 Fractures that affect the area of the growth plate of the bone are called epiphysiolysis.
Fractures that affect the area of the growth plate of the bone are called epiphysiolysis.
The growth zone is the cartilaginous tissue at the end of the long bone, and the growth plate, from which the bones grow, regulates their length and shape.
When a person's maturation is completed in the adolescent period, the growth zone closes with the bone growth stopped. Find the plate can be between the epiphysis( the end of the femur) and the metaphysis( the enlarged bone end).
This disease is not observed in adults. Such a fracture is an exceptional given of childhood and adolescence, when there are unclosed growth zones that form bones before it is closed.
Contents of the article
- A bit of depressing statistics
- Causes of injury
- Classification of the disease
- What bones can suffer
- Trauma in adolescence
- Clinical picture
- Diagnosis of injury
- What to do in case of injury?
- Possible complications
- Preventive measures
Slightly depressing statistics
Almost 30% of children's fractures occur in EGBK( epiphysis of the head of the femur).
Such bone damage requires urgent medical attention. Otherwise, you can get a bone curvature, a different length of the child's legs. Only the time prescribed by an orthopedic doctor will avoid these problems. 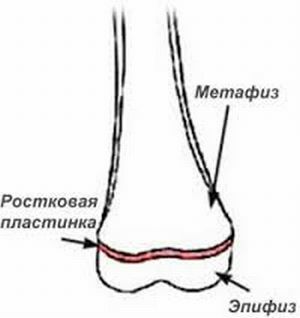
Statistics show that bones are deformed only in 1-10% of children with this disease. Boys, children, who are overweight, are often exposed to obesity.
There is a disease in children, adolescents with endocrine disorders, including growth hormone deficiency.
The disease develops in most cases slowly, but can often occur suddenly, after an injury, a fall.
Causes of trauma
Until now, there is no precise definition of the causes of epiphysiolysis.
It is assumed that the cause may be injuries, significant physical exertion, which adversely affect the condition of certain areas of cartilage and bone tissue.
Medical observations show that there are certain risk groups among children prone to such fractures. These include:
- children in the puberty period, the time of active growth;
- adolescent male( girls get sick less often);
- teenagers engaged in certain sports - football, volleyball, basketball.
The reason for such fractures of the fifth part of children are active recreation, such as skiing, skating, skateboarding, bicycling.
It is assumed that the cause of the disease may be injuries, significant physical exertion, which adversely affect the condition of certain parts of the cartilage and bone tissue.
Classification of the disease
There are several classifications of diseases, the most famous of which is the Salter-Harris system, dividing the disease into 5 types:
- in type I fracture, its line runs throughout the growth zone, which causes the entire epiphysis to separate from the bone, the plateis destroyed;
- II type can be recognized from the fracture line passing through the growth zone and affecting part of the bone body;
- for fractures of type III is characterized by a partial passage of the growth zone with the simultaneous detachment of part of the epiphysis;
- IV type damage is diagnosed by a fracture line affecting the growth zone, the body of the bone, the epiphysis;
- V type fracture - rare, occurs due to compression of the bone, leading to crushing of the growth plate.
What bones can suffer
Epiphysis is often seen in the following bones of the body:
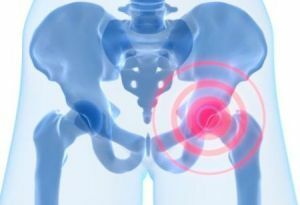
- Thigh head .At the heart of such a disease is the disturbed balance between sex hormones and those responding to
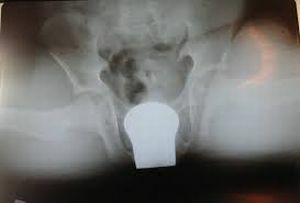
. On the photo, the epiphysis of the head of the femur
for growth. Pathology is due to a lack of the first, resulting in growth hormone causing it to increase. The proximal part of the femur, due to this, loses its strength, which can cause the epiphysis to shift.
- In the radius of the arm .Epiphysis of this bone becomes possible after a trauma in the proximal part. As a result of damage to the growth zone, it ceases to develop. The elbow zone continues to grow, so the limb is deformed.
- Tubular bones. The disease of these bones has a traumatic or pathological character. The first is due to trauma, and the second - due to developing pathologies of tubular bones. Bone covers do not lose their integrity. Diagnosis of the disease is only possible by roentgenological research.
- Bones of the external ankle .The disease manifests itself when the tibia is injured in the proximal part. It happens usually from autumn to spring, in difficult weather conditions( icy roads, skating and skiing season).
Trauma in adolescence
Refers to a rare disease diagnosed in adolescence.
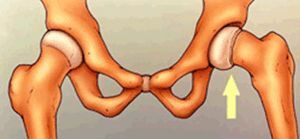
Juvenile epiphysis of the head of the femur( SEEGBC) is manifested by displacement, complete separation of the epiphysis in the area of the growth plate.
There is an acute or latent offset. The head of the hip bone, due to the decrease in the strength of the epiphysis growth zone, begins to shift, as it were, to slide down and back.
The development of the disease is associated with the onset of adolescent puberty when they grow intensively - girls 11 ÷ 12, and boys 13 ÷ 14 years.
Patients with EEGBK among children with orthopedic problems meet with a frequency of about 5 people per 100,000 cases of illness, which is 1 ÷ 5% in the amount under consideration. But there are exceptions, when such damage to the joints occurs at an earlier age - 5 ÷ 7 years.
Clinical picture of
Epiphysiolysis does not have any characteristic symptoms only for it. The clinical picture is determined by such signs of fractures of bones:
- pain, aggravated with axial load;
- appearance of hematoma in the injured area;
- the onset of edema after a short time after trauma;
- limited mobility of the affected limb.
Symptoms of a disease that arises not because of a trauma but develops due to pathological processes in this bone are:
- pain in the hip, knee joints that appear periodically for several months;
- irregularities in the gait, the appearance of lameness;
- the inability to carry the weight of the body to the affected leg;
- a turn of the diseased limb outwards in comparison with a healthy leg;
- visible leg shortening.
Diagnosis of injury
The main tools in setting the diagnosis are the study of the patient's history, external examination by an orthopedist and radiographic examination.
A doctor's examination can reveal a disease by such signs as pain that occurs with a large volume of movements of the limb and excessive strain on it, the appearance of muscle spasms. It is noted that it can not be completely bent.
Radiograph is made in two projections. More information is provided by the picture in the lateral position.
It is possible to judge epiphysiolysis by passing a fracture line through the growth zone. The resulting picture makes it possible to verify the displacement of the head relative to the neck of the thigh, which is a confirmation of this disease.
What should I do if I have an injury?
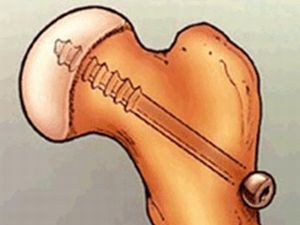 There are several methods of treating epiphysiolysis, which are prescribed depending on the type of fracture, degree of displacement of the epiphysis.
There are several methods of treating epiphysiolysis, which are prescribed depending on the type of fracture, degree of displacement of the epiphysis.
The most effective way is the operation.
The method of intra-articular interventions is not currently advised by doctors, since an open reposition of the femoral head can cause aseptic necrosis, tight joint mobility.
Treatment according to types of fractures occurs as follows:
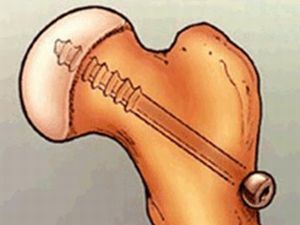
- I type .They are treated with gypsum immobilization, but more often the surgical method is used. To recreate the normal bone axis, a special pin is put in place to hold the fragments, or the spokes are inserted into the neck and thigh head during the open shoot zone. Remove the devices after the zone is closed.
- II type .These are the most common injuries of this type. They are built well when wearing an immobilization dressing from gypsum, in some cases require surgery using knitting needles, grafts.
- III type .Characteristic for older children. It requires rapid surgical intervention, fixation from the inside to restore the correct proportion of parts of the joint.
- IV type .These lesions, accompanied by a strong dislocation of the epiphysis, result in complete cessation of bone growth. Therefore, they are treated only promptly. Closed repositioning of fragments by stretching the skeleton for about a month is done, and then the osteosynthesis of the head and neck of the thigh with the help of spokes and bone graft is performed.
- V type .Treatment of such damages occurs by imposing a plaster bandage, in rare cases surgery is required.
The aim of the treatment is to prevent the femoral head from slipping further to prevent the growth zone from closing completely.
Medical measures should be started almost instantly after diagnosis, which is what doctors do, assigning surgery the next day. Rapid diagnosis allows you to quickly achieve the goal of treatment.
The main methods of treatment are three, the appointment of one of them is performed by a doctor depending on the severity of the disease. These include:
- installation of 1 surgical screw through the epiphysis and femoral neck to fix the head of the thigh;
- staging several screws in the head of the thigh with elimination of displacement;
- seizure of the growth plate with pathology and the installation of a pin preventing a new displacement.
The complexity of the disease is that some of the children with this disease go to the hospital late for treatment, when the deformity characteristic of the disease is already pronounced.
Possible complications of
The main complications of untimely treatment of epiphysiolysis are the complete arrest of the growth of the injured bone in length, the development of deformations in it, and as a result, the appearance of asymmetry in the older age.
Often results in the development of necrosis of the head of the hip bone and chondrolisis.
Necrosis develops due to the fact that the head of the femur, due to its displacement, ceases to be normally supplied with blood. It is almost impossible to determine its development in a child.
Chondrolisis, a disease expressed in the loss of cartilage of the joint, is also considered a complication of EGBC.It leads to the fact that the motor activity of the joint of this zone is lost, it does not bend, pains occur, inflammation is noted.
To restore the volume of movements after such a complication, it is possible to take anti-inflammatory drugs, intensive physiotherapy exercises.
Preventive measures
Prevention of the disease is almost impossible, because a relatively rare disease that does not have its inherent features,  is rarely diagnosed by doctors at once, in a third of cases it is not correctly determined at all.
is rarely diagnosed by doctors at once, in a third of cases it is not correctly determined at all.
As a result, treatment does not begin at the initial stages, but after months and years.
It is very important after the surgery to observe the child for about 2 years , to listen to medical recommendations.
During rehabilitation, it is necessary to limit the physical activity of the child, exclude sports activities.
Once a quarter, do an X-ray of the injury site to make sure that the pathological growth zone is closed and avoid possible problems. After closing the growth zone, you can fully increase the physical activity of the child.
Since the disease occurs only in childhood and adolescence and is rarely seen, parents should pay attention to any problems with the limbs of the child. It is easier once again to examine them at the onset of the disease, than to solve problems at an older age, with less efficiency.