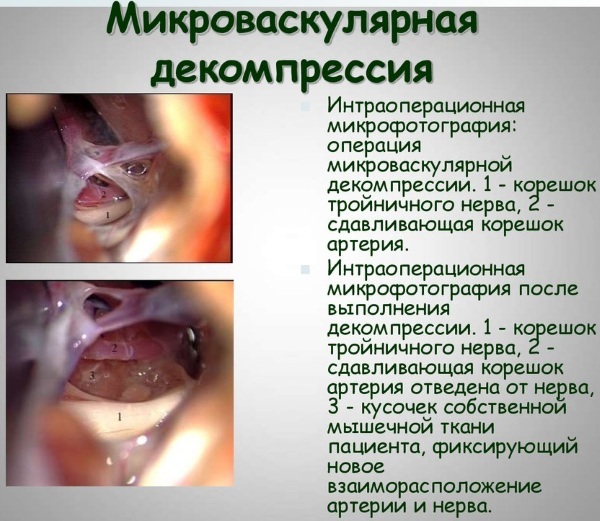
Operative treatment - to operations on nerve fibers and nodes come in two cases: the lack of results in other methods of treatment and traumatic consequences. The latter prevail in neurological surgery and consist of complex multi-stage operations. Microsurgical techniques are used with the use of high-precision optics, special instruments and ultra-thin suture material. In the case of non-traumatic development of trigeminal neuritis, a neurosurgical operation is used - microvascular decompression. The effect is achieved by installing a Teflon protector between the damaged nerve and the vessel, thereby restoring the connection between the periphery and the central nervous system. In getting rid of the patient from inflammation of the sciatic nerve, they resort to removing the provoking factor - an intervertebral hernia or part of the affected vertebra.
- Folk remedies - the main goal of traditional medicine is to relieve pain and relaxation of the nerve endings. Local application involves fresh leaves of geranium, aloe, horseradish. Leaves are applied to the sore spot and wrapped in several layers of warm tissue. For internal use, decoctions of chamomile, peppermint, sage and willow bark are used. The dried and crushed parts of plants are poured with boiling water and insisted under a lid. They relieve pain, and also have a general sedative and anticonvulsant effect. For the treatment of disorders of the facial and trigeminal nerves, a hard-boiled egg helps - it is cleaned and cut in half until it cools, then applied to the diseased area.
The human body is equipped with a dense system of nerve endings that are responsible for the full functionality of the body.
If the circulatory system plays a transport role, then the peripheral nervous system, schematically repeating it, is responsible for motor and sensory tasks. Disturbances in nerves, regardless of their location and scale, lead to various kinds of consequences - from mild inconvenience to paralyzing and painful manifestations.
Video about the human nervous system
Nervous system in 10 minutes:



