Knee-joint most often traumatized, both in childhood and in old age. In the first place among all the causes are arthrosis and bruises. Often, the pain continues for a long time. In this case, MRI will help diagnose the pathology. This type of diagnosis is safe and affordable.
Record content:
- 1 Indications for research
- 2 How is it determined
- 3 Preparation and analysis
- 4 Decoding the results
- 5 When to see a doctor
- 6 Possible complications
- 7 Knee MRI video
Indications for research
The knee, one of the large joints where the bones of the lower and upper legs meet. It moves like a hinge, allowing you to sit, walk or jump.
The knee is made up of three bones:
- femoral;
- tibia - bones in the front of the tibia;
- the kneecap is a thick, triangular bone that sits above the rest of the structures in the front of the knee.
The articular surfaces are covered with a cartilaginous layer, a slippery elastic material. Cartilage absorbs shock and allows bones to slide easily against each other as they move.
Between the tibia and the femur are two sickle-shaped
cartilage pads that reduce friction and distribute body weight across the joint:- lateral meniscus, located on the outside of the knee;
- medial meniscus, located on the inner side.
The bones are held together by the joint capsule. It consists of two separate layers - an outer layer of dense connective tissue and an inner membrane called the synovial membrane that secretes fluid to lubricate the joint.
The outer layer of the capsule is attached to the ends of the bones and is supported by ligaments and tendons:
- quadriceps tendon;
- medial collateral ligament, which gives stability to the inner part of the knee;
- lateral collateral ligament, which serves to stabilize the outer part of the knee;
- the anterior cruciate ligament located in the center of the knee to prevent excessive forward movement of the lower leg;
- the posterior cruciate ligament located in the center of the knee; it prevents the knee from moving too far back.
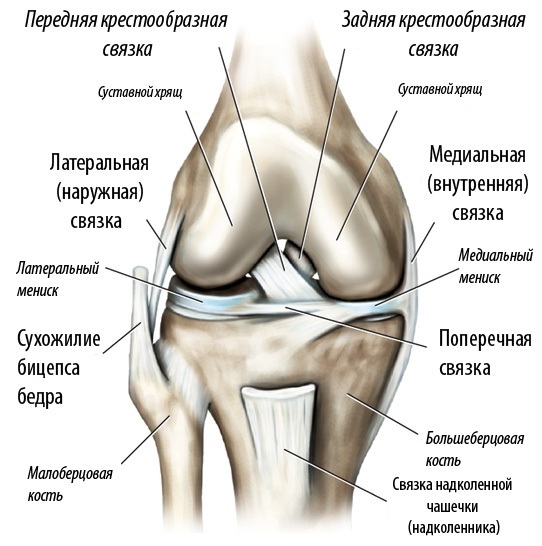
Two muscle groups support the knee:
- The hamstrings are the muscles in the back of the thigh that run from the hip to just below the knee and work to flex the knee.
- Quadriceps - The four muscles on the front of the thigh, running from the hip to the knee, help to straighten the knee from a bent position.
Knee pain is common and is associated with symptoms such as weakness, swelling, redness, and stiffness. Occasionally, strange noises, such as crackling or crunching sounds, occur in the knee area, which are caused by pain. This is more often caused by arthritis or when the joint is locked in an erect position. In case of problems with the knee joint, you should consult a doctor who will conduct an examination.
MRI of the knee joint (the price of the procedure depends on whether contrast is used) provides layered image of various structures within an organ: bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, muscles and blood vessels vessels. Detailed photos are taken from many angles.
An MRI scan is done to diagnose or evaluate:
- Meniscus: displaced tears, disc-shaped cysts, complications after surgery.
- Bone marrow abnormalities: avascular necrosis, bone marrow edema syndromes, stress fractures.
- Synovial disorders: symptomatic folds, synovitis, bursitis, popliteal cysts.
- Congenital and developing conditions: dysplasia.
- Disorders of muscles and tendons: sprains, partial or complete ruptures, tendopathy, tendonitis.
- Vascular conditions: aneurysm, stenosis, occlusion.
- Mechanical knee symptoms: pinching, crepitus, locking.
- Neoplasms of bones, joints, soft tissues.
- Infections of bones, joints, soft tissues.
- Ligament ruptures: cruciate, collateral, retinacular.
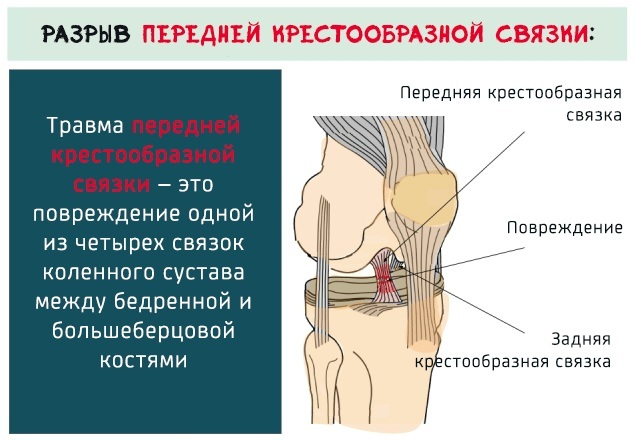
- Osteochondral and articular cartilage disorders.
- Osteochondritis.
- Degenerative chondrosis.
- Osteochondral fractures.
- Chondromalacia.
- Acute trauma.
- Fractures.
Doctors also order an MRI to determine if knee arthroscopy or other surgery is needed, and to monitor postoperative progress.
MRI of the knee joint (the price of the procedure is quite expensive) doctors do not always prescribe. With lighter pathologies and injuries, radiography is quite suitable for diagnosis.
How is it determined
MRI is a non-invasive test used to diagnose diseases. MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of the internal structures of the body.
Unlike X-ray and CT scans, MRI does not use radiation. Instead, radio waves rearrange the hydrogen atoms that naturally exist in the body. It does not cause any chemical changes in the tissues.
When hydrogen atoms return to their normal position, they emit different amounts of energy depending on the type of body tissue in which they are located. The scanner captures this energy and creates an image using this information.
In most scanners, a magnetic field is created by passing an electric current through coils of wire. Other coils are located in the machine, sometimes around the body part being examined. These coils send and receive radio waves, producing signals that are detectable by the machine. The electrical current does not come into contact with the patient.
The computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each showing a thin slice of the body. These images are viewed from different angles by a healthcare professional.
MRI is able to distinguish diseased tissue from normal tissue better than X-ray, CT and ultrasound.
The procedure is used to make a diagnosis, but the test results provide doctors with strong evidence to support the diagnosis. When faced with trauma, infection, inflammation, or joint disease, doctors often use MRI scans to not only determine the cause, but also plan treatment.
Preparation and analysis
MRI of the knee joint (the price is the same in many diagnostic centers) does not require special preliminary preparation. Food and drink recommendations before an MRI scan depend on specific examinations and institutions. Unless otherwise stated, food and medicine can be taken as usual.
Contrast injection is sometimes used. Previously, patients are asked whether they have asthma or an allergy to iodine contrast agent, drugs, food. Tomography is performed using gadolinium contrast. The drug can be used in patients with iodine-contrast allergy.
The doctor should be informed before the session about the state of health, recent surgery, kidney disease. Women in a state of pregnancy should be informed about this, as in their position, gadolinium contrast should not be received unless absolutely necessary.
If you have claustrophobia or mild anxiety from a confined space, you can ask your doctor to prescribe a sedative prior to testing.
Jewelry and other accessories should be left at home or removed prior to the MRI. Electronic and metal products interfere with the magnetic field and can cause burns.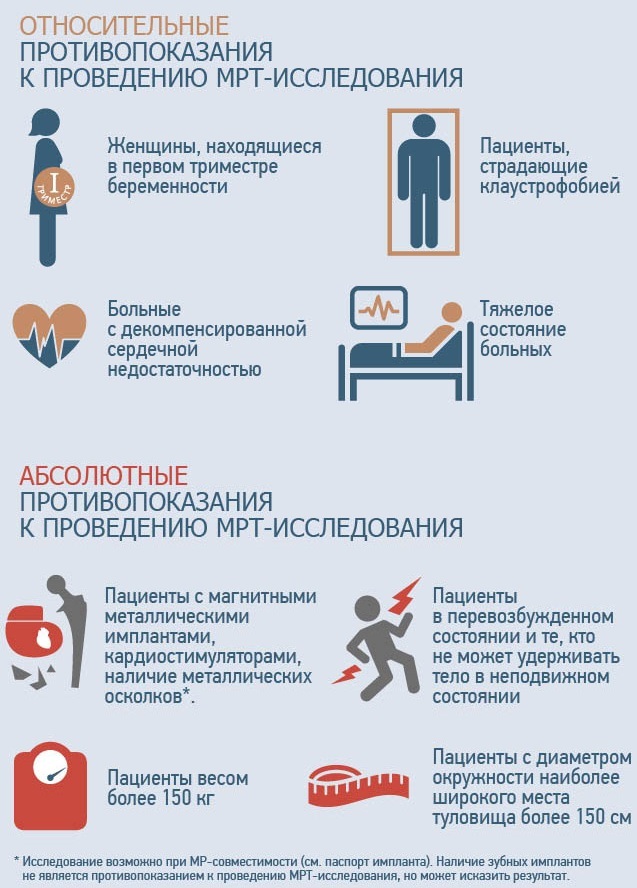
What should be left outside the office:
- hearing aids, jewelry, watches, credit cards (since they have a magnetic stripe) that can be damaged;
- hairpins, pins, metal zippers, keys and other metal objects that can affect the image;
- removable dental prostheses;
- handles with metal inserts, pocket knives, metal-rimmed glasses;
- piercing items;
- mobile phones, electronic watches.
Several types of metal implants pose a threat to scanning:
- ear implants made of multicomponent materials;
- clips, clamps, clamps used in the surgery of cerebral vascular aneurysms;
- metal coils placed inside blood vessels;
- old-fashioned cardiac defibrillators and pacemakers.
Metal objects used in orthopedics usually do not pose a risk during an MRI procedure. However, a newly installed artificial joint may require other diagnostic procedures.
The MRI machine is a cylinder with a sliding table on which the patient fits. The table delivers the examined person to the tunnel of the apparatus.
MRI procedure:
- The patient lies down on a movable examination table. It is fixed with belts and rollers so that the subject does not move.
- Small devices containing coils that send and receive RF pulses are placed around the knee to improve image quality.
- If contrast material is used, the nurse will insert an intravenous catheter into a vein in your arm. This is an indirect arthrography where the contrast is delivered into the bloodstream.
- Then the subject is placed in a magnetic MRI unit. The technologist at this time works at the computer outside the room.
- The whole procedure takes 45 minutes.
- If the contrast was not introduced initially, then after the first series of images, the substance is injected to the patient by direct or indirect arthrography. The need for this procedure is prescribed by the doctor after reviewing the images.
The cost of the procedure depends on which arthrography will be used. Direct arthrography by injecting contrast into the knee joint will help improve the accuracy of MRI. After it, bruises on the knee, discomfort, swelling, lasting several days, sometimes remain. An elevated temperature after the procedure indicates an infection.
Decoding the results
After the end of the session, the patient receives in his hands:
- Tomograms (pictures) printed on a special film in A4 format.
- Research results recorded on electronic media.
- Description of pathologies performed by the doctor who performed the MRI.
Classic MRI scans are taken in 3 angles: from the front (coronal view), from the side (sagittal view), or from above, looking down (axial view).
An MRI image is actually a very thin "slice" of a part of the body from any angle that can be viewed. Each new image is a "slice" 1-2 mm further or 2 mm less.
What MRI shows in inflammatory diseases:
- Arthritis. With the disease, inflammation of the synovial membrane of the joint occurs. Often the pain is accompanied by fever, difficulty in movement. On the screen, you can see an increase in the volume of the joint capsule due to excess fluid. You can also see osteophytes - bony growths on the surface of the tibia of the femur. They appear if arthritis has developed on the basis of osteoarthritis. All this will be written in the medical report.
- Bursitis. The inflammatory process occurs in the periarticular bags due to the accumulated fluid in them. The presence and location of edema depends on the location of the pain: in the patella or under it. An MRI scan shows a thickening of the subcutaneous fat layer under the calyx or above the knee.
- Lipoarthritis. The disorder is expressed by the accumulation of fat cells in the front of the knee. On an MRI of the anterior-lower joint, a thin layer of soft tissue and an accumulation of fat cells, Hoffa's body, can be seen. On MRI images of Hoffa's disease, fat bodies in the area of the pterygoid folds are clearly visible, their introduction into the joint space.
- Tendinitis. On the front of the knee is the patellar ligament, which becomes inflamed with tendinitis. The image shows thickened patellar ligaments, tendon ruptures, slight swelling and extensive hemorrhage.
-
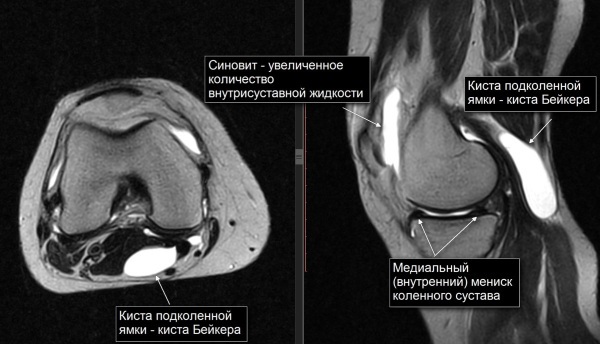
Baker's cyst. The disorder is characterized by the development of a neoplasm in the popliteal fossa. The formed cyst is a consequence of bursitis, It is filled with fluid and has elastic walls. Over time, it can disappear or increase, acquiring a solid structure. It is clearly visible on the screen as it has an intense white color. With an increase in size, it can limit the mobility of the joint, and over time it affects the mobility of the leg.
What changes in the knee are visible in degenerative pathologies:
- Knee arthrosis. The disorder occurs under the influence of impaired nutrition of the cartilage that covers the tibia and femur. The joint changes its shape, gait is disturbed, and mobility is reduced. The pictures clearly show the narrowed joint space, osteophytes can be seen on the surface of the bones.
- Osteochondropathy tibial tuberosity or Osgood-Schlatter disease. Affects children and young people between the ages of 10 and 29, especially those involved in sports. The disease progresses if the load on the bone tissue does not stop. When scanning, a pineal sprouting of the tibial tuberosity, swelling of the patella and surrounding tissues are seen.
- Chondromatosis. The disease is characterized by ossification of the synovial membrane of the joint and its degeneration into cartilaginous tissue. Instead of collagen, nodules are formed, which subsequently occupy the entire space of the joint capsule. The picture shows round formations of cartilaginous tissue that fill the articular cavity. They come in various sizes, from a few mm to 4–5 cm.
What can be seen on MRI images for various knee injuries:
- Ligament rupture. Violation of the integrity of the ligament, destroyed fibers are clearly visible on the monitor screen. The part of the ligament where the rupture occurred looks uneven, with twists, and has no continuation. And also edema and hemorrhage are visible.
- Hemarthrosis. Damage to blood vessels as a result of various injuries, damage to the meniscus, general diseases leads to the accumulation of blood in the knee cavity. Hemorrhage occurs in the joint cavity from the damaged vessel, fluid accumulates in the knee cavity, causing pain, difficulty walking. If the cause of hemarthrosis lies in trauma, then a bone fracture and soft tissue rupture will be visible on the screen. Joint capsules filled with blood are also clearly visible.
-
Rupture of the meniscus. The picture shows the detachment of a fragment of the cartilaginous plate, its displacement.
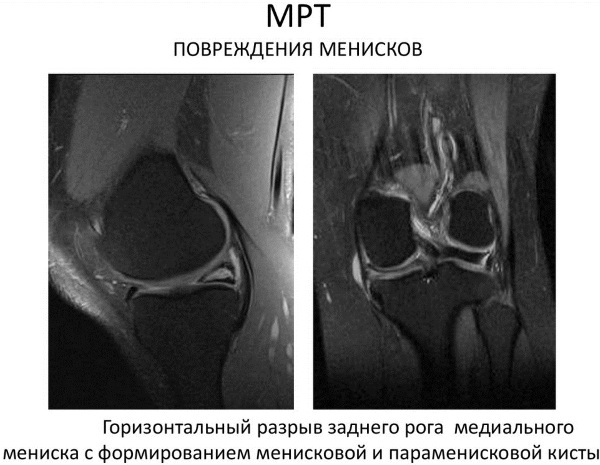
Meniscus tear on MRI of the knee - Tumors of various etiologies. In the knee area, benign, malignant tumors and tumor metastases develop from neoplasms that have appeared in other parts of the body. MRI is most effective in the early stages of the onset of tumors. The images show deformed bones, edema with an inhomogeneous structure. This is typical for osteosarcoma. In chondrosarcoma, the tumor has a lobular appearance with dense inclusions and septa.
To correctly interpret the MRI results, the doctor reading the results must be highly qualified. Even in countries with well-developed medicine, more than 25% of primary diagnoses are wrong.
This does not mean that the devices are mistaken, incorrect results are voiced by doctors who are not immune from mistakes. Often, patients undergo a high-quality examination, but the pictures are not described entirely correctly.
Typical mistakes when decoding an MRI:
- The normal MRI picture is confused with pathology, and on this basis, a diagnosis was made of a disease that does not exist.
- Pathological changes in the images were missed, therefore, the diagnosis was not made, and the developing disease was missed.
- On the basis of the images, the stage of the disease is incorrectly interpreted, this often applies to the stages of cancer development.
In order to avoid such errors, there is a service for setting a Second Opinion on CT, MRI. The resulting pictures of the study are sent to specialized centers for their reading by highly qualified specialists.
When to see a doctor
The need for diagnostics using MRI is determined by an orthopedist, oncologist, traumatologist. In most patients, primary MRI can be used to refute or confirm the diagnosis. The indications for the diagnostic procedure are visible changes in the joint, damage accompanied by pain, swelling, difficulty walking.
- In case of a knee injury, diagnostics will help determine the place and extent of damage, meniscus rupture, ligaments. The diagnostic method is suitable in case of fractures, severe bruises, accompanied by bleeding.

- Diagnosis is carried out with synovitis, since nonspecific symptoms of the disease may appear. The doctor, studying the MRI readings, observes changes in the joint cavity.
- If a meniscus rupture is suspected, an MRI scan should be done.
- The resulting effusion in arthrosis and arthritis should be investigated using diagnostics.
- Edema and hemorrhage often indicate a cruciate ligament rupture. MRI should be done to differentiate the injury from congenital processes in the knee.
Possible complications
MRI of the knee joint does not cause any unpleasant consequences for the patient's health. The study allows you to timely make the correct diagnosis, which allows you to maintain health, prevent the patient's disability.
MRI of the knee joint (the price justifies the effectiveness) never becomes the cause of complications, on the contrary, it helps to detect hidden diseases. It is they, if not detected on time, that can cause serious complications over time, up to and including impaired mobility.
MRI of the knee is a much safer method than computed tomography or radiography associated with radiation. The price of the patient's health and well-being directly depends on the correct diagnosis.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Knee MRI video
What does an MRI of the knee show and why:



