A complex of interrelated deformities in the periarticular (muscle and tendon-muscle) tissues of the shoulder joint are called impingement syndrome. There is a subacromial space between the head of the shoulder and the top of the scapula bone. Due to such violations, it is compressed, which causes pain and stiffness of the shoulder.
Record content:
-
1 What is shoulder impingement syndrome?
- 1.1 Primary subacromial impingement
- 1.2 Secondary impingement
- 2 The prevalence of the disease
- 3 Causes, risk factors
- 4 Degrees and symptoms
-
5 Medical diagnostics
- 5.1 Neer test
- 5.2 Ultrasound
- 5.3 X-ray
- 5.4 MRI
-
6 Treatment of 1-2-3 degrees
- 6.1 Conservative therapy
- 6.2 Subacromial decompression
- 6.3 Arthroscopic subacromial decompression
- 6.4 Physiotherapy
- 7 Rehabilitation measures
- 8 Folk methods
- 9 Possible complications of the disease, prognosis
- 10 Video about impingement syndrome
What is shoulder impingement syndrome?
Subacromial impingement syndrome of the shoulder joint is characterized by complex dysfunction of the periarticular apparatus (head of the shoulder, acromion, joint capsule) and entrapment of the rotator cuff, eventually leading to degeneration fabrics.
As a result of violations during shoulder movements, an incorrect collision of these elements occurs, which causes the tendons to be compressed, and the muscles are regularly injured. With any movement of the shoulder, pain appears, movements become difficult.
Soreness usually begins on the outside of the injured shoulder. Patients notice an increase in pain at night, which negatively affects their night rest and general well-being during the day, often leading to irritability.
In medical practice, two types of syndrome are distinguished:
- primary;
- secondary.
Primary subacromial impingement
Primary impingement syndrome appears against the background of irritation of the periosteal muscle tissue.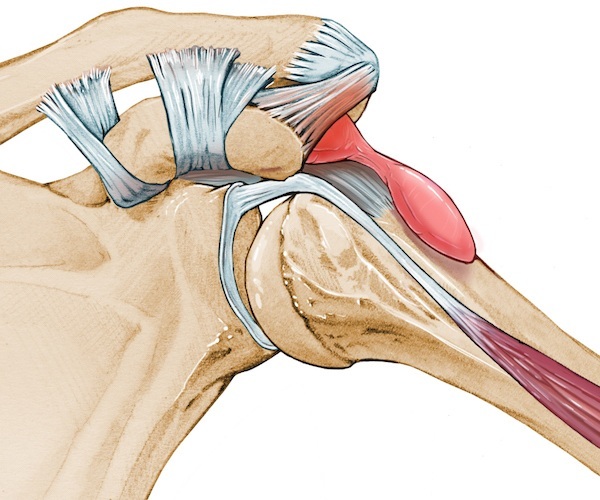
The appearance of a pathological process is facilitated by mechanical deformation of such devices of the shoulder joint:
- coracoid process;
- large tubercle of the humeral hand;
- bone growth located in the lower lobe of the acromioclavicular joint;
- rotator cuff tendons.
Also, the appearance of primary impingement is facilitated by genetic disorders of the shape of the acromial process.
Secondary impingement
The appearance of secondary impingement is facilitated by the narrowing of the subacromial space that appears as a result of such processes:
- destruction and rupture of ligaments in the area of the acromioclavicular joint;
- weakness of the ligamentous apparatus of genetic origin;
- destruction of the tendons of the biceps muscle or rotator cuff;
- weakness of the muscular system, sometimes with signs of paralysis;
- bursitis of a chronic form, in which there is a thickening of the rotator cuff or bursa;
- trauma to the large tubercle, in which the humerus is displaced.
Based on these factors, it can be noted that secondary impingement is an acquired disorder, appearing in chronic diseases, high physical exertion, inflammation of the joint and periarticular fabrics.
The prevalence of the disease
Subacromial shoulder impingement syndrome is one of the most common problems. Pathological disorders are most often diagnosed in persons over the age of 40. These are, as a rule, athletes, people employed in production with difficult working conditions, people who have survived accidents and have received previous severe shoulder injuries.
Soreness is felt in patients for no apparent reason when they try to raise their arm above their head, performing any manipulations over their heads or lying on the "affected" side of the body.
Previously, a similar condition was called "shoulder-scapular periarthritis", which Duplay patented in 1872. This term is often used by doctors today. However, in 1972, the American surgeon Neer C.S. proposed a new version of the name of the suffering in question (as the syndrome was previously called) - "shoulder impingement syndrome."
Causes, risk factors
Narrowing of the subacromial space is fundamental in the development of the syndrome. It is located between the head of the shoulder and the top of the scapula.
In a small cavity located above the joint, the following elements are placed:
- subacromial periarticular bursa (a kind of protective barrier between the protruding bone of the scapula and the tendons);
- rotator cuff tendons.
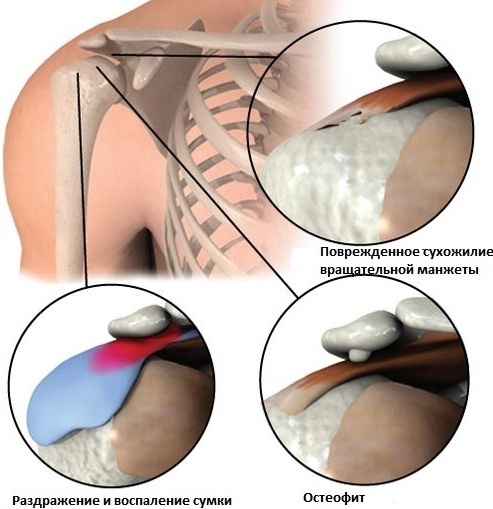
Due to the insignificant subacromial space, with its even greater narrowing, a person simply cannot raise his hand above his head, while such movements are accompanied by pain.
When the upper limb is thrown back, the head of the humerus comes into contact with the acromion (protruding bone scapula), the tendons are compressed, the tissue is injured, inflammation appears at the site of injury joint. If a person rarely performs such manipulations, the places of microdamage have time to heal.
However, with frequent and high loads on the joint, regular trauma leads to an increase in the inflammatory process and such problems:
- inflammation begins to develop actively in the lesions, which leads to the formation of fibrous scars;
- the number of microdamages increases, as a result, the tendons weaken and become thinner;
- due to regular injury and damage, the tendons that form the rotator cuff rupture.
A pathological degenerative process can spread to nearby tissues:
- bursitis (subacromial shoulder bag);
- the surface of the joint, where bone growths (osteophytes) are subsequently formed.
The following factors contribute to the narrowing of space:
- senile changes;
- pathological disorders (bursitis, proliferation of the coracoacromial ligamentous apparatus);
- anatomical features of the structure of the protruding process of the scapula.
Regardless of the cause of the development of the painful process, suffering leads to persistent degenerative changes that affect all structures of the shoulder joint, as a result of which mobility is impaired shoulder.
The reasons for the appearance of the syndrome and the factors contributing to their development:
| Cause | Influencing factor |
| Insufficient blood flow to the shoulder joint | Calcification (the formation of calculi from calcium crystals), which develops in the tendons of the shoulder joint. |
| Inflammatory process in the periarticular tissues and in the joint itself (periarthritis, bursitis) | Pathological disorders in the spine (displacement of discs, osteochondrosis, spondylosis) |
| Weakness of muscle tissue and ligamentous apparatus of an acquired or congenital nature | This is facilitated by diagnoses: hepatitis and cholecystitis |
| Injury to the skeleton and soft tissues of the shoulder | Neuropathy (damage to the nerve cells of the shoulder joint) |
| Congenital anomalies of the structure of the shoulder joint and periarticular elements | Hypothermia |
| Acquired form of rheumatism | Inflammation of the capsule of the shoulder joint (capsulitis) |
| Overgrowth of bursa and ligaments | Regular mechanical stress on the shoulder joint |
Degrees and symptoms
Subacromial shoulder impingement syndrome manifests itself clinically depending on the stage of the problem. American surgeon Neer C.S. in 1972, taking into account the signs and severity of the problem under consideration, he proposed to divide the pathology into stages, there are three of them in total (1st, 2nd, 3rd).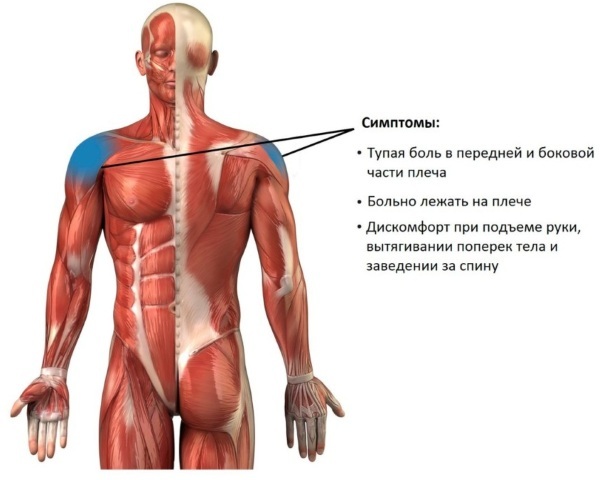
| Stage | Clinical picture | Risk group | Process reversibility | Treatment type |
| 1st stage | In the shoulder joint, swelling is noted, accompanied by hemorrhages. Soreness appears in the articular region after performing any physical activity. | Persons from 20 to 40 years old | Reversible | Conservative |
| 2nd stage | Fibrosis and tendonitis. Secondary inflammation caused by regular mechanical trauma. Causes irreversible thickening of the bursa and rotator cuff. This condition is almost always treated with a surgical method. | Persons from 30 to 50 years old | Irreversible | Surgical (acromioplasty) |
| 3rd stage | The stage is characterized by bone spur formation, tendon rupture and rotator cuff rupture. Degenerative disorders inevitably lead to instability of the shoulder joint. The head in the glenoid cavity is decentralized during hand movement, and collision occurs in different areas of the articular capsule and paracapsular tissues. The process is accompanied by inflammation of the joint and degenerative changes in the structures of the shoulder. | Persons between the ages of 30 and 70. | Irreversible | Surgical |
Subacromial impingement syndrome has specific signs, according to which the correct diagnosis is made in 90% of cases. The main manifestation of pathology is pain in the shoulder joint. Sometimes it appears at night during a rest period, however, more often it occurs with hand movements (lifting up, rotating movements, putting on outerwear, sharp jerks with the shoulder, etc.).
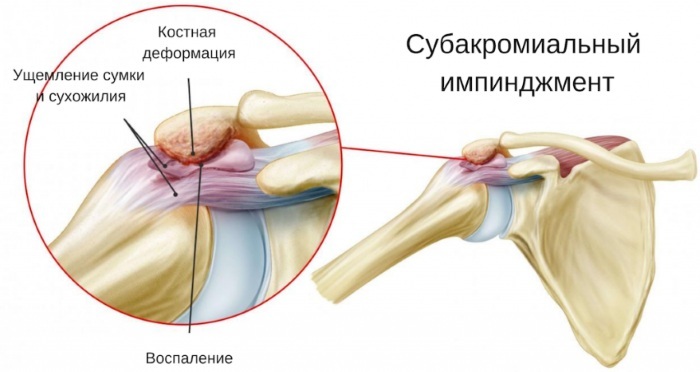
At the first stage, the patient feels mild pain without visible discomfort. But over time, the pain increases, and the range of motion of the shoulder decreases. Often, patients begin to develop subacromial bursitis (inflammation in the bursa).
In medical practice, special tests have been developed to diagnose pathology.
| Test | Technique | Features of the appearance of pain |
| Hawkins | The patient performs anterior shoulder flexion and slightly rotates the affected limb inward. | Pain appears at the time of narrowing of the subacromial space between the coracoacromial ligamentous apparatus and the large tubercle of the shoulder. |
| Painful arch | The patient raises his outstretched arm. Pain appears between 60 ° -120 °. | The pain occurs due to the collision of the head of the shoulder and structures located above the humeral-scapular joint. |
| Nir's sign | The test is performed with assistance. The doctor fixes the scapula and at the same time raises the patient's hand upward, performing rotational movements inward. | The pain appears when the large tubercle of the shoulder and the "roof" of the joint come into contact. |
| Alarm test | The doctor gently takes the patient's hand outward, while performing light rotational movements. | The onset of pain is associated with a rupture or tear of the articular lip, located inside the shoulder joint. |
If during the tests it was found that the appearance of pain is associated with raising the upper limb upwards by 160 ° -180 °, this is damage to the clavicular-acromial joint, respectively, this problem is not associated with shoulder impingement syndrome It has.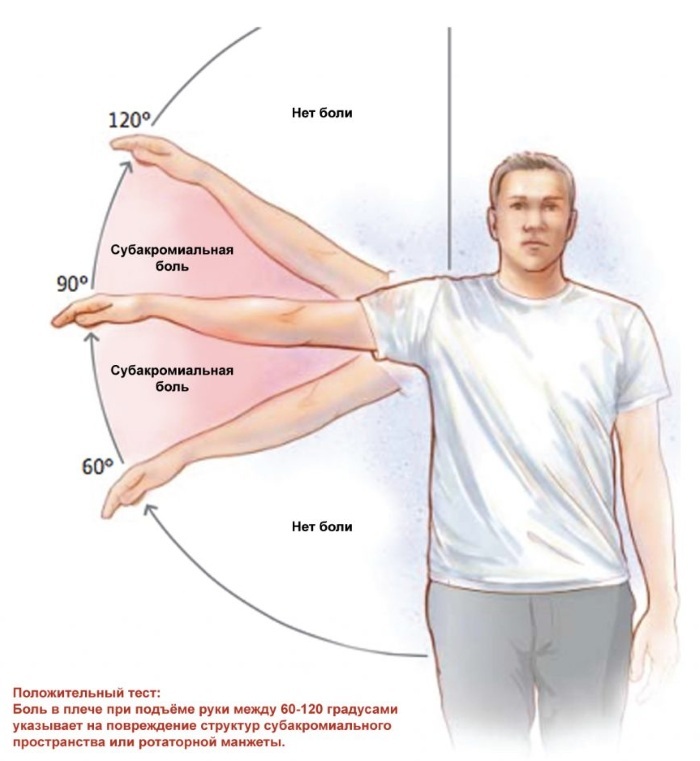
With impingement syndrome in a patient, along with pain at the moment movements of the affected limb, the following signs are also noted:
- it is rather difficult to get things out of the back pocket, while the patient feels pain;
- women find it difficult to move their hands back on their own to button the bra;
- joint stiffness after a night's rest, sometimes a similar symptom is noted during the day;
- the appearance of a crunch when lowering the hand down;
- atrophy of the infraspinatus, supraspinatus and deltoid muscles, which occurs gradually;
- a feeling of discomfort when palpating the affected area of the hand.
Medical diagnostics
The patient is examined by a traumatologist. First of all, the doctor examines the patient and conducts special tests with him to determine the cause of the pain in the shoulder joint.
Already on the basis of the signs, it is possible to make a final diagnosis with 90% certainty. But in any situation, additional instrumental diagnostics is required, which confirms the diagnosis and provides information about the degree of degenerative changes and the localization of the inflammation focus.
Neer test
The test is to determine whether the pain disappears when performing movements according to the Nira Sign after the patient is injected with an anesthetic (Lidocaine or Novocaine). The disappearance of the pain syndrome indicates the development of the impingement syndrome.
Ultrasound
The study provides information about the changes occurring in soft tissues associated with the development of impingement syndrome. An ultrasound will show a thickening of the walls of the joint bag (which is typical for bursitis) and the accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the bag. Often, along with this pathological process, degenerative changes in the tendons are revealed in patients.
On examination, they are shown by thickening and increased echogenicity.
X-ray
X-rays are an important diagnostic procedure to see changes in the bone structure of the shoulder joint. The method makes it possible to assess the condition of the coracoacromial ligament, the shoulder-shoulder joint and the acromioclavicular joint.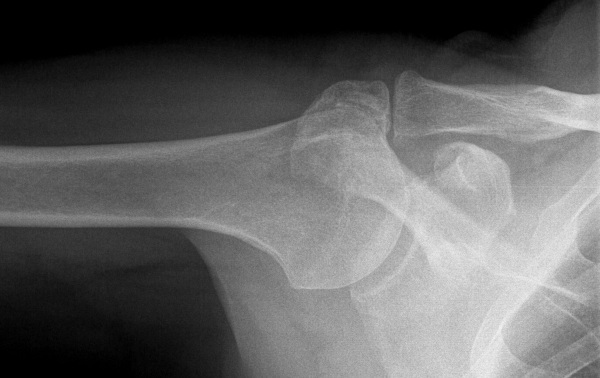
The diagnosis of impingement is confirmed by:
- decentration of the shoulder head;
- changes in the structure of the greater tubercle;
- ossification of the ligamentous apparatus;
- visual signs of arthrosis of the shoulder joint.
Indicators that are taken into account when radiography:
- acromion shape;
- the critical angle of the shoulder (the slope of the joint and the degree of its coverage by the acromial process);
- acromoumeral index (distance between the acromial cavity and the lateral surface of the acromion).
MRI
This method allows you to determine the state of the soft tissues surrounding the shoulder joint, which provides the necessary information for an accurate diagnosis and therapeutic prescription. The effectiveness of MRI with impingement is quite high - 92% -93%. But due to the high cost, the study is rarely ordered.
Treatment of 1-2-3 degrees
Subacromial shoulder impingement syndrome is treated depending on the degree of damage to the structures. At the initial stage of the disease, conservative therapy is prescribed, since there is no significant damage to soft tissues. Improvement of the condition can be achieved with the help of medicines and physiotherapy.
If, after long-term administration of drugs, the dynamics of improvement is not observed, doctors re-diagnose and determine the need for surgical treatment.
Conservative therapy
The most important thing in conservative therapy is to exclude the movement of the sore shoulder. It is recommended to fix the limb in one position for several hours, then remove it so that the hand can rest a little.
Algorithm for conservative treatment:
- Taking NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Medicines are used to relieve pain and relieve inflammation. The effectiveness of drugs is achieved after their introduction for 1-2 weeks.
-
Cortisone injections (a group of corticosteroids). The maximum effectiveness of the drug has been proven in its administration in the first 8 weeks of treatment. Cortisone relieves pain and improves joint mobility.
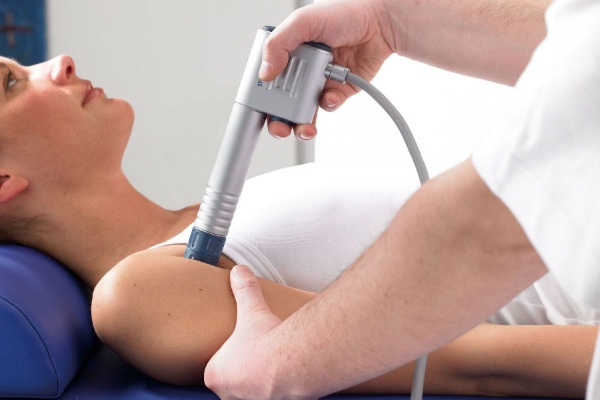
- Shock wave therapy. The procedure is indicated for calcifying tendinitis. Shock waves are directed at the deposited calcium salts in the tendons and break them down into molecules, thereby relieving soreness and improving shoulder mobility.
Subacromial decompression
This method belongs to surgical treatment. It is carried out in cases where the conservative technique has not yielded results. The operation is performed to expand the space between the acromion and the rotator cuff by reducing the pressure in the soft tissues located under the acromion. The pressure is reduced due to the resection of pathological bone growths.
Often, an insignificant area of the acromion is also removed, this also allows you to expand the space and exclude pathological contact between the structures. Acromion removal is an acromioplasty performed openly or with an arthroscope.
A successful operation eliminates possible pressure between the acromion and the shoulder bone in the future, and also reduces the pathological effect on the rotator cuff. The prognosis of recovery is favorable; after recovery, the patient will be able to perform any hand movements.
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression is the same operation on the shoulder joint with all the necessary expansion manipulations performed subacromial space, only it is carried out using a new technology (using an arthroscope - a metal tube with a slightly smaller diameter pencil).
This device allows all surgical procedures to be performed without fully opening the shoulder joint.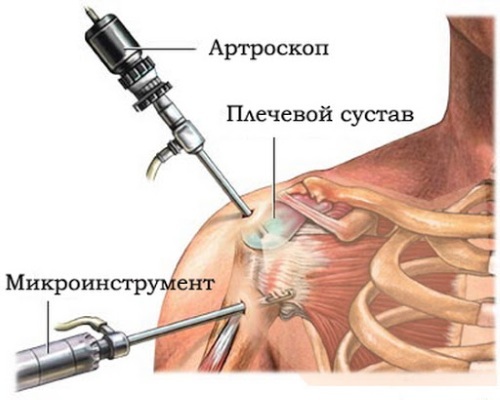
An arthroscope is an optical device equipped with a lens complex and a camera. To insert the arthroscope, it is necessary to make small holes in the shoulder, this reduces trauma to the soft tissues. The camera displays a picture of the affected joint on a computer monitor.
Together with the device, the necessary mini-instruments are introduced, with the help of which all the necessary surgical procedures are performed. The operation is carried out in water, since it requires a constant flow of fluid to cleanse the joint of blood and tissue debris.
After such a surgical treatment, the regeneration process is faster, and the patient can return home on the day of the operation and continue treatment at home.
The positive result of the operation depends not only on the surgeon, but also on the patient himself, since he is obliged to follow all the doctor's recommendations so that the rehabilitation period passes easier and faster.
Physiotherapy
Patients diagnosed with impingement syndrome are assigned physiotherapy procedures:
- thermal procedures;
- electrophoresis with novocaine;
- myostimulation;
- ozone therapy (treatment with oxygen);
- therapeutic shoulder massages.
Therapeutic manipulations help to quickly cope with the pathological process, eliminate pain, improve blood flow, stimulate shoulder mobility, and maintain muscle tone.
Rehabilitation measures
Rehabilitation measures can be started only 2 weeks after the operation, during which time the swelling of the tissues will already subside. Rehabilitation includes exercise therapy, taping and the use of fixators.
The purpose of rehabilitation measures:
- restoration of muscle tone;
- teaching the patient the correct distribution of physical activity;
- activation of blood flow in the periarticular structures of the shoulder;
- elimination of puffiness and elimination of the likelihood of stagnation;
- restoration of joint mobility;
- relapse prevention.
The effectiveness of exercise therapy is achieved if you exercise regularly. Improvement will be noticeable within 3-4 weeks after the start of classes. The movement of the limb will become easier and freer, while the pain will no longer be felt. A lasting positive result occurs only after 4-6 months of daily exercise therapy.
Effective exercises to restore the joint after surgical treatment:
- Shoulder blade movements. Body position - lying on your back, arms extended up. The raised arms alternately try to raise it even higher above the head, thereby involving the scapula in the process.
-
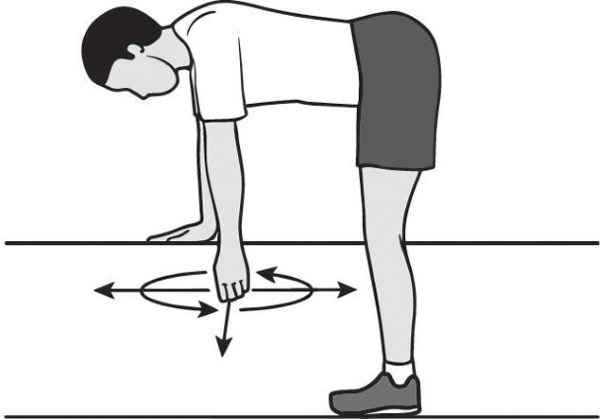
Exercise Kodman. The position of the body is standing with a tilt on the table, leaning on it with a good hand. The affected limb dangles. Swaying of the body is performed without changing the position of the sore arm. The range of motion is transmitted to the shoulder, and the arm begins to swing by itself. The swinging of the body stops, and the arm continues swinging in suspension. The exercise is performed by alternately changing the direction of swinging the body.
- Flexion of the shoulder joint under water. The patient stands in the water up to his neck, lowering his arms parallel to the body. Both limbs are spread out to the sides in a V-shape and raised up until the tips of the thumbs reach the surface of the water.
Taping is indicated for patients to relieve the condition; the technique helps to relieve puffiness and relieve pain. Elastic bands distribute the load on the muscles and balance the movement. The joint is fixed in an anterior position, which is quite comfortable, does not cause discomfort and pain.
There are two methods of taping:
- decongestant;
- stabilizing.
Taping techniques:
| Methodology | Description |
| Decongestant | Several elastic bands are applied to the shoulder joint, the point of their intersection should be in the area of greatest inflammation or the point of pain. The method is used in the acute phase. |
| Stabilizing | The deltoid and supraspinatus muscles are fixed, after which the shoulder joint is fixed with elastic bands, preventing it from shifting posteriorly. The method is used in the subacute phase. |
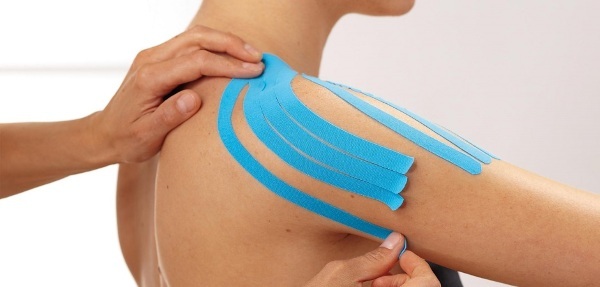
Physiotherapy is used not only as a therapy, during the rehabilitation period, they allow you to restore muscle tissue, improve blood flow, and relieve pain.
Folk methods
Herbal medicine cannot be used as an independent therapy for the syndrome, however, many proven recipes improve the patient's condition, reduce pain, relieve swelling and promote tissue regeneration after operations.
Traditional medicine recipes for impingement syndrome:
| Means | Preparation | Application |
| Herbal anti-inflammatory decoction | For the broth, plants are needed:
Take 1 tbsp. l. each ingredient and pour 1 liter of hot water. Place on the stove over medium heat, bring to a boil and simmer for 10 minutes. Then cool and strain. |
Take 3/4 cup orally half an hour before meals three times a day. The course is 3 weeks. |
| Plantain leaf compress | Rinse fresh plantain leaves and spread with a thin layer of honey. | Apply to a sore spot for the whole day or all night. From above, the compress is covered with cling film and wrapped in a light cloth. The course is 2 weeks. |
| Anti-inflammatory decoction | For the recipe you need:
Mix all the ingredients and select 3 tbsp. l. raw materials. Pour 1 liter of hot water and place on the stove. Boil for 10 minutes. Cool and drain. |
Take 3/4 cup of broth half an hour before meals 3 times a day. The course is 3-4 weeks. |
Possible complications of the disease, prognosis
Modern methods of treating subacromial impingement syndrome give a positive prognosis for recovery and complete recovery of the shoulder joint, but subject to timeliness.
At the initial stage, conservative therapy and exercise therapy allow to get rid of pain and restore the motor function of the joint. However, the neglect of the process requires a more radical approach - a surgical method. And in this case, doctors give a positive trend of recovery. The most dangerous condition is complete paralysis.
In such situations, doctors determine the need for amputation of the limb, provided that the condition threatens the patient's life. Therefore, when the first signs of impingement syndrome appear, it is important to consult a doctor and undergo a full diagnosis in order to identify the problem in a timely manner and begin its treatment.
Video about impingement syndrome
About shoulder impingement syndrome: