Lactose is one of the main components human breast milk and milk of animal origin. Lactose is a sugar component in milk and is often referred to as "milk sugar".
It is a disaccharide composed of the monosaccharides glucose and galactose. The global demand for products containing lactose has grown significantly over the past 10 years, and the list of industries for its production has increased accordingly, especially in the USA and Europe.
Record content:
- 1 Compound
- 2 What do they get from
- 3 Beneficial features
- 4 Harmful properties
- 5 Effects on the body
- 6 Side effects
- 7 Products table
- 8 Top 10 products
- 9 Video about lactose
Compound
Lactose, a carbohydrate containing one molecule of glucose and galactose bound together. Comprising approximately 2% to 8% of all mammalian milk, lactose is sometimes called milk sugar. It is the only sugar of animal origin.
Lactose is one of the sugars most commonly found in the human diet. It makes up about 7% of breast milk and about 4–5% of the milk of mammals such as cows, goats and sheep.
Lactose consists of two aldohexoses - β-D-galactose and glucose, linked in such a way that the aldehyde group on the anomeric carbon of glucose can react freely. In other words, lactose is a reducing sugar.
Lactose (O-β-d-galactopyranosyl- (1-4) -β-d-glucopyranose) is an abundant natural disaccharide that, interestingly, it is found only in mammalian milk, where it is the main source of carbohydrates and energy. Lactose is synthesized in the epithelial cells of the mammary gland from glucose and galactose absorbed from the blood.
Lactose exists in the form of two anomers, α and β, which differ in the configuration of substituent groups (OH and H) on carbon 1 of the glucose moiety. Both anomers differ in their properties, with their solubility in water being the most important: the β-anomer is soluble about seven times than the α-anomer at 20 ° C (500 against 70 g / l), but the solubility of the latter is high temperature dependent, so that at 93.5 ° C it becomes more soluble than β-anomer.
Upon dissolution, mutarotation occurs with the formation of a solution in equilibrium with 63% in the β-form. The Α-anomer crystallizes as a monohydrate, and β crystallizes in anhydrous form.
Alpha lactose is very hygroscopic, while other forms are not, so caking and clumping in dairy products due to the first, which must be crystallized before drying, if it is necessary to obtain a non-hygroscopic product.
Lactose (LAK-tose) is a white solid, tasteless and odorless. It occurs in two isomeric forms, α-lactose and β-lactose, the latter being somewhat sweeter than the former. The alpha form tends to occur as the monohydrate (C 12 H 22 O 11 · H 2 O).
What do they get from
Lactose can be made from whey in a process similar to making cheese from a cheese-making by-product, casein. Fermentation of lactose by microorganisms such as Lactobacillus acidophilus, is part of the industrial production of lactic acid.
Lactose-containing foods, topped with the only natural source of significant amounts of lactose, are mammalian milk products. Therefore, the raw material for their production is always whey or whey permeate.
Whey protein is a valuable asset, which is why lactose is currently produced using whey permeate as a starting material. Whey permeate contains 5 to 6% solids, typical dry-based formulations are 85% lactose, 10% ash and 3% protein.
The production of lactose from whey permeate consists of the following steps:
- Concentration. Usually produced by repeated evaporation. In some cases, the permeate is pre-concentrated using reverse osmosis, and concentration together with partial demineralization can be carried out using nanofiltration.
-
Crystallization. It is carried out by cooling from a supersaturated solution. As an alternative, precipitation with alkaline earth metals (Steffen process) and alcohols has been proposed.
- Extraction. Lactose crystals are recovered by decantation or centrifugation. Then the mother liquor containing most of the minerals and about 20% lactose is removed.
- Drying. Lactose crystals containing 5–12% moisture are finally dried in dryers.
- Cleaning. Further cleaning may be required depending on use. Food grade lactose does not require polishing operations, but pharmaceutical lactose requires refining. This includes redissolving the lactose crystals, treating the solution with activated carbon to absorption of a range of solutes, including riboflavin, removal of traces of residual proteins, and recrystallization.
Lactose is synthesized in the mammary glands of mammals. Animal milk contains an enzyme called lactose synthetase, which acts on the compound uridine diphosphate D-galactose to form lactose. The compound is obtained commercially from whey, a by-product of the cheese making process.
Whey solids contain about 70% by weight lactose. These solids are filtered to remove the proteins they contain. After removing the minerals in the whey, the resulting solution contains about 50 to 65% by weight, which allows crystallization from the resulting solutions.
The lactose obtained in this way is a racemic mixture of the D and L isomers. To obtain the alpha isomer, lactose is dissolved in water and treated with activated carbon to remove any color. When water evaporates from solution, α-lactose monohydrate remains.
The product is most commonly available in this form. To obtain the beta isomer, α-lactose is heated with water in the presence of a base, which converts the alpha isomer to the beta form.
Beneficial features
Foods containing lactose, the list of benefits of which has become known thanks to the latest research, helped to reveal that:
- lactose plays a role in the absorption of calcium and other minerals such as copper and zinc, especially during infancy;
- in addition, if it is not digested in the small intestine, the intestinal microbiota (population of microorganisms, which lives in the digestive tract) can use lactose as a nutrient (prebiotic);
- lactose and other milk sugars also promote the growth of bifidobacteria in the gut and may play a lifelong role in counteracting aging-related decline in some immune functions;
- breast milk contains 7.2% lactose (only 4.7% lactose in cow's milk), which provides up to 50% energy needs of the baby (cow's milk provides up to 30% of the baby's need for energy);
- lactose consists of glucose and galactose, two simple sugars that our bodies use not only as a source of energy, but also for the development of the brain and nervous system.

There are many uses of lactose today. In the food industry, lactose is used primarily as an energy source and also when low sweetness is required in the final food product.
Lactose is used in the confectionery industry to improve flavor and color in protein-containing foods, and in the bakery industry to obtain a golden brown crust.
The fortification of cow's milk with lactose is also an important application that aims to mimic the content of lactose in human milk, and a significant demand for lactose is due to its use in the standardization of milk products.
Harmful properties
Symptoms of lactose intolerance usually occur within the first 30 minutes or 2 hours after consuming dairy products. These symptoms can be mild or severe, but not life-threatening. They usually include bloating, feeling of heaviness, cramps, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gas, and nausea.
Lactose-containing foods, dairy topping the list, can cause mild symptoms that can only occasionally become serious.
The persistent onset of symptoms after eating or consuming certain dairy products may be a sign of lactose intolerance. But if you experience recurrent bouts of discomfort, this does not necessarily mean that you are lactose intolerant.
Although the symptoms are similar, lactose intolerance is not the same as a dairy allergy. Dairy allergy is an immune response to milk protein, whereas lactose intolerance occurs when an enzyme called lactase is deficient.
The small intestine produces lactase to break down milk sugar (lactose) into simple sugars, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream. Insufficient lactase levels can cause symptoms of lactose intolerance.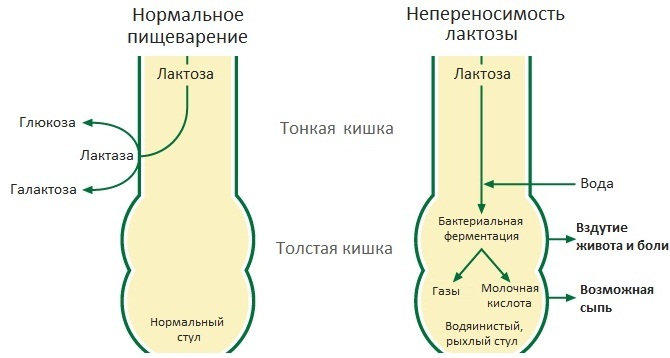
A health care provider diagnoses lactose intolerance based on family history, diet, and the prevalence of symptoms shortly after eating. Another way to confirm lactose intolerance is by physical examination and other medical tests.
In addition to avoiding dairy products, many dairy producers today offer lactose-free or lactose-reduced dairy products. The products are made by manufacturers who process regular milk with the lactase enzyme to break down lactose.
The notable difference between regular and lactose-free milk is that it tastes slightly sweeter than regular milk. In terms of storage and shelf life, lactose-free milk will store the same amount of time as regular milk.
Although there is no cure for lactose intolerance, reducing or eliminating the amount of dairy in your diet can reduce symptoms.
But since dairy is the main dietary source of calcium, if you choose to eliminate it entirely, consider adding other calcium-rich foods to your diet, such as broccoli, spinach, or canned salmon.
Some people with lactose intolerance may actually tolerate low-fat dairy products and may slowly introduce new foods. In addition, hard cheeses such as cheddar or Swiss are lower in lactose and may not cause symptoms in people with lactose intolerance.
However, many processed foods, including cereals, instant soups, and salad dressings, contain milk and lactose, so if you experience symptoms of lactose intolerance, be sure to read the labels carefully before purchasing these products
Effects on the body
The daily intake of lactose is approximately 40 g. It fills the body with energy, helps to normalize intestinal activity, reduces the development pathogens, contributes to the improvement of the gastrointestinal microflora, prevents the development caries.
Young children are most often affected by lactose deficiency. In adults, there were no obvious signs of lactose deficiency.
Indirect signs of lactose deficiency:
- lethargy;
- drowsiness;
- instability of the nervous system.
As for the excess of lactose in the body, everything is a little more complicated here, since this can entail quite serious consequences:
- symptoms of general poisoning of the body;
- allergic reaction;

- bloating;
- loose stools or constipation.
Side effects
Many people are lactose intolerant. Lactose intolerance is a condition that develops when a person lacks the enzyme lactase, which is responsible for the absorption of lactose in the body.
People who are lactose intolerant and consume lactose experience a number of unpleasant symptoms, including fluid retention, gas, cramps, and diarrhea. By some estimates, up to 75% of the world's population may be more or less lactose intolerant.
One way to combat lactose intolerance is for the person to avoid eating any food or food that contains lactose. This possibility has been somewhat simplified by the introduction of lactose-free products.
Another method to avoid the problems associated with lactose intolerance is to use biodegradable an active supplement containing lactase, which restores an enzyme for the body that it naturally lacks.
Foods containing lactose, the list of which is topped by dairy products such as yogurt, kefir, do not necessarily contain less lactose, but may easier to carry, as the bacteria used in the cultivation process naturally form an enzyme that promotes degradation lactose.
Products table
| Products containing lactose, list | Quantity (g) | Serving Lactose Content (g) |
| Skimmed milk | 250 | 8.5–12.8 |
| Reduced lactose milk | 250 | 2.5–3.5 |
| Skimmed milk powder | 30 | 11.6 |
| Processed cheese | 30 | 0.4–4.1 |
| Yogurt | 250 | 4.3–17.6 |
| Butter | 10 | 0.1 |
| Ice cream | 250 | 5.5–14.4 |
| Cottage cheese | 250 | 7-8 |
| Cream | 250 | 3.1 |
| Dry serum | 100 | 0,7 |
| Milk chocolate | 100 | 9.5 |
| Parmesan cheese | 100 | 0.05-3.2 |
Top 10 products
High lactose foods are those that contain milk. These include ice cream, milk puddings, hot chocolate, eggnuts, mac and cheese, yogurt, pancakes, milk chocolate, cottage cheese, and mashed potatoes.
Below is a list of the top 10 foods with the highest lactose content, calculated as 100 g:
- Breast milk - 6.5-7.1%
- Infant formula - 5.1-7.00%
- Cow's milk 2% fat - 4.6%
- Goat milk - 4.5%
- Kefir - 3.8-4.1%
- Cottage cheese - 4%
- Yogurt - 3.5-3.8%
- Sour cream 10% - 2.9-3.2%
- Cheese - 2.9%
- Butter - 0.81%
In addition to food sources of lactose, small amounts of lactose are found in a wide variety of medicines. However, it is usually present in milligrams rather than grams; in most drugs, this amount is biologically insignificant.
You can also find lactose in smaller amounts in foods such as bread, pancakes, biscuits, biscuits. and breakfast mixes, instant potatoes, soups, potato chips and corn chips. Refrigerated foods such as margarine and salad dressings can also contain lactose as a preservative.
Lactose can also be added to a range of foods with limited natural sweetness, such as margarine, butter, frozen vegetables, and processed meats.
Video about lactose
Composition, application, benefits of lactose:



