Content
- Definition of what it is
- The reasons for the appearance in the body of the vertebra
- Etiology and symptoms of the disease
- What is the danger?
- Types and forms
- Forecast
- Video about spinal hemangioma
The spinal cord is located in the spine, and there are also many blood vessels, so any, even minor injury is capable of provoke the development of hemangioma - a vascular tumor (neoplasm) of a benign nature that grows slowly.
Hemangioma of the body l1-l2-l3-l4, as well as th7-th10-th12 vertebrae are detected in 10% of people, often in women aged 20-30 years. In children, pathology is rarely detected. As a rule, it is discovered by chance, during the examination, due to other reasons.
Definition of what it is
Hemangioma, including the l1 vertebral body, is a vascular neoplasm. Such a tumor cannot appear only in the area where there are no vessels. The source of the neoplasm is the inner lining of the vessels and the endothelium.
Patients who have this disorder do not need to worry that this formation will acquire a malignant character. Hemangioma is not prone to malignancy.
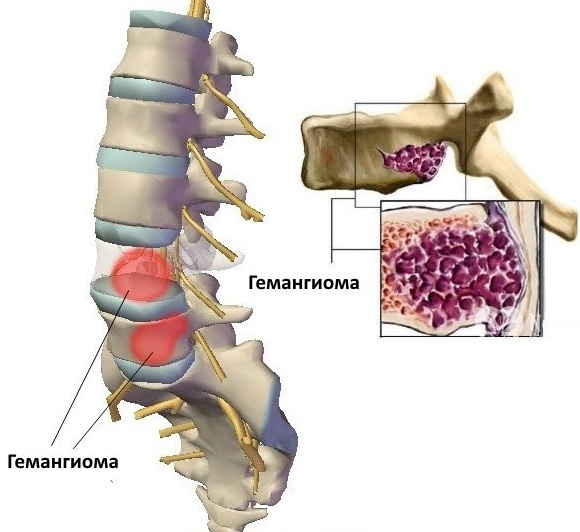
Such a tumor is characterized by the location in the substance of the spongy structure of the vertebral body, penetrated by capillaries. This is a favorable location, as the vascular ball protects the bone. Thanks to this, in the event of injury, they cannot cause massive bleeding.
According to studies, the development of pathology is carried out as follows: abnormal vascular walls located in a specific vertebra, under the influence of injuries, high loads and other provoking factors, recurrent effusions of blood occur, in this place are formed blood clots.
After this, cells are activated, which act destructively on the bone tissue. As a result, it is replaced by growing vessels with an abnormal wall, which leads to an increase in the volume of the hemangioma. Subsequently, the walls of such vessels also rupture, provoking further hemorrhages.
When a significant part of the bone is destroyed, the damaged vertebra will not be able to perform the supporting function, as its sensitivity to stress increases. The risk of a pathological fracture increases. Pathology is diagnosed almost always by chance, during examination in connection with another disease.
The reasons for the appearance in the body of the vertebra
Reliable factors in the development of hemangiomas are unknown in modern medicine. Often, the appearance of benign neoplasms is associated with hereditary congenital disorders. In this case, education occurs immediately after birth, or during development in the womb.
Sometimes babies may have 3 or more tumors on the skin of different locations, which increases the likelihood of hemangiomas forming in the vertebrae. The formation of multiple vascular neoplasms in medicine is called hemangiomatosis.
Hemangiomas can also have an acquired character, but for what reason they appear is not known for certain. There is a version that prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays contributes to this, but there is no evidence of this theory yet. Therefore, when diagnosing a hemangioma during an MRI or CT scan, it is impossible to accurately determine when it formed.
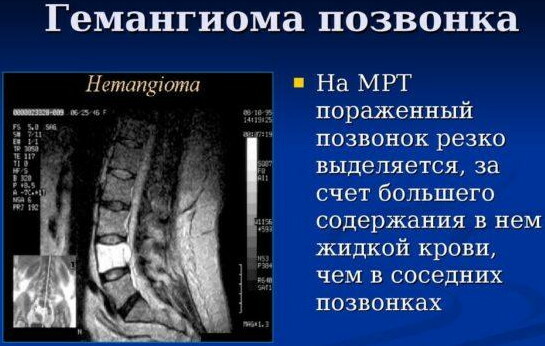
This could have happened both during the period of intrauterine development and in the near future. This pathology is diagnosed equally often in patients, regardless of gender, in every 10th. Since the exact reasons for the appearance of neoplasms are unknown, then there is no specific prevention.
Etiology and symptoms of the disease
Hemangioma of the l1 vertebral body is often asymptomatic and is detected during examination due to trauma or other pathology. Approximately 10% of patients diagnosed with this disease have pain localized to the location of the vertebra. As a rule, they are aching or dull in nature and are worse at night, or after intense physical activity.
With hemangioma of the vertebra, by stimulating the nerve endings of the posterior longitudinal ligament and periosteum, painful sensations arise.
Compression of the soft tissue substance of the tumor, located in the epidurial space, provokes the appearance in some patients of symptoms of irritation of the spinal cord and nerve endings.
In about 3% of cases, an intensive growth of the vertebral neoplasm is observed, significantly reducing the strength of the bone, which leads to pathological fractures. In some patients, paralysis, a decrease in sensitivity and dysfunction of the pelvic organs are observed, provoked by the accumulation of plasma in the extradural space.
Taking into account the ultrasound and clinical symptoms, there are 4 types of vertebral hemangiomas.
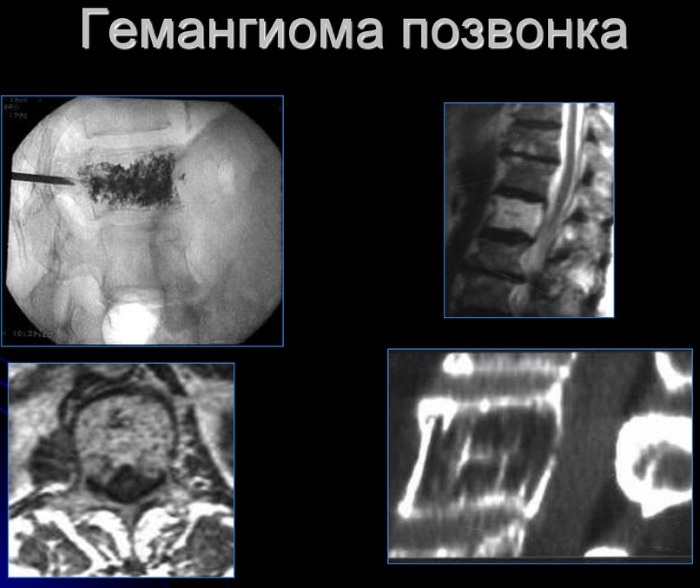
Non-aggressive:
- Asymptomatic. They are characterized by the absence of clinical and cytological signs of an aggressive course.
- Symptomatic. Clinical symptoms are present, but cytological signs of an aggressive course are not observed.
Aggressive:
- Asymptomatic. They differ in an asymptomatic course, but there are signs on ultrasound examination.
- Symptomatic. With the disease, clinical and cytological symptoms are observed.
The radiological symptomatology of the aggressiveness of the hemangioma includes the spread of the pathological process to the whole body, the placement of the tumor in the space between 3 and 9 vertebrae, blurred boundaries and spread of the cortical layer, spread of the neoplasm to the root of the arch.
In the process of research by means of MRI and CT of aggressive tumors, cells of an abnormal shape and soft tissue neoplasms in the epidurial space are revealed. The presence of 3 or more of the above symptoms indicates that the vertebral hemangioma is of an aggressive type.
What is the danger?
Hemangioma of the l1 vertebral body can be stable or grow slowly. In the first case, a minor tumor does not pose any threat. Until the time when computed tomography and MRI were used to diagnose this pathology, hemangiomas were detected by means of an X-ray diagnostic method.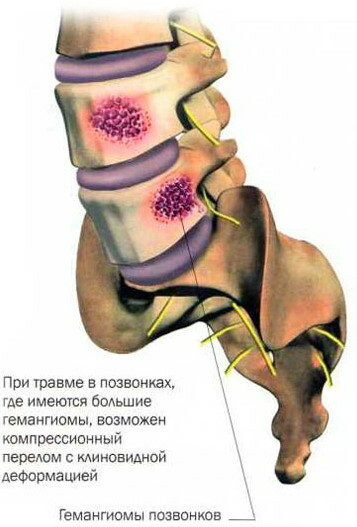
The pictures reveal light spots in the area of the vertebral body. Hemangiomas do not have specific signs, therefore, the diagnosis for life was made only with an intensive growth of the tumor, provoking regular fractures. Diagnosis was carried out during the operation, after biopsy and sending the biomaterial obtained during the surgical intervention for histological analysis.
Hemangioma does not have a tendency to malignancy and does not pose a danger.
The only threat: the mechanism of destruction of vertebral tissues, which provokes the development of the following complications:
- most often provokes fractures;
- less often, compression of the central canal occurs, followed by the formation of compression myelopathy and neurological signs corresponding to this pathology;
- it is extremely rare that the canal is compressed with damage by fragments of the bones of the dura mater of the brain and / or penetrating trauma to the spinal cord.
With vascular neoplasms, profuse bleeding never occurs, since the bone needs a minimum volume of blood supply. With this pathology, there are no complications in the form of bleeding. If the fracture is not operated on in a timely manner, the tumor, injured by bone fragments, may bleed in a confined volume.
Vascular neoplasms can reach critical volumes, at which the likelihood of developing the above complications significantly increases. However, the increased size alone is not enough to predict the further development of the disease.
So, if a hemangioma of a large size is detected in a man of large build, then it does not pose a threat. At the same time, a neoplasm of the same size, found in the 3rd cervical vertebra of a young woman, is extremely dangerous and requires urgent therapy, which will prevent the formation of complications.
There is no spinal cord at level 4 of the lumbar vertebra, so a suspected fracture in this area can trigger the onset of the syndrome horse tail, accompanied by pain in the legs of a shooting character, a feeling of numbness in the perineum, urinary disorder and erectile functions.
With a fracture of the 3rd cervical vertebra, as well as damage to the spinal cord and developing myelopathy, quadriplegia occurs, in other words, absolute paralysis of the upper and lower extremities, urinary disorders, which leads to deep disability.
The risk of hemangioma increases in proportion to the intensity of its growth. Therefore, if a small formation is detected, in the absence of any complaints in the patient, a repeated examination is prescribed annually for 2 years, then at intervals of 3 and 5 years. A stable vascular tumor should not be a cause for concern.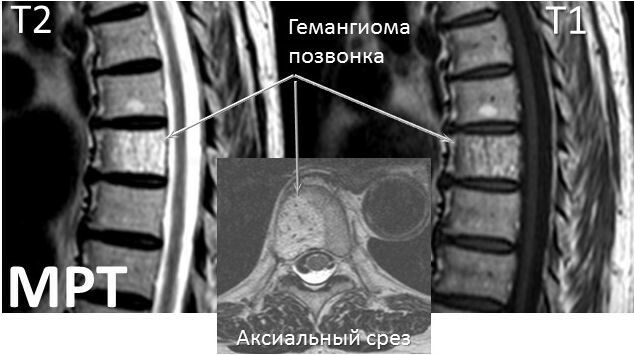
The danger of neoplasms also depends on the location of the vertebra in the body. When the hemangioma is located near the edge of the vertebra, as well as when it is separated from the external space only the thin edge of the bone, the risk of developing a compression fracture is significantly increased, in contrast to its location in center.
The condition of the bone tissue is also taken into account. If a hemangioma is diagnosed in a man at a young age, there is no need to worry about bone density.
But if a vascular neoplasm is detected in an elderly woman, the fragility of the cancellous bone will be significantly increased. In this regard, a vascular tumor of even a small size in patients with a high risk of developing osteoporosis will have a more negative prognosis than a much larger neoplasm in a healthy person.
By itself, the size of the vascular neoplasm of the vertebral body is not a decisive factor in determining the degree of danger. But if we take into account only this indicator, then the threat is posed by a hemangioma, which occupies 55-60% of the volume of the vertebral body. With intensive growth, surgical treatment is indicated.
It should be understood that a slow increase in neoplasm is not evidence of a malignant degeneration and has nothing to do with oncology. Hemangioma of the vertebral body almost never causes discomfort and is not accompanied by pain until the bone begins to collapse.
But with constant stress, the patient can feel regular false pains localized in the back, which can cause discomfort and significantly worsen the quality of life.
Types and forms
Hemangioma of the l1 vertebral body is of two types:
- non-aggressive - the neoplasm is stable, it is detected accidentally during a medical examination or computed tomography performed for another disease;
- aggressive - the formation grows intensively, accompanied by severe pain when moving.
In most patients, the hemangioma of the vertebral body is non-aggressive, does not cause any discomfort and does not threaten health. But in advanced cases, pathology can destroy bone tissue, which will lead to the development of serious complications, including disability.
A patient may develop from 1 to several neoplasms at the same time. The exact amount will be determined by a specialist during the examination.
By the number of hemangiomas, there are:
- Single. This type is more common. The tumor can be located in any vertebra.
- Multiple. A rare and dangerous type. Neoplasms can be localized simultaneously in several vertebrae, which aggravates the patient's condition.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the microscopic structure, there are 4 types:
- Capillary. Formed by a large number of intertwined capillaries. Their layers are separated by layers of adipose and fibrous tissue.
- Cavernous. Tumors in the form of an accumulation of numerous cavities of various types and sizes, with walls in the form of a thin layer of connective tissue covered with endothelium.
- Racematous. They have larger arteries and veins.
- Mixed. They have the characteristics of the above 3 types.
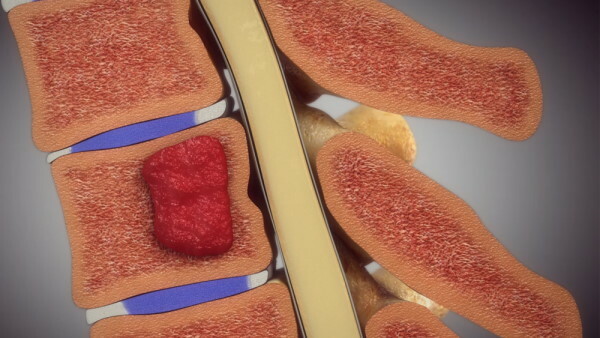
There are 5 types of vertebral hemangiomas, taking into account the extent of the lesion and location:
- The entire vertebra is affected by a neoplasm.
- The tumor has spread only to the vertebral body.
- Only the back half-ring is affected.
- Hemangioma is located on the body and part of the posterior semicircle.
- Epidural localization.
Forecast
Hemangioma of the l1 vertebral body of a stable nature and small size, as a rule, does not have a negative effect on the quality of life and its duration. Before the advent of the diagnostic method - tomography, people existed perfectly with hemangiomas of the vertebral body, which cause anxiety in modern patients. This is due to the fact that most people associate any neoplasm with oncology.
If a hemangioma of the vertebral body is detected, specialists take a wait-and-see tactic, conducting periodic examinations in order to control the dynamics of its growth. In the presence of a neoplasm, it is recommended to control weight and prevent it from increasing. Such patients are contraindicated to engage in tough, contractual wrestling and sports associated with weight lifting.
If a compression fracture still occurs, extensive surgical intervention is indispensable. In some situations, they grow together on their own and do not require intervention. However, it should be borne in mind that a vascular neoplasm in this condition will be located between bone fragments and create an obstacle for fusion.
A neoplasm that lies freely between the fragments, no longer protected by the vertebra, increases the likelihood of blood outpouring. Therefore, the basis for the correct therapy of hemangioma is the observation of the dynamics of the development of pathology, taking into account additional risk factors.
Prevention measures for hemangioma will prevent the pathology from starting and prevent the development of complications. If a neoplasm of the body l1-l2-l3-l4, as well as th7-th10-th12 vertebrae, is detected, annual examinations are recommended to control its growth. Any tumors react negatively to ultraviolet rays, so it is necessary to minimize being on the beach, exclude visits to the solarium. Increased physical activity can provoke the growth of education.
In this regard, it is necessary to abandon the practice of traumatic and power sports. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances. Only strict implementation of all the recommendations of a specialist will allow you to maintain mobility and quality of life.
Video about spinal hemangioma
Causes of spinal hemangioma: