Peripheral neuropathy is a lesion of the nerves of the peripheral nervous system. This violation can be of a different nature, depending on the cause of its occurrence, the location of the damage and the severity. In medicine, more than 100 forms of neuropathy are distinguished. In childhood, hereditary motor sensory polyneuropathies are most common.
Record content:
- 1 What is the peripheral nervous system?
- 2 What is peripheral neuropathy?
- 3 What is amazed?
- 4 Epidemiology
-
5 Causes
- 5.1 Trauma
- 5.2 Alcohol and toxins
- 5.3 Infections and autoimmune diseases
- 5.4 Medications
-
6 Types, forms, symptoms
- 6.1 Sensory neuropathy
- 6.2 Motor neuropathy
- 6.3 Autonomic neuropathy
- 6.4 Mononeuropathy
- 6.5 Polyneuropathy
- 7 Peripheral neuropathy in children
- 8 Complications and consequences
-
9 When to see a doctor? Diagnostics
- 9.1 Neurological examination
- 9.2 Hardware, instrumental studies
- 9.3 Laboratory Methods
- 10 Treatment
-
11 Domestic and local funds
- 11.1 Blood flow regulating drugs
- 11.2 Vitamins
- 11.3 Pain relievers
- 11.4 Stimulants of nerve impulse conduction
- 11.5 Homeopathy
- 12 Physiotherapy
- 13 Physiotherapy
- 14 How does music heal?
- 15 Surgical intervention
- 16 Folk remedies
- 17 Precautions for people with peripheral neuropathy. Recovery prognosis
- 18 Video about neuropathy
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The human nervous system is divided into 2 large sections: central and peripheral. The first includes those structures that are found in the brain and spinal column. The second includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects them with receptors (sensitive formations) and effectors (terminal processes of nerve cells that transmit nerve impulses to organs). As a result, adaptive reactions of the body arise, for example, contraction of muscle tissue or secretion.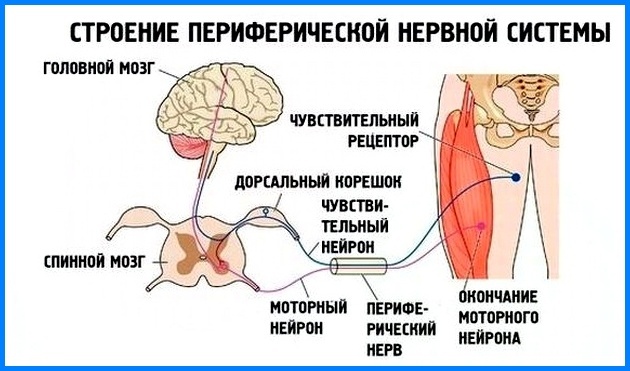
Part of the peripheral nervous system is the somatic, which supplies the skin, muscles, bone apparatus, and some internal organs with nerves. Thanks to her, interaction with the external environment is carried out. Another component of the PNS is the autonomic system, which innervates the organs. It regulates the internal processes in the body.
What is peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is nerve damage. Since the PNS covers almost the entire human body, the manifestations of peripheral neuropathy can be very different. This is not a separate disease, but a whole complex of symptoms associated with different conditions.
The lesion is based on degenerative processes leading to damage and destruction of nerve fibers (their sheaths or rods - axons). They can arise under the influence of several factors, described below. The most common symptoms are pain syndrome, sensory disturbances, and muscle weakness.
What is amazed?
With PNS neuropathy, the following parts of the nervous system can be damaged:
- 12 pairs of cranial nervesleaving the brain in the area of its base. These include the olfactory, vagus, optic, oculomotor, trigeminal, glossopharyngeal nerves and others. Accordingly, when they are violated, the organs of the head suffer. The vagus nerve also provides a connection between the central nervous system and organs located in the neck, chest, and abdomen (excluding the pelvis).
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves, which are grouped into 5 segments - cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal.
-
Nerve plexuses - cervical, shoulder, lumbar, sacral.
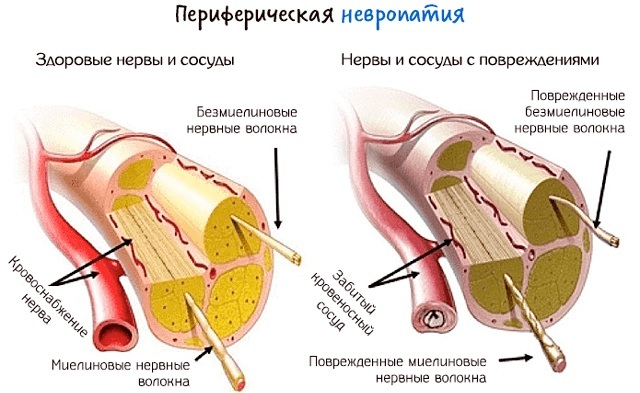
Peripheral neuropathy
With peripheral neuropathy, impulse transmission from body parts to the brain is impaired. Symptoms distinguish 4 main forms of such disorders. In the most severe cases, vital processes such as breathing and heart function may deteriorate.
Epidemiology
The average prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in different populations is 6-7%. It is much more common than central (80-95% of cases). In different conditions, the likelihood of developing neuropathy is different.
Thus, damage to the peripheral nervous system is observed in 20-40% of patients with diabetes mellitus. In acute herpesvirus infection, it develops in 20-45% of cases. In cancer patients in the last, terminal stage, this figure reaches 90%.
In some cases, clinical signs of damage to the nervous system become noticeable 5-10 years after the onset of the underlying disease. In 10% of patients with diabetes mellitus itself, diabetes is detected only after the first neurological symptoms.
Causes
Peripheral neuropathy is a pathological condition, the causes of which can be summarized in several large groups:
- trauma;
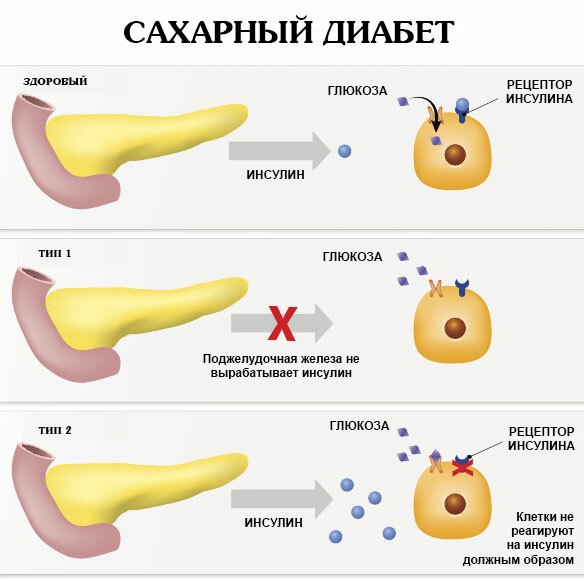
- endocrine disorders - insufficient or excessive function of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus;
- metabolic diseases - chronic renal or hepatic failure, impaired protein metabolism, with which is deposition in the tissues of the protein-polysaccharide complex of amyloid (amyloid polyneuropathy);
- diseases of internal organs (obstructive pulmonary disease, gastrointestinal tract pathology, accompanied by impaired absorption and deficiency of B vitamins);
- systemic connective tissue pathologies - periarteritis nodosa (inflammation of the walls of arterial vessels with the formation of microaneurysms, or "nodules"), systemic lupus erythematosus (immunocomplex damage to connective tissue), scleroderma (an autoimmune disease in which blood microcirculation is disturbed, inflammation and replacement of functional fibrous tissues);
- pathology of the circulatory system - the appearance of abnormal proteins in the blood (with myeloma, tumors and other diseases);
- malignant neoplasms;
- toxic poisoning and taking certain medications (including alcohol abuse, drug addiction, lead intoxication);
- infectious diseases, vaccinations and immunodeficiency states.
Trauma
With injuries, the integrity of the nerve fibers is disturbed. The potential for recovery that is embedded in peripheral nerves from the moment a person is born is severely limited. Therefore, severe injuries often lead to permanent disability. In fractures, the displaced bones also exert compression, or squeezing of the roots of the spinal nerves.
Disruption of the PNS can also occur when the hands are overstrained, which is associated with work. In this case, local trauma to the nerve endings of the palms and fingers occurs. This is facilitated by industrial vibration and exposure to chemicals (solvents, lubricants, and others).
Alcohol and toxins
In the structure of toxic neuropathies, alcoholic polyneuropathy is in the lead. It is observed in 12-30% of patients suffering from chronic alcoholism, and in a latent (latent) form is found in 97% of people who abuse alcohol.
Among the poisonings, the following types are most common:
- lead, in which movement disorders occur;
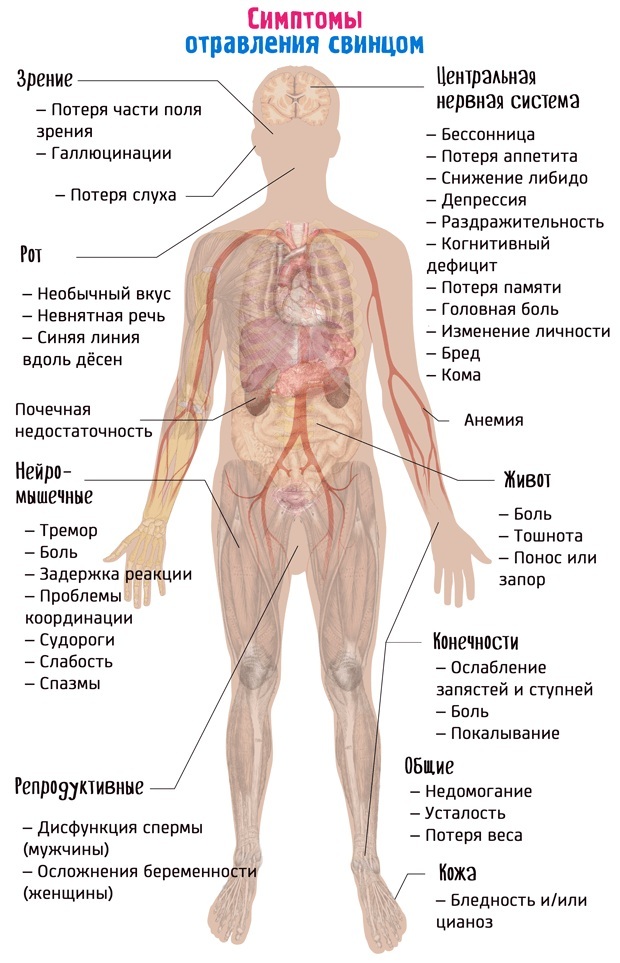
- arsenic - the use of drugs for the destruction of insects, medical supplies, as well as when melting metal (manifests itself in the form of muscle weakness, impaired sensitivity);
- organophosphate substances that are part of insecticides, lubricants, polymeric materials.
Infections and autoimmune diseases
Among all infectious diseases, neuropathy most often occurs in severe form with HIV infection. Various variants of symptomatology are noted in 20-35% of cases, but upon autopsy, signs of PNS lesions are detected in 95% of patients.
There is also a high prevalence of neuropathy in the following infections (the average number of patients in% is indicated in parentheses):
- diphtheria (20%);
- tick-borne borreliosis (up to 40%);
- herpes (up to 45%);
- viral hepatitis (up to 42%);
- leprosy (up to 95%).
Medications
The development of neuropathy can lead to the use of drugs such as:
- drugs used in chemotherapy - cytostatics for the treatment of tumors (Vincristine, Bortezomib and others);
- platinum-containing drugs, also used for malignant tumors;
- antiarrhythmics (Amiodarone);
- antihypoxic drugs (Perhexilin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (chloroquine, used for malaria, amebiasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, photodermatosis);
- antiprotozoal, anthelmintic drugs.
Types, forms, symptoms
Peripheral neuropathy can manifest itself in several forms. This is due to the individual characteristics of the course of the disease and a variety of etiological factors.
The following forms of neuropathy are distinguished:
- sensory;
- motor;
- vegetative;
- mono- and polyneuropathy.
Sensory neuropathy
Sensory (or sensory) neuropathy is characterized by the following symptoms:
- change in the sensitivity of the skin (its increase or decrease);
- sensation of itching, tingling, burning, numbness, creeping "goose bumps" in the feet or hands;
- a false sense of a foreign body in the shoe;
- insensitivity to high or low temperatures, which can result in burns and other types of injury;
- pain that occurs even with a light touch;
- the formation of ulcers with minor skin trauma;
- deterioration of reflexes.
Motor neuropathy
Motor (or motor) neuropathy manifests itself as follows:
- deterioration of fine motor skills - awkwardness when writing, tying shoelaces on shoes, buttoning up buttons, difficulty grasping and holding small objects;
- uncertainty when walking, stumbling, uneven gait, difficulty getting up from a sitting position;
- muscle twitching, involuntary movements, convulsions;
- muscle weakness;
- in severe cases, paralysis.
Autonomic neuropathy
Symptoms of autonomic neuropathy include:
- decreased (dry skin) or increased sweating;
- changes in bowel motility (diarrhea or constipation);
- urinary incontinence;
- hearing impairment (decreased hearing acuity, sensation of noise or ringing in the ears);
- dizziness;
- tachycardia, arrhythmia;
- impotence in men.
Mononeuropathy
In mononeuropathy, only one motor, sensory, or mixed nerve is affected. So, for example, neuropathy of the facial nerve manifests itself in the fact that there is paralysis of facial muscles. This condition can occur with severe hypothermia.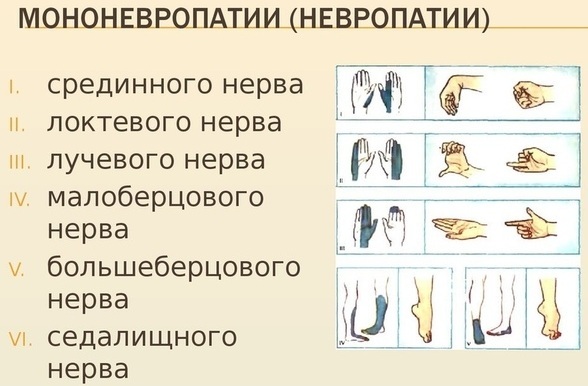
Mononeuropathy is most often associated with compression of a peripheral nerve or toxic effects, which leads to a violation of its functions to one degree or another.
Polyneuropathy
Damage to two or more nerves is called polyneuropathy. In European countries, diabetes is the most common cause. Damage to nerves occurs as a result of a violation of their blood supply, biochemical reactions (the attachment of sugar to the protein membrane of neurons) and other pathological processes.
Diabetic polyneuropathy is characterized by the following manifestations:
- absence or decreased reflexes in the lower extremities;
- diabetic foot syndrome (the formation of long-term non-healing leg ulcers);
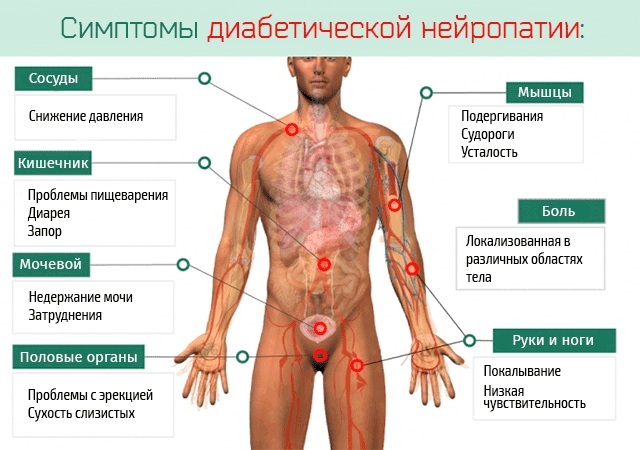
- loss of tactile and vibration sensitivity;
- muscle atrophy and other disorders.
Peripheral neuropathy in children
In addition to the disorders listed above, there are a number of hereditary diseases accompanied by the onset of peripheral neuropathy:
- peroneal muscle atrophy, in which the myelin sheath of nerve fibers is disturbed; the main symptom is muscle atrophy of the lower extremities;
- polyradiculoneuropathy - autoimmune inflammatory pathology, manifested in a decrease in muscle strength, deterioration in sensitivity, autonomic disorders (tachycardia, drop in blood pressure, arrhythmia, delayed excretion of urine and other);
- Dejerine-Sott disease, which is characterized by dystrophy of peripheral nerves; the onset of the disease occurs in the first years of life, leading to early disability of the child, and other genetic disorders.
Most often, these pathologies are characterized by the formation of symmetrical, gradually progressive atrophy of muscle tissue.
Complications and consequences
Complications of peripheral neuropathy include:
- loss of heat or pain sensitivity;
- muscle weakness;
- spontaneously arising pain;
- decreased reflexes, deterioration of motor activity;
- painful cramps;
- in severe cases - disability;
- sphincter insufficiency, involuntary urination as a result of loss of muscle tone in the bladder;
- impotence;
- with a cardiac form - orthostatic hypotension (a sharp drop in pressure when standing up, accompanied by dizziness, fainting), myocardial infarction, sudden death syndrome.
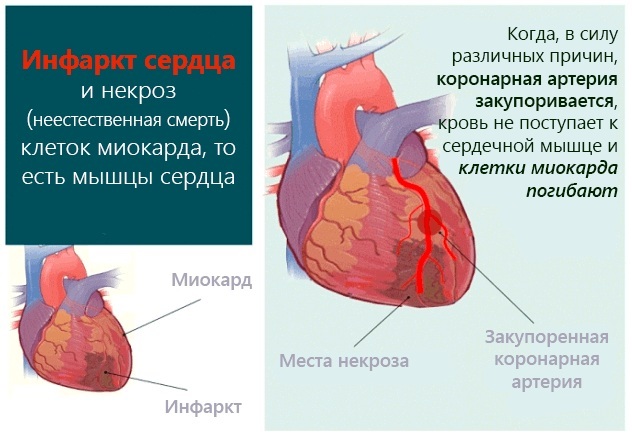
The most severe forms are characteristic of polyneuropathies that affect vital organs. So, when diagnosing the last variety (cardiac), up to 50% of patients die in the next 5-10 years.
When to see a doctor? Diagnostics
You need to see a doctor when the first signs described above appear, especially if you have a history there are diagnosed chronic diseases in which this symptom complex. At the first stage, you need to contact a therapist, who, if necessary, will refer you to a neurologist and other narrow specialists.
The diagnostic algorithm includes:
- study of the general condition of the patient, assessment of reflexes and motor ability, collection of anamnesis;
- electrophysiological studies;
- biochemical analyzes.
Neurological examination
During a neurological examination, the following parameters are determined:
- superficial sensitivity (on both feet, legs, thighs, forearms, shoulders; a cotton swab and a sharp object);
- deep sensitivity (vibration sensitivity, using a graduated tuning fork or biotensiometer applied to the thumb and ankle);
- cold sensitivity (metal and plastic);
- muscle reflexes on the limbs (using a neurological hammer);
- muscle strength.
Hardware, instrumental studies
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- electromyography, which allows you to determine the electrical activity of muscle tissue (electrodes are attached to the surface of the skin or inserted in the form of needles into it);
- electroneurography, which helps to assess the decrease in the propagation rate of electrical impulse and action potential of nerve fibers (diagnostics of the functional state of peripheral nerves);
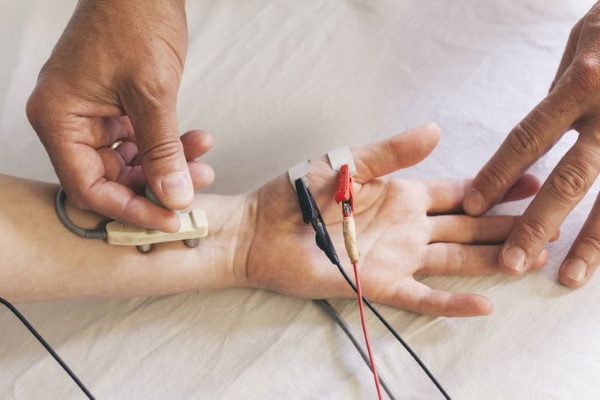
- MRI and CT of nerve fibers in the area of their intended clamping;
- ultrasound examination of nerves, which allows you to assess their structure and changes in characteristics.
Laboratory Methods
From laboratory methods, such as are used:
- biochemical blood test (determination of thyroid hormones, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, glucose, protein, B vitamins);
- general urine analysis;
- biopsy of the sural nerve followed by histological examination;
- a puncture skin biopsy to assess the density of the nerve fiber, which is significantly reduced with neuropathy.
Treatment
Peripheral neuropathy is a pathological disorder, the general treatment regimen for which includes the following measures:
- elimination of unfavorable factors causing such a condition;
- stopping the process of destruction of nerve fibers;
- restoration of normal nerve conduction, muscle strength and sensitivity.
Domestic and local funds
The appointment of certain funds depends on the type of disease, against the background of which neuropathy has developed. For example, diabetes mellitus requires normalization of blood glucose levels and constant monitoring of it.
Blood flow regulating drugs
Antioxidant and metabolic agents help reduce the damaging effects of toxic and dysmetabolic effects. The main characteristics of these drugs are shown in the table below.
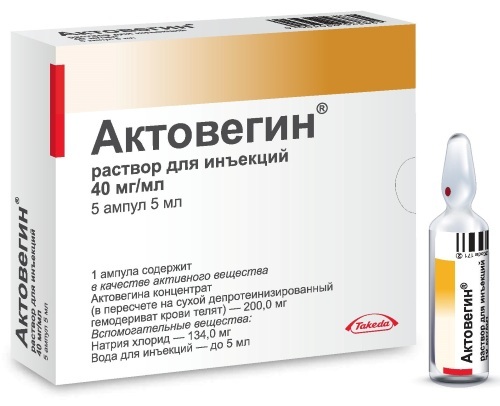
| Name | Main component | Pharmacological effect | Dosage |
| Actovegin | Deproteinized hemoderivat | Improvement of microcirculation, metabolic processes in cells, synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins. | At the first stage - 1.2-2 g per day (intravenously), subsequently - 600 mg 3 times a day (orally); long-term reception. |
| Berlition | Alpha Lipoic Acid (Thioctic Acid) | Reducing the severity of oxidative stress. | 600-900 mg daily for 3 months (IV first, then oral). |
| Thioctacid | |||
| Thiogamma |
Vitamins
To restore nerve fibers and their myelin sheath, vitamin therapy with preparations containing vitamin is indicated B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), B12 (cyanocobalamin), which are administered intravenously as a solution or orally in tablets. The average daily dosage for the first two drugs is 100 mg each, and for cyanocobalamin - 100 μg.
Pain relievers
Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder that is almost always associated with pain.
For severe pain, the following drugs are recommended (the daily dosage is indicated in parentheses):
- tricyclic antidepressants - Amitriptyline (25-150 mg in 2 divided doses);
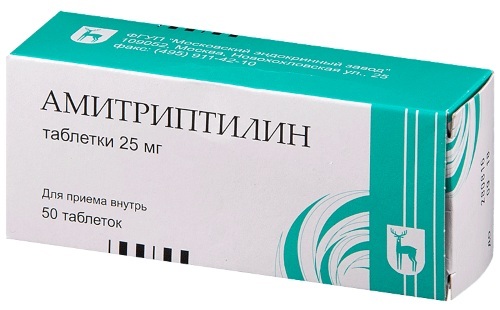
- inhibitors of the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, or SNRIs - Duloxetine (60-120 mg in 1 dose), Venlafaxine (37.5 mg 2 times);
- anticonvulsants - Gabapentin (1.2-3.6 g in 3 divided doses), Pregabalin (300-600 mg in 2 divided doses), Clonazepam (4-6 mg);
- opioid analgesic - Tramadol (50 mg once).
For pain of low and medium intensity, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - Diclofenac (100-150 mg in 2-3 reception), Ibuprofen (1.2 g), Ksefokam (8-16 mg in 2-3 doses), Meloxicam (7.5-15 mg), Ketorolac (10 mg up to 4 times a day) and other.
Stimulants of nerve impulse conduction
As drugs that improve the conduction of nerve impulses, those indicated in the table below are prescribed.
| Name | Main component | Dosage |
| Proserin | Neostigmine methyl sulfate | 15 mg 2 times a day |
| Galantamine | Galantamine | 10 mg 3 times a day |
| Ipigrix | Ipidacrine | 20 mg 2-4 times a day |
Homeopathy
Of the homeopathic remedies, the following are used:
- Traumagran;
- Coenzyme compositum;
- Discus compositum;
- Neuralgo-Reum-Inel;
- Traumeel S;
- Echinacea compositum.
Physiotherapy
Of the physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, electrophoresis with drugs is the most effective - most often an anesthetic Novocaine (5% solution) or a ganglion blocker Benzohexonium (2% solution, also for pain relief).
In case of vascular disorders, calcium and bromine ions are introduced (in the form of solutions). Electrophoresis is carried out every day for 1 procedure, lasting 15-20 minutes, the total duration of the course is 10 days.
In addition, the following treatment methods are used:
- application of an ultrahigh-frequency electric field (10 min. every other day, the course of treatment is 15 procedures);
- general exposure to ultraviolet light;
- baths with application of Naftalan oil on the extremities (15 procedures every other day);
- plasmapheresis to cleanse the blood from toxins;
- acupuncture;
- hyperbaric oxygenation (reducing the effects of oxidative stress).
Physiotherapy
With dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, the following complex of physiotherapy exercises is recommended:
- Initial position (and. - standing position, legs apart shoulder-width apart, hands on the belt. Get up and down on your toes.
- Alternate raising and lowering of the legs, bent at the knees.

- Circular rotational movements of the legs, bent at the knees, in one direction and the other.
- While inhaling, raise your arms up, while exhaling, bend forward, lower your hands.
- Circular movements of the pelvis.
- Squats (arms extended forward) on exhalation, return to and. NS. while inhaling.
- AND. NS. - lying on your back. Rotation of the feet, first in one direction, then in the other.
- Alternate bending of the knees, while the feet slide on the floor.
- Turn the legs bent at the knees to the right and left.
- AND. NS. - lying on your stomach. Raise on your hands, bending in the lower back.
- AND. NS. - standing, feet shoulder width apart. While inhaling, raise your hands up, hold your breath for 2-3 seconds, reaching up, while exhaling, lower your hands down.
- While inhaling, turn to the left, spreading your arms to the sides, then to the right.
- Bend back, putting one leg back, then the other.
All exercises are performed 4-6 times with a gradual increase in physical activity.
How does music heal?
Music therapy can be used to reduce the severity of sensory disorders. Listening to calm classical music, nature sounds and birdsong will help you relax and relax your muscles.
Surgical intervention
As surgical methods of therapy, neurolysis is used - an operative intervention that allows the nerve to be freed from the tissues compressing it. This helps to restore impaired nerve conduction and eliminate the symptoms of neuropathy.
Folk remedies
In folk medicine, there are the following methods for eliminating nervous disorders:
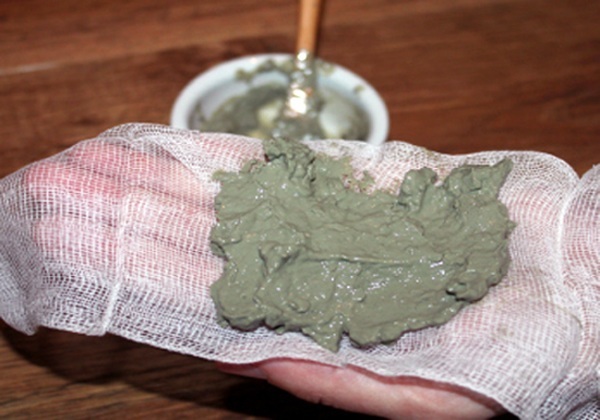
- Treatment with blue clay. It can be used internally, for which you need to roll balls out of wet clay and dry them in the sun. Clay has detoxifying properties, that is, it helps to remove harmful substances from the body, and the complex of minerals in its composition helps to restore the conduction of nerve signals. Clay is also used externally as a wet application on a sore spot. To do this, it is diluted with water to a mushy state, applied to the skin and wet gauze is applied on top. The procedure is carried out every day, until the composition is completely dry, after which it must be washed off. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.

- With neuropathy of the facial nerve, it is recommended to eat 2-3 ripe dates. 3 times a day.
- If the sciatic nerve is damaged, massage with turpentine or camphor oil is performed. They have a warming effect, which improves blood microcirculation and tissue nutrition in the area of the damaged nerve. Massage is done every day or every other day, 10 procedures in total.
- Sore spots can also be rubbed with rosemary tincture. For this, 2 tbsp. l. herbs, pour 100 ml of vodka and leave for 2 weeks in a dark place. Then strain and rub the skin in the damaged area every day.
Precautions for people with peripheral neuropathy. Recovery prognosis
Precautions for people with neuropathy include the following:
- compliance with the regime of work and rest (not to bring yourself to overwork);
- avoid infections, hypothermia;
- to treat the exacerbation of chronic diseases (sinusitis, pharyngitis, pyelonephritis, gastritis) in time to prevent a decrease in immunity;
- avoid contact with toxic substances (lead, varnishes, paints, solvents), do not abuse alcohol.
With timely treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. In advanced cases, neuropathy can lead to disability and death of the patient. The most common form of PNS lesion among patients of all age groups is peripheral polyneuropathy, that is, damage to several nerves.
This disorder requires different approaches to therapy, since its forms differ in etiology - genetic abnormalities, diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, toxin poisoning, infectious diseases and other factors. Treatment tactics are aimed primarily at eliminating the cause of neuropathy.
Video about neuropathy
About neuropathy of peripheral nerves:



