A disease such as Osgood-Schlatter is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system, in which there is change in the knee end of the tibia. Although the symptoms of this disease are quite specific, X-rays are needed to confirm the diagnosis. The basis of the pathological process is aseptic tuberosity necrosis.
Record content:
- 1 What is Schlatter's disease?
- 2 Causes and risk factors
- 3 Classification
- 4 Symptoms and degrees
-
5 Analyzes and diagnostics
- 5.1 X-ray
- 5.2 Magnetic resonance imaging
- 5.3 Ultrasound procedure
- 5.4 Differential diagnosis
-
6 How to treat a disease
- 6.1 Conservative treatment
- 6.2 Procedures and operations
- 6.3 Surgery
- 7 Treatment with folk remedies
- 8 Consequences
- 9 Osgood-Schlatter disease video
What is Schlatter's disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease (BOSH, or in medical terminology aseptic osteonecrosis of the AN, osteochondropathy of ACP) is a structural lesion of the tibial tuberosity in the knee. This disorder most often develops in boys aged 6-17 years.
At high risk are adolescents who are involved in sports with a high load on legs - running, jumping, gymnastics (football, volleyball, athletics, hockey, basketball, figure skating, ballet and others).
Since in recent years the number of girls attending sports and educational institutions has increased, there is an increase in the prevalence of pathology among them. The defeat can be both unilateral (on one leg) and bilateral. According to statistics, this deviation occurs in 20% of adolescents involved in sports, and only in 5% of children in other groups.
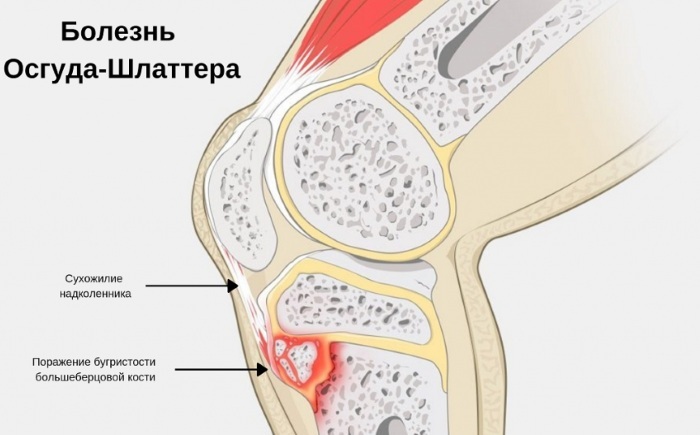
Osgood-Schlatter disease, in which X-ray is a necessary diagnostic study, is characterized by involvement in the pathological process, not only the tuberosity located under the knee, but also the mucous membrane of the bag, the patellar ligament. In many patients, the first symptoms appear spontaneously, sometimes preceded by trauma.
Causes and risk factors
The main reason for the appearance of this disorder is the immaturity of the musculoskeletal system. Tibial tuberosity is formed against the background of rapid growth in adolescents, under the influence of intense and frequent physical activity.
The mechanism of development of the pathological process is as follows:
- As a result of the load, an imbalance occurs between the strength of muscle contraction and the strength of the ossifying tissue.
- Overloads cause microtrauma, leading to rupture of the fibers of the ligaments.
- Disturbed blood supply in the area of the upper articulation of the tibia. The ends of the long bones have a weak inflow of arterial and outflow of venous blood, since most of them are covered with cartilage.
- Aseptic inflammation and necrosis develop.
Depending on how active the compensatory mechanisms aimed at restoring integrity are, changes in the bone are reversible or irreversible.
The following are also risk factors:
- fractures, dislocations, minor, sometimes imperceptible traumatic effects;
- congenital anatomical abnormalities;
- infectious purulent-necrotic processes;
- taking hormonal drugs;
- metabolic disorders;
- connective tissue diseases;
- tumor diseases of the hematopoietic and / or lymphoid tissue;
- radiation exposure.
Classification
Osgood-Schlatter disease, in which X-rays are performed in several projections, depending on the degree of development of dystrophic processes, classified into 5 stages:
- Violation of blood circulation in one of the sections of the end part of the tibia.
- Development of a secondary impression (or depressed) fracture. It can occur even with a small load due to tissue necrosis.
- Fragmentation of cancellous bone tissue and dissolution of individual elements.
- Overgrowth of connective tissue, partial recovery.
- The consolidation of debris as a result of the formation of new bone tissue, with adequate treatment, is a complete recovery.
By the nature of the course of the disease, the following varieties are also distinguished:
- patella tendonitis (inflammation and degeneration of the tendon tissue);
- infrapatellar bursitis (inflammation and destruction of the tissues of the popliteal articular bag);
- apophysitis (inflammation of the bone process);
- separation of the tibial tuberosity.
Symptoms and degrees
The signs of the disease appear gradually, most often according to the following scheme:
- There is a dense swelling with limited contours ("bump"), dense and elastic consistency. When you press on it, pain is felt, from slight to severe. The general condition of the patient does not deteriorate, the body temperature remains normal. Many patients notice pain when kneeling down, while it can radiate to the hip. On X-ray examination, the damaged area of bone tissue is still no different from normal. This stage can last for several months.
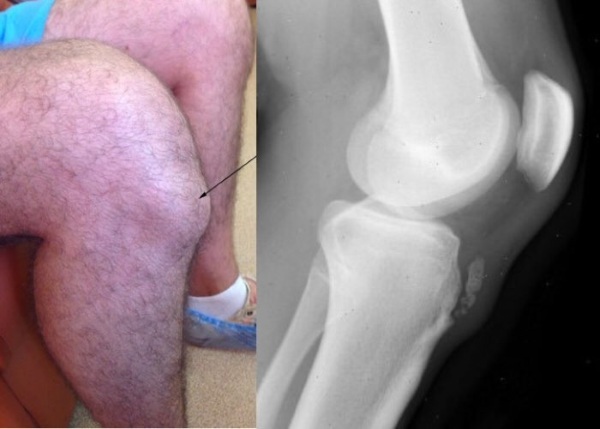
- At first, soreness in the knee occurs when walking, flexion-extension of the leg, and at rest they pass. Gradually, as the process progresses, they appear with little physical exertion (in some patients and in the absence of movement). The swelling of the tissues increases. When the knee is bent, a pronounced deformation can be seen. The maximum displacement of the limb during movement does not decrease.
- Subsequently, the characteristic sign of "floating patella" also appears, in which, on a straightened leg, the patella moves freely upward when pressed on it. The tuberosity grows due to the cartilage tissue. The second limb may be affected. The x-ray shows ossification points in the form of processes, the number of which ranges from 1 to 4.
- Pain syndrome can last for months, periodically arising and disappearing. Gradually resorption of the formed bone processes occurs, their fusion or increase. Usually this condition persists for no more than a year. By the age of 14-15, ossification of tuberosity is observed in children, separate "points" merge into one proboscis-like process. In a benign course, the tuberosity structure is restored.
Analyzes and diagnostics
The following methods are used to diagnose this pathology:
- X-ray examination;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Ultrasound.
In order to carry out differential diagnostics, the doctor may also prescribe the delivery of blood tests (clinical and biochemical) and urine tests, as well as other types of examinations. At an early stage, the disease is difficult to diagnose.
X-ray
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
X-ray is the basis for diagnosing the disease and allows you to identify the following types of changes:
- Sequest-like shadows.
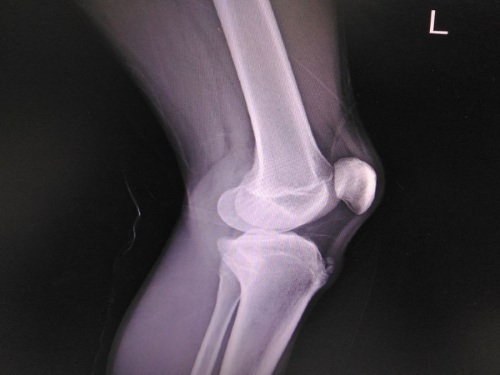 Sequesters are necrotic fragments of bone that are rejected from living tissue. They create oval, intensely shaded areas in the image, which are surrounded on all sides by bands of enlightenment. The severity of the shadow depends on the degree of compression of the bone tissue during the destruction of its internal partitions as a result of necrosis.
Sequesters are necrotic fragments of bone that are rejected from living tissue. They create oval, intensely shaded areas in the image, which are surrounded on all sides by bands of enlightenment. The severity of the shadow depends on the degree of compression of the bone tissue during the destruction of its internal partitions as a result of necrosis. - An increase in the volume of the joint capsule as a result of non-infectious inflammation.
- Deformation of the proboscis tubercle, its pushing forward, an increase in the thickness of the cartilage and ligament.
- Fragmentation of the bone, the presence of small fragments in the amount of 1 to 3.
- Erosion of the contour of the head of the tubular bone.
- Curvature or fracture of the process, the line of fracture of the tuberosity at its base.
However, in some patients, the x-ray picture may be normal. The above signs appear most often at the stage of severe pain syndrome.
In these cases, an analysis should be made of the ratio of the length of the patella to the length of the ligament (from the apex of the patella to the tuberosity), the size of the angle between the femur and the patella. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical findings.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI allows you to more clearly determine the degree and localization of the lesion, as well as to carry out differential diagnosis with other inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
At the same time, at the early stages of this pathology, the following signs are revealed:
- a decrease in the signal intensity in the T1-WI mode (used to visualize adipose tissue and hemorrhages) due to adipose reconstruction of the bone marrow;
- the presence of effusion (accumulation of exudate as a result of inflammation);
- an increase in the thickness of the cartilage tuberosity.
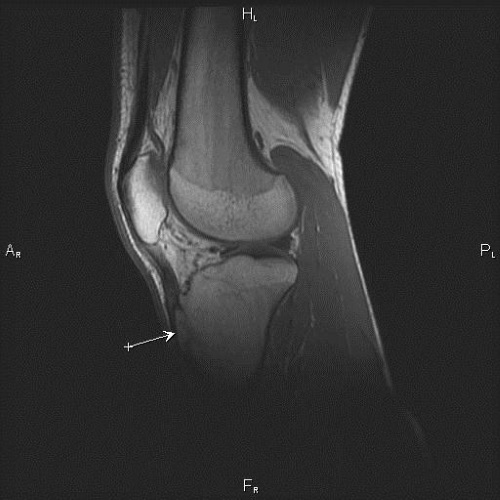
At later stages, changes are found such as:
- high intensity in the T2-WI mode (for visualization of tissues with a high water content) in the area of the affected bone;
- low intensity in T1-VI mode;
- fragmentation (fragmentation into parts);
- thickening of the cartilage tissue.
Ultrasound procedure
During ultrasound, the following types of changes can be detected:
- lifting the endplate of the knee joint;
- thickening of the patella ligament by 1-2 mm;
- bone fragments from 2 mm to 2 cm with an acoustic shadow that do not change their position when the leg is bent at the knee;
- an increase in the size and internal volume of the articular bag;
- unevenness and indistinctness of the contours of the bone;
- damage to the tissues of the joint capsule and nearby soft tissues;
- separation of the tuberosity in the form of a light formation in the upper part of the tibial head.
Differential diagnosis
Osgood-Schlatter disease, x-ray for which is described above, requires differential diagnosis with diseases such as:
- Osteomatosis knee joint, which is a benign tumor. This pathology is characterized by an increasing limitation of mobility in the joint. Irregular spots appear on X-rays.
- Ossifying myositis, developing after injury. It is an inflammatory process in the articular ligaments, in which pathological ossification occurs in the injured and surrounding tissues. At the same time, patients also develop pain syndrome and there is a limitation of mobility. Radiographically, this manifests itself in the form of calcification.
- Chondrosarcoma - a malignant tumor in the knee joint. In this case, pain is present not only during movement, but also at rest. On X-ray images, destructive foci of irregular shape are revealed.
- Chronic osteomyelitis - a purulent-necrotic process that develops in the bone and bone marrow. Inflammation of the periosteum occurs, the color of the skin on the knee changes. The pain syndrome is also permanent.
-
Osteoid osteoma - a benign, slowly developing tumor, in rare cases, arising in the bones of the knee joint. This disease is characterized by constant pain that worsens at night. The tumor is difficult to detect on radiographs. Diagnosis is carried out using scintigraphy and CT.
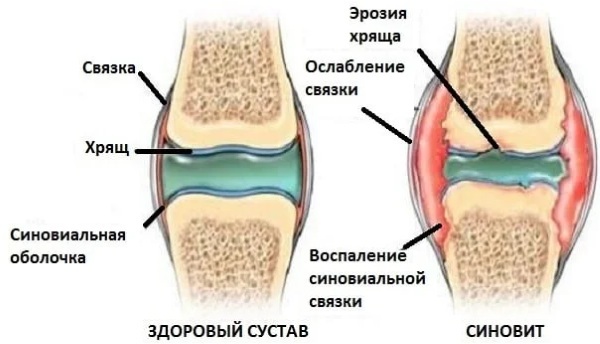
Knee synovitis - Synovitis, or inflammation of the synovium. The diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy.
How to treat a disease
The basis of non-drug treatment is the maximum possible rest of the injured leg, limitation of physical activity. This requirement must be respected after the treatment.
Avoid running, jumping, squatting and other types of stress on the knee joint. In some cases, the use of a fixation bandage, bandaging or wearing an elastic knee pad is required.
Also, during the period of treatment, it is necessary to limit the use of salt in food. After the acute process subsides, physiotherapy procedures are prescribed. Surgical intervention is carried out only in exceptional cases.
Conservative treatment
Medicines used for this disease and treatment regimens are shown in the table below.
| Drug name | Dosage, mg per day; peculiarities | Duration of treatment, days |
Systemic anti-inflammatory drugs | ||
| Meloxicam | 7.5-15 mg once (in the morning), after meals | 15-20 (in some cases or more) |
| Naproxen | 0.5-0.55 g orally 2 times, regardless of food | |
| Preparations for the protection of the gastrointestinal mucosa | ||
| Nexium | 20-40 mg at night; prescribed for the time of taking anti-inflammatory drugs | 15-20 |
| Local anti-inflammatory drugs (ointments, gels) | ||
| Dolobene | In the morning and in the evening | 2-3 months |
| Ketonal | ||
| Dolgit | ||
| Muscle relaxants | ||
| Sirdalud | 6 mg 2 times (with or without food), for withdrawal muscle tension, contributing to the development of the disease |
20 |
| 6 mg once | 10 | |
| 2 times per week | 14 (total duration 44 days) | |
| Chondroprotectors | ||
| Artra | 1 tablet (capsule) 2 times | 21 |
| Teraflex | ||
| Don | 1 tablet once a day | 6 months |
| Structum | ||
| Fermatron (synovial fluid prosthesis) | 2 ml each (intra-articular injection) | 2-3 injections every week |
Diuretics (prescribed for severe swelling)
| ||
| Furosemide | 40-80 mg 1 time | 2 days in a row every 1-2 weeks |
| Torasemid | 5-10 mg once |
Procedures and operations
Osgood-Schlatter disease, in which an X-ray creates an acceptable radiation exposure on the adolescent's body, is well treated with physiotherapy.
They improve the following processes:
- blood and lymph circulation in the affected joint;
- tissue nutrition;
- resorption of necrotic areas of bone tissue;
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- restoration of damaged tissues.
With this disease, the following methods of therapy are used:
- electrophoresis with calcium preparations (calcium chloride) in order to consolidate bone fragments;
- magnetotherapy - exposure to a magnetic field (improving tissue nutrition);
- massage and remedial gymnastics;
- heat therapy with heated paraffin or ozokerite (reduction of edema, improvement of blood circulation);
- shock wave therapy - exposure to low frequency sound waves (normalization of blood flow, elimination of calcifications);
- laser therapy (similar to heat therapy).
It is also possible to use homeopathic methods of treatment - the introduction of Traumeel by the method of biopuncture, in the form of injections. All these procedures are prescribed in the subacute period of the disease.
Surgery
If during the year drug treatment does not work, then a surgical operation is indicated. Most often, tuberosity tunneling is carried out - the formation of channels using a Kirchner spoke.
Its diameter is 2 mm. The puncture is made through the skin 1 time, in 4-5 directions, to a depth of 0.5-1.5 cm. This allows you to reduce intraosseous pressure, improve microcirculation and recovery processes. After surgery, a splint is applied to the limb for 3-4 weeks.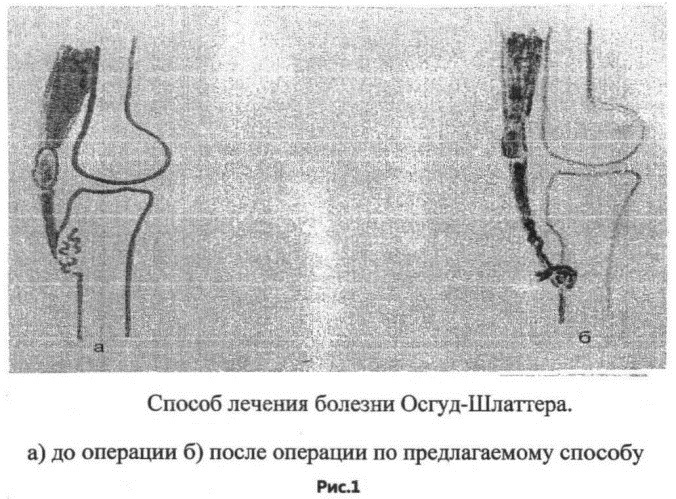
There is also a technology of laser osteoperforation, when bone tunneling is performed using a diode laser. In this case, discharge from the hospital is possible already on the second day, and the pain syndrome in the postoperative period is less pronounced. However, the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
For patients with significant fragmentation (fragmentation) of the tuberosity, fixation with bone grafts taken from the canals of the tibial tuberosity is recommended.
If the tuberosity is detached, then osteosynthesis is performed - restoration of the position of the bone fragment using a small screw Ø3.5 mm, 3 cm long. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, through a 2 cm incision. The channel for the screw is formed using a drill.
To ensure immobility after surgery, a plaster splint is applied for 1 week. The screw is subsequently removed if positive x-ray results are obtained.
In the postoperative period, treatment with chondroprotectors, analgesics, calcium preparations and physiotherapy is indicated, which are prescribed for 4-5 days. Typically, most adolescents return to normal physical activity after 1 to 2 months.
Treatment with folk remedies
For the treatment of inflammatory pathologies of the knee joint in traditional medicine, the following methods are used:
- Wash, peel, and squeeze 0.5 kg of fresh carrots in a juicer. Add 50 ml of cream and stir. This composition must be drunk on an empty stomach, before breakfast, for several weeks.

- Mash 50 g of goat cheese and mix with the same amount of chopped fresh spinach. This salad is consumed daily, for 20 days, with a break for 10 days. Treatment should be long-term.
- 1 tbsp. l. table salt mix with 1 tbsp. l. liquid flower honey. Then add 1 tbsp to the mixture. l. mustard in the form of a paste and 1 tbsp. l. warm water, stir. The resulting ointment is stored in the refrigerator for no more than 5 days. The ointment should be rubbed into the sore knee in 3 doses. It is best to apply it at night. Then the joint must be wrapped with cling film, warm cloth. The course of treatment is 5 days.
- 5 buttercups with leaves, without roots, pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for half an hour. After that, pour the infusion into a bowl and add more warm water. The foot bath must be done for 15-20 minutes, you can apply gauze moistened with broth to the sore joint.
Consequences
The disease in most cases is benign, but pathological processes, which can have an undulating course, last up to 2 years. By the age of 17-19, when bone growth ends, recovery often occurs. The bony protrusion remains, but the functions of the knee joint are not impaired. However, this requires limiting physical activity during the entire period of the disease.
Otherwise, dislocation may occur due to improper formation of tuberosity, or hyperextension of the knee joint. As a result, walking stability is reduced.
Other possible complications are:
- osteoarthritis, in which there is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of all elements of the joint;
- upward displacement of the kneecap;
- deformity of the knee joint.
Therefore, in all cases, conservative treatment and supervision by a doctor are required. Late diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease can lead to osteoarthritis of the knee joint. X-ray reveals a shift in the epiphysis of the tibia, bone growths, fragmentation and other changes.
All patients require long-term treatment, and in some cases, surgery. With a favorable course of the disease, relief of symptoms occurs within several months.
Osgood-Schlatter disease video
About Osgood-Schlatter disease: