At present, in boys born with intrauterine malformations, 7% of diseases are in the genitourinary system. Anomalies can be either quantitative, for example, absence, decrease or increase in the number of testicles, and associated with a change in their normal position. The last group of diseases includes cryptorchidism.
Contents
- 1 Description of the disease
- 1.1 Video: child urologist andrologist KSAbramov about cryptorchidism
- 2 Congenital, acquired, right-sided, left-sided, bilateral, inguinal, abdominal, false and other forms of cryptorchidism
- 2.1 Retention and pseudo-retardations
- 2.2 Ectopia
- 3 Causes and factors of the disease development
- 3.1 Hormonal and analgesic agents, the use of which provokesdevelopment of pathology, pictured
- 4 Symptoms in adult men and newborn boys
- 5 Diagnosis and differential diagnostics
- 5.1 Differential diagnostician
- 6 Treatment of testicular non-invasion: methods, age at which therapy can be started, and other nuances
- 6.1 Operational correction of cryptorchidism and rehabilitation after
- intervention 6.1.1 Feedback from parents and patients who underwent orchidectomy
- 6.1.2 Video: cryptorchidismchildren - treatment with
- operation 6.2 Conservative treatment method
- 6.3 Exercise: what exercises can be performed
- 6.4 Folk remedies
- 6.1 Operational correction of cryptorchidism and rehabilitation after
- 7 Prognosis of treatment and possible complications: testicular cancer, infertility and other opacitiesnye consequences
- 8 pathology prophylaxis
- 8.1 Video: Webinar EOKomarovskiy about the lifestyle of a pregnant woman and its effect on the health of the fetus
Description of the disease
Cryptorchidism is a congenital or acquired pathology characterized by the non-emptying of one or both testicles into the scrotum.
During development of the boy in the womb of the mother, the testicles are located in his abdominal cavity. Normally, with the beginning of the eighth month, the testicle passes through the inguinal canal and descends into the scrotum. If the pregnancy was premature, the child can be born with the pathology, caused by the non-rejection of the testes.
In the risk group are all premature babies - the disease among them is much more common.
It is also possible that in case of full-term boys the testicle sticks along the path of descent:
- in the abdominal cavity;
- in the inguinal canal;
- at the entrance to the scrotum;
- under the skin.
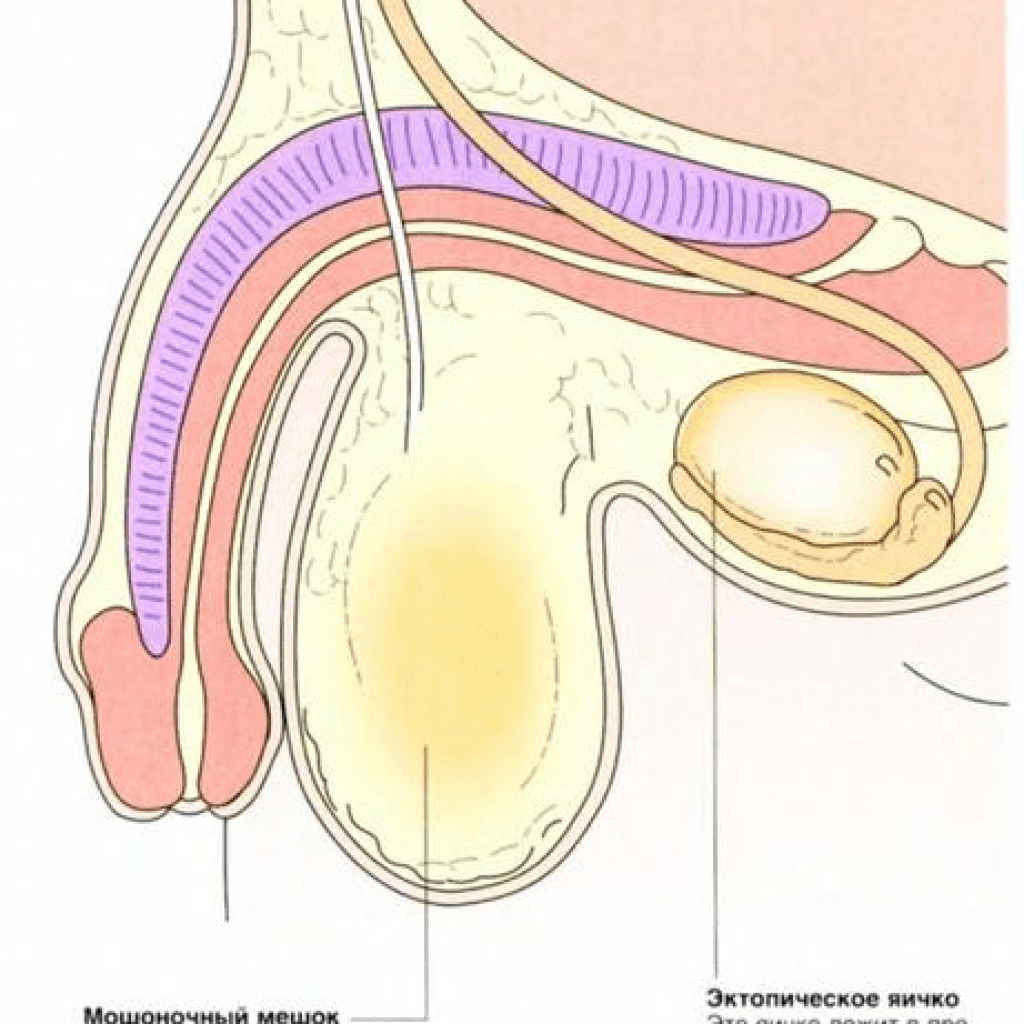
Cryptorchidism is the most common developmental abnormality of the testicles
Adult cryptorchidism can be detected due to lack of early diagnosis, and also as a consequence of trauma. In this case, the operating method is the only way out of the situation, because the wrong location of the testicles increases the probability of oncology and infertility several times.
When diagnosing a disease, you should not postpone a visit to a surgeon, andrologist and urologist. This will allow timely treatment and avoid complications.
Video: child urologist andrologist KSAbramov on cryptorchidism
Congenital, acquired, right-sided, left-sided, bilateral, inguinal, abdominal, false, and other forms of cryptorchidism.
Establishing the type of cryptorchidism is important in determining therapies and the age appropriate for conducting an operation.
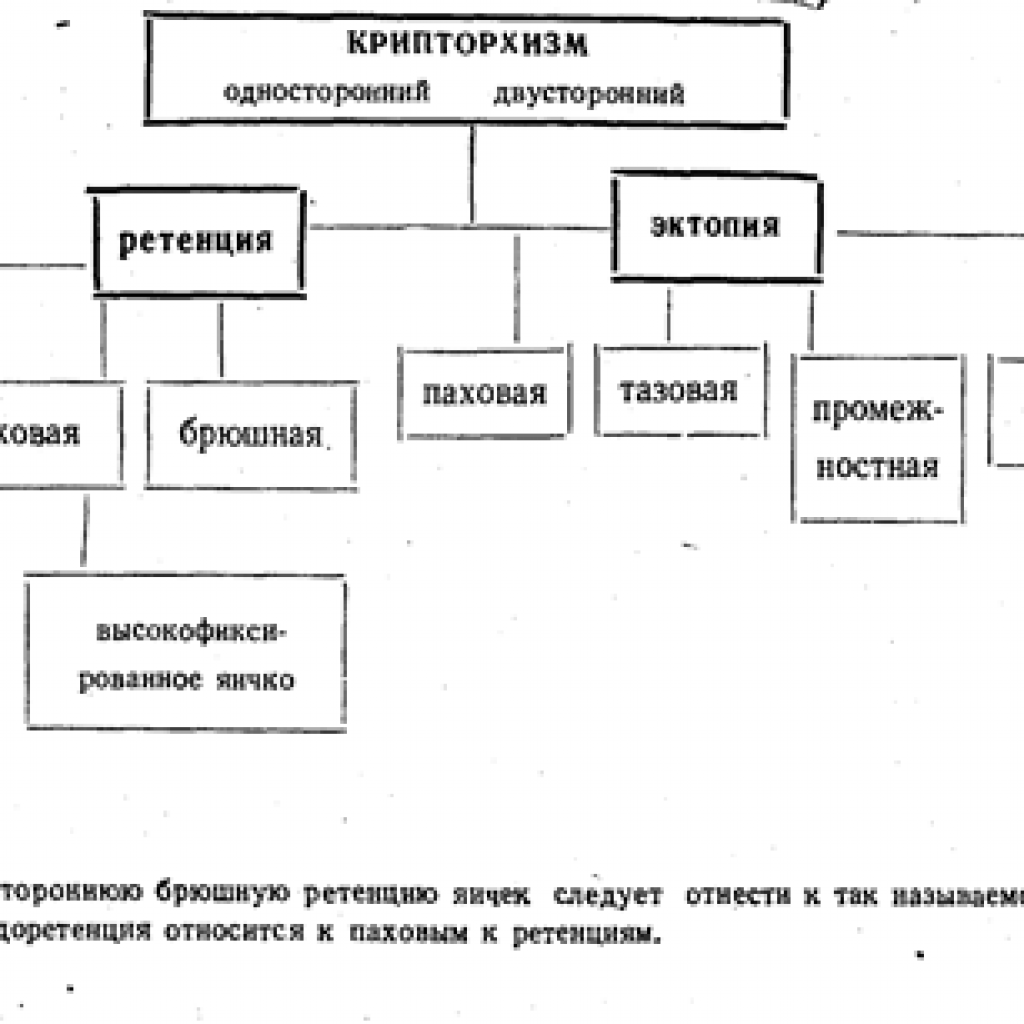
To clarify the forthcoming scope of interventions, classification of cryptorchidism
is of great importance. Retention and pseudo-retention
True cryptorchidism( retention) is considered the non-admission of one or both testicles. With this variant of the disease, the scrotum is always underdeveloped.
It is impossible to dip the testicle into the scrotum by palpation because of the location of the gland in the abdominal cavity, behind the peritoneum or in the inguinal canal.
Also, when manual examination is not always possible to determine the correct location of the testicle.
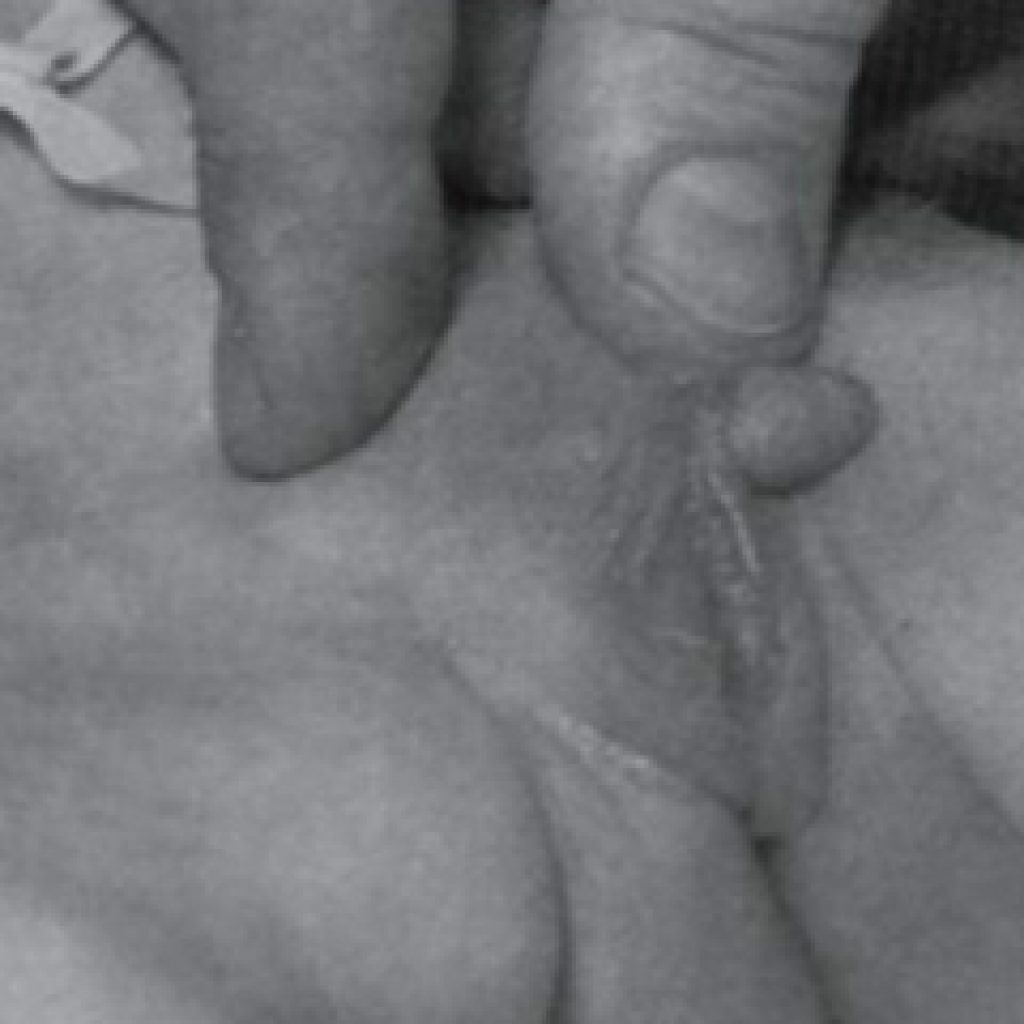
True bilateral cryptorchidism is a common pathology in premature babies
In case of false cryptorchidism( pseudo-retention) the testicle is movable, it can be in the inguinal canal and fall back into the scrotum.
With pseudo-retention, the testicle can easily be returned to its place by palpation.
The cause of pseudo-retention is a small testicle size in comparison with the inguinal canal and the tone of the ligaments holding them. False cryptorchidism manifests itself in sports, over-cooling and stressful situations. Usually with age, the anomaly disappears, so it does not require additional treatment.
By localization, that is, depending on which part of the scrotum the testicle has not undergone, distinguish:
- right-sided form of cryptorchidism;
- the left-hand.
The first variant is most common - in half of patients, the second - in 35-40%, the remaining 10-15% account for bilateral cryptorchidism.
Very rarely( 1-3% of cases) diagnostic methods determine the absence of one testicle( congenital monochromism) or both testicles( anarchism).

Right-sided cryptorchidism occurs in half of patients
In addition to the above-mentioned forms, the acquired cryptorchidism is distinguished. This is a neurotic disease that is a consequence of a groin injury or a result of a hernia operation and wearing a bandage during the rehabilitation period. There is also a variant of development of anomalies in boys under the age of 10 due to the fact that the growth of the spermatic cord does not keep up with the formation of the child's organism as a whole, it shortens and the testicles rise back to the groin area.
Ectopia
In addition to retention, the patient can diagnose the state of ectopia.
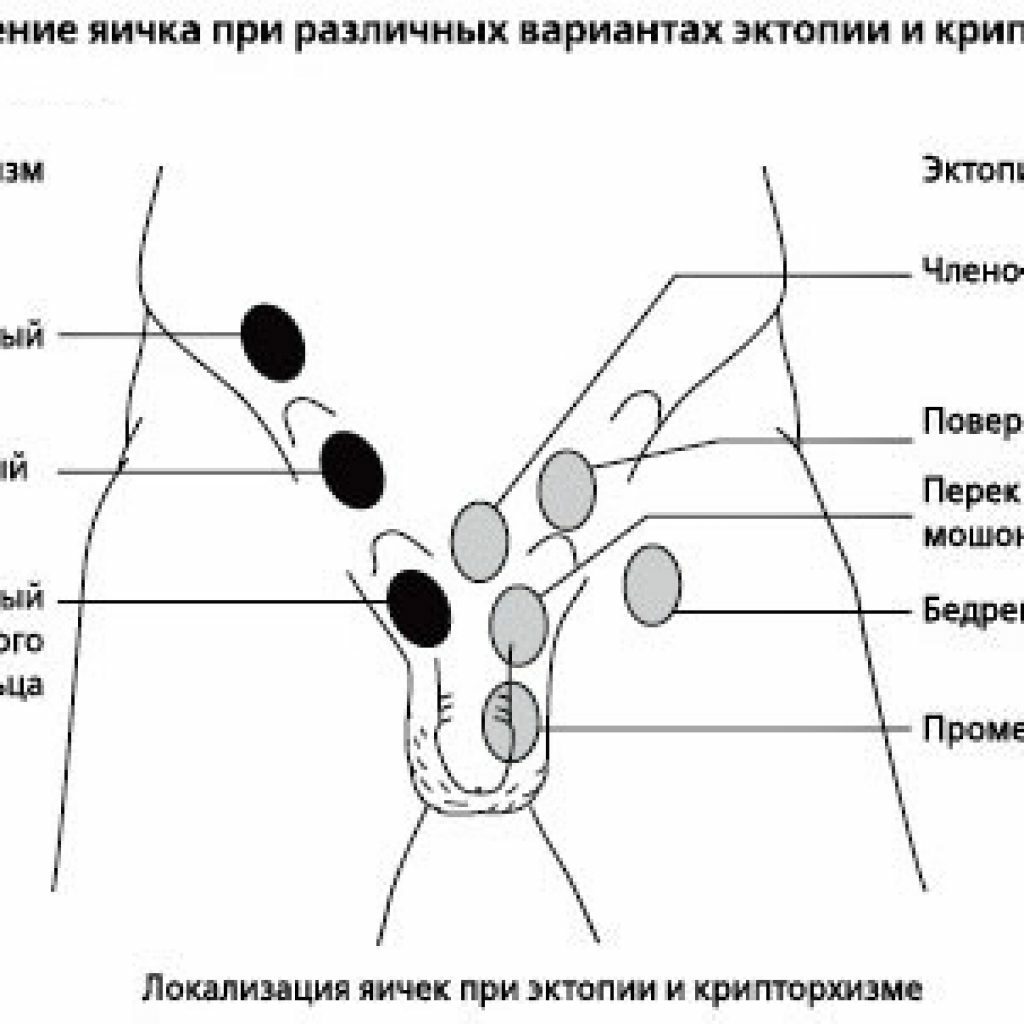
Ectopia - displacement of the testicle from the scrotum to an abnormal position
Ectopia refers to the displacement of the testicle from the scrotum to an abnormal position:
- into the inguinal canal;
- under the skin in the groin;
- in the perineal region;
- at the root of the penis;
- in the opposite part of the scrotum( rare form - cross ectopy);
- on the inside of the thigh;
- in the abdominal cavity.
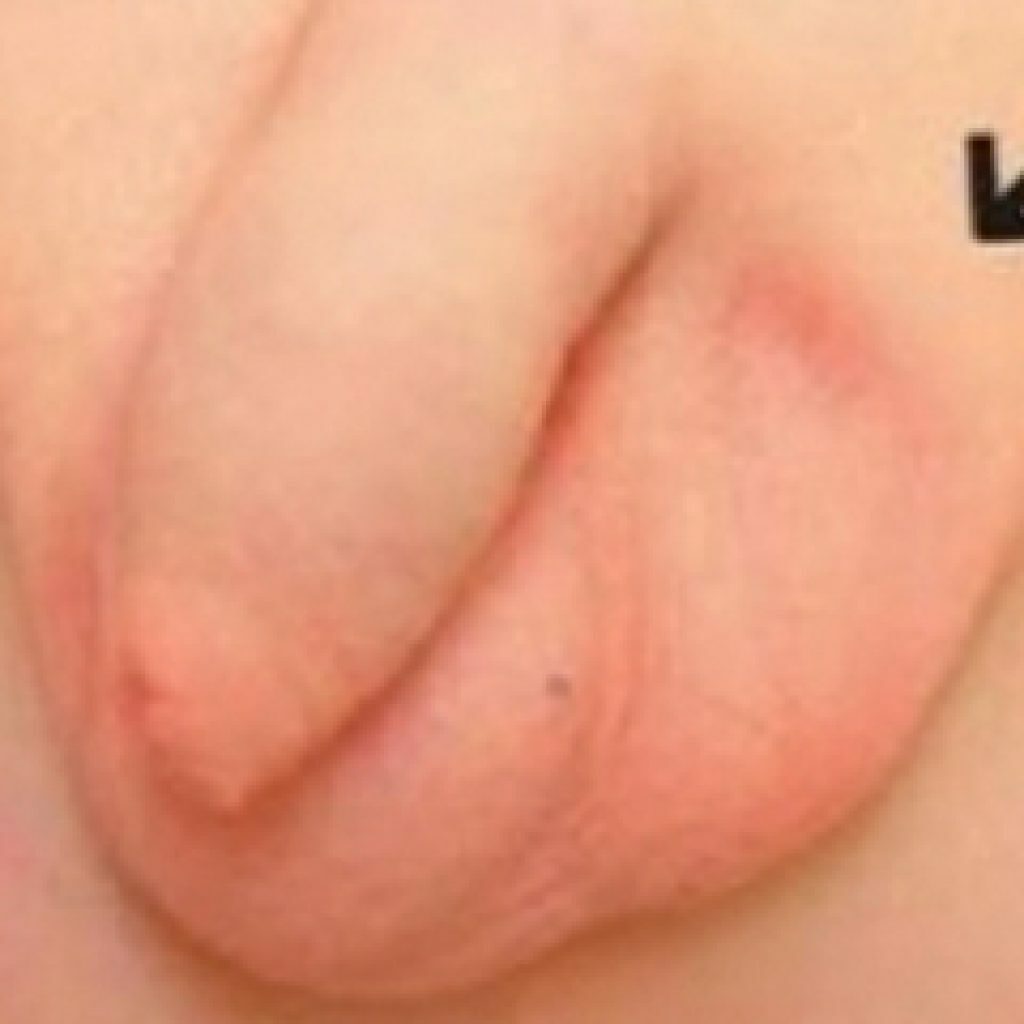
In case of inguinal cryptorchidism, the testicle is probed in the inguinal canal
. In contrast to retention, the ectopia develops always in utero and is characterized by a normal descent of the testicle through the outer inguinal ring, only after a time there is a deviation from the path to the scrotum and movement to an abnormal location.
Causes and factors of the development of the disease
Disturbance of the normal process of ovulation of the testicles gives rise to the development of cryptorchidism. The main causes of the disease are:
- Specificity of anatomy, characterized by the presence of mechanical obstructions in the path of the testicles into the scrotum:
- narrowing of the inguinal canal;
- short seed process;
- poor nutrition of the testicle( as a consequence of vascular deformation), etc.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine glands: decrease in the number of male hormones produced in the body of the baby in the womb, as well as the lack of gonadotropic hormones in the pregnant woman.
- Chromosomal abnormalities due to the influence of external adverse factors:
- transfer of a viral disease to a pregnant woman( flu, rubella);
- harmful working conditions in the mother( the effect of chemicals, toxins, pesticides, radiation);
- bad habits of a pregnant woman( taking drugs, smoking, alcoholism);
- is a bad ecology.
- Admission of non-recommended drugs by the mother during fetal gestation:
- analgesics( Analgin, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen);
- hormonal( dexamethasone).
- Heredity.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Early birth - small children are particularly prone to cryptorchidism.
Hormonal and painkillers whose use provokes the development of pathology
 Analginum-
Analginum- analgesic Paracetamol is not recommended for women during pregnancy
analgesic Paracetamol is not recommended for women during pregnancy  Dexamethasone-hormone preparation
Dexamethasone-hormone preparation  Ibuprofen intake may provoke cryptorchidism in a newborn
Ibuprofen intake may provoke cryptorchidism in a newborn Symptoms in adult men and newborns
ObviousSymptom of the disease in newborns is asymmetric scrotum with unilateral cryptorchidism, as well as lack ofIe in her testicles when palpation. With bilateral retention, the scrotum is empty and compressed.
As a rule, abnormally located testicles can be palpated manually through the abdominal wall or through the skin, sometimes it is impossible to determine their position.
In addition, cryptorchidism in adults is manifested by pain in the groin and in the abdomen. Pain often increases with:
- doing sports;
- constipation;
- sexual arousal.
Men may have semen discoloration.
Diagnosis and differential diagnostics
Diagnostics involves collecting an anamnesis and conducting an examination. When analyzing the course of pregnancy of the mother, the presence of factors provoking the formation of cryptorchidism is considered.
Important! The anomaly is difficult to determine from the data of laboratory tests, so this method of diagnosis is not sufficient. Only with the development of pathological processes can you see indicators that indicate inflammation.
Diagnosis is carried out by probing. If the testicles failed to palpate in the inguinal canal, inspect the hips and crotch to identify it.
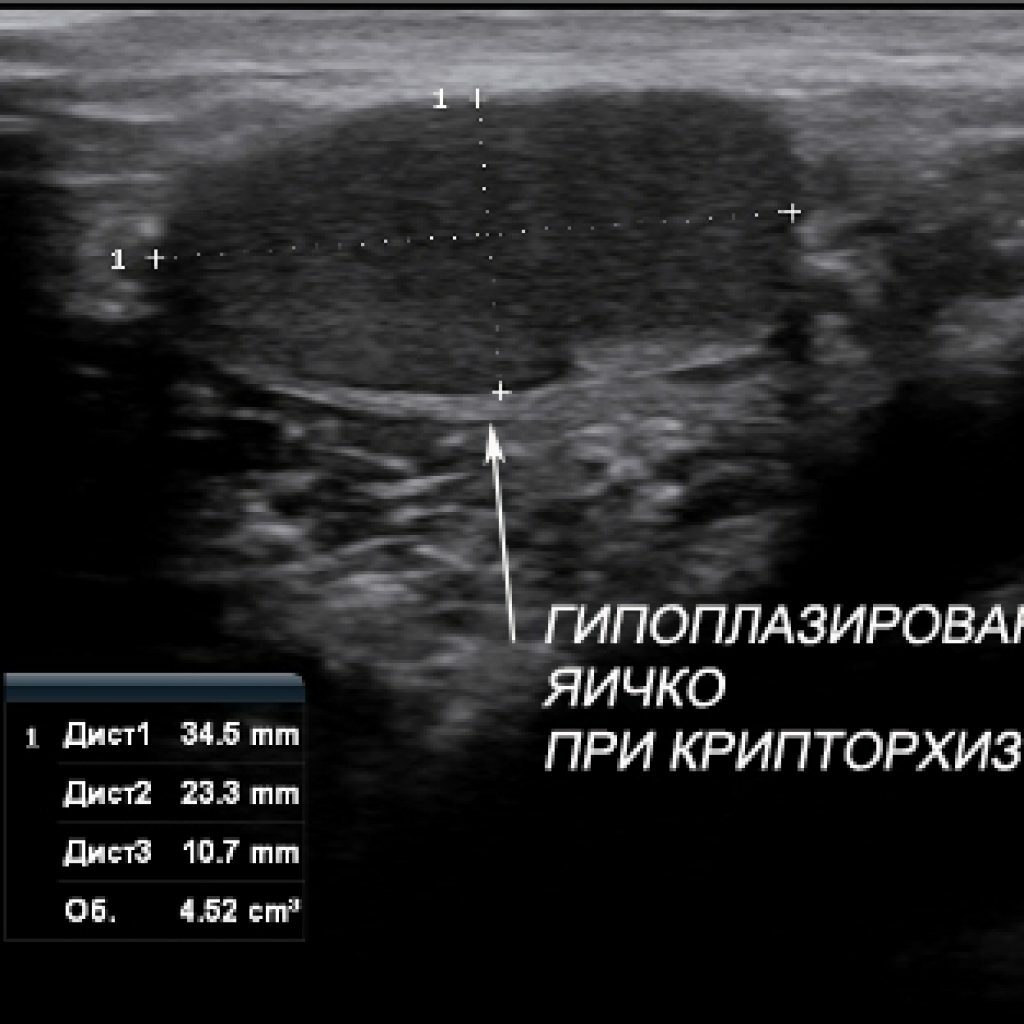
Detection of cryptorchidism with ultrasound of
In the event that the missing testis can not be detected with a probe, another examination is performed:
- contrast vasography is performed by introducing a contrast vein into the vein. After this, an X-ray is taken, on which the vessels leading to the abnormally located testicle are visible. In the absence of blood vessels, monarchism is diagnosed;
- CT - gives an idea of the three-dimensional image of organs;
- Ultrasound with dopplerography - is performed to detect violations of blood flow in the vessels and their patency, as well as to prevent congenital absence of the testicle and, as a consequence, to eliminate the need for surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of the disease requires consultations of specialists: a surgeon, andrologist, urologist.
Differential diagnosis
The examination of the baby is performed by the method of palpation.
Important: Diagnosis should be carried out in a warm room.
In case of non-detection of the testicle in the scrotum, the inguinal canal is probed and when the testicle is located there evaluate its consistency, the presence of pain sensations. When palpating, try to return the testicle to the correct position: if possible, the disease is classified as a pseudo-retention. This procedure is the basis for deciding in favor of true or false cryptorchidism.
Treatment of testicular non-rejection: methods, age at which to start therapy, and other nuances of
There are two ways of treating cryptorchidism: operating and conservative.
Operative correction of cryptorchidism and rehabilitation after intervention
Applicable after the first two years of life of the child. It is believed that after this time, an independent solution to the problem is no longer possible. The course of the operation depends on the condition of the testicle and the presence in it of degenerative modifications. In the case when the testicle has undergone serious morphological changes, resort to removal of the organ.
The chances of finding a healthy organ or its excision are equal.
If the organ has not lost its functions, then orchid surgery is performed, during which the egg is brought down and fixed to the skin of the thigh through the scrotum.
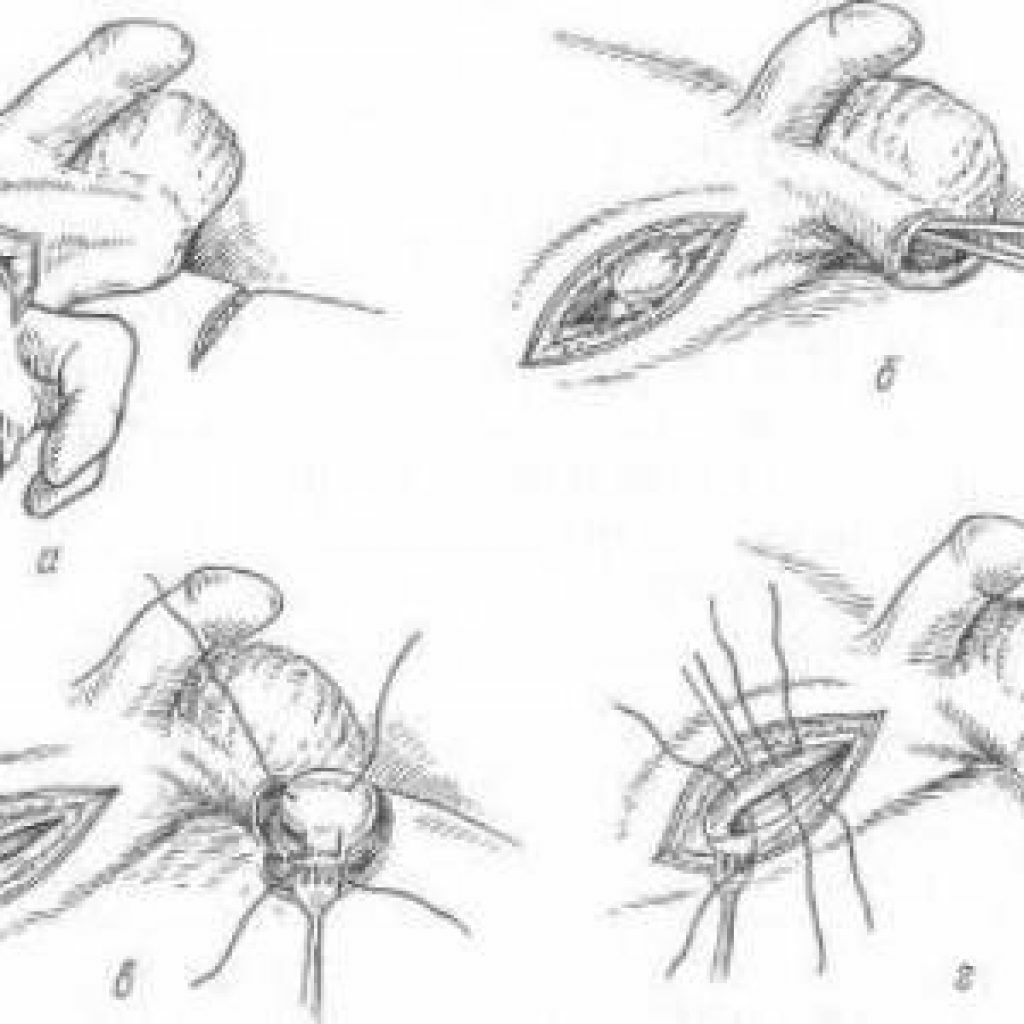
Orchipexy( also referred to as orchiopexy and orchidopexy) is a surgical operation used in cryptorchidism, the purpose of which is to attach the testicle to adjacent tissues with
seams. After 9-12 months after surgery, the scrotum is surgically removed from the hip.
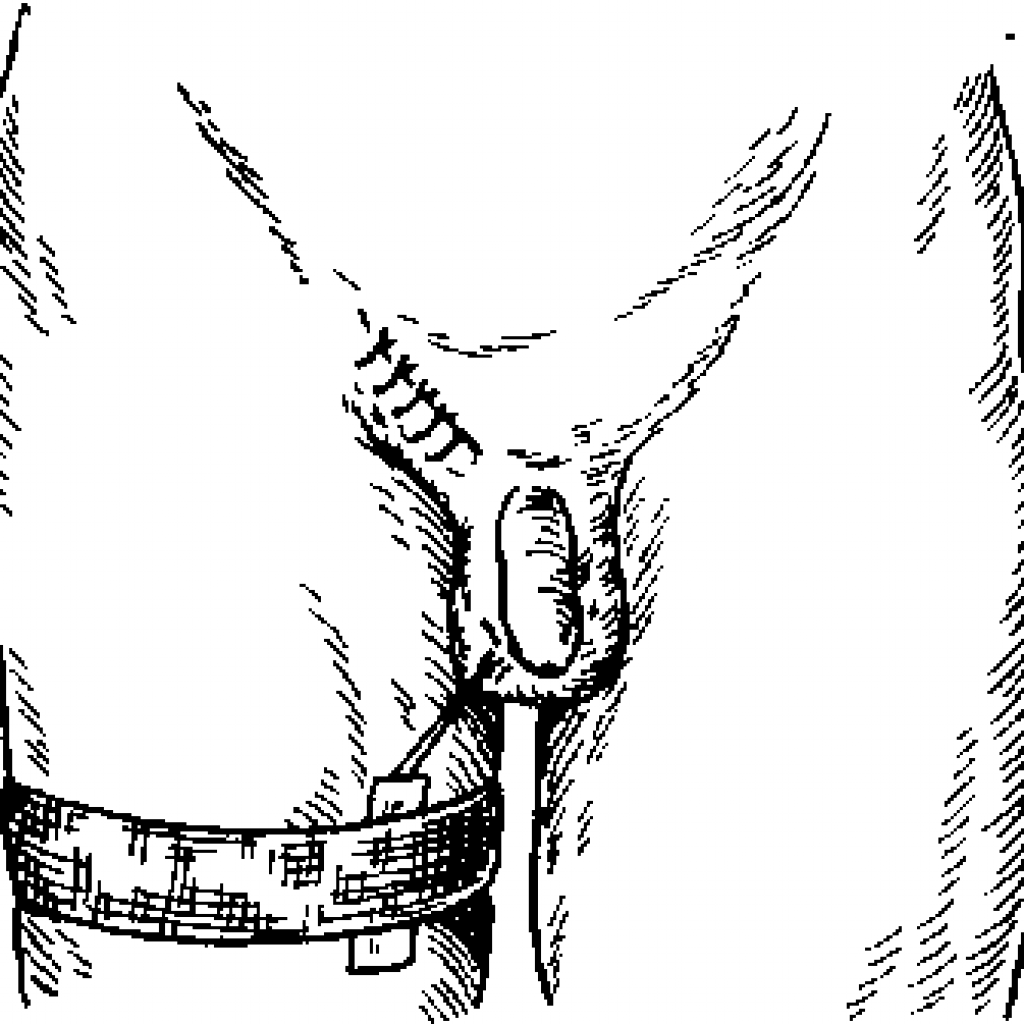
Patient after two-stage orchid surgery
- . By cutting soft tissue, access to the inguinal canal is opened.
- Enter the testicle into the scrotum.
- Make the plasty of the walls of the inguinal canal.
- Stitches are applied.
After surgery, orchids are allowed to get up on the third day, to 10-12 remove the stitches. After four weeks of exclusion of physical activities, including strength exercises, the patient returns to the usual way of life.
When performing an intervention in adolescence, it is extremely important to pay attention to psychological aspects. Recommended observation of young men from psychologists and conducting sessions of psychotherapy to exclude the emergence of complexes and feelings of inferiority.
To exclude psychological problems, specialists recommend that such operations be performed at a younger age.
Contraindications to surgical intervention are:
- Blood clotting disorder.
- Severe systemic diseases.
Reviews of parents and patients who underwent orchidectomy
Video: cryptorchidism in children - treatment with
operation Conservative method of treatment
The correction of the disease by hormonal drugs is possible at the age of up to a year and is recommended only in the form of false cryptorchidism. Treatment is carried out by the chorionic gonadotropin from the age of six months of the baby, when a spontaneous drop of the testicle is still possible. Also, hormone therapy is used to prepare the patient for surgical intervention.
Treatment of cryptorchidism should be started with chorionic gonadotropin, and the greatest effect is achieved in children with bilateral and inguinal retention
. In the treatment of patients in the pubertal period, hormone therapy with methyltestosterone is carried out along with the administration of the chorionic gonadotropin. With such therapy, there is no inhibitory effect on the development of testicles.
Many experts are very negative about hormonal therapy in small boys, because it affects the retardation of development and maturation of the testicles. In the United States, this treatment for cryptorchidism is not carried out because of lack of evidence of effectiveness.
In the absence of positive dynamics after conservative treatment, orchidopexy is also performed.
LFK: what exercises can be performed by
During conservative treatment, the patient is recommended to do special exercises that help to lower the testicles in the correct position:
- gymnastics for the pelvic muscles;
- gymnastics for the abdominal;
- movement by feet on the floor, performed similarly to rubbing the floors;
- swimming;
- cycling.
Folk remedies
Treatment of cryptorchidism with folk remedies is contraindicated, as it not only does not bring the desired effect, but it can also harm a healthy body. The best option is to contact a specialist and get a qualified consultation.
Prognosis of treatment and possible complications: testicular cancer, infertility and other dangerous consequences
Often parents prefer hormone therapy instead of surgery. The effectiveness of such treatment is small( about 30%).With a timely surgical intervention( up to 1.5-2 years), the prognosis is positive. Currently, postoperative complications are rare, but the likelihood of their development still exists. So, the consequence may be:
- development of bleeding, edema;
- incorrect placement of testis in the scrotum;
- testicular atrophy;
- damage to the vas deferens;
- development of inflammation in the testicles or appendages;
- infection of sutures.
In the absence of proper treatment for cryptorchidism, the following consequences may develop:
- painful sensations due to incorrect anatomical location of the testicle;
- inguinal hernia;
- infringement, torsion of testicular hydatids;
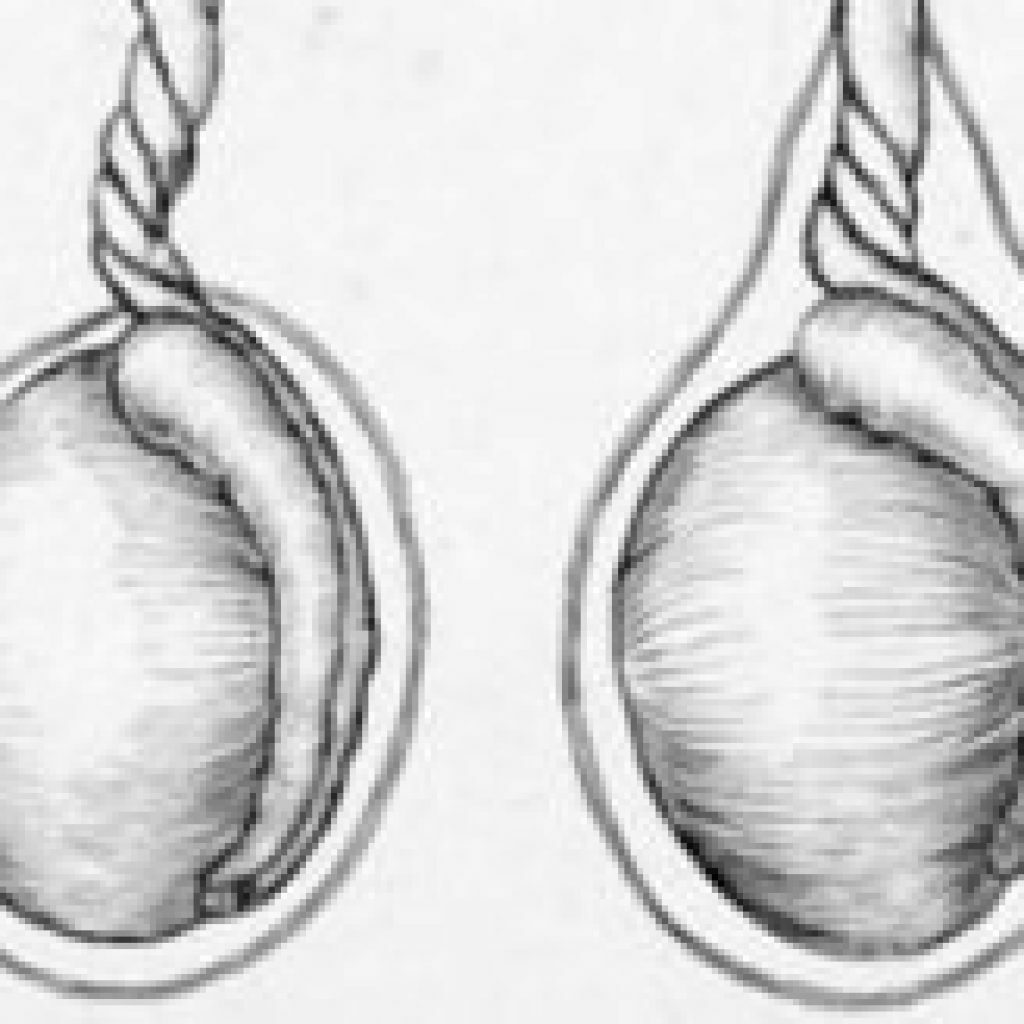
Testicular torsion is a very dangerous situation, in which blood flow is disturbed in a short time, accompanied by severe pain, and the subsequent organ dying for several hours.
- oncology( testicular cancer).The development of malignant tumors in cryptorchidism is due to the presence of the testicle in a medium whose temperature is more than necessary for the full function of the gland. This provokes tissue mutation and leads to severe changes;
- infertility.
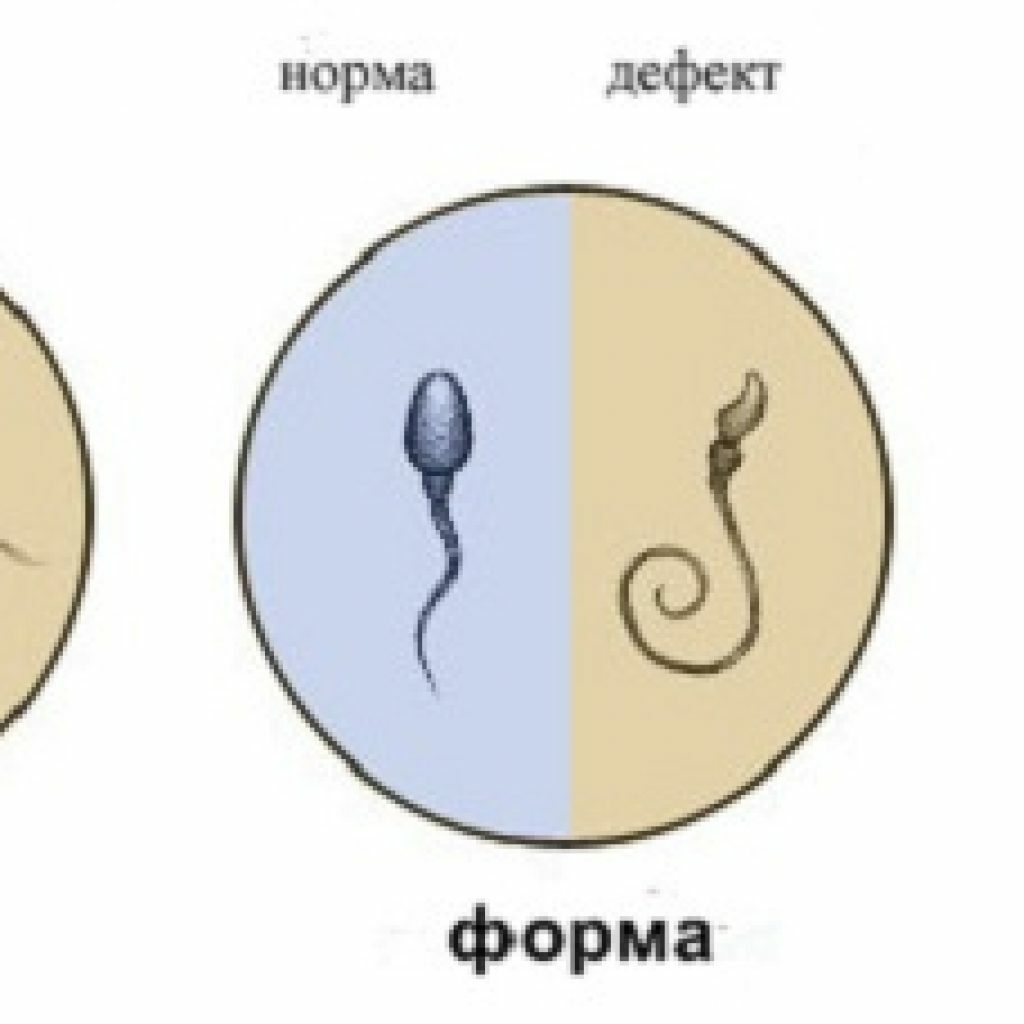
When the testicle is in the inguinal region or in the abdominal cavity, too high a temperature that prevents the formation of healthy spermatozoa
Preventing the development of the pathology
The healthy lifestyle of a pregnant woman is a warning of the occurrence of possible abnormalities in the fetus, including cryptorchidism. When the baby is born, the future mother must observe the following rules:
- Refusal from bad habits( alcohol, smoking, drugs).
- Avoid contact with viral patients, if possible - pre-vaccination against influenza, rubella.
- Only pharmacies are taken under the supervision of a doctor.
- When working in hazardous production - a change in the type of activity, the transition to easy work.
- Pregnancy planning, preliminary estimation of the hormonal background and treatment of the revealed violations before conception.
- Avoidance of stressful situations.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle( proper nutrition, normal physical activity) before and during pregnancy.
Video: Webinar E.O.Komarovskiy about the lifestyle of the pregnant woman and its effect on the health of the fetus
When diagnosing cryptorchidism, one should not despair, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the attending physician and not be frightened of the appointment of the surgery, since the risks of complications after surgery are much less than the threat of consequences with unprocessed therapy.