What is it?
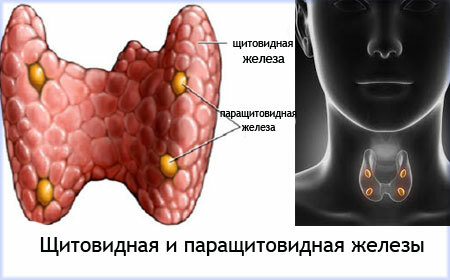
AIT, an autoimmune thyroiditis of the thyroid gland is one of the forms of organospecific pathologies of autoimmune genesis, characterized by inflammatory processes in the thyroid gland that cause lymphoid infiltration and destruction of the follicular tissues of the organ.
The disease has a hundred-year history and was first described by the Japanese surgeon Hashimoto. Subsequently, the pathology began to be called his name -
"goiter or thyroiditis Hashimoto."
Mature women are mainly affected by adulthood( 45-60 years of age), which is due to the X chromosome disorder and estrogenic effect on the cells of the lymphoid system participating in the immune response mechanism. In some cases, it affects young people and children. In more than 20%, autoimmune thyroiditis occurs in pregnant women.
About the causes and development of
The genesis of AIT development is caused by phagocytic aggression of immunity to the thyroid tissues, perceiving them as a foreign "agent" and producing antibodies to them. This fact causes autoimmune processes of inflammation and destruction of the body cells, including those that produce hormones.
This explains the development of autoimmune thyroiditis, hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis, when there is a decrease, or an increase in hormonal synthesis. In addition, autoimmune inflammatory processes in the tissues of the thyroid gland give impetus to the development in them of cystic and nodal neoplasms.
Autoimmune thyroiditis is referred to the division of genetically inherited diseases, which is often confirmed by the presence of pathology in relatives close to the patient's relatives. But genetic predisposition is not the only cause of AIT.To launch a phagocytic malfunction and hormonal dysfunction can:
- frequent pathologies of a viral and bacterial nature;
- chronic ENT infections;
- harmful environmental factors provoking an increase in immune activity;
- excessive exposure to radiation and UV radiation;
- prolonged uncontrolled intake of hormones and iodine-containing drugs;
- iodine deficiency in the body;
- periods of hormonal changes;
- immune insolvency and predisposition to allergy
- surgical interventions on the thyroid and trauma;
- Nervous pathology and stress. Such patients are often accompanied by other autoimmune diseases - diffuse processes in the thyroid gland( Basedova's disease), the development of asthenic bulbar paralysis( myasthenia gravis), Graves' endocrine ophthalmopathy, lacrimal and salivary gland involvement due to the "dry syndrome" of Shagren, collagenosis( connective tissue pathology),diffuse proliferation of lymphoid cells( lymphoid hypophysitis).
Content
- 1 Symptoms of autoimmune thyroiditis by forms
- 2 Symptoms of autoimmune thyroiditis thyroid
- 3 treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis, drugs
- 3.1 AIT - treatment Endonormom
- 3.2 Possible consequences
Symptoms of autoimmune thyroiditis by forms
AIT has different variations, the genesis of all its forms has the samethe nature of development, the type of aseptic inflammatory process, gradually taking the form of transient hypothyroidism. It appears:
- Autoimmune chronic thyroiditis is a consequence of immune phagocytosis aggression, leading to destructive changes in thyroid gland and causing the development of hypothyroidism.
- Postpartum thyroiditis, which develops as a result of excessive activity of phagocytic protection in the period of pregnancy. In pregnant women predisposed to endocrine disorders, this type of pathology can later be transformed into autoimmune thyroiditis of chronic course.
- The type of painless thyroiditis( silent) is similar to that of postpartum thyroiditis, but genesis is not associated with pregnancy.
- A cytokine-induced form of the disease develops in patients with long-term therapy with "Interferon", with blood diseases and hepatitis "C".
Clinical signs of abnormalities in the thyroid gland are determined by the shape of the AIT flow:
- Hypertrophic, characterized by a uniform increase in the entire thyroid gland or with signs of nodular formations. Functions of the gland are not violated, or slightly reduced. In the initial period, thyrotoxicosis is possible. The progression of the autoimmune process leads to a decrease in functions, a worsening of the condition and the development of hypothyroidism.
- Atrophic, the most severe form of autoimmune thyroiditis, provoked by the extensive process of destruction of thyroid follicular cells, sharply reducing its functions.
Symptoms of autoimmune thyroiditis of the thyroid gland

The AIT clinic is characterized by a four-phase course of the disease: euthyroid, subclinical, thyrotoxic and hypothyroid, which, after succession, can last for years.
Autoimmune thyroiditis is characterized by a slow development of symptoms. Often, the pathological process can occur asymptomatically or with mild symptoms, which is characteristic of the euthyroid and subclinical phase. SHCHZH cells are affected insignificantly and there are no special functional disorders of the organ. This course of the disease can last for dozens of years.
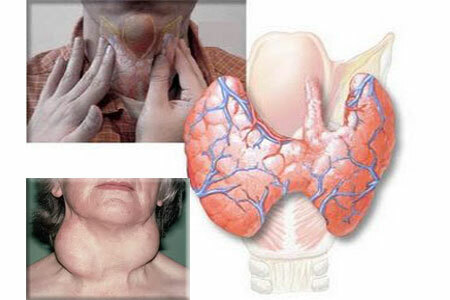
There may be only a slight discomfort in the thyroid zone, in the form of a lump on the throat, there is slight fatigue and weakness, soreness in the joints.
The main symptom of autoimmune thyroiditis is the growth of the colloid goiter. The remaining signs are a reflection of the violation of the process of hormonal synthesis, its reduction or increase - hypothyroidism, or hyperthyroidism( thyrotoxicosis).The clinic of thyrotoxicosis is usually observed in the first few years of development of pathology.
As the development of atrophic processes in the thyroid tissues develops, it is marked by a temporary transient character in the ethereal phase, with the subsequent transition to the phase of hypothyroidism.
A persistent increase in the hormonal level( with thyrotoxicosis) is manifested:
- with a small subfebrile condition of the body;
- by cardiac arrhythmia and hyperhidrosis;
- self-dyspnea, without the influence of loads;
- trembling in the limbs and weight loss;
- insomnia( insomnia) and neuroses( hysteria, irritability).
The hypothyroid phase of AIT is termed the final, due to cellular destruction of the majority of thyroid gland and insufficient hormonal synthesis left by unaffected cells. The decrease in the hormonal level( hypothyroidism) is typical symptomatology:
- chronic fatigue;
- significant increase in weight;
- hypothermia( low temperature) and swelling;
- rough features;
- defects of diction, sluggishness and drowsiness;
- malfunctions in the menstrual cycle, signs of libido and infertility.
Treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis, preparations
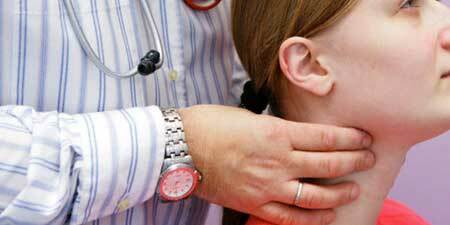
Diagnosis of the disease using the method of palpation and ultrasound examination of thyroid. Deviations of a serious nature are expressed by difficulties in swallowing and breathing caused by compression of adjacent organs. In terms of blood, changes are noted due to inflammatory reactions in the thyroid tissue. The parameters of the immunogram help to determine the increased or decreased level of hormones. Criterion for diagnosis - increased level and aggression of antibodies in thyroid gland - AT-TPO.
Most of the symptomatology is typical for various pathological processes that do not intersect with AIT, therefore, appropriate differential diagnosis is performed.
There is no clear scheme for the treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis. Therapeutic effect is aimed at relief of the symptoms of the disease depending on the phase of the current - thyrotoxic, or hypothyroid. Includes:
- Replacement hormone therapy.
- Therapy is the suppressive hormonal function of thyroid.
- With a strong increase in the body - surgical intervention.
In patients with AIT with signs of hypothyroidism, conservative therapy with the drug "Levothyroxine", "Mercazolil", "Tiamazole", and adrenolitics "Alfa-adrenoblockers", aimed at hormonal regulation, is prescribed.
If the process has an acute course, glucocorticosteroid preparations are added - for example, Prednisolone. Anti-inflammatory non-steroid drugs - Voltaren, Indomethacin, and others are prescribed to reduce the aggression of antibodies to thyroid tissues.
AIT - treatment by Endonorm
The therapeutic complex includes the treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis by Endonorm. A drug is prescribed to reduce the attack of antibodies and replenish macro and microelements of thyroid tissues. Homeopathic supplements, which are part of the drug, help restore the adrenal glands and glands of the reproductive system affected by hormonal imbalance.
So are the preparations of adaptogens that help the body to adapt to harmful effects, vitamin complexes and immunomodulatory therapy.
The most terrible thing that can be expected from autoimmune thyroiditis is the development of autoimmune diffuse processes in various organs and systems of the body, indicating a profound lesion of the endocrine system.
Possible consequences of
The effects of autoimmune thyroiditis are rare and in those cases where no adequate treatment has been performed.
- Among adult patients, mental disorders caused by a depressive syndrome may progress. To manifest a syndrome of decline and underdevelopment of the intellect. Development of cardiac and vascular diseases.
- In childhood, manifested underdevelopment of the organs of the reproductive system, a delay in mental and mental development, down to idiocy and pituitary nanism( dwarfism).
- Consequences of autoimmune thyroiditis in pregnant women can result in signs of gestosis, placental insufficiency and premature termination of pregnancy.
Autoimmune thyroiditis can not be cured completely. The patient will have to depend on lifelong maintenance therapy for life. Timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment, will ensure a full life and eliminate possible complications. Will preserve childbearing functions and physical activity, will help to achieve long-lasting and long-term remission for many years.