Abdominal muscles are part of a group of muscles that form the walls of the abdominal cavity from the front and from the sides.
The group includes:
- outer and inner oblique;
- transverse;
- straight.
They are arranged in layers and intersect at an angle: this gives strength to the wall.
Record content:
- 1 Anatomy and function
-
2 Major injuries and illnesses
- 2.1 Neuromuscular disorders
- 2.2 Trauma
- 2.3 Causes of pathologies
-
2.4 Symptoms
- 2.4.1 Myopathies
- 2.4.2 Myotonia, myoplegia and myasthenia gravis
- 2.4.3 Stretches and tears
- 2.4.4 Wounds and abdominal bleeding
- 2.5 Diagnostics
-
3 Treatment
- 3.1 Medicines
- 3.2 Surgical manipulations
- 3.3 Physiotherapy and massage
- 3.4 Folk remedies
- 4 Possible complications
- 5 Abdominal Muscles Videos
Anatomy and function
The external oblique muscle of the abdomen begins on the outside of the ribs (IV-XII pairs). It goes diagonally to the junction of the pelvic bones. This muscle is broad and superficial. In fact, it lines the anterolateral abdominal wall.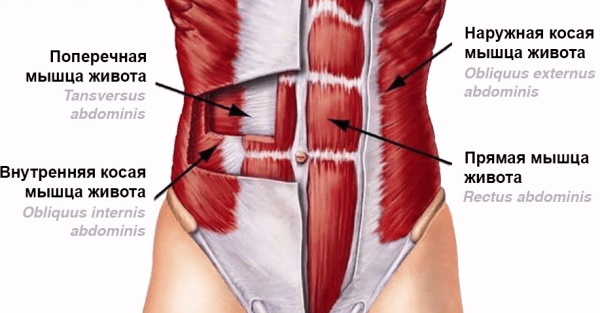
In the upper part, the muscle has teeth. The upper ones connect with the muscles of the chest, and the lower ones with the muscles of the back. From below, the muscle bundles end at the midline of the abdomen and pelvis, developing into an extensive aponeurosis.
The external oblique muscle of the abdomen responds to signals transmitted from the intercostal, iliac and inguinal nerves. Blood is supplied by the posterior intercostal arteries, the lateral thoracic artery and the superficial artery surrounding the ilium.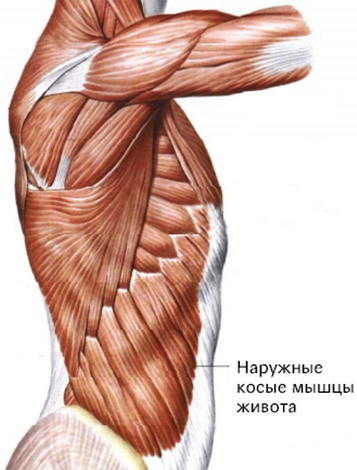
With a bilateral contraction on exhalation, the ribs fall, the spine bends. When contracting from one side, the body turns to the other side. In a horizontal position, the pelvis rises.
Major injuries and illnesses
All pathologies of the muscular system can be divided into two large blocks: trauma and nerve damage. Traumatologists and neurologists adhere to strict classifications when making a diagnosis.
Neuromuscular disorders
In neuromuscular diseases, muscular disorders develop due to disruption of the nervous system.
These include:
- Primary and secondary myopathies.
- Congenital myopathies.
- Myotonia.
- Hereditary paroxysmal myoplegias.
- Myasthenia gravis.
Myopathy is a condition in which a muscle undergoes degenerative changes. In primary myopathies, the muscle is directly affected. It can be caused by inflammation due to a viral or bacterial infection, autoimmune disorders, or mitochondrial malfunction.
Secondary myopathies appear as a symptom of peripheral nerve pathologies. They are congenital, early and late childhood. At first, the disease has no clinical manifestations, so doctors do not immediately diagnose such diseases. As you get older, the disease progresses, gradually leading to muscle atrophy.
Congenital myopathies are distinguished by the fact that at the time of birth, a certain muscle or muscle group no longer works in a child. Such diseases do not progress. They cannot be treated, so the child learns to live with his own peculiarity. At the same time, there are no deviations in development.
Myotonia is the involuntary contraction of a muscle. Spasms can be spontaneous or occur with epilepsy. Heredity and stress matter. Myoplegias have the opposite property: in them, the patient is disturbed by sudden attacks of muscle weakness. With myasthenia gravis, the patient has constant muscle weakness. This is usually a congenital condition.
Trauma
Another big block of muscle damage is injury. They are:
| Closed | |
| A type | Characteristics |
| Bruises | |
| Stretching | Muscle dislocation occurs, sometimes it is accompanied by rupture of individual fibers. |
| Breaks | With a complete rupture of the muscle, its integrity is violated. |
| Prolonged Compression Syndrome | a condition that occurs when a muscle is squeezed for a long time by an external factor (tourniquet or stone). Tissue necrosis begins, but due to the suppression of blood flow, dangerous decomposition products accumulate in the damaged area. When the pressure factor is removed, these substances are injected into the circulating blood and enter the vital organs. In the case of the muscles of the abdominal wall, the mere fact of compression is sufficient for a lethal outcome: there is no bone skeleton in this area, therefore, together with the muscles, the internal organs are squeezed. The syndrome occurs when buildings collapse, when a person is trapped in massive debris, and rescuers need time to clear a path to him. |
| Open | |
| By the mechanism of application | Description |
| Wounds | Cut, chipped, stab-cut, torn, bitten, chopped, crushed, bruised, gunshot. |
| Burns | Grade I is characterized by damage to the upper layer of the skin. II degree consists in the defeat of the upper layer of the skin with the formation of a blister. Grade IIIA is a deep lesion of the skin; a thin, intact layer remains at the bottom of the wound. IIIB degree - complete necrosis of the skin to adipose tissue. IV degree - the death of adipose, muscle and bone tissue. |
Causes of pathologies
The causes of many neuromuscular diseases are either hereditary characteristics, when such a disease was observed in a close relative, or a violation of embryonic development.
Early childhood myopathies first appear in toddler or preschool age, and late ones occur before puberty. Congenital defects are visible to pediatricians immediately after the birth of a baby, but usually it concerns the muscles of the lower extremities, less often the upper ones. In isolated cases, the mimic muscles suffer. There is no evidence of a congenital abdominal muscle defect.
If myopathy manifests itself in adulthood, then doctors talk about the primary nature of the disease. A virus or bacteria will not immediately infect muscle tissue, because it is not a favorable environment for them. However, inflammation can be transmitted to the muscles if it was in adjacent tissues and was not treated.
Purulent abscesses are found in the subcutaneous fat in the abdominal region and quickly pass the thin fascia that covers the abdominal muscles.
Involuntary muscle contractions or relaxation in both children and adults have a complex origin. They can be symptoms of a serious neurological disease, or they can be caused by a person's intense stress.
The abdominal muscles stretch a lot during pregnancy. If a woman has an athletic physique, then the likelihood of muscle complications after childbirth is greatly reduced. In this case, the abdominal wall is well strengthened, and the musculature is highly developed, therefore it can tolerate internal pressure more calmly.
In women who did not give the abdominal muscles physical activity, after childbirth, the return of the body to its normal state is slower. An increase in the waist during this period is normal. Moderate abdominal exercise will help your abdominal muscles return to their previous state faster.
Symptoms
Each pathology has its own symptomatology:
Myopathies
The main symptom of myopathies is a decrease in muscle performance. Gradually, it becomes impossible for the patient to use the affected muscles. In the case of the external oblique muscle, it is difficult to rise from a horizontal position, the patient lies down on his back with support on his hands, it is also difficult for him to turn the body to the other side of the weakened plot.
Over time, the muscle begins to atrophy as it is not being used. The disappearing muscles are replaced by connective tissue. It is dense and inelastic, and to the patient the replacement looks like a trained body.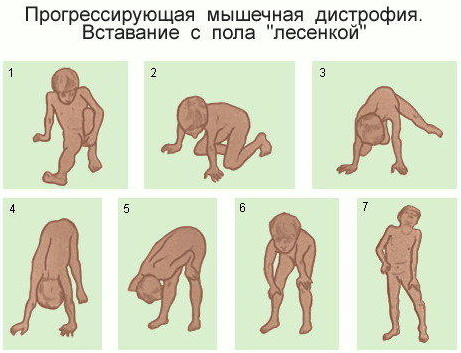
In this case, contracture occurs - a condition where the muscle cannot stretch. With contracture of the anterior muscles of the trunk, it is impossible to bend back or turn.
Myotonia, myoplegia and myasthenia gravis
It is easy for the patient to notice a myotonic attack: it is a sharp, strong and sudden muscle contraction. If this is not an isolated case, you need to see a doctor.
Myoplegic attacks also require professional supervision, since relaxation of the muscles involved in the act of breathing can impair a person's ability to breathe. Such cases are life-threatening. Myasthenia gravis rarely affects the muscles of the trunk separately. Rather, they will be affected along with the lower limbs and back muscles.
Stretches and tears
The abdominal muscles are painful, limited in movement. Swelling and minor bruising are possible, since sprains of the external oblique muscles occur during injury. The patient notes that he was involved in sports and hard work shortly before the onset of unpleasant sensations.
When a muscle ruptures, pathological increases in its function are noted: the area becomes too mobile, since there is no restraining factor. There is a protrusion of the torn end, extensive edema and hemorrhage, far beyond the gap.
Wounds and abdominal bleeding
Wounds that reach the muscle tissue are marked by profuse bleeding, which is difficult to stop on your own. There are no large vessels in the abdomen that lie close to the surface of the body, so the patient needs urgent, but not emergency, care. Such injuries do not threaten the victim's life.
If the wound is inflicted with a sharp object and has cut the abdominal wall so that through the hole you can get directly into the abdominal cavity, then this condition is dangerous. The integrity of the internal organs is violated, which cannot function normally. Such injuries are accompanied by acute pain.
With both injuries and closed injuries, there is a possibility of abdominal bleeding. In the case of small vessels, the patient notes weakness, cold sweat, pallor of the skin and a decrease in blood pressure.
In case of rupture of larger vessels, the victim is worried about severe pain, loss of consciousness or shock is possible. With internal bleeding of any scale, a person is uncomfortable lying, so he strives to take a sitting position. This is called the Vanka-Vstanka symptom.
Diagnostics
The main methods for diagnosing neuromuscular diseases:
- Blood chemistry. It can be used to determine the level of muscle enzymes: creatine phosphokinase (CPK), myoglobin and aldolase.
CPK is involved in biochemical reactions between neurons and muscle fibers. As a result, the nerve impulse is amplified and the muscle cell contracts with the necessary force. If the CPK level is increased in the analysis, this means that the enzyme is uncontrollably released into the blood and is not enough for biochemical transformation. The impulse does not increase and the muscle does not contract as it should.
Myoglobin is a muscle tissue protein that helps transport oxygen. Normally, it is inside the cell and is not found in the blood. When myoglobin is released from cells into the blood, muscles do not receive enough oxygen and cannot function normally.
Aldolase is involved in energy metabolism, its function is the breakdown of carbohydrates. High concentrations of aldolase are found in muscle fibers, as this tissue requires a lot of energy to work. With a decrease in aldolase, muscle cells lack "charge".
- Electrophysiological research. These include electromyography and electroneuromyography. Sensors are attached to the patient to record the strength of muscle contractions. At this time, the doctor gives the muscle a load and looks at the readings of the instruments. This allows you to determine the degree of development of the disease.
- Biopsy. A small piece of the affected muscle is taken from the patient and sent to the laboratory for examination. This method helps to differentiate between primary and secondary myopathies.
- Genetic testing. It is carried out in infants when it is impossible to establish verbal contact with the child. By analyzing DNA, geneticists can identify hereditary diseases or chromosomal mutations in a patient.
To diagnose injuries, doctors use:
-
Radiography. If you suspect a muscle strain or rupture of the abdominal wall, doctors need to understand if the ribs are affected. A fracture can only be detected on an X-ray or computed tomography.
- Ultrasound procedure. An ultrasound scan allows the doctor to see abdominal bleeding and assess the condition of the internal organs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. A reliable method for examining soft tissues. Shows a layered image of the scanned area.
Treatment
The external oblique muscles of the abdomen are rarely affected by disease or injury. However, if this happens, there are several ways to solve the problem.
Medicines
Neuromuscular diseases cannot be completely cured, the disease is constantly progressing. Drug therapy is aimed at slowing down this process and alleviating the patient's condition.
The doctor can prescribe drugs that stimulate metabolism, calcium preparations, vitamin complexes. In severe cases, hormonal drugs are prescribed. We must be prepared for the fact that medicines will have to be taken throughout life.
Medical treatment for injuries depends on the severity. With slight stretching, it is enough to use a warming ointment to increase blood flow in the injured area and speed up the recovery process. In case of incomplete ruptures, the torn tissue is immobilized: the body is tightly covered with an elastic bandage, wearing a bandage is mandatory.
In the presence of a hematoma, the patient is prescribed antibiotics to prevent inflammation in the blood clot, and he was able to dissolve himself. You will have to take painkillers for some time to drown out the pain.
Treatment of open wounds is surgical, but the patient has to take care of himself in the postoperative period himself.
Immediately after removing the stitches, it is recommended to treat the skin with alcoholic antiseptics, for example, fucarcinum or brilliant green. On top of this, an antibacterial powder is applied. Healing ointments can be used later.
If the internal organs were injured during injury and their function was impaired, then the doctor prescribes drugs to compensate for this deficiency. These drugs include tablets or suspensions containing enzymes produced in the damaged organ. The patient will also take antibiotics and pain relievers.
Surgical manipulations
Only injuries are subject to surgical treatment. In case of muscle ruptures, the surgeon sutures the torn ends together, stops bleeding in case of damage to the vessels, and removes the resulting hematoma.
The external oblique muscle of the abdomen develops into an extensive aponeurosis, which can also rupture. Surgeons cope with such cases, but the rehabilitation process will take longer, since the connective tissue is less elastic, it is less well supplied with blood and its cells divide more slowly.
In the case of wounds, surgeons have protocols for operations. The doctor will first remove any non-viable tissue. Then he will carry out an antiseptic treatment of the wound and begin to stitch the edges in layers, installing drains. If necessary, the surgeon stops bleeding from damaged vessels.
Physiotherapy and massage
Neuromuscular diseases are inextricably linked to physiotherapy. So that the connection between the muscles and the nervous system does not break, it is recommended to resort to neurostimulation or myostimulation: depending on the problem, external sources will force neurons or muscles work. In the initial stages, the patient is engaged in physiotherapy exercises.
Massage is a way to correct blood flow. It heats up the right place and disperses the blood. Enhanced nutrition keeps the muscles in working order.
Physiotherapy is an indispensable element of rehabilitation after sprains and ruptures. Without it, the injured muscle "gets used" to its inoperative position and remains in it. Physical therapy, UHF and massages prevent this.
Folk remedies
Neurological diseases cannot be treated with folk methods. Such patients should be accompanied by a qualified professional. They need hardware rehabilitation methods and evidence-based drug therapy.
The same applies to open wounds, burns and tears of muscles and tendons. If the injury looks threatening or if there is severe pain, it is necessary to contact the clinic for a reliable diagnosis.
However, minor sprains can be dealt with on your own. Immediately after the injury, it is necessary to apply cold to this place. To protect against frostbite, it is best to place a towel under the cold compress. After two days, the cold can be changed to warming compresses. For this, decoctions of tansy or cornflower are suitable.
Possible complications
In the case of neuromuscular disorders, complications cannot be avoided due to the progression of the disease. Over time, this will lead to the immobilization of the patient. The lethal outcome occurs due to atrophy of the respiratory muscles.
A delayed complication of open wounds can be suppuration and scarring. Surgeons try to make neat stitches, rinse the wound as much as possible, and do regular dressings. But there is always a risk that the wound will fester: you will have to do a second operation, but the guarantee of a beautiful suture will no longer be given.
Tears and sprains, if not properly treated, can turn into contracture. In this state, the muscle is dysfunctional, and every attempt to use it will be painful.
The abdominal muscles are rarely subject to injuries and diseases: the back and lower legs remain the leaders in traumatology. The external oblique muscle quickly recovers from injuries and injuries, and qualified doctors will help this process to proceed comfortably for the patient.
Abdominal Muscles Videos
Functional anatomy of the abdominal muscles:



