Sharp or chronic dental inflammation neurovascular tissues are called pulpitis. Their extensive classification is based on the causes of the pathological process, the nature of its course. When diagnosing and treating inflammation, its morphological signs must be taken into account.
Record content:
- 1 Definition of disease
- 2 Causes of occurrence
-
3 Classification of pulpitis
- 3.1 Types of acute pulpitis
- 3.2 Types of chronic dental pulpitis
- 4 Diagnostics
-
5 Methods and stages of treatment
- 5.1 Surgical
- 5.2 Medication
- 6 Features of the treatment of pulpitis in children
- 7 Why does a pulpous tooth hurt?
- 8 Possible complications
- 9 Forecasts
- 10 Video about pulpitis
Definition of disease
Simplified pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental nerve, accompanied by unbearable pain.
The disease affects:
- connective tissue;
- periosteum;
- periodont - a complex of soft fibers that surround the tooth and hold it in the alveolar socket;
- bone trunk.
Pulpitis (classification, diagnosis, treatment) are allocated to a separate area of dentistry. With such a disease, dental tissues react sharply to external stimuli, especially to temperature exposure.
The pain is worse at night. The prevalence of pulpitis is second only to caries. Every 5th patient goes to the dentist with just this disease. According to the WHO classification, pulpitis is assigned the KO4.0 code.
Such a disease is defined as an acute or chronic inflammatory pathology of the pulp. Periapical tissues are affected by the destructive process. The pulp is the name for the connective fibers of a loose structure, which fill the dental cavity.
They contain nerve endings, blood vessels and lymph vessels. Inflammation of this connective tissue, which is responsible for nourishing the teeth, is called pulpitis.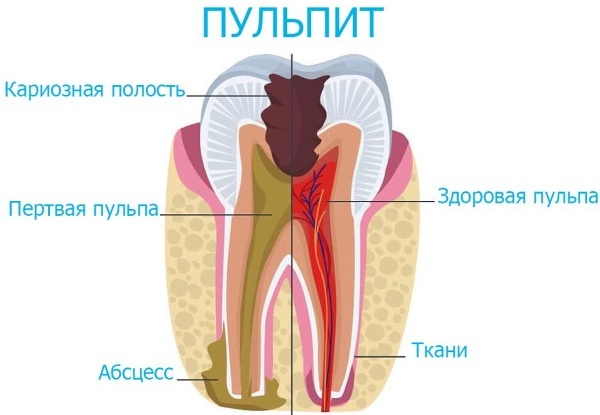
Pulp functions:
- plastic, which is realized due to the biological activity of odontoblasts that form the peripheral tissue layer;
- protective - the production of immunoglobulin lgG, the utilization of dead cells, the formation of tertiary dentin;
- trophic, carried out due to the developed vascular network;
- sensory, due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings;
Inflammation of the pulp not only causes severe pain, but also leads to tissue necrosis, fraught with tooth loss and infection of the entire salivary-jaw apparatus.
Causes of occurrence
This pathological condition is caused by several etiological factors.
The most common causes of pulpitis are:
- advanced caries, which destroys enamel and affects the deep tissues of the dental organ;
- toxic effects of materials and medicines used for filling;
- The use of antiseptic agents in excessive concentration when disinfecting the dental cavity;
- strong heating of the pulp during the photobleaching procedure, aesthetic restoration, preparation of bone tissue for further installation of the prosthesis;
- bacterial lesions of the oral cavity;
- chronic sinusitis associated with infection of the maxillary teeth.
Pathogenesis is often associated with medical errors - the use of low-quality filling material, improper turning, inaccurate surgical intervention.
The most common cause of pulpitis is microbial influences. Fractured or chipped parts of the tooth can cause inflammation of the loose tissue. Typical provocateurs of the development of the pathological process are streptococcal infections that penetrate the dental cavity through the hematological route.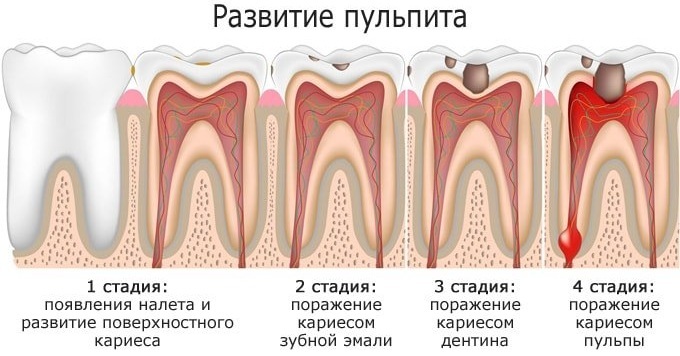
Diabetes mellitus and osteoporosis contribute to increased wear of the teeth. Violation of the integrity of the jaw structures creates favorable conditions for the penetration of pathogenic microflora.
Theoretically, incorrect selection and installation of braces can trigger the development of inflammation, as they destroy enamel and expose the inner layers of the teeth. A common cause of children's pulpitis is non-observance of oral hygiene, as a result of which pathogens accumulate and multiply there.
Classification of pulpitis
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the dental cavity is divided into several forms and subspecies. Clear structuring and clear classification of pulpitis are necessary for accurate diagnosis and correct treatment tactics.
By the nature of the inflammatory process, they are divided into 4 types:
- Sharp, which affect only the coronal pulp tissue. The duration of such an inflammatory process is 3-5 days. It is accompanied by a sharp pain syndrome.
-
Chronic. Acute pulpitis not cured in time passes into this form. Chronic inflammation is characterized by gradual death of nervous tissue. Its decomposition is fraught with the formation of suppuration. The pain is moderate or absent.
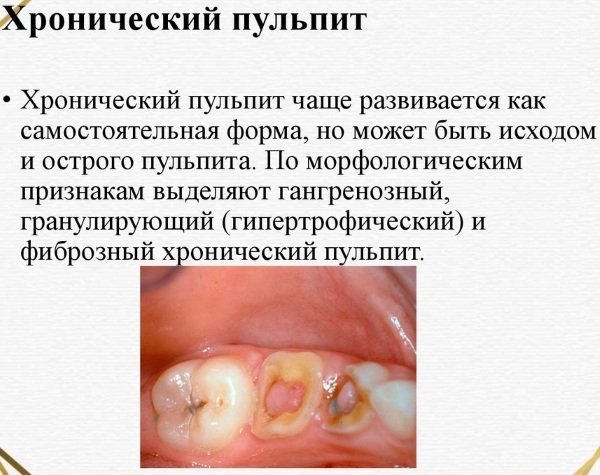
- Exacerbation of chronic pulpitis. In some cases, such inflammation is not formed from the acute stage, but bypasses it. Sometimes chronic pulpitis occurs with periodic exacerbations. Usually they are caused by pathogenic microflora. Gradual tissue necrotization proceeds slowly, but with periodic bouts of pain.
- Condition after depulpation. This inflammatory process affects the root and gum tissue.
Pulpitis (classification, diagnosis, treatment requires an accurate determination of the nature of the course of the disease) of the acute type are localized in the immediate vicinity of the carious cavity. This pathology is focal or diffuse.
Chronic pulpitis has more varieties, morphological signs and variants of the course of the inflammatory process. Such dental diseases are classified as reversible or irreversible. Their main difference is the possibility of saving a tooth or the need for amputation.
Types of acute pulpitis
Inflammatory processes of this type have pronounced symptoms and are accompanied by severe prolonged pain. The frequent pathogenesis of this condition is an extensive carious lesion.
Classification of acute pulpitis:
| Pathology type | Clinical characteristics |
| Serous limited | The initial phase of the lesion of the pulp. Purulent exudate is not released. Inflammation develops due to infection with pathogenic pathogens of serous fluid. |
| Pulp hyperemia | Reversible inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. There are no spontaneous night pains. Short seizures provoke external stimuli of the mechanical and thermal type. |
| Serous diffuse | The carious cavity spreads to the entire bottom. Dental intubation causes an attack of severe pain that radiates to the branches of the trigeminal nerve. Clinical symptoms can last up to 2 weeks. There is a large amount of softened dental tissue. |
| Purulent | There is a pulpal abscess with the release of purulent exudate into the oral cavity. The level of serous substance in the pulp increases against the background of oxygen deficiency. |
| Traumatic | It occurs when the pulp cavity is opened with the subsequent introduction of pathogenic pathogens and foreign bodies into it. |
A common characteristic feature of all acute pulpitis is severe attacks of pain of varying duration. Cysts and purulent cavities are formed in the apical zone. As a result of the acute course of the inflammatory process, there is a pronounced vascular hyperemia in the microcircular beds.
Types of chronic dental pulpitis
Diseases in this category are often asymptomatic, with rare bouts of toothache. They have a sluggish character and an unclear clinical picture.
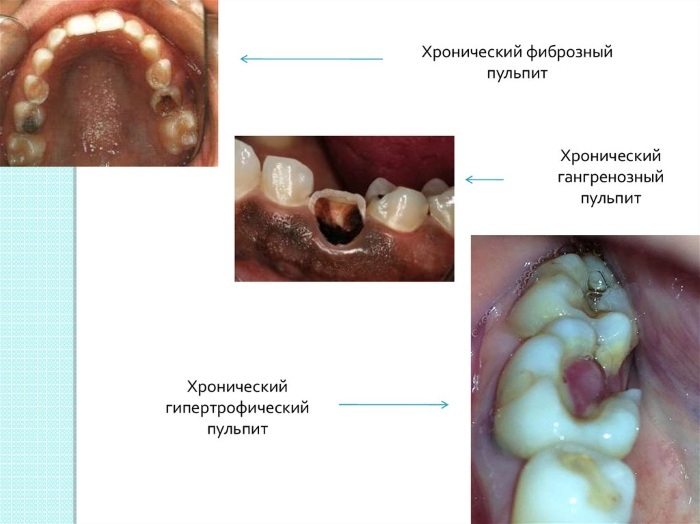
There are the following types of chronic pulpitis:
- fibrous;
- gangrenous;
- hypertrophic;
- calculous;
- retrograde.
Fibrous-type pulpitis is characterized by minor and short bouts of pain. The classification of such inflammations of the neurovascular bundle of the dental cavity is based on the morphological signs of the pathological process. Their diagnosis and treatment reveal reduced electrical excitability of the tooth.
The fibrous form of chronic inflammation of the pulp is characterized by a gradual change in the structure of the affected tissue and the outflow of pathological exudate. The reaction of the dental organ to temperature stimuli is slowed down.
X-ray examination reveals the sparseness of bone fibers in the area of the root apex. Gangrenous pulpitis is characterized by moderate pain while eating. There is a putrid odor in the mouth.
Periodically, there is a paroxysmal pain syndrome radiating to the trigeminal nerve region. On the X-ray, destructive transformations of the peri-apical tissues are noticeable.
Chronic pulpitis of a hypertrophic (proliferative) variety is characterized by the absence of subjective pain symptoms. Loose tissues of the inner cavity of the tooth grow, the coronal part is destroyed.
Hypertrophic changes in the pulp are noticeable, and the periapical fibers retain their natural anatomical structure. During periodic relapses, prolonged intense painful sensations occur, which intensify under the influence of mechanical and thermal stimuli.
With a calculous form of pulpitis, a dystrophic state of the neurovascular bundle, an increased content of dentin and calcifications in the internal cavity of the dental organ are found.
Chronic retrograde pathology with subjective symptoms resembles trigeminal neuralgia. Pulp inflammation progresses due to infection of the dental canal and affects the root of the tooth. Often the pathological process accompanies periodontitis.
Diagnostics
For the appointment of adequate treatment, it is extremely important to accurately determine the form and nature of the course of the inflammatory process.
Diagnostic measures include the following procedures:
- collection of anamnesis;
- instrumental-visual examination by a dentist of the oral cavity;
- X-ray examination of pathological dental organs;
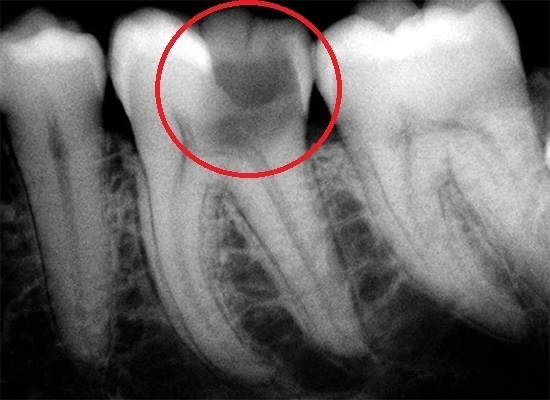
- electroodontic test;
- thermal test;
- analysis of salivary fluid for the content of immunoglobulins.
Such measures are aimed at clarifying the nature, morphological signs and depth of pulpitis. Instrumental sounding in acute serous form causes severe pain.
Percussion (tapping) with a hard object on the enamel surface increases the discomfort in the affected dental organ. In chronic purulent pulpitis, the clinical picture is the opposite.
Differential diagnostic methods are used for an accurate diagnosis. It allows you to distinguish pulpitis from caries or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. An important diagnostic method is the thermometric test. With its help, the reaction of the affected tooth to temperature stimuli is determined.
Electroodontodiagnostics provides for the supply of low voltage currents. The procedure allows you to assess the depth and degree of pathological changes in the neurovascular bundle, to determine the exact localization of the inflammatory focus.
Methods and stages of treatment
Elimination of the inflammatory process and restoration of the natural structure of the dental organ is carried out by the method most suitable for the diagnosed form of pulpitis. Each type of inflammation of the dental neurovascular bundle has individual characteristics of treatment. If the depth of the inflammatory lesion is large and the tooth cannot be restored, it is amputated.
Pulpitis, classification, diagnosis, the treatment of which is closely interrelated, are eliminated by surgical or biological methods. When restoring an affected tooth, the dentist performs local anesthesia and cleans the cavity affected by the inflammatory process.
Conservative treatment with preservation of the neurovascular pulp bundle is carried out only in the initial stages, when the affected tissue can still be restored. An important stage of therapeutic measures is the relief of pain syndrome.
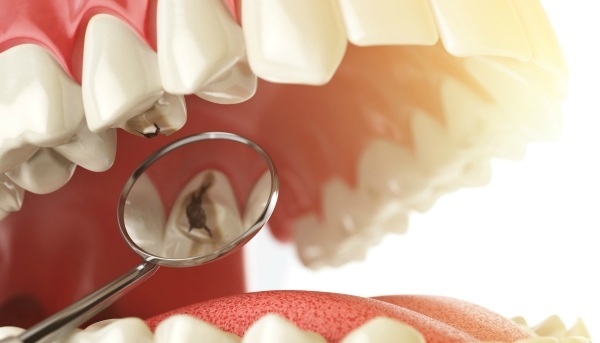
If the pulpitis is purulent, the tooth in most cases must be removed and replaced with a prosthesis. To suppress the infection, special dental antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs are used.
Their task includes:
- destruction of pathogenic microflora;
- regeneration of pulp cells;
- relief of pain syndrome.
This method has some contraindications. It is not performed for children with active resorption of the roots of deciduous teeth. The procedure for treating pulpitis is multi-stage and requires several visits to the dental office.
A neglected chronic disease involves extirpation - complete removal of the loose tissue lining the inner cavity of the tooth. When treating pulpitis, it is important not to harm the healthy tissues surrounding the inflammation focus.
Surgical
Vital, devital amputation or a combined method is used. The latter is used for acute diffuse, chronic fibrous and hypertrophic forms of pulpitis. To apply the combined method, the electric excitability of the tooth should not exceed 40 μA.
This option of surgical treatment consists in the complete or partial removal of the pulp from the channels with normal patency or its mummification. The dentist amputates the crown area of the tooth, and covers the unaffected surface of the inner cavity with a calcium-based therapeutic paste.
The vital technique provides for the removal of pathological tissue without pretreatment with medications. In most cases, the pulp is partially amputated. The root part remains viable and continues to feed the organ. Such dental procedures are performed using conduction anesthesia.
Vital amputation is often performed in the treatment of deciduous teeth. It is used in the treatment of focal or chronic fibrous pulpitis in patients under 40 years of age.
Stages of pulpoectomy:
- Local anesthetic injection.
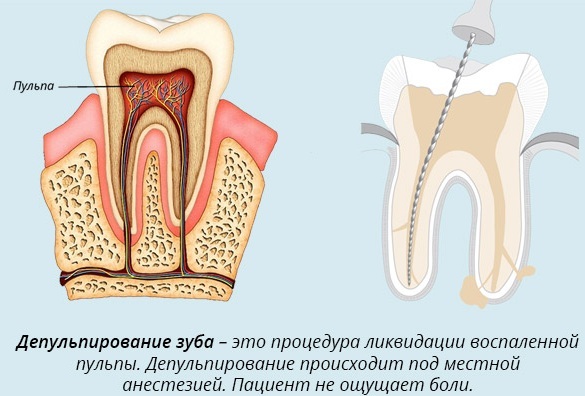
- Opening of dental canals and amputation of inflamed carious tissues.
- Partial or complete removal of loose fibers.
- Surface treatment with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medicines.
- Installation of a temporary seal.
- Sealing the tooth with a permanent photopolymer material.
Devital extirpation involves the removal of dead pulp after necrotization with a potent toxic drug. This technique allows you to cure pulpitis in 1 visit to the dental office. Its disadvantage lies in the fact that the dental organ ceases to receive nutrition, therefore, the installation of a crown is desirable.
Medication
With this method of treatment, the cavity of the affected tooth is first cleaned, and then processed and filled. In this case, the inflamed nerve is amputated. They use toxic medicines with a strong anti-inflammatory effect - Calzodont, Life, Dical.
They use proteolytic enzymes that have decongestant, antiseptic, necrolytic effects. They stimulate the natural regenerative capacities of the soft tissues and hard fibers of the pulp tooth, allowing it to remain fully functional after treatment.
Dentists use medications with a high content of calcium hydroxide. A paste-like composition of this category is used to treat the surface of the cleaned cavity. These drugs stimulate dentin production and create a chemical barrier to pathogens, preventing reinfection.
Pulpitis (classification, diagnosis, treatment of diseases are inseparable from each other) of the serous type are eliminated mainly with medication. With such pathologies, purulent exudate is not released. An anti-inflammatory drug is applied to the pulp.
Features of the treatment of pulpitis in children
Milk teeth are largely susceptible to the development of an acute inflammatory process of the neurovascular bundle and loose tissues. This is due to their anatomical structure. In children's teeth, the enamel has a loose structure, the pulp is soft, and the vessels are close to the surface.
Therefore, infections occur frequently. Serous pulpitis literally in a few hours turns into a purulent form, fraught with infection of the entire oral cavity and the spread of infection beyond it. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomy of the milk tooth, the pulp chamber rapidly develops and expands in it.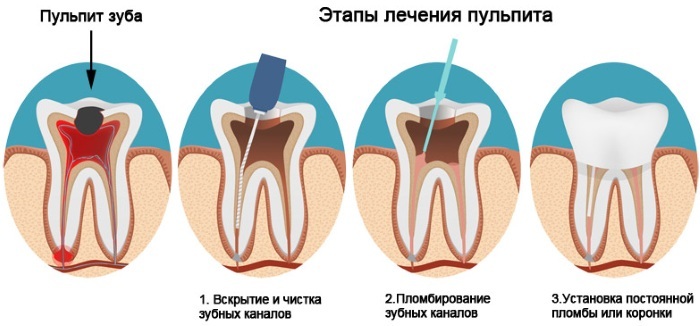
In such pathological conditions, not fully formed roots are rapidly destroyed, and a large apical cavity with a hole is formed in them. Through it, pathogens are introduced into the periodontium. Streptococci, characteristic of tonsillitis, affect the jaw apparatus just as easily as the tonsils.
During treatment, the dentist injects an anesthetic drug, opens the dental canals with a special tool, cleans them together with the entire tooth cavity. After that, the surface is treated with an antiseptic solution - most often dentists use etonium. Then the tooth is filled.
A biological method of treatment, involving the preservation of the pulp, is used if the pathological process has not yet become irreversible. The main goal is to relieve inflammation without disrupting the functional characteristics of the infected organ.
Why does a pulpous tooth hurt?
When all the treatment procedures are completed, and a permanent filling is installed, unpleasant sensations may occur in the treated organ. Dentists disagree about their causes.
Some argue that this is a natural reaction of the body to medical intervention. Others are inclined to suspect incorrect placement of the filling and the use of materials that irritate the pulp cavity.
Allergic reactions can be accompanied by painful sensations even with amputated dental nerves. In some patients, anaphylaxis to filling materials, toxic and necrotizing drugs, medicines containing calcium is manifested by swelling, discomfort in the treated tooth.
Another reason is the careless performance of dental procedures with damage to the root and gum tissue. In this case, there may be pain, bleeding, suppuration. Sometimes discomfort occurs due to a violation of the filling technology by a low-skilled doctor.
Insufficiently experienced dentists often accidentally make a hole or cause other damage to the tooth root. For this reason, bleeding, suppuration, painful sensations occur, which become noticeable after the end of the anesthesia and can last up to 3 weeks.
Possible complications
Pulp inflammation requires immediate treatment.
If timely dental care is not provided, the following complications are possible:
- flux formation;
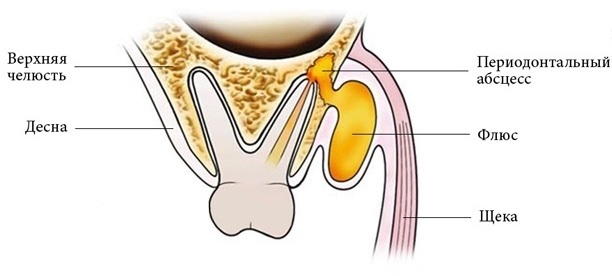
- the development of osteomyelitis - a purulent-inflammatory disease of the jaw bones;
- numerous abscesses of various sizes and localization in the oral cavity;
- the occurrence of phlegmon - pathological destruction, which is characterized by the penetration of pathogenic microflora and purulent exudate into the soft tissues of the facial zone;
- periostitis - a combination of an infectious lesion of the pulp with necrosis of the bone structures of the jaws;
- infection of other teeth.
Dental infections can spread throughout the body and reach the brain. The most common complication is periodontitis, which is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the ligaments of the tooth affected by pulpitis.
After removal of the nerve, the pulped organ becomes fragile, easily crumbles and quickly collapses. This natural but unpleasant effect is usually classified as a complication. A rational solution is to install a crown, which will strengthen the tooth and give it aesthetics.
Forecasts
The lifespan of a pulped organ depends on the technology used, the quality of the filling material used and the qualifications of the dentist. Good cleaning and disinfection of canals helps to preserve the tooth for a long time. However, it is recommended to strengthen the pulped organ with a crown.
It will protect the tooth from darkening and decay. Pulpitis is the most severe dental pathology. They have a ramified classification, and the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory processes with different morphological characteristics are associated with some difficulties.
Video about pulpitis
What is pulpitis: