Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) plays an important role in ensuring the motor functions of the knee joint and is anatomically one of its internal ligaments.
Record content:
- 1 The structure and function of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint
-
2 Causes, degree, symptoms of damage, degenerative changes in the anterior ligament
- 2.1 Why are injuries and changes in the knee ligament dangerous?
- 2.2 First aid
-
3 How is it diagnosed?
- 3.1 Ultrasound procedure
- 3.2 X-ray
- 3.3 MRI
- 3.4 Arthroscopy
-
4 Treatment
- 4.1 Immobilization
- 4.2 Medicines
- 4.3 Surgical intervention
- 4.4 Possible complications
- 5 Folk remedies
- 6 Rehabilitation
- 7 How long does the cruciate ligament recover?
- 8 Forecast
- 9 Anterior cruciate ligament video
The structure and function of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint
The joint includes:
- patella;
- femoral;
- tibia.
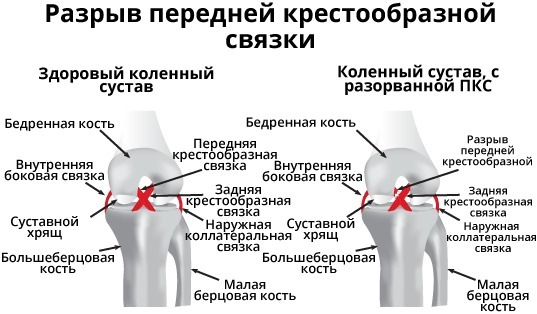
Given the poor correspondence of the articular surfaces to each other, menisci are present here. The joint is strengthened with external and internal ligaments and a fibrous capsule. The main structure that ensures its stability is the internal ligaments (posterior and anterior cruciate).
They complement each other functionally. PKS is a connective tissue strand (on average, length 32 mm, width 9 mm), which located between the outer condyle of the femur and the anterior intercondylar eminence tibia.
 It prevents the shin from moving in the frontal direction at the moment of flexion of the limb and limits the displacement inward of the tibia during extension. It is considered as a passive joint stabilizer.
It prevents the shin from moving in the frontal direction at the moment of flexion of the limb and limits the displacement inward of the tibia during extension. It is considered as a passive joint stabilizer.
Causes, degree, symptoms of damage, degenerative changes in the anterior ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (its anatomy is described in the article for informational purposes) is damaged during joint injuries (during sports or during time of car accidents, if the person in the front seat is not wearing a seat belt and in a collision receives a sharp blow from the dashboard on knees).
Trauma can be contact if it occurs with the participation of an external force (for example, a collision with another player in team sports), and non-contact - under the influence of internal forces (a sharp turn on the support leg).
In the acute period, sprains, ligament ruptures (full or partial) occur. With frequently repeated injuries, especially of the same type, degenerative changes in tissues occur over time.
Factors predispose to injury:
- disproportionate development of the muscles of the thigh (front and back groups);
- women and adolescents often initially have some instability in the knee joint (due to more elastic ligaments and less strongly developed muscles);
- non-observance of the correct technique for performing exercises (for example, improper landing when jumping);
- fatigue after exercise;
- inappropriate equipment for sports (sneakers, ski boots);
- previous damage.
Damage reasons:
- Flexion, abduction and rotation of the lower leg outward with a fixed foot (skiing, hockey, car accidents) provoke damage to the anterior, tibial collateral ligaments and internal menisci (the so-called "Unhappy triad").
- Flexion, adduction and turn of the lower leg inward (wrestling, direct blow to the knee in bent condition) lead to trauma to the cruciate and peroneal collateral ligaments, as well as the iliotibial path).
- Sharp extension of the adducted joint.
Given the very close interaction of bones, ligamentous apparatus, joint capsule of the joint, isolated damage to the ligaments never occurs.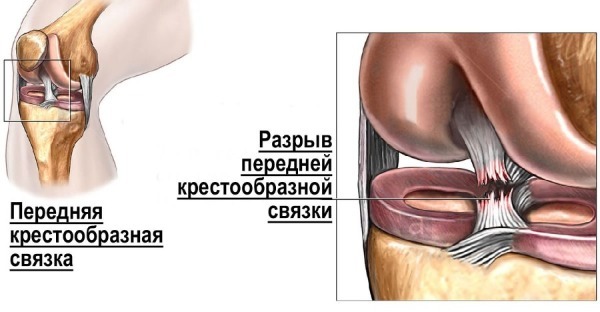
Therefore, their degrees are classified as the severity of the unstable state of the entire joint:
|
Degree Indicators |
Compensated | Subcompensated | Decompensated |
| Joint instability | Missing |
Appears sometimes |
Always present |
| Forecast for the elimination of pathological shin displacements | Completely eliminated | Partially eliminated | Not eliminated |
| Limb support | Normal | Normal | Reduced |
| Lameness | No |
Appears after physical activity |
There is always |
|
Execution of special tasks (walking, running, jumping) |
No restrictions | Restrictions arise after exercise, jumping is difficult |
Walk without outside additional fixing difficult, running and jumping impossible |
|
Periarticular strength muscle |
Regular | Slightly reduced | Significantly reduced |
|
Endurance thigh muscles to long work |
Does not suffer | Slightly reduced | It is even difficult to carry out household loads |
| Joint pain complaints | No pain |
May sometimes appear after significant loads |
Always present, even at light loads |
| Synovitis (inflammation characterized by the accumulation of serous fluid in the joint) |
May arise and pass on one's own |
Occurs under heavy loads, on your own not passes |
Occurs at light loads, not stops independently |
The anterior cruciate ligament (its anatomy determines the nature of possible trauma) can be subjected to sprains, partial or total ruptures.
Symptoms of a ligament injury include:
- acute pain in the knee at the time of injury;
- a pop or pop inside the joint;
- rapidly developing hematoma and edema;
- lack of stability in the joint after injury.
In the later stages of pathology, muscle wasting develops.
During the examination, characteristic symptoms can be identified:
-
Front drawer symptom. The injured leg needs to be bent at the knee joint to 120 °, with one hand they hold the thigh, and with the other they try to move the lower leg forward. An offset of 5-10 mm indicates grade I, 15 mm is typical for grade II, more than 15 mm indicates grade III.
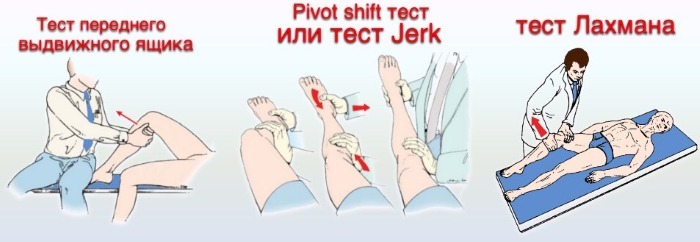
- Lachman test: the patient is in the supine position, the injured knee joint is slightly bent and the shin is shifted forward. It is possible to accurately measure the amount of displacement with a special device, an arthrometer. There are 4 degrees: I - shin displacement by an average of 5 mm, II - 8 mm displacement, III - 13 mm displacement, IV - 18 mm or more displacement.
- Symptom of the anterior dynamic subluxation of the lower leg. Having laid the patient on his back, the doctor takes the injured leg by the foot with one hand and turns the lower leg inward, with the other hand palpates the lateral epicondyle of the thigh. When the joint is flexed to 30-40 °, an anterior subluxation of the tibia is observed, which is eliminated with continued flexion.
- Quadriceps muscle test. The knee joint is bent 90 °, the injured one should lie on the back, the foot is pressed to the surface. Then the patient must straighten the leg, while the tibia is displaced relative to the thigh.
- Symptom of active dynamic subluxation of the lower leg. The patient tries to bend the leg at the knee joint 90 °, while the tibia is displaced forward relative to the hip.
Why are injuries and changes in the knee ligament dangerous?
If treatment is not started on time, or not carried out at all, as well as with regularly recurring injuries (in athletes), late complications develop. These include chronic decompensated joint instability, the development of post-traumatic arthrosis. Then it will be possible to return the ability to move only with the help of knee arthroplasty.
First aid
The anatomical structure of the anterior cruciate ligament is such that in the event of an injury, it is necessary to provide rest to the joint:
- lay the patient with a slightly raised affected limb;
- perform immobilization with a tire or any available means (boards, thick sheets of cardboard, etc.);
- put ice on the joint area.
If possible, you need to anesthetize the victim. Functional tests (“front drawer” symptom and others) must not be performed immediately after the injury before the patient is admitted to the hospital and performed X-ray of the joint, since intra-articular fractures are not uncommon with trauma, then check for the presence or absence of these symptoms at all contraindicated.
How is it diagnosed?
Due to the complex anatomical structure of the knee joint, it is recommended to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of its injuries and pathologies. Specific examinations are prescribed by a traumatologist after a visual examination and on the basis of anamnesis.
Ultrasound procedure
The method allows you to see soft tissues, edema, to identify fluid in the joint cavity. It is possible to assess the degree of divergence of the articular surfaces without radiation exposure.
X-ray
Diagnostics reveals indirect and additional signs in case of joint injury. The ligament itself (since it is not a bone structure) is not visible on examination. 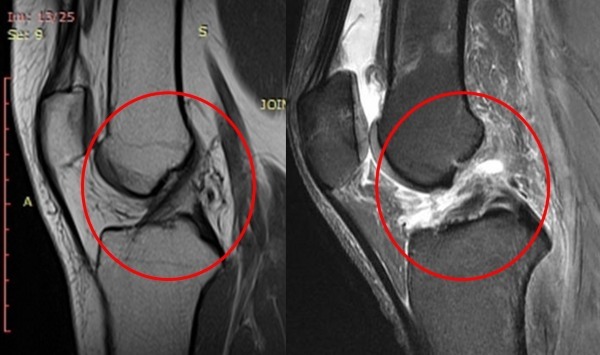 In the acute period, radiography makes it possible to exclude intra-articular fractures, and later (already with advanced joint instability) reveals signs of deforming arthrosis.
In the acute period, radiography makes it possible to exclude intra-articular fractures, and later (already with advanced joint instability) reveals signs of deforming arthrosis.
MRI
Anterior cruciate ligament (its anatomy is clearly visible on MRI, which is the most accurate non-invasive diagnostic method) normally looks like a dark strip of low-intensity signal inside joint.
Signs of damage on MRI:
- the ligament is not visible at all;
- there is no continuity of its fibers;
- the remaining fibers are incorrectly oriented;
- the ligament has a wavy outline.
Arthroscopy
It is an accurate but invasive method for diagnosing ligament damage. However, arthroscopy can be performed in acute trauma and can be used not only as a diagnostic method, but also as a therapeutic one (surgical repair of the ligament). The best results are achieved when the ligament is sutured within 2 weeks from the moment of injury.
Treatment
Treatment of pathologies and injuries of the knee joint is carried out in a complex manner, since a rather quick effect from the measures taken is desirable. The procedure for using the techniques is determined by the attending physician (surgeon or traumatologist).
Immobilization
The method is used in acute conditions after injuries or obvious instability of the joint.
To ensure immobility (or limited movement) of the joint, knee pads, orthoses are used, and in severe cases, plaster casts are used.
They can be used in conditions of all severity, however, it is undesirable to use them longer than 2 weeks.
With prolonged immobilization, atrophy of the thigh muscles begins, which further complicates rehabilitation and worsens the prognosis.
Medicines
In case of anterior cruciate ligament injury, drugs from the group of anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal) drugs are used (they have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic effects). The main contraindication in this case is an exacerbation of gastric ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer.
For therapy, the following are mainly used:
- Arcoxia 90 mg 1 tab. 1 time per day, it is possible to use up to 2 weeks.
- Ibuprofen 200 mg 1 tab. 3-4 times a day, but not more than 5 days.
- Ortofen 25 mg 3 times a day for 5-7 days.
If it is necessary to take these drugs for a long time, it is necessary to take in parallel Omeprazole 20 mg, 1 capsule 2 times a day, to prevent the occurrence of ulcers in gastrointestinal tract.
Surgical intervention
The intervention is most effective up to 2 weeks after a ligament rupture.
Techniques used:
- stitching the ligament;
- autotransplantation (cutting out a new ligament from the patellar ligament of the patient himself);
- prosthetics with synthetic materials.
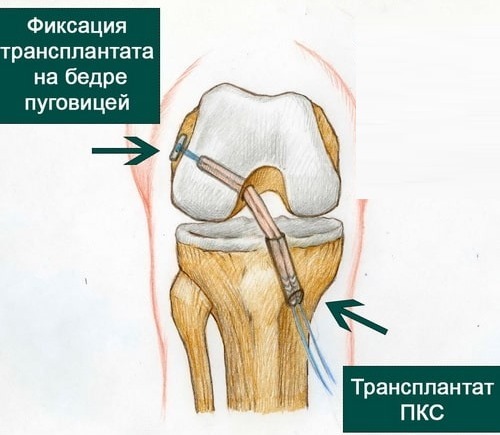
Currently, it is preferable to perform the operation endoscopically (arthroscopy), but sometimes traditional open interventions are also used. In addition to the reconstruction of the ligament itself, during the operation, blood is also removed from the joint cavity (hemarthrosis always accompanies trauma), which subsequently also reduces the risk of arthrosis.
Possible complications
Possible complications after surgery are infection of the joint cavity, rejection of synthetic prostheses. They are very rare. The efficiency of the operation is usually high.
Surgical treatment is preferable for athletes and people engaged in manual labor, young able-bodied men. In elderly people leading a sedentary lifestyle, after treatment (without surgery), if subcompensated joint instability remains, this does not affect their quality of life.
However, the lack of treatment of the anterior ligament (or its low effectiveness) provokes the development of instability of the joint as a whole and, accordingly, creates conditions for the progression of its pathological states. According to statistics, about 40% of cases of hemarthrosis are not associated with trauma, but occur in a state of relative or complete rest.
Folk remedies
The anterior cruciate ligament (its anatomy does not provide for therapeutic effects in difficult situations) is most often the field of activity of traumatologists.
However, it is possible to use folk remedies as auxiliary methods of treatment. For the most part, all of them are aimed at stopping or reducing pain and inflammation. The therapeutic effect is quite rare.
Several folk recipes used for treatment:
- Badyaga. The product is released in powder form. It is necessary to dilute it with water to the consistency of gruel, apply to the knee joint, rinse off after 20 minutes. The medicine should be used daily, there are no restrictions on the duration of treatment.
-
Blue clay. 3 tbsp. l. should be mixed with water or chamomile decoction, applied to the sore knee, covered with cling film on top, rinsed with water after 15 minutes. The procedure must be carried out twice a day. There are no restrictions on the duration of the course of treatment.
- Aloe juice. You can mix the pomace with honey in a 1: 1 ratio. Before going to bed, the specified composition is rubbed into the joint area, a woolen knee pad or scarf must be worn on top. The medicine works all night long.
- Semi-alcohol (vodka) compresses. The fabric impregnated with vodka is applied to the joint, from above it is necessary to wrap it with cling film, then a woolen scarf. The compress is applied for 30 minutes twice a day.
- Alcoholic tincture of Adam's apple. Grated Adam's apple is required to pour 0.5 liters of vodka or 40-45% alcohol solution (it is more effective to use single distillation moonshine) and leave in a dark place for 2 weeks. You need to use the medicine 2-3 times a day for local rubbing of the affected area or as a compress for 2-1.5 hours. The course of treatment is 10-15 days, followed by a monthly break. Adam's apple is poisonous and cannot be used inside. After use, hands should be thoroughly washed with soapy water.
Rehabilitation
Recovery takes place in a complex way:
- Physiotherapy methods. Electrophoresis, paraffin therapy, magnetotherapy with a course of up to 10 procedures are widely used.
- Therapeutic gymnastics is essential for successful rehabilitation. The course must be taken under the supervision of an exercise therapy doctor. It is better to start in the acute period, even with immobilization of the joint, to prevent muscle wasting.
- Elastic bandages, orthoses, bandages can be used in the acute period, preferably no more than 3 weeks. In case of chronic instability of the joint, it is recommended to use them for prolonged walking or other stresses affecting the joint.
How long does the cruciate ligament recover?
A ligament with a complete rupture does not recover on its own. Such damage can only be repaired by prompt methods. If the operation was not performed, then during the right rehabilitation the function of the ligament is taken over by other stabilizers of the knee joint.
The role of active stabilizers (thigh muscles) is great, therefore, therapeutic exercises are indispensable in treatment. Usually, subcompensated instability in the knee joint remains in the future. In case of stretching and incomplete rupture, the restoration of the ligament is possible in 3-6 weeks.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the degree of damage to the ligament, the quality of treatment. With timely therapy, the prognosis is usually favorable, but with frequent lesions of the same type in the long term, degenerative damage to the ligament, arthrosis, often develops.
With an untreated complete rupture, poor rehabilitation, atrophy of the muscles of the limb develops, decompensated chronic instability of the knee joint, since the anatomical significance of the anterior cruciate ligament lies precisely in knee stabilization.
Anterior cruciate ligament video
Cruciate Knee Ligament Treatment:



