L-arginine is an amino acid which helps to produce enzymes and hormones. The body usually reproduces it on its own in sufficient volumes.
Arginine is also found in most protein-rich foods, including fish, red and white meats, soy, cereals and grains, legumes, and dairy products. The amount of this substance in each of them can be seen in the comparative table. In the form of a dietary supplement, L-arginine can be administered orally and topically.
Record content:
- 1 Compound
- 2 Usage rate
-
3 Effects on the body
- 3.1 During pregnancy and breastfeeding
- 3.2 For certain groups of people
-
4 Beneficial features
- 4.1 Supporting the body in severe diseases
- 4.2 Promotes the movement of blood through the arteries
- 4.3 Helps Treat Erectile Dysfunction
- 4.4 Helps people with type 2 diabetes
- 4.5 Combines with lysine to help relieve anxiety
-
5 Arginine benefits for athletes
- 5.1 Increases the rate of regeneration
- 5.2 Increases endurance and reduces fatigue
- 5.3 Promotes Fat Burning
- 6 Harmful properties
- 7 Side effects
-
8 Products table
- 8.1 Meat
- 8.2 Nuts
- 8.3 Seeds
- 8.4 Dairy
- 8.5 Cereals and cereals
- 9 Arginine video
Compound
In free form, this amino acid is not attached to protein or other compounds.
Arginine is essential for the human body for many factors. It is one of three substrates for the formation of creatine, the most important nutrient, the lack of which provokes mental retardation. It is used in the body and in the reproduction of agmatine, a signaling molecule; in the urea cycle, it is an intermediate component in combination with L-ornithine and L-citrulline.
Arginine also promotes protein synthesis and stimulates the release of insulin. As part of the nitric oxide cycle, the compound has significant benefits for physically active people. This makes it a popular dietary supplement for athletes.
L-arginine supplements come in capsules or powders. Both forms are equally effective, but the former may require 2 to 3 doses per day, while the latter usually requires only one. Powders also provide faster results because the body absorbs them faster, but they must be mixed with liquid before ingestion.
There are also L-arginine creams available on the market, which are used to improve blood circulation. Substance injections can only be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Usage rate
Arginine in foods (the comparative table indicates its amount in each type of food), rich in protein, allows you to meet the physiological needs for it in most people.
Adults consuming the RDA of protein (0.8 g / kg body weight) receive 0.25 mmol of arginine for each kg of their weight. On average, proper nutrition provides the body with about 3-6 g of this amino acid per day.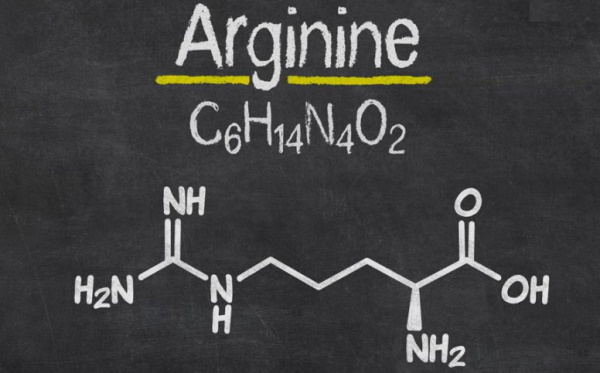
However, it may not be sufficient for people with certain conditions, such as severe burns, sepsis, and HIV / AIDS, as well as those involved in active sports. If you take arginine as a dietary supplement, the usual dose is 2-3 g. 3 times a day. However, you can consume up to 20 g of this substance daily without side effects.
However, the dosage indicated on the package should always be checked before taking a dietary supplement. It is recommended to take arginine with meals to avoid the onset of the laxative effect.
The dosage of arginine in the form of a dietary supplement and the duration of the course may be different, depending on the purpose of the intake:
- For chest pain and angina pectoris: 2-6 g three times a day, for 1 month.
- For erectile dysfunction: 2.5-5 g per day. Lower doses may not be effective.
- With high blood pressure: 4-24 g per day for 2-24 weeks.
- For narrowing of the blood vessels causing poor blood flow to the extremities (peripheral arterial disease): 6-24 g daily for up to 8 weeks.
- In case of complications of pregnancy, accompanied by high blood pressure and protein content in the urine (preeclampsia): 3 g per day for 3 weeks.
- For high blood pressure during pregnancy: 4 g daily for 10-12 weeks.
For serious intestinal disease in premature infants (necrotizing enterocolitis or NEC), arginine is added to oral feeding daily at a dosage of 261 mg / kg for the first 28 days of life.
Effects on the body
Arginine's effects on the body are more related to its ability to produce nitric oxide, which affects many processes (including regulation of blood flow, mitochondrial function, and cellular communication). This has certain positive health effects and improves athletic performance.
Nitric oxide causes blood vessels to dilate to improve blood flow. L-arginine also stimulates the body to release growth hormone, insulin and other substances.
L-arginine is considered partially or conditionally essential because it is synthesized on its own under normal conditions. However, under certain circumstances and conditions, it is necessary (including pregnancy, early childhood, serious illness and injury).
In addition, it acts as a precursor to other amino acids, including glutamate, proline, and creatine, and is essential for the health and functioning of the immune system. Arginine is also essential for the development of T-lymphocytes, white blood cells that play a central role in the immune response.
Arginine is involved in a variety of bodily processes, including:
- promotes wound healing;
- helps the kidneys to remove waste products;
- supports immune and hormonal functions;
- provides elasticity to the arteries.
One of the important functions of arginine is the elimination of ammonia, which is extremely toxic to the central nervous system. Because this compound dilates blood vessels, many people take supplements based on it to treat heart disease and erectile dysfunction.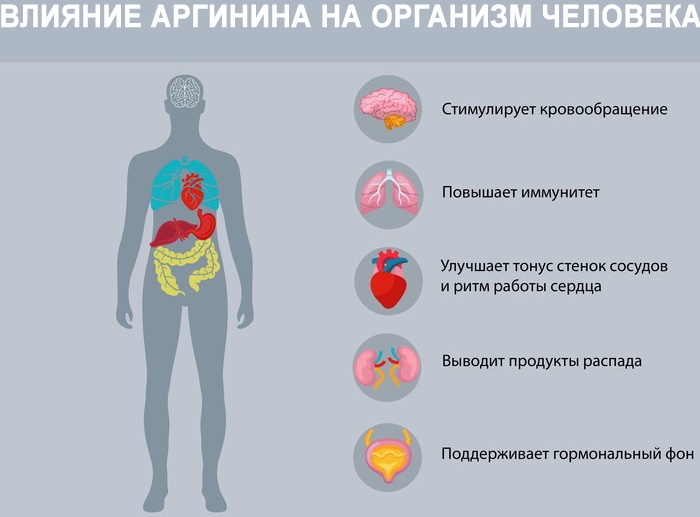
However, the effectiveness of arginine in these cases has not been proven. One study even found that taking this amino acid could even be potentially harmful to people who have had a heart attack.
Too much arginine can also block the production of lysine, an amino acid used to treat cold sores. People with this condition should reduce their intake of this substance by avoiding foods high in it.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
L-arginine is used in pregnancy for certain conditions, including preeclampsia. Supplementation of this amino acid in such cases is usually prescribed and monitored by a physician.
There is some evidence that L-arginine supplementation can improve pregnancy and support the health of the baby and mother. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy, the body's need for amino acids increases due to the development of the fetus and the growth of the placenta.
As a result, it cannot be satisfied through diet, especially in women living with limited resources and lacking access to protein-rich foods. However, taking supplements during pregnancy should always be approved and monitored by your doctor.
The effect of L-arginine supplementation on lactating women has not been investigated. For this reason, taking the substance should only be started with the approval of a doctor.
For certain groups of people
The safety of L-arginine has been demonstrated for everyone, including pregnant women and the elderly. However, some people, including those with liver or kidney disease, should avoid taking this compound.
Arginine supplements are sometimes used in children in a clinical setting and are considered safe when given in certain doses. However, their intake by children should always be monitored by a doctor. It is not recommended to give your child L-arginine unless medically required.
Beneficial features
Since L-arginine plays a very important role in the body, a deficiency in this amino acid can disrupt cell and organ function and lead to serious adverse health effects.
This connection is made in several ways. So, it can be synthesized from the amino acid citrulline by breaking down proteins or obtained by consuming protein with food.
Additionally, L-Arginine can be obtained by taking supplements. They are widely available commercially and can be found in powder, liquid, capsule, and tablet form. Although the safety of additional intake of the substance is detailed has not been studied, it is often recommended for people with conditions such as:
- protein deficiency;
- burns;
- infectious diseases;
- active sports and muscle building.
Supporting the body in severe diseases
Arginine becomes essential when the body is compromised by conditions such as infections and injuries. The need for this compound is greatly increased due to the changing physiological needs.
Under these conditions, the body can no longer synthesize arginine, so it must be obtained from external sources. Depletion of this amino acid during a serious illness or after surgery leads to serious side effects, including impaired immune function and blood flow. To avoid these potential complications, you need to take arginine supplements.
Promotes the movement of blood through the arteries
Arginine is converted to nitric oxide during metabolism in the body. It is a neurotransmitter that helps the arteries pump blood and improves blood circulation in general. Thus, it provides the prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system.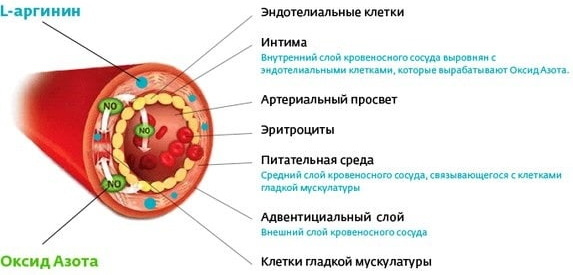
There is experimental evidence that arginine can improve blood flow in the arteries leading to the heart. This phenomenon can relieve blockages, chest pain, angina, or coronary artery disease. It is useful for people with peripheral vascular disease and, therefore, impaired blood flow in the extremities to the extremities.
Helps Treat Erectile Dysfunction
Considering the aforementioned effects of arginine, it can help men with erectile dysfunction. In many cases, the cause of this condition is related to heart disease. Problems with blood circulation in the arteries can reduce the flow of blood to the penis, and this can interfere with erections.
According to some researchers, arginine supplementation improves blood flow throughout the body. Because of this effect, doctors prescribe this compound to patients with erectile dysfunction.
Helps people with type 2 diabetes
It has been proven that in patients with type 2 diabetes, the content of L-arginine in the body is reduced when compared with the indicators of a healthy person. Therefore, its addition is able to restore the molecular imbalance in this disease.
Type 2 diabetes causes oxidative stress in patients. One controlled human study confirms that arginine supplementation can reduce this manifestation of the disease.
At the same time, there is evidence that L-arginine indirectly activates a free radical scavenger protein that helps reduce oxidative stress in the body. In addition, its association with nitric oxide levels reduces the damage caused by oxygen species.
Combines with lysine to help relieve anxiety
One experiment used a combination of arginine and lysine for people with increased anxiety. The subjects received 3 g of these substances per day. The results confirmed that during stressful situations, the test group released more hormones that reduce feelings of fear and anxiety.
Arginine benefits for athletes
Arginine in food, the table listing which contains an indication of its content in each of them, allows you to maintain good health with a properly composed diet. Taking additional amounts of this substance is often practiced by those looking to take their performance to a higher level.
If a person plays sports and gets enough rest, certain dietary supplements and protein may be recommended. These include arginine or L-citrulline, which is converted to arginine in the body. This compound has great benefits in sports because of its effects on the body.
Increases the rate of regeneration
After an intense workout, it is not uncommon to experience a strong feeling of exhaustion and fatigue, as a result of which it takes several days to fully recover. It is during this time that arginine is able to help as it increases nitric oxide levels. This substance promotes blood flow to tissues, stimulating muscle relaxation.
This, in turn, helps deliver large doses of oxygen to the muscle tissue. The most important condition for fast regeneration is that the muscles get enough nutrients after intense training, so improving blood flow is important. It is important to understand that this effect can only be achieved with proper nutrition and fluid intake.
Increases endurance and reduces fatigue
Endurance is related to the amount of oxygen entering the muscle tissue. It spreads in the blood, which helps you train longer without feeling tired.
Since arginine improves blood circulation, it can increase endurance and improve athletic performance. This effect has been confirmed in professional cyclists and track and field athletes with extended periods of fatigue.
Promotes Fat Burning
Researchers have also begun to study the effect of L-arginine on accelerating fat burning. Body drying athletes should consider adding a dietary supplement with this compound to their diet.
Researchers have also studied the effect of nitric oxide on glucose metabolism during exercise. The results showed that in athletes taking arginine, glucose was delivered to muscle cells much faster.
In addition, the addition of arginine to food causes an increase in the concentration of non-esterified fatty acids and glycerol. This means that the body burns fat as a source of energy.
Harmful properties
Oral or topical use of L-arginine is generally considered safe.
But in some cases, taking a substance can cause the following conditions:
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- abdominal pain;
- bloating;
- allergic response;
- airway inflammation or worsening asthma symptoms;
- exacerbation of gout.
L-arginine is not recommended after a heart attack due to concerns that it may increase the risk of death. In addition, this dietary supplement can worsen gout, allergies, or asthma. In the presence of these conditions, it must be used with caution.
Care must be taken when taking L-arginine and if there is herpes in the body (including genital). Consuming too much of this supplement could potentially activate the virus that causes these conditions.
Side effects
Research confirms that arginine is rarely associated with side effects when consumed for 3 months. However, they can present with nausea, cramps, abdominal pain and diarrhea, and headaches.
Arginine in food (the comparison table contains its quantitative value in each of them) does not affect the action of other dietary supplements and drugs. However, consuming it as a food supplement at the same time as other substances can cause unwanted effects in the body.
Arginine can react with drugs, dietary supplements and medicinal herbs applied in the following conditions:
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs that reduce blood clotting. Taking L-arginine with them may increase the risk of bleeding.
- Arginine can lower blood pressure in people with high blood pressure. Its combination with drugs for hypertension increases the risk of too much pressure drop.
- L-arginine can lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, so dosage adjustments will be required when taking medications with the same effect.
- Using the heart medications isoproterenol and nitroglycerin along with arginine can cause your blood pressure to drop too much. The same effect can occur while taking arginine with sildenafil (Viagra and other drugs for erectile dysfunction contain it).
- Potassium-sparing diuretics (amiloride, spironolactone, or triamterene) should not be taken with L-arginine. These medications can raise potassium levels, increasing the risk of hyperkalemia (excess of this mineral in the body).
Products table
Arginine in food, the table with a list of which offers to compare its amount in each of them, is quite sufficient for most people. Additional additives based on this substance are not required.
| Food | Arginine content (mg / 100 g edible portion) |
| Whole cow's milk | 130 |
| Egg | 94 |
| Beef | 1831 |
| Pork | 1684 |
| Mutton | 1398 |
| Chicken | 1410 |
| Halibut | 1520 |
| Cod | 3759 |
| Tuna | 1794 |
| Herring | 1304 |
| Mackerel | 1376 |
| Salmon | 1284 |
| Shrimps | 1882 |
| Soy flour | 2903 |
| Soya beans | 3153 |
| Wheat bran | 1098 |
| Rice | 174 |
| White bread | 308 |
| Beans | 370 |
| Lentils | 659 |
| Young peas | 708 |
| Broccoli | 176 |
| Cabbage | 140 |
| Mushrooms | 333 |
| Onion | 120 |
| Spinach | 324 |
| Almond | 1995 |
| Walnuts | 1580 |
| Hazelnut | 1310 |
| Spirulina | 4148 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 4033 |
| Peanut | 3349 |
As you can see, arginine is found to a greater extent in red and white meats, dairy products and fish. It is also present in large quantities in pumpkin seeds, soybeans, peanuts and other nuts, legumes (especially chickpeas and lentils) and algae (spirulina).
Meat
As one of the best sources of protein, meat contains all the amino acids the body needs, including arginine.
It is advisable to choose white varieties that are characterized by a low fat content (in particular, turkey and chicken fillets). Of the red meat, beef is the leader, offering 4.131 g for every 500 g cooked. However, it should be borne in mind that it contains more fat than other sources of protein.
Nuts
The arginine rich food table contains many types of nuts.
Among them, the best sources of this compound are:
- walnuts;
- hazelnut;
- pecan;
- peanut;
- almond;
- cashew;
- Brazilian nut.
They are all rich in protein and are also an excellent source of fiber and essential vitamins.
Seeds
The seeds contain a significant amount of arginine. At the same time, pumpkin seeds contain one of the highest concentrations of this substance (in 1 tbsp. of the dried product, there are 6.905 g of amino acid). Other seeds high in arginine include watermelon, sesame, and sunflower.
Dairy
Dairy products (such as milk, yogurt, and cheese) are important sources of arginine. In addition, they contain many other important nutrients such as protein, calcium, magnesium, vitamins (B1, B2, B6 and B12, as well as A, D and E) and folic acid.
It is believed that a high-protein diet containing a lot of dairy products on the menu allows you to achieve a lower body mass index.
Cereals and cereals
Whole grains are a rich source of arginine and are believed to help lower blood cholesterol levels. Their antioxidant properties can also reduce the risk of heart disease.
Cereals high in arginine include:
- oats;
- corn;
- buckwheat;
- brown rice
Most adults produce enough arginine in their bodies, but children need to absorb additional amounts from food to support growth and development. In addition, some disorders can lead to a deficiency of this substance.
In this case, a person may need to include foods rich in arginine in the diet (it is advisable to follow the comparison table of foods). Before taking dietary supplements with this amino acid, you should consult your doctor to avoid overdose or negative combination with other drugs.
Arginine video
L-arginine - what is it? Benefit and how much is needed: