Tertiary and quaternary nitrogen compounds included in the pharmacological category M-cholinomimeticsblock the natural functions of the parasympathetic fiber neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The mechanism of action of such drugs is reversible or irreversible.
Record content:
- 1 What are cholinomimetics, classification
-
2 Mechanism of action
- 2.1 Reversible M-cholinomimetics
- 2.2 Conditionally irreversible M-cholinomimetics
- 3 Indications for use
- 4 Side effects
-
5 Review of M-cholinomimetic drugs
- 5.1 Atropine
- 5.2 Proserin
- 5.3 Pilocarpine
- 6 Cholinomimetics video
What are cholinomimetics, classification
Such substances reproduce parasympathetic pulsation, innervate the sweat, salivary and lacrimal glands, selectively excite muscarinic receptors of neurons and organ tissues. Cholinomimetics inhibit or activate cholinergic nerves.
Their effect depends on the type of preparation and the pharmacological characteristics of the main active ingredient. Choline receptors that are the object of the influence of such drugs are genetically determined lipo- or glycoprotein protein molecules.
They are constantly disintegrating and re-synthesizing. The biological life of cholinergic receptors is about 7 days. Such physiological elements are subdivided into muscarinic and nicotone, with several subtypes.
M-cholinomimetics have a mechanism of action aimed at inhibiting or stimulating muscarinic receptors. In the physiological reaction of increasing their activity, intracellular nucleotides of the group of cyclic guanosine monophosphates, calcium, sodium and potassium ions are involved.
The classification and principle of action of anticholinergic drugs are associated with this physiological process. Such receptors are localized in all organs and functional systems.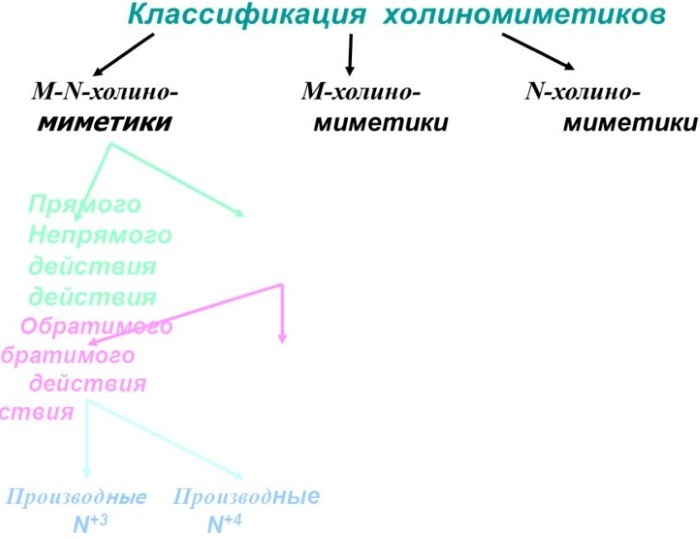
Therefore, cholinomimetics are widely used in clinical practice and various branches of medicine. The neurotransmitter causes parasympathetic innervation.
Its inhibition or, on the contrary, an increase in activity leads to various physiological effects. Interaction of the drug with M1-cholinoreceptors of the central part of the nervous system causes their sharp excitement.
The influence of the intramural (intramural) parasympathetic plexuses of the digestive system on similar elements enhances the secretory abilities of the glands of the gastrointestinal tract.
N-cholinomimetics act on nicotinic receptors. Most of the substances in this pharmacological category are natural alkaloids or their laboratory synthesized analogs that do not represent significant therapeutic value and serious scientific interest.
The most actively used nicotine cholinomimetics are lobelin and cytisine - respiratory analeptics used in pulmonary practice and included in drugs for weaning from smoking.
Another classification category is constituted by substances of combined action. Nicotine-muscarinic cholinomimetics interact with both types of receptors.
In clinical practice, they are used to a limited extent due to too sharp and short-term influence. When taken orally, such drugs are ineffective, since they are quickly hydrolyzed.
A typical active ingredient of drugs of this pharmacological group is acetylcholine or its synthetic analogue carbocholine. The latter, in a modified form, is used in medicines intended for ophthalmic diagnostics.
It is used in complex treatment:
- glaucoma;
- atony of the bladder and intestines;
- paroxysmal tachycardia;
- the initial phase of hypertension;
- obliterating endarteritis;
In obstetrics, H-, M-cholinomimetics are used to stimulate labor. Acetylcholine in the form of hydrochloride is used in experimental physiology and pharmacology.
According to their chemical structure, cholinomimetic substances are divided into tertiary and quaternary ammonium compounds. The latter poorly overcome the blood-brain barrier due to low lipophilic activity.
They have a selective effect on peripheral cholinergic receptors. Substances from the classification group of tertiary amines, on the contrary, have increased lipophilic activity and easily penetrate into the structure of the central nervous system.
They have a stimulating effect on peripheral and endogenous neurons. These properties determine the areas of clinical, diagnostic and experimental use of cholinomimetics.
Mechanism of action
The principle of the physiological effect of such substances is due to the ability to imitate parasympathetic pulsation, to selectively excite the receptors of the neurons of the effector organs.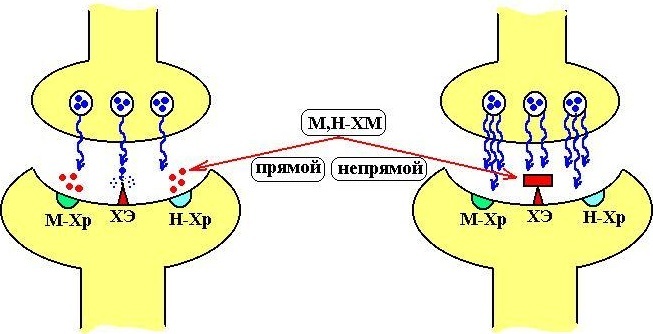
Ammonium compounds of the tertiary and quaternary types innervate tissues:
- heart apparatus;
- visual organs;
- smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract;
- walls of the bronchial cavity;
- excretory glands.
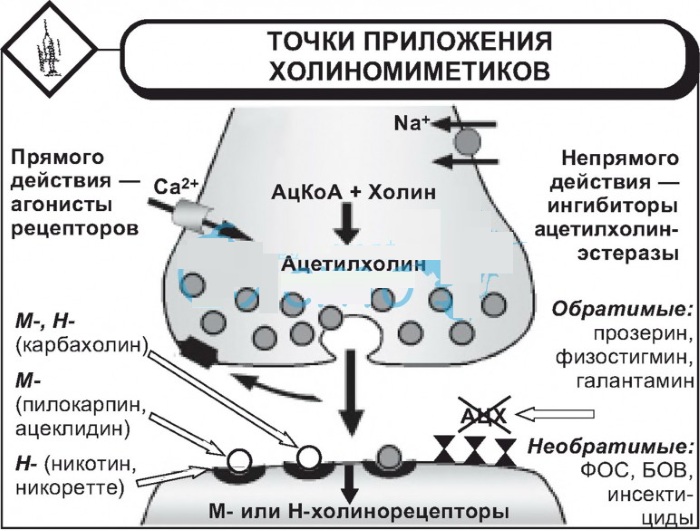
M-cholinomimetics have a peripheral or centralized mechanism of action. With their pharmacological properties, they resemble anticholiesterase drugs, which prolong the effect of an endogenous neurotransmitter.
Ammonium compounds have a direct effect on choline receptors, which leads to an increase in the efferent effect in the vegetative department of the nervous system on:
- abdominal organs;
- secretory glands;
- sensory apparatus;
- urinary tract;
- respiratory canals;
- skin;
- mucous membrane.
The principle of the biochemical effect of such pharmacologically active compounds depends on their type and the location of the target receptors.
Therapeutic and diagnostic effects achieved by the use of M-cholinomimetics:
| Localization of target receptors | Stimulating effect | Depressing and inhibitory effect |
| Visual apparatus | Constriction of the pupil, outflow of intraocular secretions, hypotension, protrusion of the lens. | Mydriasis, increased pressure. |
| Bronchial tree | Narrowing of the cavity, causing a spasmodic state. | Relaxation of the walls, bronchodilation. |
| Digestive system | Increasing tone, strengthening the secretory functions of the glands, improving peristalsis. | Atony, suppression of the functionality of the glandular elements. |
| Cardiovascular mechanism | Bradycardia, an increase in the number of contractions of the heart muscle and an increase in the conduction of nerve impulses. | Tachycardia, decreased impulse conduction. |
| Uterus and bladder | Hypertonicity | Decreased tone |
| Metabolism | Increased glycogenolysis and lipolysis, increased oxygen consumption. | Slowing down of catabolic processes. |
Activation by the active substance of the drug M2-cholinoreceptors of the heart leads to a decrease in the frequency of myocardial contractions. The most numerous effects of such medications are due to the excitation of smooth muscle fibers and exocrine glands.
Reversible M-cholinomimetics
The mechanism of the biochemical effect of drugs in this category is based on the inhibition of acetylcholiesterase, a special hydrolytic enzyme found in synapses. He takes an active part in neurotransmitter catalytic reactions.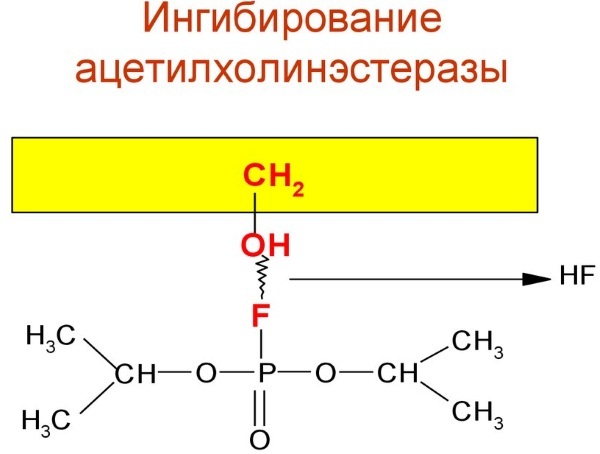
Inhibition of the enzyme is accompanied by the cumulative accumulation of acetylcholine in the zones of the location of the synapses. Under the influence of M-cholinomimetics of the reverse action, the process of disintegration of the target biochemical compound is accelerated, which manifests itself for a short time.
Their pharmacological mechanism is realized by means of an endogenous (own) ammonium substance. The action of such drugs lasts 2-10 hours. These include physostigmine, proserin, galantamine.
Conditionally irreversible M-cholinomimetics
This pharmacological category includes only one chemical compound and its modified derivatives - fosacol, which is an organic ester of phosphoric acid.
This is a substance with the highest level of toxicity. Therefore, it is only limited to ophthalmology. It is gradually being abandoned in this clinical area. The period of physiological influence of fosacol is calculated in weeks, and sometimes months.
M-cholinomimetics of the conditionally irreversible type based on organophosphorus compounds strongly bind to muscarinic receptors. The mechanism of action of such drugs is due to the injection of endogenous acetylcholine into the nerve-conducting tissues and the persistent inhibition of the AChE enzyme.
Indications for use
Choline receptors have different sensitivities to the effects of pharmacologically active compounds. This is the reason for the indications for the use of such drugs.
M-cholinomimetics are used in:
- ophthalmology;
- cardiology;
- general and maxillofacial surgery;
- endocrinology;
- dentistry;
- obstetrics;
- gastroenterology.
For therapeutic purposes, medications stimulating muscarinic cholinergic receptors are prescribed for the atonic state of the bladder associated with neurogenic disorders of the deurination function.
Such drugs are used to a limited extent in dental practice. Pilocarpine causes an increase in the secretion of salivary fluid. With the help of this medicine, xerostomia is eliminated - pathological dryness of the oral mucosa.
M-cholinomimetics are characterized by significant toxicity during systemic resorption. Therefore, they are used in small dosages. In maxillofacial surgery, reversible anticholiesterase drugs are used.
They block the pharmacological activity of competitive antidepolarizing type muscle relaxants, which directly affect the cholinergic receptors of the end plates of skeletal muscle.
As a result of breaking the bond with acetylcholine, the muscles stop contractile activity, which makes it possible to perform the necessary surgical manipulations. To eliminate this effect and accelerate postoperative rehabilitation, Proserin and other stimulants of muscarinic cholinergic receptors are used.
Preparations of the atropine group are used in outpatient dental practice to regulate the secretory activity of the salivary glands in the phase of exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process.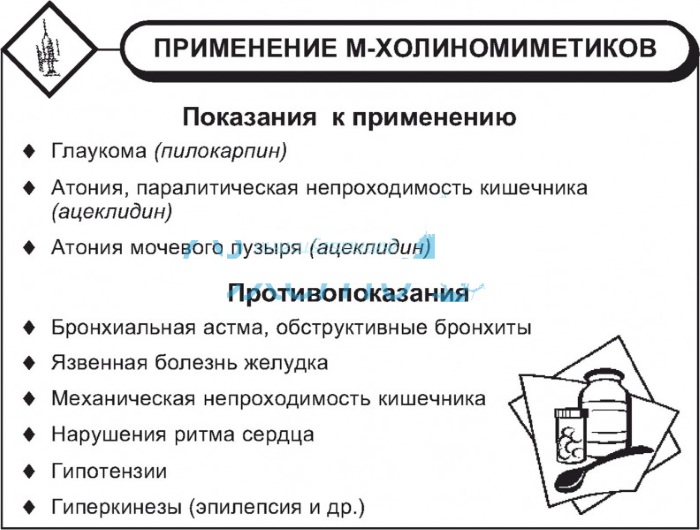
Such M-cholinomimetics are prescribed for vegetative neurosis associated with increased salivation. Atropine has the ability to reduce the vagal effect on the heart muscle of general anesthetics, eliminate the spasmodic state of smooth muscles, and reduce lacrimation and salivation.
In surgical practice, anticholiesterase agents are mainly used, which affect neurotransmitter processes in the peripheral and vegetative parts of the nervous system.
Ophthalmologists prescribe such medications for the treatment of chronic forms and acute attacks of angle-closure glaucoma, diagnostic manipulations, and induction of accommodation paralysis. M-cholinomimetics stabilize intraocular pressure and regulate the functioning of the lacrimal glands.
In obstetric practice, drugs of this pharmacological category are used to increase the uterine tone, with subinvolution of the reproductive organ, to quickly stop postpartum bleeding.
Anticholiesterase drugs are effective in treating central retinal artery thrombosis. Such medicines are used in the diagnosis of gastroenterological diseases - fluoroscopy of the esophagus, gastric cavity, duodenum 12.
M-cholinomimetics, the mechanism of action of which is aimed at stimulating or, conversely, suppressing muscarinic receptors, allow you to quickly return the pupil to its natural state after the installation of mydriatic solutions.
Side effects
The negative effects of drugs are due not only to the chemical characteristics and the level of toxicity of the main pharmacologically active component. Side effects can provoke drug excipients.
Their list is more diverse than the list of cholinomimetic compounds. Therefore, all drugs have a different set of negative manifestations.
Common side effects for topical M-cholinomimetics in frequency of occurrence are as follows:
- Migraine headaches of varying intensity and duration.
- Follicular conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctival membrane and lymphatic follicles of the eye organ.
- Contact dermatitis of the skin of the eyelids is an allergic reaction to certain components of medicines.
- Severe constriction of the pupillary element for a long period of time when using conditionally irreversible M-cholinomimetics.
When taken orally, nausea and vomiting are most often noted, which is associated with the increased toxicity of M-cholinomimetic drugs. Chills and increased sweating are less common.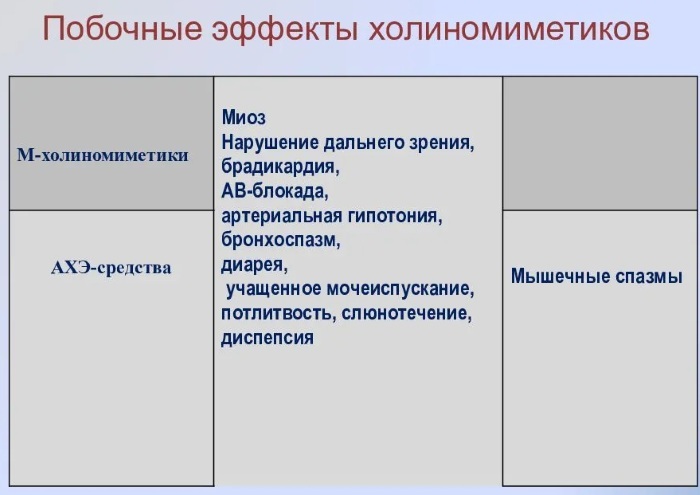
Such side effects are explained by the stimulation of the endocrine system by ammonium compounds. Sometimes, while taking oral or injectable M-cholinomimetics, there is an increase in the urge to urinate.
Renorrhea, lacrimation and increased salivation are associated with the ability of such substances to increase the functional activity of the exocrine glands. With the ophthalmic use of drugs of this pharmacological category, a temporary visual impairment is observed.
Other side effects include hyperemia, flushing of the face, and a sharp jump in blood pressure. The respiratory system may respond to the administration of anticholinesterase substances with bronchospasm, pulmonary edema, and shortness of breath.
Induced myopia develops within 15 minutes. after topical application of the drug and reaches a maximum after 1-1.5 hours.
In ophthalmological practice, some patients had:
- nuclear cataract - clouding of the central part of the lens;
- swelling of the corneal endothelium;
- atypical disc-shaped keratopathy, manifested by increased photosensitivity, sensation of a foreign body in the orbit, hyperemia, pain syndrome.
The digestive system is characterized by such side effects as pain in the epigastric zone, increased intestinal peristalsis, and impaired stool.
Review of M-cholinomimetic drugs
The category of such medicines is not very broad. Due to the increased toxicity and strong effects, organophosphorus compounds are used less and less. Below is a list of M-cholinomimetics that continue to be relevant.
Atropine
The most famous and actively used drug, widespread in ophthalmology, gastroenterology, neurology. Atropine is an anticholinergic that blocks muscarinic receptors. Available in the form of eye drops and injection solution.
The main active ingredient is atropine sulfate, which has antispasmodic and anticholinergic properties.
It is a natural alkoloid that effectively blocks muscarinic receptors:
- heart muscle;
- smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract;
- secretory glands;
- optical system;
- urinary apparatus.
Atropine paralyzes accommodation, the eye's natural ability to change focal length. The natural alkaloid is used in cardiology due to its properties to suppress the inhibitory effect of the vagus nerve. This increases the activity of the heart muscle.
Indications for the use of Atropine:
- stomach ulcer;
- intestinal perforation;
- chronic gastritis;
- bronchial asthma;
- spasm of the bile ducts;
- hypersalivation;
- Parkinson's disease;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals;
- bradycardia;
- carrying out dental intervention;
- renal colic;
- atrioventricular block;
- laryngospasm.
The drug is used when performing X-ray studies of the gastrointestinal tract, for premedication before surgery and during ophthalmic diagnostics. In the capital's pharmacies, Atropine in the form of 1% eye drops costs about 55 rubles. for a bottle of 5 ml.
Proserin
Synthetic M-cholinomimetic, restoring the transmission of neuromuscular impulses, reducing the heart rate, activating the secretory functions of the glands. It is produced in oral tablets, in the form of an injection solution for subcutaneous, intramuscular and intravenous administration.
M-cholinomimetics, the mechanism of action of which is based on the ability of neostigmine methyl sulfate to cause accommodation paralysis, used in ophthalmic operations and diagnostic research. Proserin belongs to the category of such drugs. The drug is highly toxic and has a large number of contraindications.
Synthetic cholinesterase inhibitor does not apply when:
- the patient's tendency to epileptic seizures;
- cardiac disorders - arrhythmias, brady and angina pectoris, ischemia;
- severe atherosclerosis;
- hyperkinesis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- chronic bronchitis;
- acute phase of infectious diseases;
- malignant and benign neoplasms of the prostate gland;
- mechanical obstruction of the digestive system;
- inflammation of the urinary tract;
- peritonitis;
The calculation of the dosage and the very appointment of Proserin is an exclusive medical competence. An anticholinergic drug can cause many side effects. An ampoule medication with an active substance concentration of 0.5% for intramuscular administration costs about 110 rubles. per pack of 10 1 ml.
Pilocarpine
Ophthalmic preparation of direct cholinomimetic effect. It is produced in the form of 1% eye drops in special dosing bottles with a volume of 1, 2 and 5 ml. The drug is distinguished by pronounced miotic and antiglaucoma properties.
Pilocarpine in the form of hydrochloride causes paralysis of the ciliary muscle, pulls the root of the iris, increases the permeability of the trabecular segment of the optic organ. It is used to quickly reduce intraocular pressure, improve the outflow of tear fluid.
Installation of a 1% solution is effective in primary open-angle glaucoma. Intraocular pressure during the course of taking the drug is reduced by 25% of the initial indicator. Pilocarpine is prescribed for conjunctivitis, corneal abscess, retinal pigment degeneration.
Do not take the drug:
- patients with iritis and iridocyclitis;
- minors;
- with renal failure;
- during pregnancy and lactation.
The ophthalmologist calculates the dosage and frequency of use individually. Atropine and other inhibitors of muscarinic cholinergic receptors are considered to be antagonists of pilocarpine.
A medicine in pharmacies costs about 70 rubles. for a bottle of 1 ml. The category of M-cholinomimetics includes Aceclidine, an ophthalmic drug, the mechanism of action of which is due to the ability of the main active component to cause a miotic effect.
Cholinomimetics video
Basic pharmacology of cholinomimetics:



