Azithromycin is a potent drug, which is used in the treatment of acute and chronic bronchitis, as well as other inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. This drug belongs to the pharmacological group of synthetic macrolide antibiotics, which is a subgroup of azalides.
Azithromycin is indicated for a course admission for adults and children who have been diagnosed with infectious bronchitis nature of origin, and pathogens are sensitive to the constituent substances of this medication. Reviews of the majority of patients who followed Azithromycin therapy confirm its excellent pharmacological properties.
Record content:
- 1 Forms of release and composition of the drug
- 2 Pharmacological properties
- 3 Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- 4 Indications for use
- 5 Contraindications
- 6 At what age can the drug be used?
-
7 Instructions for use, dosage
- 7.1 For children
- 7.2 For adults
- 8 Side effects
- 9 Overdose
- 10 special instructions
- 11 Drug interactions
- 12 Analogs
- 13 Terms, conditions of sale and storage
- 14 Price
- 15 Video about the drug
Forms of release and composition of the drug
Azithromycin is an effective drug used in the treatment of bronchitis, the main form of release of which is round tablets, coated with a protective shell. This medication has a rich white color.
The drug is produced in dosages of 125, 500 and 1000 mg, depending on the individual needs of each patient. Azithromycin is packed in blisters made of plastic and sunscreen foil.
Each pack contains 1 or 2 blisters with tablets. The main packaging of the antibacterial agent is a rectangular cardboard box, complete with detailed instructions for its use. Reviews of patients who took Azithromycin confirm a fairly convenient form of release of this medication. 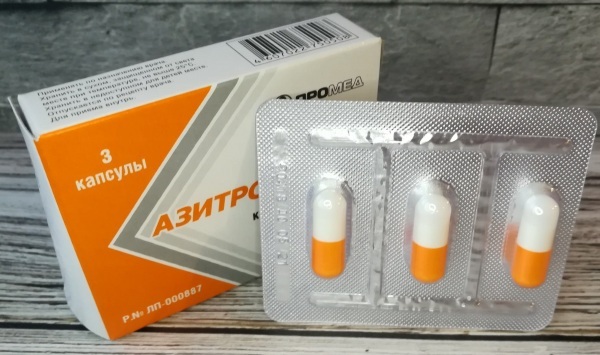
Azithromycin tablets have a simple but effective biochemical composition. The table below describes in detail the main and auxiliary components of this medication.
| Components of the medication | Pharmacological properties |
| Azithromycin dihydrate | This is the active substance of the drug, which has a pronounced antimicrobial effect. It has a direct effect on harmful microorganisms, slowing down their growth and reproduction. When using large dosages of this medication, the bactericidal properties of Azithromycin are realized. |
| Lactose (milk sugar) | Tablet excipient that is a natural preservative. This component is contraindicated in patients suffering from individual lactose intolerance. |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | This is an auxiliary component that is part of the protective coating of the tablets. It is considered a neutral substance that does not react with other chemical compounds. |
| Titanium dioxide | It is used as a safe colorant that gives the tablets a snow-white hue. It is found in the food and pharmaceutical industries under the E 171 label. |
| Magnesium stearate | It is an anti-caking agent that makes the structure of the drug more dense and prevents its premature disintegration. |
| Povidone | This is an excipient of this medication, which is a water-soluble polymer. Povidone acts as a chemical stabilizer for Azithromycin. |
| Talc | Talc is an additional component that is used so that the tablets do not break down to the state of the powder during transportation, storage and practical use in therapeutic purposes. |
All of the above components are completely safe for the human body, do not have carcinogenic, toxic or mutagenic properties.
Pharmacological properties
Azithromycin for bronchitis (reviews of patients taking this drug indicate its excellent therapeutic properties) shows high efficiency in the fight against the main microorganisms that provoke its development.
This antibacterial agent has the following pharmacological properties:
- has a pronounced antimicrobial effect;
- helps to suppress the acute inflammatory process, stabilizing the general well-being of the patient;
- exhibits bacteriostatic activity in the case of taking standard therapeutic doses;
- accelerates the process of restoring the stable functioning of the respiratory system;
- increases the body's resistance to pathogens of pathogenic infection, which provoked the development of bronchitis of bacterial etiology;
- has a bactericidal effect in the treatment of the maximum permissible doses of this medication.
Full implementation of the pharmacological properties of Azithromycin is possible only if the instructions are strictly followed. on its use, as well as the dosage regimen established for the fight against infectious microorganisms of a specific strain.
This agent is not effective against bacterial agents that are not sensitive to its active ingredient. In this regard, before starting therapy with Azithromycin, it is imperative to undergo a study on the microflora of mucus, which comes from the inflamed bronchi during coughing.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Azithromycin for bronchitis (reviews of pulmonologists who prescribe this drug to their patients are positive) allows suppress signs of an acute inflammatory process, reduce the frequency of the urge to cough, cleanse the respiratory system from excess amounts mucus.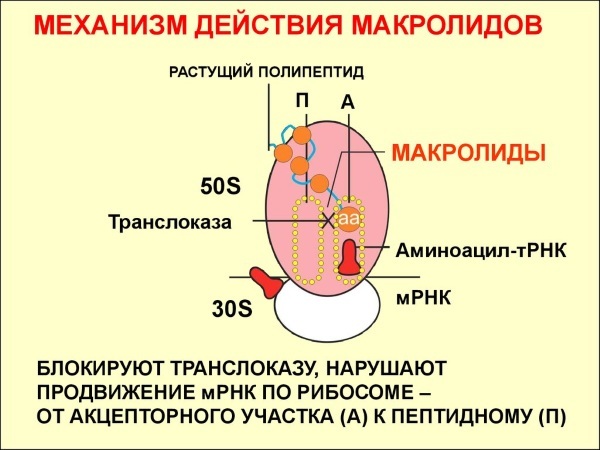
The pharmacodynamics of this medication is characterized by the fact that its active substance has a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. Azithromycin is an exclusively synthetic antibiotic azalide that belongs to the macrolide group. In this regard, most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms do not have natural immunity to its active component.
The mechanism of the antibacterial activity of this medication is to disrupt the process of protein synthesis that occurs inside the cell of an infectious agent. Under the constant influence of Azithromycin, bacterial microorganisms stop dividing, the process of their spread in the organs of the respiratory system slows down.
A patient with acute or chronic bronchitis of infectious etiology begins to feel a positive trend towards a decrease in the inflammatory process in the lower respiratory tract. The use of large doses of Azithromycin allows you to achieve not only a slowdown in the growth of bacterial microorganisms, but completely destroys their cellular structure.
A distinctive feature of the antibiotic Azithromycin is that its active substance is effective against representatives of anaerobic infections, as well as microorganisms that parasitize inside human cells organism.
The following microorganisms have individual sensitivity to the main component of this drug:
- streptococci that cause bacterial pneumonia;
- Staphylococcus aureus (including those strains susceptible to methicillin);
- haemophilus influenzae;
- bacterial infections from the genus Legionel, which cause severe diseases of the respiratory system;
- clostridia;
- mycoplasma;
- enterococcus;
- pathogens of borreliosis;
- chlamydia.
The pharmacodynamic properties of Azithromycin extend to infectious microorganisms that have natural and acquired resistance to antibiotics of the penicillin series. The active substance of this medication is evenly distributed over the tissues of the lungs and bronchial tree.
Pharmacokinetics of Azithromycin is characterized by its rapid dissolution in the gastrointestinal tract with further absorption into the general bloodstream. After a single dose of a therapeutic dosage in the form of 500 mg of the drug, the bioavailability of its main component reaches 37%. The primary metabolism of Azithromycin occurs immediately after it enters the liver tissue.
In this regard, the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma rapidly decreases, and its maximum is reached 2 hours after taking the standard dose of this antibiotic. The transportation of the active substance of the drug is carried out by phagocytes, and its release occurs directly in the focus of infectious infection of the bronchi and lung tissues.
Azithromycin easily overcomes all types of histohematogenous barriers. In this regard, the presence of this medication can also be found in the tissues of other internal organs. The metabolism of this antibacterial agent occurs in the liver tissues. The resulting half-life products do not have antimicrobial properties.
The period of metabolic transformation of Azithromycin has a long duration, which varies from 35 to 50 hours. The therapeutic concentration of the active substance remains in the blood plasma for the next 7 days from the moment of taking the last dose.
Only 6% of Azithromycin is excreted from the patient's body by the kidneys. The rest of the decay products are utilized from the body through the intestines.
Indications for use
Azithromycin for bronchitis (reviews of the medication are positive in 9 out of 10 cases) is used as the main drug, or it is included in the course of general antibiotic therapy.
In general, this drug is indicated for use in the following cases:
- infectious lesion of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- inflammation of the inner ear;
- acute tonsillitis;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- sinusitis with a sluggish inflammatory process, or in an exacerbation stage;
- pharyngitis;
- pneumonia;
- acne, as well as dermatological infections;
- bacterial infection of the urogenital organs (as a monotherapeutic agent, this drug is used only if there are no signs of complications);
- Lyme disease
- erythema of the migratory type.
The drug Azithromycin is equally effective in the treatment of chronic and acute bronchitis. The main thing is that the infectious microorganisms that caused this disease have individual sensitivity in relation to its active component.
Contraindications
Azithromycin for bronchitis (reviews of the drug are positive from doctors and patients) and other infectious diseases of the body categorically contraindicated for use in the following cases:
- a tendency to manifest allergic reactions to antibacterial agents related to the pharmacological group of macrolides and ketolides;
- severe violations of the functional activity of the liver and kidney tissues (taking this medication can aggravate the current diseases of these organs);
- the state of pregnancy;
- lactation of a newborn baby with mother's milk;
- simultaneous therapy with drugs based on dihydroergotamine, as well as ergotamine.
 The antibiotic Azithromycin is prescribed with extreme caution to elderly patients, patients with concomitant diagnosis in the form of myasthenia gravis, bradycardia, heart failure, hypokalemia, arrhythmia, with a violation of water-salt balance.
The antibiotic Azithromycin is prescribed with extreme caution to elderly patients, patients with concomitant diagnosis in the form of myasthenia gravis, bradycardia, heart failure, hypokalemia, arrhythmia, with a violation of water-salt balance.
At what age can the drug be used?
Azithromycin is indicated for admission to children who have reached the age of 12 years, and also have a body weight of more than 45 kg. Otherwise, the medication is contraindicated, as the risk of side effects and other undesirable reactions of the body increases.
Instructions for use, dosage
Azithromycin tablets are taken orally, regardless of the schedule, diet and diet.  The duration of the therapeutic course is set individually and depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms.
The duration of the therapeutic course is set individually and depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms.
For children
Children over 12 years old who have signs of acute or chronic bronchitis should take 500 mg of this antibiotic once a day. In the absence of complications and the presence of positive dynamics to recovery, Azithromycin is taken within 3 days. Dermatological infections and progressive acne require taking 250 mg of the medication 2 times a day.
The duration of treatment is 3 to 9 days. Therapy for erythema migrans involves taking Azithromycin at a dosage of 500 mg 2 times a day on the 1st day from the start of treatment, followed by a switch to 500 mg of the drug daily. The general course of treatment is 5 days.
Urethritis, acute cervicitis, as well as other infections of the genitourinary system, require taking 500 mg of Azithromycin 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor based on the results of a microbiological study.
For adults
For patients of the adult age group, the same dosage and procedure for taking Azithromycin tablets are provided, as for children over 12 years old.
Side effects
Therapy with the antibacterial agent Azithromycin may be accompanied by the following side effects:
- diarrhea;
- cramping pains inside the abdominal cavity;
- loss of appetite;
- yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- necrotic processes in the tissues of the liver;
- anaphylactic shock;
- tachycardia;
- the appearance of red rashes on the body, accompanied by itching;
- increased nervousness;
- feeling anxious and panic attacks;
- increased aggressiveness;
- renal failure;
- vaginitis or progressive candidiasis.
 Patients who show signs of Azithromycin side effects should discontinue further use of this antibiotic, as well as seek additional advice from your to the attending physician.
Patients who show signs of Azithromycin side effects should discontinue further use of this antibiotic, as well as seek additional advice from your to the attending physician.
Overdose
Violation of the dosage regimen with Azithromycin, which is established by the instructions for use of this drug, entails the onset the following symptoms:
- loose stools;
- complete hearing loss, which is of a short-term nature (as the antibiotic is removed from the body, the functions of the inner ear are restored);
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- discharge of vomit.
In case of an overdose with Azithromycin, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the signs of intoxication of the body. For this, the patient must take sorbent preparations, undergo a gastric lavage procedure. Intravenous droppers with isotonic solution are indicated for patients with signs of impaired water-salt balance.
special instructions
Throughout the course of therapy, it is recommended to be especially careful during administration vehicles, machinery and equipment that requires increased attention and quick psychomotor reactions.
In case of unintentional skipping of the therapeutic dose of Azithromycin, the next pill must be taken as soon as possible. Patients with hypersensitivity to the main component of the antibiotic may observe signs of an allergic reaction 5-7 days after the complete withdrawal of the drug.
Drug interactions
It is not recommended to carry out simultaneous therapy with Azithromycin and other drugs in the form of Fluconazole, Co-trimoxazole, Cyclosporine, Midazolam, Digoxin, Terfenadine, Zidovudine. Concomitant use of ergotamine-based drugs increases the risk of liver toxicity.
Analogs
There are many antibacterial agents on the pharmacological market that have identical properties and contain the active substance azithromycin. The table below shows drugs analogs of Azithromycin, as well as their average cost in retail pharmacy chains.
| Drug name | average cost |
| Azitral | RUB 290 |
| Azitrox | 342 r |
| Sumamed | 371 r |
| Hemomycin | 333 r |
| Zitrolide forte | RUB 208 |
| AzitRus | 121 RUB |
The appointment of the above medicines should be carried out exclusively by a general practitioner, infectious disease specialist, pulmonologist, pediatrician (if signs of bronchitis are diagnosed in a child). The unauthorized use of these analog drugs is contraindicated, as it can harm the patient's health.
Terms, conditions of sale and storage
The release of Azithromycin tablets is carried out only with a doctor's prescription.  The medicine should be stored in a dark and dry place where the air temperature does not exceed +25 degrees Celsius. The shelf life of this drug is 3 years, after which its further use is prohibited.
The medicine should be stored in a dark and dry place where the air temperature does not exceed +25 degrees Celsius. The shelf life of this drug is 3 years, after which its further use is prohibited.
Price
The average cost of the drug Azithromycin in a therapeutic dosage of 500 mg is 215 rubles. per packing.
Azithromycin is a potent antibiotic from the macrolide pharmacological group. This drug has a completely synthetic nature of origin, which makes it effective against most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms.
Regular intake of Azithromycin allows you to destroy bacteria that are resistant to penicillin antibiotics.
In acute and chronic bronchitis, this medication is used in short therapeutic courses lasting from 3 to 5 days, but in a dosage of at least 500 mg per day. Reviews of this antibiotic are predominantly positive, which confirms its high efficiency.
Video about the drug
Doctor about Azithromycin:



