Anticoagulant therapy Is a treatment aimed at preventing excessive blood clotting by preventing blood clots. According to the type of exposure, anticoagulants are divided into 2 large groups.
They differ in their mechanism of action - indirect anticoagulants suppress the production of prothrombin in the liver, and direct-acting drugs reduce the activity of thrombin in the blood itself. Further in the article will be a list of the best means of the second group.
Record content:
- 1 Description of the group, mechanism of action
-
2 Classification of drugs and their features
- 2.1 Local heparins
- 2.2 Intravenous and subcutaneous heparins
- 2.3 Heparinoids
- 2.4 Thrombin inhibitors - hirudins
- 3 Indications for use
- 4 Contraindications
- 5 Side effects
-
6 New generation direct-acting anticoagulants
- 6.1 Unfractionated heparin preparations
-
6.2 Low molecular weight heparin preparations
- 6.2.1 Dalteparin (Fragmin)
- 6.2.2 Enoxaparin (Clexane, Novoparin, Flenox)
- 6.2.3 Nadroparin (Fraxiparin)
- 6.2.4 Bemiparin (Cybor)
-
6.3 Heparinoids
- 6.3.1 Sulodexin (Wessel Douai F)
- 6.3.2 Pentosan Polysulfate
-
7 Hirudin preparations
- 7.1 Fondaparinux (Arixtra)
- 7.2 Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
- 8 Anticoagulant videos
Description of the group, mechanism of action
Direct-acting anticoagulants are drugs that have a direct effect on blood clotting in the vascular bed. The mechanism of action of these funds is based on blocking the active centers responsible for blood clotting, which leads to the loss of their coagulation properties.
The active ingredients of the drugs in this group are hirudin and heparin. Heparin is a substance isolated from the liver of animals, and hirudin is an anticoagulant found in some types of snake venom and in the salivary glands of leeches.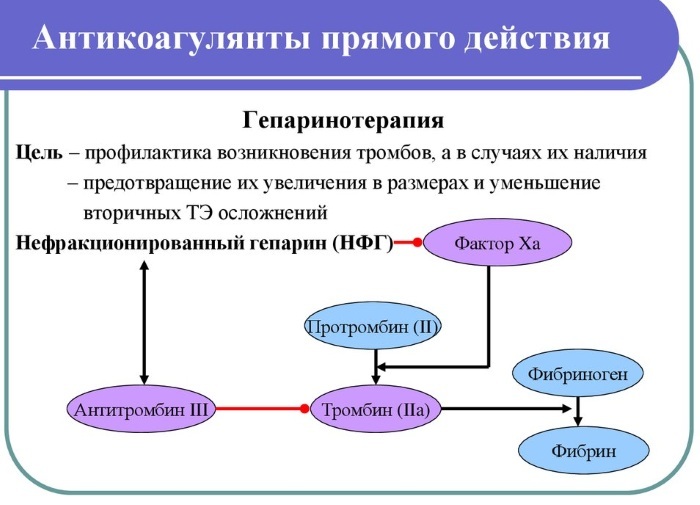
The direct effect of anticoagulants of this group is due to the fact that they act directly on active thrombin and prevent the transition of fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin, on the other hand, is a high molecular weight protein composed of fibers that form blood clots when blood clots.
Classification of drugs and their features
Direct-acting anticoagulants are drugs, the list of which will be given later in the article, which contain active substances that promote blood thinning.
In medical practice, these funds can be used in different ways and therefore are graded according to the following parameters:
- local heparins;
- intravenous and subcutaneous heparins;
- heparinoids;
- thrombin inhibitors - hirudins.
Local heparins
Local heparins have the following properties:
- decongestants;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antigranulomatous;
- anticoagulant;
- antiexudative (protect against penetration of blood into the inflamed tissue through the walls of blood vessels).
These drugs include Heparin ointment, which is used for:
- migrating phlebitis;
- thrombophlebitis of superficial veins;
- varicose ulcers;
- chronic venous disease (with varicose veins);
- with complications after surgical operations on the veins.
Intravenous and subcutaneous heparins
For intravenous and subcutaneous administration, heparins are available as solutions. This application is much more effective, since the increased blood clotting stops faster. So, with the introduction of solutions intravenously, blood clotting stops almost immediately. With intramuscular injection - after 15-30 minutes, with subcutaneous injection - after 40-60 minutes.
The introduction of heparins subcutaneously and intravenously is practiced in acute conditions:
- myocardial infarction;
- thrombosis of cerebral vessels;
- pulmonary embolism;
- deep vein thrombosis.
Heparinoids
Heparinoids are structurally similar to heparin and are found mainly in the walls of blood vessels and cartilage. These substances are related to heparins in structure, but differ in the characteristics of their effect. This group of drugs is used mostly for the treatment of vascular pathologies that occur in patients with diabetes mellitus.
In addition, they are widely used in patients for the prevention of thrombosis during surgical manipulations, as well as to prevent blood clots during hemodialysis - extrarenal cleansing blood.
Thrombin inhibitors - hirudins
Direct-acting anticoagulants are drugs, the list of which will be discussed later in the article, that can thin the blood, make it less thick. A special place among them is occupied by thrombin inhibitors - hirudins. As noted earlier, hirudin is a naturally occurring substance (peptide) found in the salivary glands of leeches.
It is considered a powerful natural thrombin inhibitor (inhibitor). In comparison with antithrombin, the action of hirudin is aimed at suppressing only active thrombin, blocking of this component in that specific gravity in the blood composition, in which it is necessary to prevent coagulability.
It is hirudin that prevents the formation of clots and blood clots. It is used both injectable and topically in the form of a cream.
In some parameters, hirudin is superior to other anticoagulants and thrombolytics, since it does not interfere with the biological activity of other serum proteins.
Indications for use
Direct-acting anticoagulants are drugs, the list of which is quite extensive, which are now used in a number of vascular diseases. At the same time, the main purpose of prescribing such medications in various situations is the same - to prevent excessive thickening of the blood and to prevent thrombosis of blood vessels and veins.
Prescribe drugs of this group for the treatment and prevention of the following conditions and diseases:
- thrombosis of the renal veins, deep and superficial veins of the lower extremities;
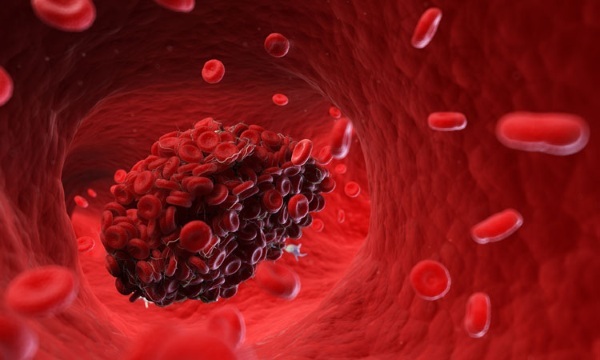
Direct anticoagulants are used for thrombosis - treatment and prevention of emerging thromboembolic complications associated with atrial fibrillation (flutter);
- with myocardial infarction, embolic and thrombotic strokes;
- with atherosclerosis of the vessels of the brain, coronary arteries;
- for the treatment and prevention of the development of the formation of microthrombi and microcirculation disorders arising from diuresis, glomerulonephritis;
- for the prevention of blood clotting during blood transfusion (blood transfusion), heart surgery, hemodialysis.
Heparin is also used as an immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory agent in some autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis), as well as to reduce the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and lipoproteins.
Contraindications
Direct-acting anticoagulants are drugs, the list of which is not small, which is not suitable for everyone. There are a number of diseases and conditions in which these blood-thinning medications are prescribed with caution or are generally contraindicated.
So these drugs are not prescribed to patients who have:
- kidney stone disease;
- ulcerative changes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- liver disease;
- active tuberculosis;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- hemophilia (hereditary bleeding disorder);
- female uterine bleeding;
- hemorrhoidal bleeding;
- intestinal tumors;
Also, the use of direct anticoagulants is prohibited for other diseases in which there is a reduced blood coagulability and increased vascular permeability. For example, with thrombocytopenia - when the platelet count is low in the bloodstream, which can cause internal hemorrhage at any time.
Side effects
The use of anticoagulants is associated with certain risks when the drugs cause a number of side effects. The main danger posed by the use of direct anticoagulants is the high risk of bleeding. This happens especially often against the background of an overdose of drugs, or existing renal failure.
As a result, the following may develop:
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract (especially with peptic ulcer disease);
- hematuria (the presence of blood in the urine);
- hemarthrosis (hemorrhage in the articular cavity);
- hematomas - if anticoagulants are injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
Also, the use of drugs that thin the blood can cause allergic reactions - urticaria, swelling of the nasal mucosa, difficulty breathing.
In addition, drugs containing heparin can provoke the development of immune thrombocytopenia, therefore, during treatment, it is imperative to control the number of platelets in the blood.
Long-term use of heparin (more than 30 days) can cause osteoporosis and bone fractures, especially in the elderly.
New generation direct-acting anticoagulants
New generation anticoagulants have been developed relatively recently.
To date, in clinical practice, heparin is presented in 2 variations:
- classic non-fractional heparin (UFH);
- low molecular weight heparin (LMWH).
Unfractionated heparin preparations
Standard non-fractional heparin mediates by inhibiting (suppressing) the main enzymes responsible for blood clotting, which leads to antithrombotic and anticoagulant effects. In the human body, this substance can be found in muscles, lungs, intestinal mucosa.
For medical use, heparin is reduced from the lungs of cattle and the mucous tissues of the intestines of pigs. It is used in the production of drugs that have a general effect (heparin for injection) and local (heparin ointment, thrombless, Lioton 1000).
| Compound | Mode of application | Dose | Indications | Price | |
| Heparin injection solution |
Sodium heparin is the main substance. Benzyl alcohol, sodium chloride are additional components. |
|
5000 IU | Deep vein thrombosis, coronary arteries, thrombophlebitis, acute myocardial infarction | From 41 rub. up to RUB 1,760 (depending on the country of origin) |
| Heparin ointment |
sodium heparin ( benzocaine, benzyl nicotinate) |
Outwardly, the ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected area |
0.5-1 g of ointment per area with a diameter of 30-50 mm | Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, elephantiasis, trophic ulcers of the leg, inflammation of hemorrhoids after childbirth | From 72 rub. |
| Lyoton 1000 | Heparin, neroli oil, lavender oil, ethyl alcohol. | The gel is applied to the affected skin | Extrude a strip with a length of 3 to 10 cm | To reduce swelling and bruising after blunt trauma, with varicose veins, phlebitis, periphlebitis, after removal of the great saphenous vein of the thigh | From 330 to 690 rubles. |
| Trombless | Sodium heparin, ethanol, carbomer, purified water | Outwardly, rubbing movements are applied to the affected area 1-3 times a day | From 210 to 280 rubles. |
Low molecular weight heparin preparations
It is believed that drugs in this group are safer and more effective than conventional non-fractional heparin. Medicines in this category have an average molecular weight of 500-4000 daltons (atomic mass unit), which is significantly lower than in standard non-fractional heparin.
Due to this, low molecular weight heparins are able to indirectly inhibit (restrain) the activity of thrombin. Low molecular weight heparins are obtained by chemical fermentation of non-fractional heparin obtained from the intestinal mucosa of pigs.
Dalteparin (Fragmin)
Fragmin belongs to the group of direct anticoagulants containing low molecular weight heparin - sodium dalteparin. In addition to the main active ingredient, the product contains sodium hydroxide and sodium chloride. Fragmin is available in the form of solutions for intravenous and subcutaneous administration. This drug is not administered intramuscularly.
The indications for the appointment by a doctor (and it can be acquired only after receiving a prescription) of this drug are:
- prevention of thrombus formation after surgical procedures;
- blood dialysis (to prevent disruption of coagulation processes);
- the presence of blood clots in deep veins;
- venous thromboembolism;
- prevention of the development of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer.
Dalteparin should be used in accordance with the doctor's recommendations, since the dosage is determined on a case-by-case basis.
| Reason for prescribing the drug | Dosage |
| Hemodialysis | Depends on the disease for which the procedure is performed |
| Acute deep vein thrombosis | The drug is injected subcutaneously into the abdominal area at the rate of 200 IU per 1 kg of body weight once a day, or 100 IU per 1 kg of body weight twice a day. |
| Surgical operations | Depends on the type of operation:
|
| For malignant tumors (for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism) |
|
Depending on the country of origin, the price of Fragmin ranges from 1,970 rubles. up to 4 200 rubles.
Enoxaparin (Clexane, Novoparin, Flenox)
Enoxaparin contains the active ingredient of the same name - enoxaparin sodium. It is also contained in its three analogues - Novoparin, Flenox and Kleksane.
The indications for the appointment of these drugs are:
- prevention and treatment of deep vein thrombosis;
- prevention of the development of hypercoagulability during hemodialysis;
- myocardial infarction (necrosis of the tissues of the heart muscle, resulting from blockage of blood vessels by a thrombus) and angina pectoris;
- prevention of thromboembolism during surgery.
Except in some special cases, enoxaparin and preparations containing it are injected deep under the skin into the abdominal area. The recommended single dosage for administration is 20 mg or 40 mg once a day. The drug is not administered intramuscularly.
Prices for medicines based on enoxaparin sodium vary from 650 rubles. up to RUB 4500
Nadroparin (Fraxiparin)
This direct-acting anticoagulant comes in the form of a colorless solution (sometimes the shade may turn light yellow). The maximum concentration of the active substance, calcium nadroparin, is reached 3 hours after drug administration and is present in the bloodstream in a biologically active form for another 3.5 hours.
In their composition, nadroparin and fraxiparin have:
- the main substance is calcium nadroparin;
- auxiliary component - calcium hydroxide.
Medicines are indicated for use:
- for the treatment of thromboembolism (blockage of blood vessels by a thrombus), unstable angina pectoris;
- with necrosis of the heart muscle (myocardial infarction);
- to prevent blood clotting during dialysis;
- to prevent thromboembolic complications arising from:
- surgical procedures;
- orthopedic operations;
- high likelihood of occluding blood clots in heart and acute respiratory failure.
Both agents are diluted with water for injection and injected into the subcutaneous tissue in the peritoneal region. The dosage is determined in each specific case by the attending physician and depends on the patient's weight (on average, the dose can range from 5000 IU to 15000 IU per day).
The cost of drugs in this group also fluctuates and depends on the country of origin - an average of 720 rubles. up to RUB 3200
Bemiparin (Cybor)
Bemiparin differs from other second-generation LMWH drugs in that it has the lowest molecular weight (3600 daltons). It is the only drug in this group that is approved in Western European countries for postoperative initial prophylaxis.
Cybor is an analogue of Bemiparin and both drugs have one active ingredient - sodium bemiparin.
Drugs are prescribed in the following cases:
- to prevent the development of thromboembolism after general surgical interventions;
- to prevent clogging of blood vessels with blood clots during orthopedic surgery;
- to reduce the risk of blood clotting during hemodialysis.
Dosages of the drug differ depending on the patient's history:
| When carrying out general surgical operations | 2500 IU:
|
| For orthopedic operations | 3500 IU:
|
| With extrarenal blood cleansing | Enter during a hemodialysis session:
|
The drugs are injected alternately subcutaneously from the right and left sides into the anterolateral zone of the abdomen or into the posterolateral lumbar region. The price for drugs containing sodium bemparin ranges from 2300 rubles. up to 2800 rubles.
Heparinoids
Direct-acting anticoagulants include not only heparins, but also heparinoids. As mentioned earlier, these substances, similar to heparins, are structurally related to them, but differ in the characteristics of the effect. These drugs are more often prescribed for patients with a history of diabetes mellitus, since in this case the list of approved drugs may be limited.
Sulodexin (Wessel Douai F)
Sulodexin and Wessel Duet F are analogs and contain the same active ingredient - sulodexide. The substance itself is an extract from the mucous membrane of the small intestine of pigs. It contains about 80% heparinoid.
Sulodexin is produced in ampoules for intramuscular and intravenous administration, as well as in the form of capsules for oral administration.
The drug is indicated:
- with chronic venous insufficiency;
- to prevent the formation of blood clots in deep veins;
- with thrombophilia, antiphospholipid syndrome;
- in acute disorders of blood supply to the vessels of the brain (strokes);
- with discirculatory encephalopathy provoked by diabetes mellitus, vascular dementia, atherosclerosis.

Usually, sulodexin therapy involves parenteral (injection) administration of the drug with a further transition to taking capsules. Sometimes only capsules are prescribed. In each case, the scheme is selected by the doctor individually. The most common treatment regimen is to take 1-2 capsules between meals.
Depending on the diagnosis, the drug is also prescribed intramuscularly and intravenously, the dosage being set individually:
| Thrombosis after acute myocardial infarction | In the 1st month of treatment, the drug is administered intramuscularly at 600 LE of sulodexide daily. Then they switch to taking capsules - 1-2 daily (500-1000 LU / day). |
| Acute ischemic stroke, rehabilitation after it | For setting the drip infusion - 600 LU for 15-20 days, then 1 capsule 2 times a day for 30-40 days. |
| Dyscirculatory encephalopathy associated with diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, vascular dementia | 1-2 capsules 2 times a day for 3-6 months, or with infusion - 600 LE of sulodexide per day for 10-30 days. |
| Chronic venous disease and prevention of recurrent deep vein thrombosis | Orally - 2-4 capsules daily for 2-6 months. When administered with the help of droppers - 600 LE per day, the course - from 10 to 30 days. |
The cost of preparations containing sulodexin in capsules is from 750 rubles. up to 2500 rubles, in the form of solutions for infusion - from 2000 rubles. up to 2600 rubles.
Pentosan Polysulfate
Another agent of the heparinoid group that affects blood clotting is Pentosan Polysulfate. The drug is produced in the form of a solution for injection, as well as in the form of tablets.
One tablet contains 25 mg of sodium pentosan polysulfate, as well as excipients - sucrose and lactose. 1 ml of injection solution contains - 100 mg of sodium pentosan polysulfate and also auxiliary substances.
The active ingredient prevents the development of thrombosis, helps to reduce the level of lipids (fat cells) and cholesterol in the blood. After subcutaneous or intramuscular administration, the bioavailability (percentage of penetration into the bloodstream) of the administered substance in the body reaches 100%.
Pentosan Polysulfate is shown:
- with thrombotic, thromboembolic and atherosclerotic diseases in acute and subacute form;
- to prevent the risk of thromboembolic and thrombotic complications.
Before starting to use the drug, it is necessary to analyze the prothrombin index in the blood to exclude hemorrhagic diathesis (increased tendency to bleeding). Further, in the course of treatment, blood clotting indicators should be monitored - every 3-4 days to take tests during the first 3-4 weeks of using the drug.
Pentosan injections are injected subcutaneously (in the abdomen), as well as intramuscularly. In each case, the dosage is selected individually by the attending physician, but the most commonly used scheme is 100 mg of the drug 2 times a day intramuscularly for 10 days.
The price of the drug in capsules (30 pcs.) Is 8600 rubles, in ampoules - from 6000 rubles. up to RUB 6300
Hirudin preparations
Hirudin is the most studied component of leech saliva, blocking all known reactions, the activator of which is thrombin. Recombinant hirudin, which is not significantly different from natural, was obtained for the manufacture of drugs by genetic engineering.
It is able to deprive thrombin of the ability to increase the anticoagulant potential of the blood and thereby protect the body from dangerous manifestations of thrombosis and disorders in the blood coagulation system.
Fondaparinux (Arixtra)
This product is available in the form of a solution for subcutaneous and intravenous administration. The active ingredient is fondaparinux sodium.
The drug is indicated:
- to prevent the development of venous thromboembolic complications in patients who have undergone surgery (orthopedic and abdominal);
- with blockage (thrombosis) of deep veins;
- with the formation of blood clots in the pulmonary artery;
- with acute coronary syndrome.

For subcutaneous administration, Fondaparinux is injected alternately into the left and right zones of the surface of the anterior abdominal wall. When used intravenously, the drug is injected into a catheter with sodium chloride solution. Depending on the specifics of the disease and the patient's weight, the prescribed dosage can vary from 2.5 mg to 10 mg per day (specific proportions are determined by the doctor).
The cost of this tool is quite high - from 7200 rubles.
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Xarelto is an oral (tablet) anticoagulant from the group of direct inhibitors, manufactured by the pharmaceutical company Bayer. The tablets are covered with a brownish-red film, have a rounded convex shape.
Each tablet contains micronized rivaroxaban (the main active ingredient), as well as auxiliary components - cellulose, lactose, magnesium stearate.
The indications for the appointment of Xarelto patients are:
- prevention of stroke and systemic thromboembolism in patients with atrial tachyarrhythmia;
- treatment and prevention of pulmonary embolism;
- deep vein thrombosis treatment;
- prevention of recurrence of DVT (deep vein thrombosis).
Xarelto tablets are taken orally:
- 0.15-0.20 g - directly at the time of eating;
- 0.10 g - regardless of food intake.
The specific dosage is set by the attending physician. The price of tablets starts from 1500 rubles. and can reach 10,000 rubles. depending on the dosage and the number of blisters in the package.
Direct anticoagulants are drugs that slow down the blood clotting process and prevent blood clots. The list of these drugs includes new oral anticoagulants, as well as drugs for parenteral administration, which were discussed above.
Anticoagulant therapy is both prophylactic and therapeutic in nature and can only be prescribed by a doctor, after clarifying the complete clinical picture. The use of these drugs in a number of cases helps to save patients' lives, as well as to prevent recurrence of dangerous vascular diseases in the future.
Anticoagulant videos
Basic pharmacology of anticoagulants: