Sacrum fracture - This is a violation of the integrity of bone structures as a result of mechanical impact on this anatomical area. The treatment and consequences of a fracture differ depending on the cause of the pathology.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 First aid
- 8.2 Mode
- 8.3 Medications
- 8.4 Folk methods
- 8.5 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about sacrum fracture
Views
There are several types of sacral fractures:
- Vertical fracture. Has the character of one-sided damage. Most often occurs with fractures of the pelvic bones.
- Horizontal fracture. With this type of fracture, the damage zone extends to the lower part of the sacral articulation.
- Transverse fracture. This fracture runs at an oblique angle across the bone.
-
Comminuted fracture. It bears this name because of the formation of many "fragments" of bones after an injury.
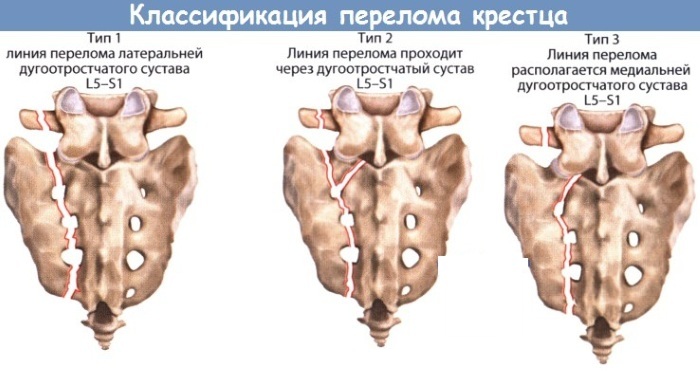
And also fractures of the sacrum are divided by types:
- Fracture without displacement. With this type of injury, the displacement of the vertebrae does not occur.
- Fracture with displacement. It is characterized by the formation of separate vertebrae from each other, which, due to their position, can injure the adjacent areas.
Fracture of the sacrum (treatment and consequences differ depending on the complexity of the injury) in complicated cases is accompanied by damage to the pelvic organs, blood vessels and nerves. Including lesions of the pelvic ring, rupture of joints and ligaments, massive bleeding and the development of shock may be present.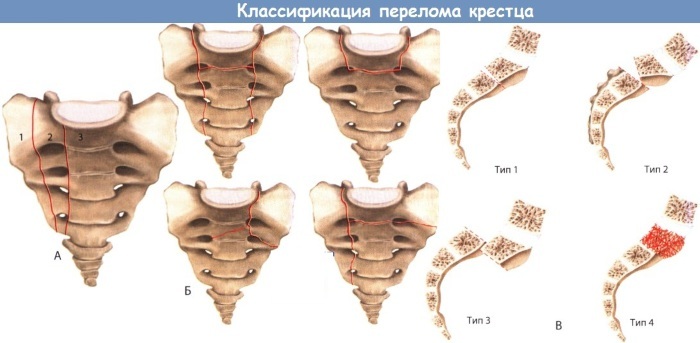
An uncomplicated fracture is accompanied only by damage to one of the sacral vertebrae and does not pose a threat to the patient's life.
Stages and degrees
Fracture degree:
- Complete fracture. It occurs with a complete violation of the integrity of the bone. This degree is typical for transverse and vertical fractures, as well as for other types of sacral fractures.
- Incomplete fracture. It is characterized by a partial violation of the bone (crack). It can occur with the vertical and horizontal form of the fracture.
The stages of fractures are acute and chronic. Acute occurs with fractures, the causes of which are trauma and injury. Chronic fractures can occur during osteoporosis, with vertical, oblique and transverse fractures.
Symptoms
| Fracture without displacement |
|
| Displacement fracture |
|
Reasons for the appearance
The reasons for the development of a fracture depend on its type:
| Vertical fracture | Accident, fracture due to progression of osteoporosis |
| Horizontal fracture | Fall from a height, onto a hard surface (ice, asphalt) |
| Transverse fracture | Traffic accidents, injury during extreme sports, falling from a great height |
| Comminuted fracture | Traffic accident, falling from a great height, gunshot wound |
Diagnostics
Sacrum fracture (treatment and consequences depend on correct diagnosis) diagnosed comprehensively and consists of the following methods:
-
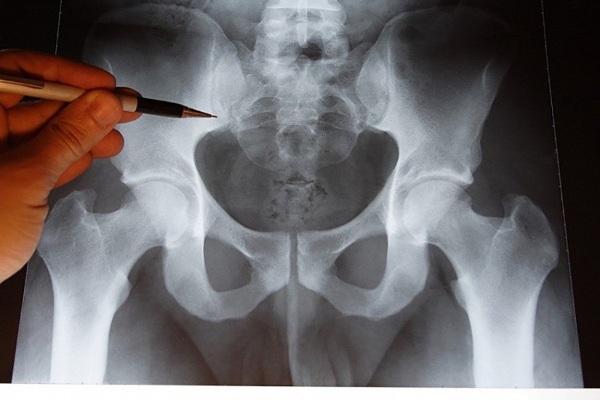
Radiography of the lumbosacral spine. It is carried out in two projections (direct and frontal). It is the most common method for examining bone fractures, in particular, and a fracture of the sacrum. The X-ray will show the location and extent of the fracture.
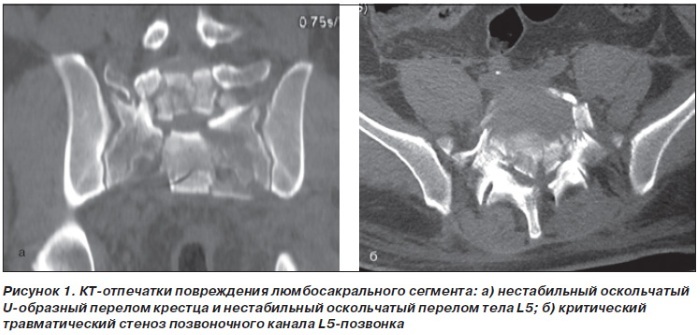
- Computed tomography (CT). It is the most informative diagnostic method for detecting a fracture. During the study, a three-dimensional model of the damaged area is created, thanks to which the doctor can with accurately determine how badly the sacrum is damaged, as well as assess the condition of the joints, ligaments, blood vessels and nerves. The procedure does not require special preparation. It can be carried out both with the introduction of a contrast agent, and without it.
-
MRI. It is used for suspected ruptures of the articular and ligamentous apparatus, as well as for suspected damage to the pelvic organs.
These studies are carried out in a trauma center or a trauma department of a general hospital. For urgent indications, these studies are carried out free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
If the patient wants to go to a private clinic on his own, the cost will depend on the research method. For computed tomography, the cost of diagnosing one section of the spine will cost approximately $ 5,000. rubles. And when conducting an MRI, the price can be from 4 thousand. up to 6 thousand rubles. The cost may vary depending on the region where the person wants to be tested.
When to see a doctor
For any type and degree of sacrum fracture, you should immediately consult a doctor. Such a doctor is a traumatologist or a surgeon.
Prophylaxis
In general, there are no specific methods for preventing sacral fracture, but There are some things you can do to reduce your risk of injury:
- If possible, avoid dangerous situations in which the risk of fracture increases. For example, the risk of sacrum fracture increases with particularly traumatic sports.
- Treatment of diseases of the skeletal system. Such diseases include osteoporosis, which, as it progresses, can lead to the development of pathological fractures.
- Maintaining optimal body weight. Being overweight can contribute to an increased risk of fractures.
- Diet with sufficient mineral content. Elderly people should be especially careful about diets with sufficient calcium content, as the skeletal system becomes weaker with age.
- Quitting smoking and other bad habits.
- Sports activities. Optimal physical activity is beneficial for all parts of the spine.
- The use of a medical corset after surgery. If the patient has had spinal surgery, he needs to wear a special medical corset that prevents the development of a fracture.
- Avoiding heavy lifting. With various injuries of the sacrum or diseases, in no case should you lift a weight that exceeds 5 kg.
Treatment methods
A sacrum fracture is a very serious pathology, therefore, the approach to treatment must be comprehensive, since an incorrect approach can cause serious consequences. Treatments for sacral injury may vary depending on the severity of the fracture.
The main methods of treatment are conservative therapy or surgery. Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are also of great importance, especially in the early rehabilitation period.
First aid
Fracture of the sacrum (treatment and consequences require competent first aid) is a common spinal injury, therefore, immediately after the injury, it is necessary to provide the victim with assistance literate help, and then deliver him to the trauma department:
- It is necessary to reassure the victim.
- Give the victim an anesthetic drug (1 tablet of analgin). This type of pain relief is applicable for mild pain syndrome. With severe pain, which can lead to the development of shock, you need to inject a solution of morphine or other narcotic analgesic.
- Stop bleeding (if present). To do this, apply a pressure bandage (for venous bleeding) or a tourniquet (for bleeding from an artery).
- To reduce the risk of developing a state of shock, you need to cover the victim with warm clothes.
- The victim is transported in a prone position. Place rollers under your knees. It is necessary to transport the victim as carefully as possible so that there is no displacement of the bone structures.
Mode
After the fracture, strict bed rest is prescribed for a long time. Usually this interval is from 1 to 6 months, depending on the complexity of the fracture.
The patient is not allowed to take a sitting position until the bone tissue is completely fused. In bed, the patient can lie on his back, side or stomach. Care must be taken when turning the patient over.
To avoid congestion in the lungs, it is necessary to apply vibration massage (light tapping in the projection of the lungs).
Gradually, the regime expands after bed rest, the patient can slowly begin to sit down and then walk.
Medications
For uncomplicated and isolated fractures of the sacrum, complete rest is prescribed, immobility and symptomatic therapy, which is aimed mainly at reducing pain syndrome.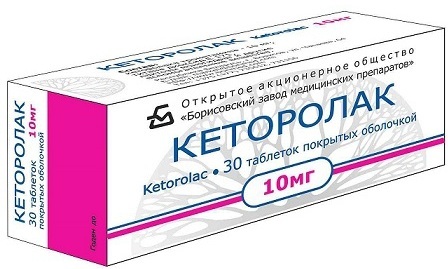
For pain relief, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used. These include ibuprofen, ketorolac. The oral dose is 1–2 tab. 3 times a day. For intramuscular administration, a single dose is 1 ml (30 mg) of the drug every 4-6 hours. until the pain stops completely.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics (ceftriaxone, cefipime) are used to prevent infectious complications. The drug is administered 2 times a day, 1 mg (diluted in 5 ml of novocaine or saline). The course of antibiotics is 10 to 14 days.
In a hospital setting, drugs are given out for the treatment of a patient free of charge.
Folk methods
In combination with the methods of official medicine, folk remedies can be used to treat a sacral fracture.
These include:
- Herbal ointments.
- Compresses.
- Infusions.
An anti-inflammatory and analgesic ointment can be prepared from bearberry and yarrow. These herbs must be crushed to a powder and then add Vaseline and stir until smooth. You need to apply the ointment once a day (at night) for 14 days.
Compresses from grated raw potatoes have proven themselves well. Apply it 1-2 times a day until the edema disappears completely.
To reduce pain, you can brew an infusion of black currant leaves. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. To prepare it, pour boiling water over blackcurrant leaves and let it brew for half an hour. You need to drink the infusion 1-2 times a day until the pain disappears completely.
Other methods
These include the operation for combined injuries or comminuted sacral fractures. Surgical intervention consists in placing pins in the damaged vertebrae. In case of sacral fractures, which are combined with injuries of the pelvic bones, the extent of the surgical intervention is determined by the doctor.
And also other methods of treatment include:
-
Physiotherapy methods (electrophoresis with drugs). This method allows for greater efficacy from pain medications.
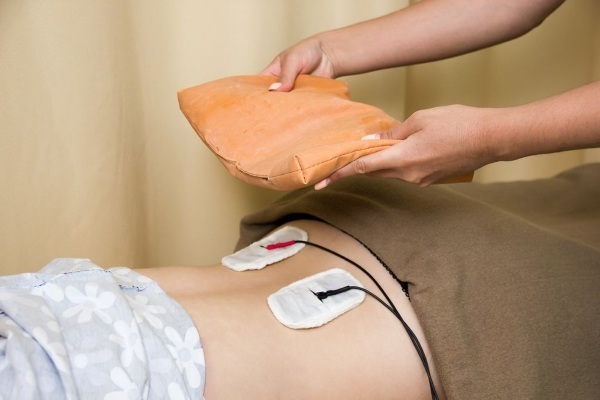
- Massage. Massage is prescribed after the complete disappearance of pain and no earlier than a month after the injury. The massage provides the correct muscle tone, relaxes the sacral region and improves blood circulation in it.
- Physiotherapy. They begin to carry out in the early rehabilitation period, after the main clinical manifestations subside. It is dosed based on the patient's well-being.
The course of treatment is usually 1 to 6 months. The cost of treatment depends on the specific region where the patient is receiving therapy. Most of these procedures can be obtained free of charge from a public health facility.
Possible complications
Complications of a fracture depend on its complexity and the degree of damage to the vertebrae and surrounding organs and tissues.
If the fracture is not treated, the following consequences may occur:
- Pathological changes in the nervous system. Paralysis, paresis may occur. A person can completely lose the ability to move independently.
- Pathological changes in the pelvic organs. These include chronic pelvic pain syndrome, reproductive disorders, chronic inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. And also there may be urinary incontinence, pain during urination.
- Pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. Patients who have suffered a sacral fracture may experience fecal incontinence or, conversely, a prolonged absence of defecation.
- Pathological changes in the musculoskeletal system. Intervertebral hernias, joint contractures, arthritis and arthrosis of the joints of the lower extremities may develop.
A sacrum fracture is a very dangerous injury, the treatment of which must be started immediately, since serious consequences can develop if medical care is not provided in a timely manner.
Video about sacrum fracture
Doctor about the symptoms of a tailbone fracture: