Content
- What types of breathing are there?
- How does chest breathing work?
- Inhale
- Exhalation
- Gas exchange process
- Features of abdominal breathing
- Breathing in women is normal
- Male breath
- What are the differences between male and female breathing
- Danger of chest breathing for a woman
- How to develop the correct breathing technique
- Exhale with additional resistance
- Diaphragm breathing
- Posterior chest breathing
- Video about breathing types in women
Breathing is a physiological process of ensuring stable vital activity of all systems and departments of the human body. Nasal canals, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lung tissue and alveoli are directly involved in saturating the blood with the required amount of oxygen.
External respiration is a continuous process that is regulated by the central and peripheral nervous systems. Reflex contraction of skeletal muscles activates biological mechanisms responsible for the functioning of the respiratory system. Normally, in women of all age categories, the chest type of breathing prevails.
What types of breathing are there?
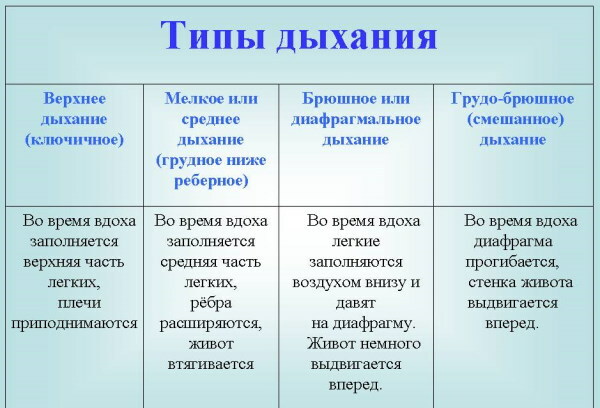
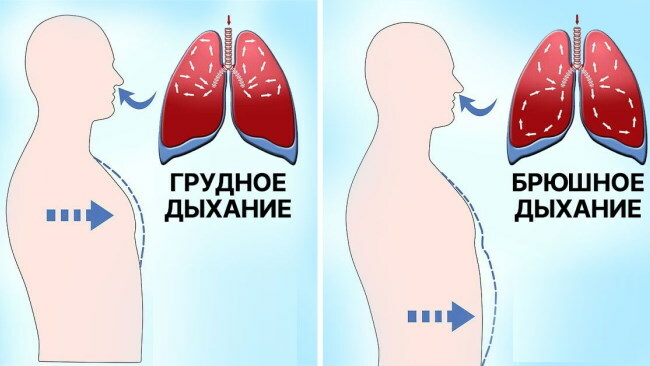
Normally, a healthy person has chest or abdominal breathing. During inhalation in women, the muscles of the chest are more involved, and in men, the muscles of the diaphragm are activated.
The table below describes the types of breathing in men and women in the absence of pathologies of bronchopulmonary tissue.
| Breathing types in a healthy person | Characteristics of the physiological process |
| Pectoral | In people with this type of breathing, the depth and frequency of inspiration depend on the stable work of the external muscles located in the intercostal space. At the moment of filling the lungs with air, a smooth rise of the anterior chest wall occurs. This type of breathing is common among most women, as it allows you to maintain a stable functioning of the respiratory system, provides a full-fledged gas exchange of the body even in the last stages of pregnancy, when inhalation with the activation of the abdominal muscles is physically complicated. Chest breathing is noted in sick people who suffer from an acute form of ascites. Men with paralysis of the diaphragm muscles switch to chest breathing. In patients with massive neoplastic neoplasms in the upper abdominal cavity, the main physical activity for the absorption of oxygen falls on the muscles of the chest. |
| Abdominal | This type of breathing depends on the synchronous contraction of the muscles of the diaphragm in response to the request of the human body to provide sufficient oxygen. Gas exchange with the participation of the abdominal muscles is common among the male population. In women, this type of breathing occurs with paralysis of the muscles of the intercostal space, ankylosing spondylitis, acute pleural pain. |
 Physiologically normal breathing patterns are present in healthy men and women. Diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, diseases of skeletal muscles, consequences injuries and surgical operations lead to disturbances in the work of the muscles of the diaphragm and intercostal space of the thoracic cells.
Physiologically normal breathing patterns are present in healthy men and women. Diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, diseases of skeletal muscles, consequences injuries and surgical operations lead to disturbances in the work of the muscles of the diaphragm and intercostal space of the thoracic cells.
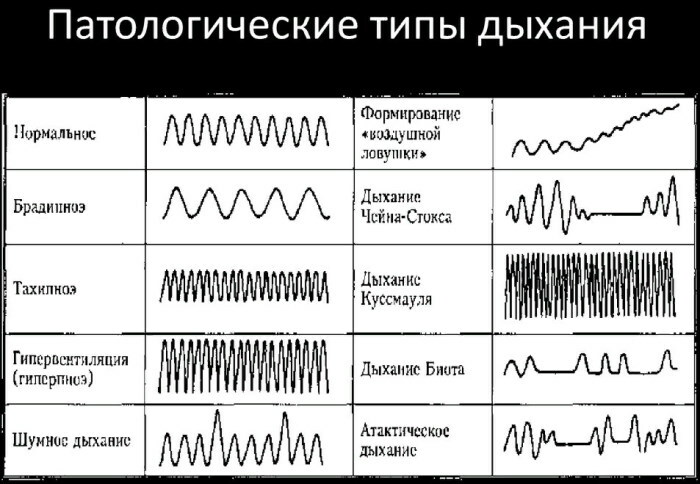
The table below describes the pathological types of breathing that are periodically diagnosed in women and men of different age categories.
| Pathological type of breathing | Characteristics of the physiological process |
| Unilateral | This type of breathing is characterized by a significant weakening of the mobility of the muscles of the chest on the right or left side. In this case, one part of the sternum works normally without signs of obvious violations. This type of pathological respiration is equally common in women of all ages. The main reason for dysfunctions of thoracic breathing is fibrous lesion of the pleura, pneumothorax, accumulation of excess fluid inside the pleural space. |
| Paradoxical | In the presence of this type of breathing, paradoxical mobility of all parts of the chest is noted. At the moment of inhalation, the anterior wall of the sternum falls, which excludes the maintenance of full gas exchange in the body. The paradoxical type of work of the respiratory system occurs in women with a fracture of the ribs or chest. A similar symptomatology can be traced in patients with an acute form of respiratory failure. |
| Reinforced | This abnormal breathing pattern can occur in people who breathe through the chest or the muscles of the diaphragm, but at the same time their musculature of the intercostal space does not ensure the maintenance of a stable gas exchange. In this case, the body additionally activates the trapezoidal, mastoid or scalene tissues. Forced breathing occurs in people with acute respiratory failure. At the moment of inhalation, the patient draws in the intercostal spaces, with the palms of his hands he tries to lean on the edge of the table or any other hard surface. With increased breathing, the shoulder girdle is constantly in a stabilized state with simultaneous hypertonicity of the trapezius muscles. |
 The type of breathing in women (normally, a smooth and measured contraction of the muscle tissues of the intercostal space should be preserved) is different creating an increased load on the muscles of the chest, which is activated in response to the innervation of the peripheral nerves of the autonomic systems.
The type of breathing in women (normally, a smooth and measured contraction of the muscle tissues of the intercostal space should be preserved) is different creating an increased load on the muscles of the chest, which is activated in response to the innervation of the peripheral nerves of the autonomic systems.
How does chest breathing work?
Chest breathing is a natural process of the body's vital activity, which is involuntary or voluntary. These functions of the bronchopulmonary tissue, skeletal muscles are coordinated by the centers of the brain and the somatic nervous system. The muscles of the chest, intercostal space alternately contract and relax, providing inhalation and exhalation, saturation of the body with vital oxygen.
At the moment air enters the respiratory system, the function of active ventilation of the alveoli is realized, which take part in gas exchange. At the time of exhalation, concentrated carbon dioxide is removed from the bronchi, as well as a small amount of depleted oxygen.
Inhale
The moment of inspiration is the initial stage of the implementation of the respiratory function in women in the presence of thoracic breathing.
This process includes the following physiological mechanisms:
- the muscle fibers located on the side of the inner surface of the chest are reduced;
- the costophrenic sinus opens;
- the dome of the diaphragm is smoothed.
During moderate and deep inspiration, the upper portions of the lungs receive the greatest ventilation. As the chest is saturated with the required volume of air, the underlying rib rises in relation to the overlying one.
Due to this, it is visually noticeable how during chest breathing there is a smooth raising and lowering of the anterior chest wall. At this stage of the physiological process, the load on the ribs is compensated by the inspiratory muscles. This is the internal interchondral and intercostal muscles.
Exhalation
At the moment of exhalation, the expiratory muscles, which belong to the internal intercostal muscles, contract synchronously. During their relaxation, the overlying rib of the chest is pulled towards the underlying rib. For a faster exhalation in conditions of chest breathing, the expiratory and inspiratory types of muscle tissues are simultaneously activated. In this case, the scalene, sternocleidomastoid and dentate muscles are included in the work.
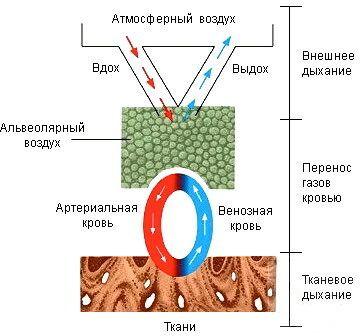
Gas exchange process
Atmospheric air passes through the nasopharynx, trachea, and then enters the lung cavity. At this stage, a mixture of ambient gases is passed through the bronchi of the lobar, segmental, lobular type and alveolar passages. Only after that, atmospheric air enters the pulmonary alveoli. The alveolar sacs and passages, together with the respiratory bronchioles, form a single alveolar tree in the form of the respiratory parenchyma of the lung tissue.
The physiological process of gas exchange is provided by the following biological mechanisms of the female body:
- atmospheric air passes through the membrane of the alveoli, where the maximum amount of oxygen is extracted from its composition;
- the resulting oxygen enriches the blood, which enters the heart, and then spreads through the arterial vessels through the tissues of the entire body;
- the end product of gas metabolism is carbon dioxide, which flows through the venous vessels back into the membrane of the alveoli for its further exhalation into the environment.
It has been scientifically proven that in the process of consuming 1 liter of pure oxygen, the human body releases up to 20.9 kJ of energy. This figure is 5 kcal. A similar effect occurs due to the oxygen oxidation of fats and carbohydrates.
Features of abdominal breathing
The abdominal type of breathing is predominantly found in men, and is also characterized by the presence of the following distinctive features:
- at the moment of inhalation, the main physical load falls on the diaphragmatic muscles;
- the muscle tissue of the intercostal space is practically not involved;
- during the act of breathing, the chest of a person breathing with a diaphragm has slight fluctuations;
- on inspiration, there is a smooth rise of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity with a relatively calm state of the sternum;
- on exhalation, a contraction of the muscle tissues of the diaphragm is observed, which leads to a reflexive retraction of the abdomen inward.
In the rest of the process, abdominal breathing proceeds according to exactly the same physiological principle as saturation of the body with air through the activation of the intercostal muscles of the chest. The distribution of oxygen through the blood, tissues of internal organs and the musculoskeletal system remains unchanged.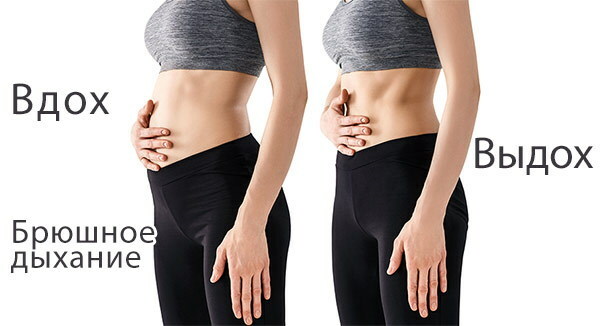
At the same time, it is believed that abdominal breathing is more efficient, since during muscle contraction, the diaphragm improves ventilation properties of bronchopulmonary tissue, facilitates the outflow of venous blood from the abdominal cavity towards the heart muscle.
Breathing in women is normal
The type of breathing in women (normally, the work of the muscles of the chest should remain stable) is characterized by a lower rhythm of inhalation and exhalation. The depth of the inhaled air directly depends on the volume of bronchopulmonary tissue, age, presence or absence of concomitant diseases of the body, physical form.
In women, the normal resting breathing rate is 18 to 22 repetitions. In the presence of a respiratory volume of the lungs of 0.5 liters for 1 min. about 7 liters of air passes through the organs of the female respiratory system.
A woman who is in a state of physical rest can fill her lungs with 500 ml of clean air during 1 breath. This is the normal tidal volume of a healthy person. A similar volume of air enters the environment after exhalation, but with the products of gas exchange. The maximum tidal volume in women, which is within the physiological norm, is 2000 ml of air. When you exhale, exactly the same amount of gas should be released.
Normally, the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide is constantly maintained in the lungs of a healthy woman. This is the residual functional capacity of the bronchopulmonary tissue, which provides full alveolar ventilation. At moments of physical exertion, psychoemotional overstrain and stressful situations, the rate of female respiration can increase to 12 liters per minute.
A woman who does not have diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory system can live without breathing for 5 to 7 minutes. After the specified period of time, irreversible changes are triggered in the cells of the brain, which entails the onset of biological death.
Male breath
The type of breathing in women (normally, in a calm state, the frequency of inhalation and exhalation does not exceed 22 repetitions) is chest to reduce physical stress on the muscles of the abdominal cavity. Male breathing is the activation of the musculature of the diaphragm.

The presence of this anatomical difference in the work of the body is also due to the peculiarities of the uniform distribution of the load between the muscle tissues. For example, in men who work hard physically, abdominal breathing is almost always present. If a man's chest breathing prevails, then this is also not a sign of pathology.
What are the differences between male and female breathing
The main differences between male and female breathing are that during inhalation, most women activate the intercostal muscles. Due to this, at the moment of air absorption, a smooth rise of the chest upward with its lowering down on exhalation is observed. This is a thoracic type of breathing that is necessary for women to relieve the muscles of the abdominal cavity during the period pregnancy, when the fetus grows so large that it puts pressure on the muscles diaphragm.
Due to the expansion of the rib cage, women are able to breathe with their breasts without creating the effect of squeezing the developing child. Male breathing involves minimal expansion of the chest, which is achieved by activating the muscles of the abdominal cavity while flattening the diaphragm.
Muscle tissues located in the intercostal space receive minimal stress. In the process of male breathing, venous blood from the tissues of the abdominal cavity returns much faster to the cavity of the heart muscle.
Danger of chest breathing for a woman
The type of breathing in women (normally at the moment of inhalation all the muscles of the intercostal space work synchronously) is pectoral, and in men, the muscles of the diaphragm are more active. By itself, chest breathing does not pose a danger to the female body. Its only drawbacks are considered to be a low level of efficiency, as well as energy costs.
For example, more effort is spent to activate the muscles of the intercostal space than to flatten the diaphragm during abdominal breathing. Also, pulmonologists note that the chest type of air absorption often leads to the development of shallow and shallow breathing. In the future, this may cause functional disorders in the work of the cardiovascular system and organs of the lower respiratory tract.
How to develop the correct breathing technique
To master the correct breathing technique, it is recommended to use special exercises aimed at the development and formation of the normal functioning of the bronchopulmonary tissue.
Exhale with additional resistance
With the help of this exercise, the mechanical functions of the respiratory system are improved, the quality of gas exchange increases.
An exhalation with resistance is performed as follows:
- Take a position while standing or sitting on a chair.
- Take as deep a breath as possible, activating the muscles of the chest.
- Slowly release air for 6 seconds through the lips, which are twisted into a tube.
This exercise should be repeated up to 5 times a day. The average duration of 1 workout should be at least 15 minutes. Exercise "Exhale with additional resistance" allows you to improve the technique of chest breathing.
Diaphragm breathing
Regular performance of this exercise will allow you to master correct abdominal breathing, and to master it, it is recommended to adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- Lie on your back on a couch or on a flat or hard floor.
- Draw in your stomach.
- On the count of "one, two, three" take a sharp deep breath through closed lips
- During inhalation, activate the abdominal muscles.
- On the count of four, take an additional deep breath, thrusting your belly forward.
- Sharply tighten the abdominal muscles.
- Coughing up all the air from the lungs, keeping the abdominal muscles tense.
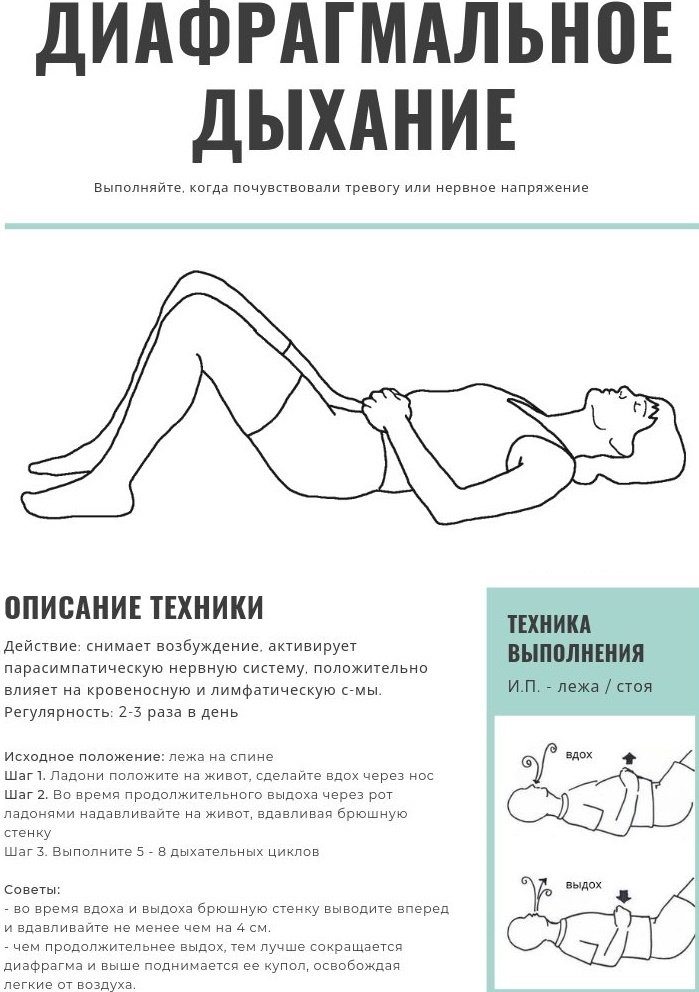
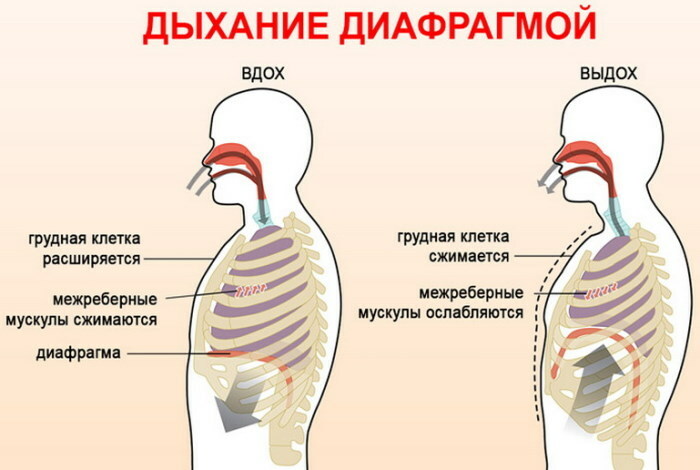
At the initial stages of mastering the technique of diaphragmatic breathing, it is recommended to perform this exercise from a prone position. After sufficient strengthening of the abdominal muscles, you can take up a sitting and standing position. This exercise is performed daily in the morning and in the evening for 10-15 minutes.
Posterior chest breathing
The use of this breathing technique is indicated for women who want to improve the thoracic type of breathing, to strengthen the muscles of the intercostal space.
To master the technique of posterior chest breathing, the following rules must be followed:
- Put your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Straighten your back and straighten your shoulder blades.
- Hold the hands at the level of the shoulder girdle.
- At the expense of "times" you need to take a sharp deep breath, and then at the same time clasp your chest with your hands.
- Hold air in your chest for 5 seconds.
- Exhale slowly through the closed lips, removing your hands from the surface of the chest.
Mastering the technique of posterior chest breathing requires regular training of bronchopulmonary tissue for 1-2 months. This exercise is performed for 30 repetitions in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Breathing is a vital physiological process, during which all tissues and cells of the human body are provided with the required amount of air. Normally, women take 18 to 22 breaths per minute. This is provided that they are in a state of physical and psychological rest.
The anatomical feature of the female body is that they are dominated by the thoracic type of breathing. This is necessary in order to reduce the physical stress on the abdominal muscles, which are in a state of hypertonicity in late pregnancy. Diaphragmatic breathing is common in men.
Video about breathing types in women
Abdominal and chest breathing: