Azithromycin is a domestic antibiotic with a large spectrum of action. The drug allows you to destroy the infection in a short time and at the same time has a small list of side effects in comparison with other antibiotics.
In this regard, the remedy is popular for the treatment of children. Of the variety of dosage forms, Azithromycin in the form of a syrup is considered the most convenient in dosage and use.
Record content:
- 1 Release form and composition of the drug
- 2 Pharmacological properties
- 3 Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- 4 Indications for use
- 5 Contraindications
-
6 At what age can the drug be used?
- 6.1 Instructions for use, dosage for children
- 7 Side effects
- 8 Overdose
- 9 special instructions
- 10 Drug interactions
- 11 Analogs
- 12 Terms, conditions of sale and storage
- 13 Price
- 14 Video about the drug Azithromycin
Release form and composition of the drug
Azithromycin is produced in the form of a powder for preparing a suspension (the agent is not produced in the form of a ready-made syrup). The powder is white in color and also has a caramel (or fruity) aroma and flavor. The product is placed in plastic bottles in the amount of 20 g. For convenience of dosing, a measuring spoon or a measuring syringe is included in the package along with the bottle.

The main element of the same name (azithromycin, which has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect), the preparation may contain 100 or 200 mg per 5 ml.
Also, the antibiotic contains:
- xanthan gum. Used as a thickener and stabilizer. Additionally, the substance attracts toxins and accelerates their removal, and also improves the absorption of the drug in the intestine;
- colloidal silicon dioxide. The component allows you to keep the powder flowing (not to crumple during storage), and also attracts toxins and removes them from the body;
- sucrose. The substance imparts a sweetish taste to the suspension;
- sodium phosphate. The element is an emulsifier (that is, gives the finished suspension the desired appearance) and a stabilizer;
- hyprolosis. The component protects the mucous membrane of the digestive tract from the harmful effects of the remaining components of the antibiotic;
- titanium dioxide. The substance gives the powder the desired white color;
- flavors. Manufacturers can use different flavors, more often they use caramel, strawberry, vanilla, as well as banana or raspberry.
Azithromycin can be bought not only in the form of a powder for suspension, but also in the form of tablets, capsules and a lyophilisate for preparing a solution for injection.
Pharmacological properties
Azithromycin is an antibiotic with a fairly wide range of action. That is, the tool is used to eliminate pathologies that are caused by the activity of pathogenic bacteria.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Azithromycin - syrup (for children, this form of antibiotic release is more convenient to use), which after oral administration immediately enters the focus of concentration of pathogenic microbes and disrupts protein synthesis in bacterial cells, and also suppresses the process of their growth and reproduction.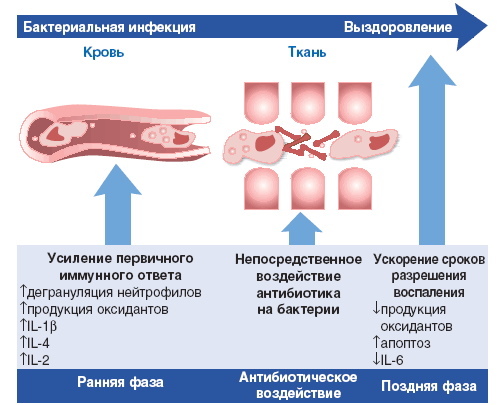
As a result, new cells of the pathogenic infection do not appear, and the existing ones quickly die. The main element can penetrate all tissue barriers in the body.
The effect of the drug is observed approximately within 2-3 hours after taking the drug. In this case, most of the active substance is concentrated in the tissues (mainly in the places of localization of the infection), a smaller part enters the blood. Azithromycin penetrates into the tissues of the urinary and respiratory systems, as well as into the skin and muscles.
The antibacterial effect can persist for 5-7 days after the end of the therapeutic course. The active element of the antibiotic is metabolized in the liver, and the metabolites no longer have antibacterial activity. The agent is excreted from the body mostly through the intestines (about 50%) and about 6% through the kidneys.
Indications for use
Azithromycin should be used only after the patient has passed tests and the type of pathogen has been identified. Since the remedy is not effective for viral and fungal pathologies, on the contrary, the use of a medication will provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
An antibiotic is prescribed by specialists to eliminate pathologies that are listed in the table below:
| Indication lists | Examples of diseases |
| Detection of bacterial infection in the tissues of the upper and lower respiratory tract | For example, bacterial rhinitis, bacterial pneumonia, tonsillitis. |
| diagnosing a bacterial infection in the ear tissues | Otitis media can be both external and middle or internal. Treatment is more often used in a complex with the use of local antibiotics and pain relievers. |
| Detection of bacterial infection in soft tissues | For example, suppuration of a wound or suture after surgery. Also, the agent is prescribed to prevent the development of bacterial infection in fractures. |
| Diagnosis of pathogenic bacteria in the organs of the urinary system | For example, urethritis (damage to the urethra by the inflammatory process of a bacterial nature), cystitis (inflammation of the bladder of bacterial etiology). |
| Identification of pathogenic bacteria in the genitals | For example, cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix as a result of the action of pathogenic bacteria), chlamydia (bacteria can infect both external and internal genital organs). |
| Diagnosing stomach ulcers | The development of pathology is more often triggered by the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori. |
| Identification of bacteria in the digestive tract | For example, salmonellosis, dysentery, botulism. |
| Tick-borne bacterial diseases | Borreliosis at the initial stage, erythema migrans. |
| Dermatological pathologies complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection | For example, erysipelas (manifested by reddening of the skin and fever), impetigo (manifested by pustular eruptions), the presence of acne (when the rash manifests itself in a severe form). |
Also, Azithromycin is prescribed for acute respiratory infections, which proceed in a severe form and are complicated by the ingestion of a bacterial infection.
Contraindications
Azithromycin is a syrup for children that can only be used after being prescribed by a pediatrician. It is an antibiotic that can cause serious side effects. When prescribing, the specialist not only determines the need for the use of the medication, but also the exact dosage, and also identifies the presence of contraindications.
The list of prohibitions for the use of Azithromycin includes:
- intolerance to the substances that make up the suspension;
- the presence of the likelihood of an allergy to the components of the antibiotic;
- diagnosing severe liver diseases;
- severe renal impairment.
Also, Azithromycin must be taken with caution and under the supervision of a specialist in the following cases:
- the patient has myasthenia gravis. Pathology is characterized by rapid muscle tissue fatigue;
- violation of the activity of the kidneys and liver in mild and moderate severity;
- with severe arrhythmia. It manifests itself as a violation of the rhythm of heart contractions;
- in case of violation of the water-salt balance in the body. For example, when the illness is accompanied by profuse vomiting and diarrhea;
- if the patient has bradycardia. Pathology is manifested by a low value of the number of heartbeats;
- severe heart failure;
- the patient has diabetes mellitus.
The main element of the antibiotic penetrates the placenta, so the use of the medication during the period of gestation is prohibited.
Also, during lactation, it is necessary to transfer the baby to artificial feeding for the period of taking the antibiotic. It should be borne in mind that the active substance is excreted from the body within a week after the end of the course.
At what age can the drug be used?
Azithromycin in the form of a suspension is allowed to be given to children after reaching 6 months, but provided that the weight of the baby is at least 5 kg. Also, if the child was born prematurely, then the possibility of using the antibiotic is determined by the pediatrician.
Instructions for use, dosage for children
Azithromycin in the form of a suspension is more often prescribed to eliminate bacterial pathologies in children. This dosage form is more convenient to dose and drink for small patients. Before starting the course, you must first familiarize yourself with the basic rules for the preparation and use of "syrup".
The list of the main subtleties when using Azithromycin in suspension:
- azithromycin should be used only once a day, it is necessary to take the suspension at the same time;
- you need to drink the prepared "syrup" about 1 hour before a meal or approximately 2 hours after a meal;
- after using Azithromycin, the child should be given a drink of water to wash off the remaining suspension from the oral cavity;
- to prepare the suspension, it is necessary to pour filtered water into the bottle with the powder up to the mark indicated on the bottle. Then you need to close the bottle and shake the contents well;
- the bottle must be shaken before each use, since the constituents of the suspension begin to precipitate approximately 20 minutes after its preparation;
- the finished suspension should be dispensed with a special measuring syringe or measuring spoon. In this case, after taking the antibiotic, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the syringe / spoon;
- antibacterial properties are retained in the medication for 5 days, from the date of preparation of the suspension. The required temperature range for storage is indicated in the instructions, as it has different meanings depending on the manufacturer;
- if you accidentally skip the time of taking an antibiotic, you need to drink the prescribed dosage immediately, after finding the pass (the dosage is standard, it is not required to increase it) and then take the medication already counting in a new way (that is, from reception time). For example, Azithromycin was consumed at 2 pm, the pass was found at 6 pm, then the antibiotic should be taken at 6 pm, and the next dose at 6 pm the next day.
When taking a course with Azithromycin, it is recommended to simultaneously take drugs to normalize the intestinal microflora in order to avoid the development of dysbiosis.
The following is the dosage of Azithromycin, depending on the purpose of using the antibiotic:
| Purpose of use | Single dosage per 1 kg of weight | Course duration, days |
| Elimination of pathogenic bacteria in the upper and lower respiratory organs | Requires 10 mg | 3 |
| Diagnosis of bacterial pathologies in the tissues of the ear | It is necessary to take 10 mg for the first 3 days, then the dosage should be reduced to 5 mg. | 5 |
| Detection of bacterial infection in soft tissues | Use 10 mg. If the course is prescribed for up to 5 days, then on days 4 and 5, the dosage must be reduced by 2 times. | 3-5 |
| Elimination of pathogenic bacteria in the organs of the urinary system | Assign 20 mg | 1 |
| Diagnosis of bacterial pathologies in the genitals | Use 10 mg. With the passage of a five-day course, the dosage must be reduced by 2 times after 3 days of treatment. | 3-5 |
| Identifying a stomach ulcer in a patient | Apply at 10 mg. After 3 days, the dosage must be reduced by 2 times. | 5 |
| The presence of pathogenic bacteria in the digestive tract | Use 20 mg for the first 2 days, then the dosage is reduced to 10 mg. | 5 |
| Borreliosis or erythema migrans | The first 24 hours you need to take 20 mg, then the dosage should be gradually reduced to 10 mg. | 5 |
| Dermatological diseases complicated by bacterial infection | Use 10 mg per day for 72 hours. Then a break of 1 week and then 10 mg every 7 days for 9 weeks. | 66 |
| ARI complicated by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the body | Assign 10 mg. If the course is prescribed for 5 days, then the dosage is required for 4 and 5 days to be reduced to 5 mg. | 3-5 |
When calculating the dosage, it should be borne in mind that 10 mg of the drug is 0.5 ml of the finished suspension (when using Azithromycin with a concentration of 100 mg per 5 ml). That is, for example, for a child weighing 5 kg, a single dosage will be 2.5 ml.
Side effects
Antibiotics cannot be used without a doctor's prescription, since the use of a medication is often accompanied by a dangerous negative reaction.
Azithromycin has the following side effects:
- the development of allergic manifestations in different types and forms of severity;
- blurred vision;
- development of vomiting;
- stomach ache;
- frequent and loose stools or, on the contrary, the development of constipation;
- a decrease in the number of lymphocytes and leukocytes;
- development of viral and fungal pathologies in the vagina and oral cavity (thrush is more common);
- headache;
- severe dizziness, fainting;
- the patient may begin to react worse to external irritants;
- the development of seizures;
- change or loss of taste;
- deterioration or loss of smell;
- sharp weight loss;
- an increase in the amount of gas in the intestines;
- breakdown of inflammatory processes in the stomach;
- pathological changes in the composition of the blood, including a decrease in the number of platelets and a decrease in the iron index;
- increased fatigue;
- deterioration in sleep;
- the development of joint pain;
- increased anxiety and nervousness, these symptoms may be accompanied by aggressiveness;
- disruption of the liver and kidneys or exacerbation of pathologies of these organs;
- increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet light;
- a feeling of palpitations and chest pain;
- development or exacerbation of arrhythmia;
- lowering the pressure indicator;
- breathing disorder;
- the development of nosebleeds;
- hearing impairment. It can manifest itself as ringing in the ears and the development of complete deafness.
The listed signs are extremely rare (in about 2% of patients) and are reversible, that is, after the antibiotic is withdrawn, the patient's well-being is restored.
Sometimes there is an increase in the symptoms of the disease. These deviations are typical in cases where bacteria are not sensitive to Azithromycin. And since antibiotics reduce immunity, the disease begins to progress.
Overdose
Azithromycin - syrup (for children, an overdose of medication can be fatal, especially in infants), which should be taken in a strict dosage prescribed by a doctor and no longer than 5 days.
When using the suspension in a large dose or for a longer time, there is an exacerbation of the listed side effects, the development of cirrhosis of the liver is not excluded, followed by the refusal of the organ in work.
In case of poisoning with Azithromycin, it is required to rinse the stomach as soon as possible and immediately give the victim sorbents. If more than 1 hour has passed since the overdose, then an emergency visit to the hospital is necessary to monitor the work of all organs and systems and the selection of treatment.
special instructions
Before using the Azithromycin suspension for the treatment of children, you need to familiarize yourself with the following nuances of its use:
- if the patient has restrictions on use (for example, mild to moderate severity of the kidneys and liver, or diagnosis of diabetes mellitus), you should adhere to the individual course of treatment, which is prescribed by the treating person a specialist. And also it is necessary to monitor the work of the liver, kidneys and check the amount of sugar in the blood;
- if any of the signs of a negative reaction is detected, you need to immediately replace the antibiotic;
- with the development of diarrhea, fixing medications should not be used. It is necessary to take medications to normalize the microflora in the intestine
- in the absence of improvement in the patient on the second day from the start of treatment, it is necessary to check the sensitivity of bacteria to Azithromycin;
- the suspension should not be taken with food, as food reduces the effectiveness of the antibiotic;
- if necessary, rapid penetration of the antibiotic into the blood (required for severe bacterial pathologies) Azithromycin in the form of a suspension is not used, since the agent is found in the blood only 2-3 hours after reception.
It should also be borne in mind that for the period of the course and within 7 days after its completion, it is not advisable to drive vehicles and perform work related to special attention.
Drug interactions
Azithromycin is a syrup (this dosage form can be used for children and adults), which must be used with caution in combination treatment.
With the following medicines:
- a drug for normalizing heart function Digostin and Azithromycin can cause the development of severe poisoning;
- azithromycin enhances the effect of medicines used to thin the blood, as a result, the development of internal bleeding is not excluded;
- heart medications and azithromycin can cause impairment of the heart;
- medicines containing aluminum and magnesium reduce the effectiveness of the antibiotic. In this regard, it is required to take medications at intervals of at least 2 hours;
- Azithromycin enhances the negative reaction of Cyclosporin (immunosuppressant).
When using Azithromycin in combination with other antibiotics, there is an increase in side effects from both medicines. In this regard, when prescribing a drug, a specialist is required to immediately warn about the drugs already used.
Analogs
If the Azithromycin suspension does not "fit" the patient (the drug is not effective for the identified bacteria, the patient there are contraindications or side effects have appeared), then the doctor (only a doctor) must choose the appropriate analogue.
The list of substitutes for Azithromycin includes:
- Sumamed in the form of a suspension. The active ingredient of the antibiotic is also azithromycin. You can use the product from 6 months;
- Azitrox in the form of a suspension. The main element is also azithromycin. The drug is prescribed at 6 months;
- Macropen suspension. The medication is approved for use from 3 years old. The main element of the antibiotic is midecamycin;
- AzitRus suspension. The active ingredient is azithromycin. You can use the product from 6 months;
- Zi-Factor suspension. The antibiotic is prescribed from 6 months. The main element of the drug is azithromycin.
If the patient has an intolerance to the main component, then the drug should be used with another active ingredient.
Terms, conditions of sale and storage
After purchase, Azithromycin powder can be stored for 2 or 3 years (depending on the manufacturer). After preparing the suspension, the antibiotic must be used within 5 days. The temperature range for storing the medication also depends on the manufacturer.
Importantly, the drug can only be purchased with a prescription. After purchase, Azithromycin must be "kept" out of the reach of children.
Price
The cost of the antibiotic depends on the dosage of the main component in the composition, as well as on the manufacturer's company. The price for a bottle with a dosage of 100 mg per 5 ml is 190-250 rubles. And the cost for a bottle with a concentration of 200 mg per 5 ml is in the range from 280 to 400 rubles.
Azithromycin is an effective antibiotic, and its use is accompanied by a minimal list side effects, but only if all the rules of preparation and use are followed "Syrup". It is especially important to adhere to the instructions when using the drug for the treatment of children.
Video about the drug Azithromycin
Azithromycin - instructions for the use of an antibiotic, analogs:


