What is it?
Hyperparathyroidism is an endocrine disease that increases the production of parathyroid hormone( the main hormone of the parathyroid glands).
The latter( PTH) regulates the amount of calcium in the blood, ensuring its normal values. With a decrease in calcium, there is an increase in the production of parathyroid hormone in the parathyroid glands, with an excess of calcium, respectively, the formation of this hormone is inhibited.
Normally, parathyroid hormone is an important regulator of bone tissue renewal. Under its influence, calcium from the bone passes into the blood, which leads to stimulation of normal bone formation. It also delays the release of calcium through the kidneys, and the removal of phosphorus, on the contrary, increases.
Indirectly, the parathyroid hormone affects the increase in calcium intake, by forming a special form of vitamin D, which facilitates the absorption of the microelement in the intestine.
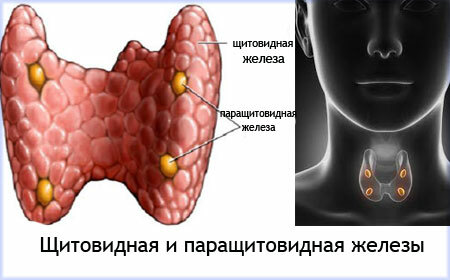
With a short impulse on the bone, parathyroid hormone will stimulate bone formation, and with prolonged and continuous bone destruction. In general, disruption of the parathyroid glands is observed in adults.
- Hyperparathyroidism in children is formed quite rarely, it can occur in a child if the family had cases of this disease. In newborns, it is possible to detect temporary hyperparathyroidism, if during pregnancy the mother had a decrease in the production of parathyroid hormone. The manifestations and causes of hyperparathyroidism are identical to those of adults.
content
- 1 Primary hyperparathyroidism
- 2 Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- 3 symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism
- 3.1 symptoms of secondary hyperparathyroidism
- 4 Treatment hyperparathyroidism - drugs and methods
- 4.1 On the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism
- 4.2 Prediction
Primary hyperparathyroidism
In primary hyperparathyroidism, the parathyroid gland formation PTH does not depend onthe amount of calcium in the blood. Often from the time of the onset of this disease to the diagnosis is a long time, although hyperparathyroidism is the third most common endocrine disease( in the first place - diabetes, the second - the increase in thyroid function).
The reason for late diagnosis may be insufficient attention to the change in the amount of calcium in the blood, the range of which is very narrow and is 2-2.8 mmol / l.
Often the increase in normal numbers is ignored, although the double registration of hypercalcemia is the basis for the diagnostic search for hyperparathyroidism. The peak of the development of the disease falls on 40-50 years, women suffer more often in the period after the onset of menopause.
The causes of primary hyperparathyroidism are conditions that lead to increased production of parathyroid hormone by altered parathyroid cells:
- Parathyroid adenoma, or parathyroid - is a tumor that consists of active cells that produce a hormone. In 80% of cases, this tumor is solitary, that is solitary. Multiple adenomas are detected in 5% of patients;
- Hyperplasia, i.e.increase in the size of the glands due to proliferation of normal gland tissue( 15%);
- Syndromes of multiple endocrine neoplasias: MEN-1 and MEN-2A.When identifying signs of hyperparathyroidism, it is necessary to check the patient for the presence of other components of these syndromes: medullary thyroid cancer, pancreatic islet tumors, pheochromocytoma.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
This form develops as an organism's response to a decreased amount of calcium in the blood. In response to low calcium, there is an increase in the production of parathyroid hormone. The causes of secondary hyperparathyroidism are the following conditions that contribute to a decrease in the level of calcium in the blood:
- Renal failure, in which a number of biochemical disorders cause a decrease in calcium in the blood, as well as the formation of the desired form of vitamin D;
- Diseases of digestion: malabsorption syndrome, which leads to impaired absorption of calcium and vitamin D;cirrhosis of the liver, in which there is a violation of the transformation of vitamin D, resulting in a decrease in the intake of calcium from the intestine into the blood;
- Conditions after operation on the digestive tract, such as total gastrectomy and the Bilrot-2 operation;
- Permanent and prolonged lack of sun, leading to a decrease in the synthesis of vitamin D in the body.
Renal form of secondary hyperparathyroidism is observed in connection with the frequent use of hemodialysis and an improvement in life expectancy in individuals with chronic renal failure. The causes of tertiary hyperparathyroidism are hyperplasia or adenomas of parathyroid glands, due to prolonged secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism
 Symptomatic disease depends on the form of the disease, we begin with the symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism.
Symptomatic disease depends on the form of the disease, we begin with the symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism.
In the initial period of the manifestation of the primary form, the symptoms are non-specific, which makes diagnosis difficult. Patients complain of muscle and general weakness, rapid fatigue, lethargy. The further development of the disease has various manifestations.
There are several forms in which the leading one is a characteristic, or a combination thereof:
- Bone form;
- Visceropathic form;
- Neuropsychic form;
- Mixed form.
Bone changes. With a constantly elevated level of PTH, bone destruction predominates over its recovery. The destruction of bone tissue is observed in half of patients with hyperparathyroidism. Manifestations of osteodystrophy are:
- Pain in the bones, especially along the spine;
- Bone deformities, development of cavities in them, cysts detected on X-rays;
- "Duck" gait, as a consequence of deformation and pain;
- Pathological fractures, i.e. Fractures that occur with less impact on the bone, rather than with a normal injury;
- Teeth prolapse as a result of osteoporosis of the jaws;
- Chondrocalcinosis of the joints - the deposition of calcium in the cartilaginous tissue of the joint, which leads to the limitation of its mobility, the appearance of spines, pain during movement. It develops often.
Renal symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are expressed in 50% of patients, it is:
- The earliest symptoms are thirst and a large amount of excreted urine, which in laboratory studies has a low density. This can be mistakenly regarded as a manifestation of diabetes insipidus;
- Kidney stones are found in 25% of patients, often this condition is accompanied by pyelonephritis. The presence of stones in the kidneys can not be felt at all, but can be manifested by renal colic. Pyelonephritis is expressed by signs of inflammation in the form of the appearance of leukocytes in the urine, pain in the lower back and a rise in body temperature. In 2% of all patients with urolithic pathology primary hyperparathyroidism is detected;
- Nephrocalcinosis - the deposition of calcium salts in the tissues of the kidneys, is rare, it is difficult, leading to kidney failure.
Changes in the psyche of have been the only symptoms of hyperparathyroidism for a long time:
- Depression, depression;
- Drowsiness;
- Decreased intellectual abilities;
- Memory impairment.
Neuromuscular signs of of hyperparathyroidism are caused by irritation of nerve endings with destruction of bone structures of the spine, as well as a violation of normal muscle contractions. Manifestations of this form:
- Muscular weakness, most pronounced in the limbs;
- Pain in the spine;
- Muscle atrophy;
- Symptoms of tension;
- Paralyzes of the muscles of the pelvis, lower limbs;
- The appearance of parasthesias - unpleasant sensations on the skin in the form of tingling, burning, crawling creepy.
Gastrointestinal organs - manifestations of disorders can be observed in half of the patients:
- Lack of appetite, weight loss, nausea, bloating, constipation. These manifestations are observed even at the onset of the disease;
- Acute pain in the stomach, can be regarded as manifestations of "acute abdomen" - urgent surgical pathology;
- Peptic ulcers of the stomach, 12 duodenum develop in 10% of patients with elevated parathyroid hormone. Such ulcers are prone to frequent recurrence;
- Changes in the pancreas: chronic inflammation( pancreatitis), there is rarely a calcium deposit in the gland tissue - pancreatocalcinosis and the formation of stones in the ducts - pancreoccalculosis.
Other organs and systems of the body
Changes in the cardiovascular system are expressed in increasing blood pressure and disturbing the normal heart rhythm. With ECG, it is possible to detect an increase in the size of the left ventricle, which is a risk factor for death in this pathology.
Severe, although rare complication of primary hyperparathyroidism is a hypercalcemic crisis. It develops if the level of calcium in the blood rises to 4 mmol / l. It can be triggered by the use of diuretics of the thiazide series, prolonged bed rest, and the erroneous appointment of calcium and vitamin D preparations to treat osteoporosis without clarifying its true causes.
The sharp increase in calcium levels in the blood corresponds to the following symptoms that attach to the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism:
- Excitation, a psychosis that quickly becomes stupor and to whom. A coma is difficult to distinguish from a coma caused by another cause;
- Gastrointestinal symptoms increase;
- Dehydration and weakness rapidly develop;
- Urination stops - anuria develops;
- Muscular disorders develop in the upper half of the body, up to the termination of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which requires the initiation of artificial ventilation of the lungs;
- Characteristic increase in temperature to 39oS.
Symptoms of secondary hyperparathyroidism
The manifestations of secondary hyperparathyroidism are due to the symptoms of the disease that led to its development. Most often - a manifestation of chronic kidney failure.
Specific manifestations of the secondary form: pain in bones and joints, muscle weakness, fractures and deformities of bones. The deposition of calcium salts in the joints of the hands and feet leads to the appearance of hard knots around the joints.
Red eye syndrome refers to the combination of inflammation and calcification of the conjunctiva and the cornea.
Treatment of hyperparathyroidism - drugs and techniques
In laboratory confirmation of hypercalcaemia and increase in PTH levels, identification of symptoms characteristic of primary hyperparathyroidism, treatment consists in surgical removal of adenoma. After the elimination of hyperparathyroidism, drug therapy is carried out for the destruction of bone tissue.
Absolute indications for adenoma removal:
- Rescue of life;
- Young patients without other health problems;
- In patients older than 50 years with asymptomatic flow, if hyperparathyroidism is detected by accident. The operation is performed with the progression of osteoporosis, calcium level more than 3 mmol / l, the presence of calcified kidneys, a decrease in creatinine clearance below 30%.
If, for some reason, surgical treatment of hyperparathyroidism is not performed, patients need to drink plenty of fluids, move more actively, inhibit the development of dehydration, control pressure, and postmenopausal women receive estrogen.
It is forbidden to take thiazide diuretics( eg, hypothiazide), as well as cardiac glycosides.
Every 6 months you need to check the level of calcium and creatinine in the blood, the level of excretion of calcium in the urine. Annual studies are ultrasound of the abdominal cavity organs and measurement of bone density( densitometry).
- If any parathyroid gland is hyperplastic, then remove all 4 glands, which are then transplanted into the fiber in the hand.
Treatment of hypercalcemic crisis:
- Intravenous drip introduction of physiological solution to eliminate dehydration;
- IV injection of bisphosphonates( for the control of osteoporosis): pamidronate, ethyl dronate from 4 to 24 hours;
- In / m administration of calcitonin-hormone, whose action is opposite to the parathyroid hormone;
- Furosemide is administered only after removal of dehydration, 30 minutes after the beginning of infusion of saline solution;
- When phosphorus levels are lowered, phosphate salts are used in the blood;
- If the crisis is provoked by the use of vitamin D - use glucocorticoids;
- Crysis on the background of renal failure requires dialysis with the use of non-calcium buffer.
On the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism
Secondary hyperparathyroidism requires treatment of the underlying disease. To prevent the increase in the production of parathyroid hormone in the presence of renal insufficiency, it is necessary to prescribe medications that bind phosphorus: calcium gluconate, citrate, lactate in order to maintain a phosphorus level in the blood of not more than 1.5 mmol / l.
Assign formulations of active form of vitamin D: rokaltrol and control the release of calcium in the urine( no more than 300 mg per day).
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism with the formation of adenoma requires only surgical treatment.
Forecast
If early detection of impaired production of parathyroid hormone leads to adequate treatment of hyperparathyroidism - a favorable outlook.
Without treatment, all manifestations of the disease worsen, especially bone destruction, increased fractures, the formation of severe complications due to calcium deposition in the tissues of organs such as nephrocalcinosis, pancreaticacinosis, etc., development of urolithiasis, arrhythmias, recurrent stomach ulcers and 12the rectum.