Tuberculosis has been known since ancient times, exploring the human remains of the Stone Age, scientists have found the abnormalities characteristic of this disease.
In ancient Egypt, doctors described the symptoms of tuberculosis: a debilitating wet cough with an admixture of blood and a fever that drains the patient. And today, in the 21st century, the problem of tuberculosis in society is still relevant.
Contents of
- 1 Tuberculosis of the lungs - what is it?
- 2 TB forms are easy,
- 3 classification How is pulmonary tuberculosis transmitted?
- 4 Signs of early tuberculosis in an adult
- 5 Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
- 6 Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults
- 7 Prevention of pulmonary tuberculosis
Tuberculosis of the lungs - what is it?
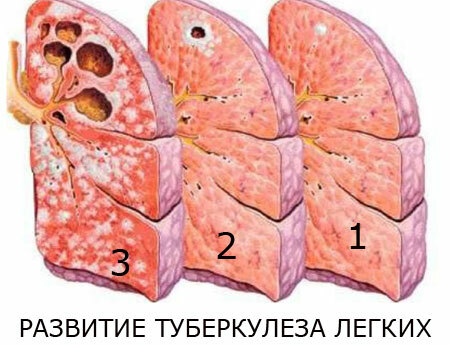
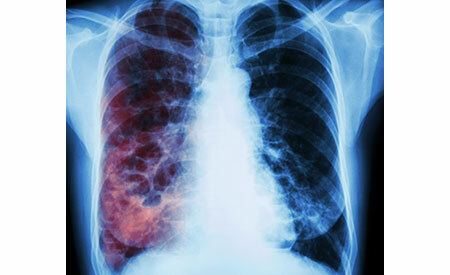
Tuberculosis development, photo
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by specific bacteria called Koch chopsticks. They are named after the German scientist Robert Koch who opened them.
According to WHO, every third person is the carrier of the causative agent of the disease, but only in the presence of favorable conditions it can cause disease.
Annually around 10 million cases of tuberculosis are registered in the world, one third of which is lethal.
As Koch's rod multiplies rapidly in unsanitary conditions, it is believed that the disease occurs only in the poor, but everyone can get tuberculosis, regardless of age and status in society.
Forms of tuberculosis are easy, classification
Depending on the infectiousness of the patient, the following forms of pulmonary tuberculosis are distinguished:
- Open form. When a patient coughs, a bacterium is excreted into the external environment, which infects others. When examining a smear with pulmonary discharge, Koch's wand is found.
- Closed form. In this case, a person suffers from tuberculosis, not identifying bacilli and not infecting others.
On the development of tuberculosis:
- Primary. In this form, the bacterium enters the body for the first time and may not appear for a long time. It ends with formation in the lungs of hardening sites.
- Secondary. Occurs from the primary, due to weakening of the body, for example, after a cold.
Depending on the distribution and location of inflammatory foci, the forms of tuberculosis are distinguished:
Disseminated. Lung tissue forms a large number of small dense patches with a large concentration of Koch sticks. He is subacute or chronic. Develops slowly, can not bother for years.
Miliary. Inflammatory foci occur not only in the lungs, but also in the tissues of the liver, the spleen, and the membranes of the brain. In most cases it occurs in an acute form with symptoms of intoxication of the body.
Focal. In the lung tissue, few, small areas of hardening are detected. Has a lingering current.
Infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis. In one or both lungs, tubercular foci are identified, in the center of which is the necrosis zone. Clinically, it can not be manifested in any way and is found by chance on the X-ray. Casey pneumonia. Severe form of pathology, in which decay sites are observed in the lung tissue. They eventually dissolve with the formation of cavities.
Tuberculoma. In the lungs, fossilization areas up to 5 cm in diameter are formed. They can be single or multiple.
Cavernous. Are formed areas of the absence of tissue around which there is a slight inflammation. This form develops with the progression of other types of tuberculosis.
Fibrous-cavernous. Around the formed voids a dense fibrous ring is formed. It arises as a complication of the cavernous form.
Cirrhotic. Characterized by the replacement of normal tissue by the connective and arises from other forms of the disease.
How is pulmonary tuberculosis transmitted?
A person is infected with tuberculosis mostly airborne, and rarely by the food route. It is transmitted when the healthy person inhales microscopic parts of the patient's pulmonary discharge. For the development of pulmonary tuberculosis, the Koch sticks concentration should be quite high.
Therefore, infection occurs more often with prolonged, reusable contact with the patient. An exception is an open form, in which infection occurs many times faster. But not always the presence of a pathogen means the development of tuberculosis.
Only with favorable bacterial conditions can the disease develop and symptoms and first signs of pulmonary tuberculosis will manifest.
Active propagation of Koch sticks is promoted by:
- Weakening of the body after a flu or cold.
- Decreased immunity.
- The presence of hormonal diseases.
- Chronic diseases.
- Diseases of the respiratory tract.
Signs of tuberculosis in the early stages of the adult
The incubation period depends on the body's resistance and can last up to several years. In the early stages, the immune system is activated, destroying the pathogen. If for some reason it does poorly with its functions, tuberculosis foci develop in the lungs.

First signs of tuberculosis infection in an adult:
- Frequent uncaused dizziness.
- Weakness. Insomnia and sweating at night.
- Pale skin.
- Weight reduction.
- Poor appetite.
- Constant low temperature, up to 37 degrees.
If a person is concerned about one or more of these symptoms, you need to see a doctor and take a lung X-ray.
More: Symptoms and first signs of tuberculosis
With the further progression of the process, the following symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis are observed:
- Permanent dry or wet cough.
- Shortness of breath, which appears even at rest.
- Horny, can be heard by a doctor while listening.
- High fever, especially in the morning.
- Eyes shine, skin pale.
- Sharp causeless weight loss.
- Sputum production with blood.
- Pain in the sternum, during inspiration and at rest.
Recent symptoms indicate a severe form of tuberculosis, which requires urgent treatment.
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
Begins with the collection of complaints with the further appointment of instrumental and laboratory studies. On examination, the doctor pays attention to the increase in lymph nodes and the presence of wheezing when listening to a phonendoscope.
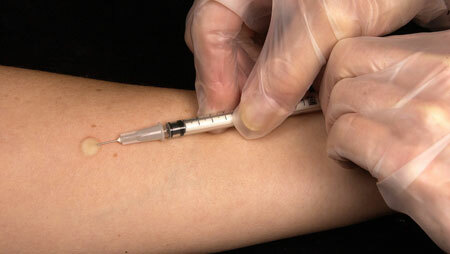
If suspected of tuberculosis, the Mantoux test is performed. The antigen of the Koch sticks is injected subcutaneously and after a couple of days the place of administration is carefully inspected. If there is an agent, a red spot of large size will be observed. But there are cases when the Mantoux test gives incorrect results.
An informative method for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis is radiography. X-ray reveals characteristic changes in lung tissue, but it is impossible with 100% guarantee to tell if it is tuberculosis.
The next step is to examine the sputum. He is done three times, after a certain time. If Koch's wand is found in the phlegm and there are changes on the X-ray, an antituberculous treatment is prescribed.
Additional diagnostic methods include bronchoscopy, pleural puncture and biopsy.
Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults
Treatment is prescribed taking into account the stage and form of tuberculosis, bacterial activity. It should be long and not interrupt. For the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults, there are schemes that include the appointment of three to five specific drugs. Only together, they will destroy the bacterium-pathogen, unauthorized intervention in the treatment procedure is unacceptable.
In addition, prescribe drugs that increase immunity and physiotherapy procedures. With severe form of tuberculosis, surgical treatment is performed - removal of damaged areas of the lungs.
With timely diagnosis and the appointment of adequate treatment, tuberculosis is cured completely and without consequences.
If the disease is started, treatment is prescribed late or incorrectly, as well as with a complicated form of the disease - in the lungs there are defects that have a lifelong effect on their function.
Increased risk of recurrence of tuberculosis foci in the lung tissue. A person who has ever had a discovered Koch's wand should be on a dispensary record.
Every second untreated case of tuberculosis ends with the patient's death. Associated diseases worsen the prognosis.
In severe cases, complications are likely:
- Bleeding from the lung.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax.
Prevention of pulmonary tuberculosis
The basis of prophylaxis is the prophylaxis of the population for the purpose of early diagnosis. It is advisable for every person to take X-rays of the lungs annually.
Specific prevention begins in the hospital. The newborn is given BCG vaccine - a small number of inactive Koch sticks.
This is necessary for the formation of immunity against tuberculosis. The introduction of the vaccine does not guarantee that the person will not get sick. However, he can bear the mild form of tuberculosis. Re-vaccine is given after 5 years.
Every year the reaction is determined - the Mantoux test. If it is slightly positive, it means that a person has strong immunity.
Trying to avoid contact with patients is not a guarantee against infection with tuberculosis, but will significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Another important factor is healthy eating and the right way of life, which stimulates good immunity. In this case, if you get a stick of Koch, the immune system will cope with it.