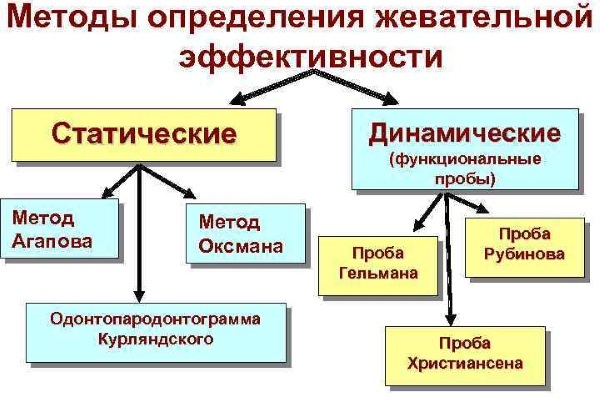
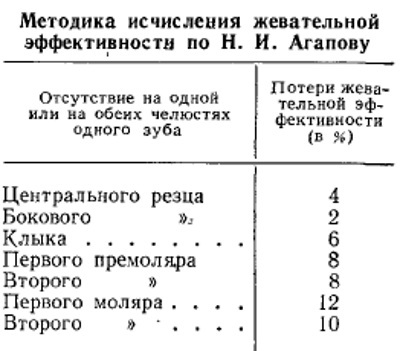
Dental apparatus - morphological complex, which has several functional tasks. One of them is chewing. Its effectiveness is determined by the Agapov method. Chewing is the initial stage of the digestive process, during which the contents of the oral cavity are crushed and moistened with salivary secretion.
Record content:
- 1 Anatomical features of abutment teeth
- 2 Requirements for abutment teeth
- 3 Condition assessment
- 4 Causes and signs of deviations
- 5 Average values of pressure on teeth in kilograms
- 6 Calculation principles
-
7 Load calculation
- 7.1 Agapov odds
- 7.2 Oxman odds
- 8 Decoding chewing coefficients
- 9 Measures to be taken in case of lack of support efficiency
- 10 Features of the installation of the bridge structure
- 11 Clasp devices
- 12 Chewing Effectiveness Videos
Anatomical features of abutment teeth
Chewing force is the physiological pressure exerted by the muscles of the mandibular structure. The abutment teeth play an important role in this process, helping to grind food and form a partially chemically processed food lump for further swallowing.
To assess the chewing efficiency, the strength and anatomical structure of all elements of the jaw structure are of great importance. For the force of physiological pressure, the compression power of the weakest of the abutment teeth is taken.
This value is determined based on the following features of the morphological structure:
- chewing surface area;
- number of roots;
- the degree of tuberosity;
- the interval between the abutment tooth and the angle of the mandibular bone;
- the functional state of the periodontium - the complex of soft tissues surrounding the dentin, which hold the incisor in the alveolar bed;
- transverse canals of the neck.
Abutment teeth are used to attach prostheses when restoring chewing function using an artificial structure. They are selected based on the results of a comprehensive diagnostic examination.
The dentist studies the type and features of the bite, the relationship of the proposed abutment tooth with the neighboring ones, the general condition of the periodontal tissues. The dentist evaluates the mobility and strength of the dentin element. What matters is the proportion between the length of the root of the abutment tooth and the size of the crown to be installed.
Agapov's chewing efficiency is the volume of chopped food for a certain period of time. This factor is important when choosing pillar elements for installing a bridge structure. The formula for the sum of the coefficients for each side of the jaw apparatus: 0 + 5 + 6 + 4 + 4 + 3 + 1 + 2 = 25%
Requirements for abutment teeth
Such units must meet several criteria.
Key Requirements:
- intact (intact and uninfected) periodontal tissues;
- sufficient area and height for the installation of a clinical crown;
- proper occlusive properties;
- location at a short distance from the defect to be corrected.
- healthy tissue of the tooth chosen as supporting;
- the integrity of the enamel coating.
 These requirements are almost never fully met. Usually, teeth requiring dental intervention or already treated teeth are located near the defective area of the jaw apparatus.
These requirements are almost never fully met. Usually, teeth requiring dental intervention or already treated teeth are located near the defective area of the jaw apparatus.
When choosing support units, the high mechanical stress created by the prosthetic structure on the periodontal tissue and the bone fibers of the tooth is taken into account. This increases the risk of developing a pathological process and increases the frequency of exacerbations of chronic diseases of the dental cavity.
The installation of the bridge structure on the selected supports is carried out only after a detailed diagnostic examination and the elimination of all defects amenable to therapy. Compliance with the requirements for abutment teeth ensures the proper functionality of the prosthesis.
For patients seeking dental care, there are virtually no ideal conditions for placing crowns. It is permissible to use teeth with caries as supports after carrying out the necessary therapeutic procedures.
Pulp inflammation is eliminated by obturation (blockage) of the canals with filling material. Teeth with chronic periodontitis can be used as supporting teeth after the required therapeutic measures have been taken.
Crowns and prosthetic bridges are installed even on incisors affected by a fistula or cyst, provided that the size of the root part is sufficient for installation. Preliminary, the apex of such a tooth is resected and the internal cavity is filled.
Condition assessment
When crushing and chewing solid food, fragments of the jaw rows experience an increased load both in the vertical and lateral planes. The force and pressure vector are determined by the type of dental element and its preserved functional parameters.
Standard level of stress on teeth of different types:
| Variety | Pressure force, kg |
| Incisors | 5-10 |
| Fangs | 12-15 |
| Premolars | 15-20 |
| Molars | 20-30 |
These values are not limiting for the indicated teeth and the surrounding periodontal tissues. Half of the maximum permissible chewing load is indicated. The remaining 50% is a reserve used for prosthetics.
Agapov's chewing efficiency provides for an accurate calculation of the expected load before the installation of crowns and bridges. When choosing reference points, the functional state of all anatomical structures and morphological complexes involved in the formation of the food bolus is assessed.
Elements that will serve as the basis for an artificial structure for a long time are being investigated for:
- periodontal tissue health;
- bite features;
- occlusive interaction of chewing fragments in the area of the defect to be repaired;
- stability in the alveolar bed;
- the ratio of the size of the crown and root part of the tooth;
- the quality of the filling, if performed;
- the shade of the enamel coating;
- the level of mechanical abrasion;
- placement and spread of teeth in the jaw row.
Assessment of the anatomical state of the masticatory apparatus is carried out:
- visual inspection;
- sounding methods;
- percussion;
- X-ray examination;
- palpation of the alveolar process.
To clarify the mechanism of occlusive interaction, a special diagnostic model-impression is used. X-ray allows you to assess the presence and degree of atrophy of dentin tissue and morphological periodontal complex.
Investigate the ratio of the inner and outer surfaces of the alveolar bed to determine the stability and stability of the abutment tooth. When mobility is detected, a reinforcing splint is installed, attaching it to closely spaced elements.
The anatomical configuration of the crown is important. It is especially important when installing a prosthesis on a clasp system. Relative contraindications for using a tooth as a support include a conical shape and insufficient height. In such a situation, the build-up procedure is performed.
Causes and signs of deviations
The chewing function is impaired with caries, periodontal disease, mechanical damage to the jaw apparatus.
Etiological factors are subdivided into:
- infectious;
- pathological;
- traumatic.
With caries, pathogens destroy the mineral-organic components of the outer enamel coating and dentin. As a result, there is a deviation of the chewing efficiency from the established normal indicator.
With the progression of dental caries, acute inflammation of the pulp and connective fibers of the slit cavity between the dental root and the alveolar plate occurs.
A common cause of chewing dysfunction is periodontal disease. The pathological condition is characterized by dystrophic changes in the connective fibers.
Teeth become unstable and loose. Typical signs of periodontal disease are bleeding gums and pain when pressing on the segments of the jaw row affected by the pathological process.
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- bacterial viral infection;
- impaired metabolism;
- digestive dysfunction;
- hypovitaminosis;
- unbalanced diet.
Chewing efficiency, determined by the Agapov method, often deviates from the norm due to malocclusion and anatomical destruction of individual elements of the jaw apparatus.
A congenital or acquired deformation of the dentition can lead to such a disorder. The loss of a certain number of chewing elements, provoked by pathological reasons or functional overload, causes anatomical distortions of the morphological complex of chewing.
One of the reasons for the decrease in the efficiency of chopping food, dentists call disruptions in the work of the adductor muscles of the dentoalveolar mechanism.
Etiological factors of this condition:
- spasm with tetanus or meningitis;
- neurological disorders;
- paralysis of individual muscles;
- postponed traumatic brain injury;
- infectious lesions.
Extensive or local inflammation in the dental cavity leads to a violation of the chewing function. These include gingivitis and stomatitis. They impede the formation of a nutritive lump and its chemical treatment with salivary fluid.
Such pathologies are manifested by an increase in pain sensitivity of dental cells and the occurrence of anaphylactic reactions. A separate etiological category is diseases of the temporal and mandibular joints.
Significantly reduce chewing efficiency:
- arthritic destruction;
- arthrosis - dystrophic changes in the articular cartilage;
- tendinitis - an inflammatory deformation of the tendons;
- synovitis.
Inflammation of the synovium of the bursa is most often affected by elderly patients.
Average values of pressure on teeth in kilograms
Chewing efficiency is measured by a dynamic method or gnatodynamometric method using a special device. The average value for the anterior teeth is 15-36 kg, and for the molars - 45-78 kg. This indicator is taken into account when installing prostheses.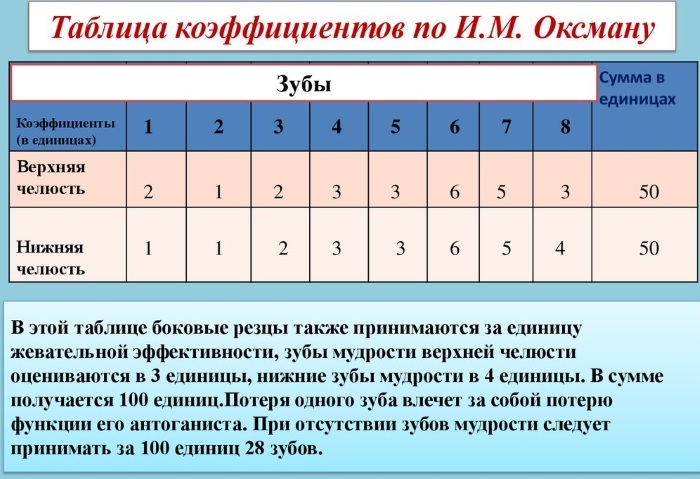
It determines the susceptibility of the periodontal tissues to mechanical pressure and allows the correct selection of the bridge structure. Average values are based on practical observations.
In women, the chewing pressure on the incisal teeth is 20-32 kg, and in men - 25-45. N. AND. Agapov compiled tables of distribution of the minimum, average and maximum pressure maintained by each element of the jaw row.
The cumulative ultimate endurance of the periodontal morphological complex surrounding the tooth is 936 kg for women and 1408 for men. In practice, it is not implemented, since the contractile power of the muscles of the jaw apparatus is limited to 390 kg.
Calculation principles
Gnatodynamometry is an outdated technique for determining the chewing ability of the muscles of the jaw apparatus, the endurance of the morphological complex of periodontal disease and dental elements. This method is rarely used in modern dental practice due to a number of significant disadvantages.
The gnatodynamometer only determines the pressure in the vertical plane, excluding the horizontal and radial compressive forces. Therefore, the method does not give a very accurate result. The spring in the device deforms quickly, which further distorts the readings.
With this method of measurement, the result strongly depends on the patient's psychosomatic state, which is unstable and can change several times throughout the day. The dynamic method allows you to make a more accurate judgment about the chewing ability of the jaw apparatus.
It takes into account all movements and the general condition of the dental complex:
- neuroreflex interactions;
- glandular system;
- motor functions of muscles;
- soft tissues of the oral cavity;
For prosthetics, the developed by S. E. Gelman functional chewing test and physiological test I. From Rubinov. Their essence is similar and consists in grinding a certain amount of the product (almonds or walnuts) with the jaws during the control time.
Load calculation
When choosing and installing dentures, the load capacity of the supporting elements plays a decisive role. Calculate the average and maximum value for the surrounding periodontal tissues. There is a special method for determining these values, which is used for prosthetics.
Chewing efficiency according to Agapov is the main parameter showing the ability of abutment teeth and of the morphological complex of the periodontium to withstand a certain pressure for a long time without negative consequences. This indicator is expressed in an individual coefficient assigned to each unit of the jaw row.
When determining the value, the chewing ability of the entire mechanism of preparing the food bolus for swallowing is taken as 100% efficiency. The starting point is the weakest unit of the dentition. It is a small cutter that is assigned a value of 1%.
Agapov odds
This method of calculating the bearing capacity of each unit of the jaw row involves the use of a gnatodynamometer. The device is equipped with sensors located in a replaceable measuring part. The sensors are connected to a microammeter and contain a brass plate in their construction.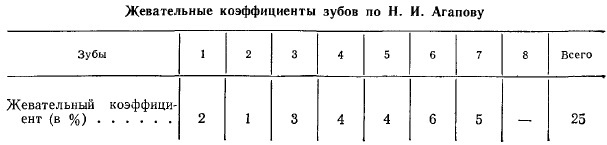
Algorithm for measuring chewing efficiency:
- The patient is seated in a dental chair.
- A measuring element with load endurance sensors is immersed in the dental cavity.
- Next, you need to squeeze the inserted device with your teeth with maximum force.
- The chewing efficiency indicator is recorded on the scale.
The final result is obtained by summing the coefficients of all elements of the jaw arch. Each tooth is counted with a percentage value up to 1 to 6. The definition is carried out by the number of paired units of the lower and upper jaws. Single teeth do not actually participate in chewing.
Oxman odds
With this method of counting, chewing ability is calculated according to a specially developed anatomical and physiological scheme. The load susceptibility of each unit of the jaw row is evaluated, taking into account the surface area of the pressure and the cutting edge.
Oxman's coefficient takes into account the topology of the dental plane and the physiological state of the roots. For such a method of determination, it is important to study the features of the morphological structure of the periodontium and evaluate the functional and chewing value of each unit of the jaw row.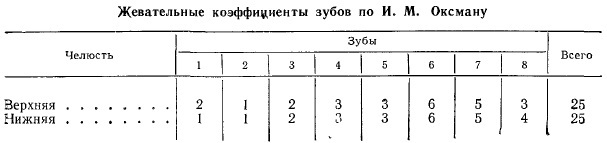
Based on this data, all elements are assigned coefficients of 1-6. The end result is obtained by summation. The difference between the endurance of periodontal tissue and dentin tissue, not exceeding 2 points, is considered normal.
Decoding chewing coefficients
The effectiveness of the jaw mechanism depends on the ability to crush food of the weakest link in the system - the small incisor. This is the constant from which the rest of the coefficients are measured. Each tooth is assigned a constant value. Any deviation is considered a decrease in the chewing efficiency of the entire jaw row.
The digestive value of dentin, according to this technique, does not depend on the functional state of the periodontal tissues. The mobility of the tooth in the alveolar bed does not affect the coefficient. This is a significant disadvantage of the calculation method proposed by Agapov.
In practice, during prosthetics, Oksman's physiological corrections are introduced into it. Mobility classes are assigned to chewing units. In the first of them, stability is considered absolute and is taken as 100%. In the 2nd class, the chewing efficiency is 50%. The 3rd and last category is equivalent to the absence of a dental element.
Measures to be taken in case of lack of support efficiency
The installation of additional stiffeners on the prosthetic structure allows to prevent exceeding the load endurance of the periodontal complex and hard dentin.
In dental practice, a method is used to reduce the functional area of the crown to the size of the premolar. Another option is to flatten the topology of the plane of the reference unit, eliminating the tuberosity entirely.
This allows the elements of the jaw arch to withstand high mechanical stress. To eliminate the lack of chewing efficiency of abutment teeth, dentists create an additional contact area between the natural structures and the prosthetic structure.
This increases rigidity, increases load-bearing capacity and engages in the physiological process. chewing food periodontal even in the case of significant damage and reduced functionality fabrics.
Features of the installation of the bridge structure
Chewing efficiency according to Agapov provides for the observance of several prerequisites for the installation of a jaw prosthesis. It is selected and designed in such a way as to neutralize the natural defects of the morphological complex.
The coefficient sum of the supporting units should exceed the tabular index of the chewing efficiency of the missing teeth by 2 units or more. The supports belonging to the same functional category are selected.
Their number should fully compensate for the loss of natural chewing ability as a result of:
- alveolar dystrophy;
- pathological instability in the bed;
- insufficient dimensional proportion between the length of the root system and the height of the coronal segment;
- damaged state of the morphological complex of the periodontium.
Additional stiffeners of the bridge structure are connected by splinting or integrated into the prosthesis to partially relieve the load from the weakened anchor points.
Clasp devices
The units of the jaw arch for the attachment of such a prosthesis must meet the general requirements and special conditions. Before installing the clasps, the abutment teeth are given the correct anatomical configuration by grinding, grinding and building up.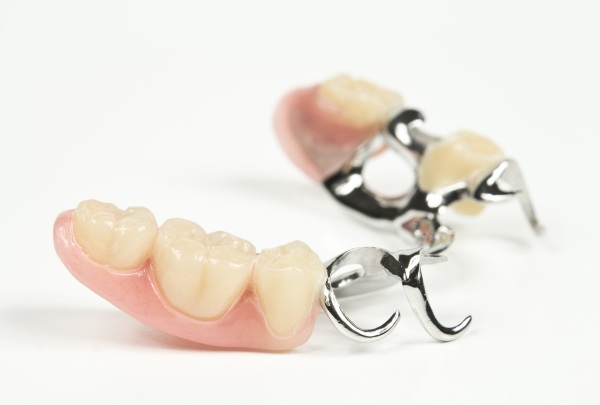
Tapered and too low supports with a bare root collar are not suitable for such an attachment. Elements with such defects are first brought into a form suitable for installing a crown, and then an anatomically flawless artificial structure is installed.
It is necessary to ensure the parallel arrangement of the abutment teeth in order to avoid distortion of the prosthesis. The minimum deviation during the installation of the fixing clasp devices is allowed, but the use of the holding devices requires strict parallelism.
It is necessary to ensure the ideal interaction of the mandibular supports with similar elements located on the maxillary arch. When using an onlay or augmenting dental composition on one of them, the bite will inevitably be distorted and it will not be possible to achieve chewing efficiency.
Therefore, complete symmetry is required. If necessary, use a special occlusal foot or install a crown with a cervical protrusion. The latter option is used for hyperestization of the enamel coating or tilt of the support towards the defect to be repaired.
Clasps are installed along an imaginary straight line. It should go through the center of the anchor points. Chewing efficiency is restored by a clasp construction with clasps of the supporting-holding type. For it, the coefficient is calculated according to the Agapov method, taking into account the additional load created by such a prosthesis.
Chewing Effectiveness Videos
Technologies for restoring chewing efficiency:



