 The knee joint is considered to be one of the most complex in structure and functional load in the human skeleton.
The knee joint is considered to be one of the most complex in structure and functional load in the human skeleton.
It does not just carry the full weight of the body, but also provides shock absorption when walking and running( striking the ground), protecting it with a spinal column.
According to different statistics, the frequency of knee joint damage is more than 7% of all injuries of the lower limbs.1/5 of them account for damage to the ligament apparatus and meniscus.
Successful treatment of such injuries provides prevention of chronic inflammation( arthritis) or exchange-dystrophic changes( arthrosis) in the cartilage and contacting bone surfaces.
The content of the article
- The structure of the knee joint
- Why does a rupture of ligaments occur?
- Classification of trauma types
- Clinical manifestations of
- Features of cruciate ligament injury
- Diagnostic methods
- How to provide first aid?
- What is the treatment for
- When is the need for surgical treatment?
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Rehabilitation after injury
- Consequences of injury
Knee structure
The complex anatomy of the joint and the constant load contribute to its vulnerability to mechanical damage, increased wear of the constituent surfaces.
To individual structures of the joint, as an organ can be attributed:
- bone,
- ligament,
- muscle.
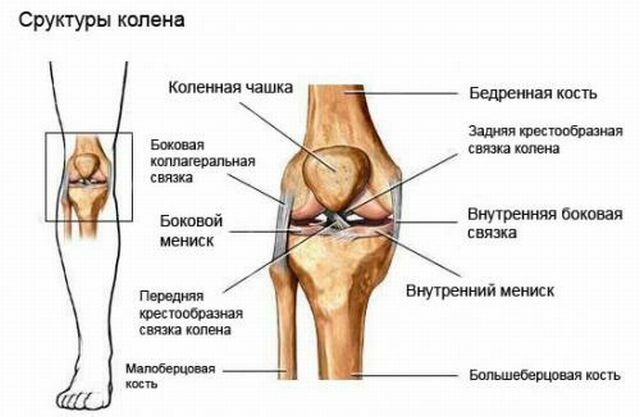
The knee joint connects the lower end of the femur, the upper part of the tibia, the round patella( "calyx").From the sides, both bones form hinge surfaces - condyles.
Between the bony surfaces is a cartilaginous layer up to 6 mm thick. It is responsible for amortization and ensuring a good slip. 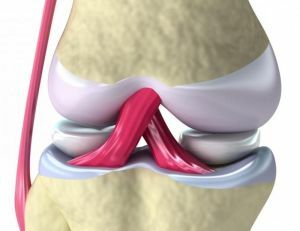
And in the junction of the condyles forms semi-circular pads - menisci( inside and outside).
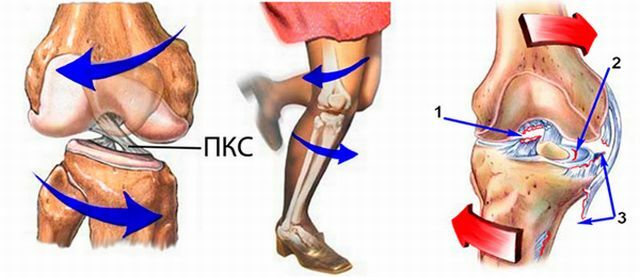
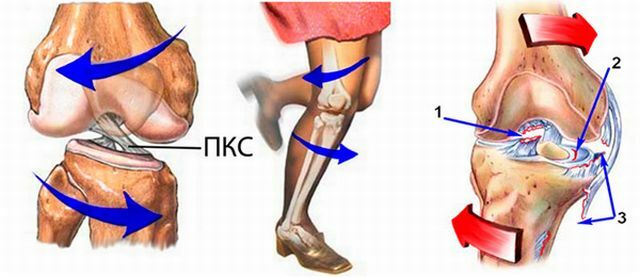
The ligament apparatus is represented by powerful internal cruciform cords( anterior and posterior) and lateral ligaments. They keep the bone joints and do not allow "falling out" from the area of the joint bag forward, back and sides.
The fibers of the ligaments are elastic, in a healthy person they are stretched in length by 5%.
Knee muscles are divided into:
- flexors( front) - quadriceps and tailors;
- extensors( posterior) - biceps, semimembranous and semitendinous;
- internal( leading) - large and thin muscles.
This mass of strong muscular formations attaches to different parts of the connecting bones with their tendons and contractions providing the necessary volume of movements not only in flexion and extension, but also rotates.
Nerve impulses to the joint come through the trunks of the ischium bundle. The popliteal arteries and veins pass next to the nerves.
Why does a rupture occur?
To break the dense tissue of the ligament apparatus, it is necessary to apply force in a certain direction.
The mechanism of ligament damage is as follows:
- front cruciate - the force should be directed with the bent joint behind, push the bones forward;
- posterior cross-shaped - the leg sharply unbends to the limit or the blow is applied to the bent knee in front;
- external lateral - is damaged when the shin is tilted inwards when tucked in, unstable walking in high-heeled shoes;
- inner side - the drumstick should swerve outwards.
Scientists have proved the influence of hormones( progesterone, estrogen) on the elasticity of the ligament apparatus. The higher their level, the less strong the ligaments become. This contributes to the rupture.
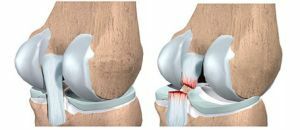
Joint injury can involve the simultaneous damage of several ligaments, with vascular rupture. This causes a hemorrhage in the joint bag( hemarthrosis) and complicates the treatment.
Classification of injury types
In addition to indicating the location of the rupture and determining the injured ligament, there are 3 degrees of damage:
- first - the overall integrity of the ligament is retained, only a small fraction of the fibers are ruptured;
- second - more than half the mass of the ligament is damaged, movements in the joint are limited;
- the third is a complete ligament rupture, in the joint there is unusual mobility.
The most frequent mechanism of damage is sports injuries, jumps from height to straight legs, blows during a fight, an awkward drop on the knee, a sharp braking, women have a love for high heels.
Clinical manifestations of
Assuming a rupture of the ligaments of the knee joint is possible if the following symptoms appear:
- severe severe pain;
- increase in joint size due to swelling;
- sensation of affected cod in the joint at the time of injury;
- unusual dislocation of the shin anterior or to the sides;
- limited mobility, impaired function or pathologically expanded range of motion;
- patellar mobility with hand pressure;
- the inability to stand on the injured limb.
Features of the cruciate ligament injury
 The rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee occurs with a sharp impact from the back of the shin or thigh, when falling back with fixed feet and shin.
The rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee occurs with a sharp impact from the back of the shin or thigh, when falling back with fixed feet and shin.
Physicians treat sportsmen as skiers, slalomists, hockey players, volleyball players, football players to the risk group.
In the diagnosis, simultaneous detachment of the patella is important, forwarding the bone components of the joint.
Unlike the anterior, the posterior ligament is better protected. It breaks with massive leg injuries during car accidents.
Patients complain of a feeling of "emptiness" in the knee. Other symptoms( pain, swelling) do not differ from ruptures of the lateral ligaments.
Diagnostic methods
In the presence of these symptoms, you should contact a trauma unit or a polyclinic with a trauma doctor.
The physician should carefully inquire about the mechanism of injury, inspect and probe the injured compound.
To confirm the diagnosis help:
- X-rays in different projections;
- joint ultrasound;
- magnetic resonance tomography.
At the same time, muscle damage, fractures of bones, and blood in the joint cavity are checked.
How to provide first aid?
In the event of a rupture of the knee ligament, first aid measures must be taken before the final medical diagnosis.
For this it is recommended: 
- give peace of mind, put a small cushion under the knee for maximum muscle relaxation;
- cold compress on a sore spot, change 4 times a day in the first 24 hours after injury;
- to reduce pain, you can take a tablet of Analgin, Butadione, Ibuprofen.
The patient must be transported after the limb is immobilized with tires or by using crutches.
What is the essence of
treatment? The main goal of treating ligament rupture is to return all of its functions to the knee joint, to prevent the development of arthritis, hemarthrosis, arthrosis.
For this purpose it is shown:
- compliance with the regime of restraint, rest for the limb;
- cold compresses to reduce swelling, reduce blood vessels, reduce internal bleeding;
- for mobility restrictions apply pressure on the knee area with elastic bandaging, a special bandage, such devices as orthoses, teips help fix the knee joint;
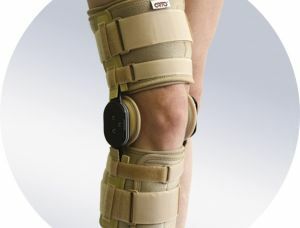
- it is desirable to keep the foot in an elevated position to obstruct the flow of blood and to remove puffiness;
- for the removal of pain used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs( Ketorolac, Ibuprofen), they can be used in the form of ointments;
- thermal procedures are prescribed on the third or fifth day, they promote the adhesion of the ligament tissues, eliminate inflammation in the joint.
When surgical treatment is necessary
Surgical methods of treatment have to be used with:
- combined injuries;
- complete rupture of several ligaments, accompanied by bleeding into the joint;
- with ineffective conservative therapy.
Types of surgical interventions:
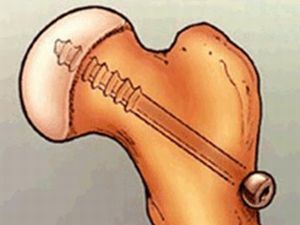
- stitching of damaged ligaments using microsurgery;
- replacement of the damaged ligament with its own autograft, which is taken from another joint;
- stitching of the donor ligament or artificial tendon.
In large trauma centers, operations are performed through small incisions using endoscopic techniques. After operation, wearing an orthosis is recommended.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies can be used in the recovery period, but do not replace them with medical prescriptions.
For this healers recommend:
- to prepare an ointment from clay and apple cider vinegar and make compresses for it at night;
- grease the joint with a composition of crushed eucalyptus leaves and grated garlic on pork fat;
- packs of grated potatoes with onions.
Rehabilitation after injury
To repair damaged tissues, the following are used:
- physiotherapy techniques - paraffin applications, electrophoresis, diadynamic currents, UHF;
- recommends exercises for the muscles of the lower leg, hips, exercises on the stationary bike, prescribe a massage;
- mud applications and foot baths are performed in sanatoriums, they have reparative effect by their biological natural activators;
- application of acupuncture can be carried out on the recommendation of a doctor.
The recovery times differ depending on the degree of damage: with an incomplete break, it takes three months, with extensive injuries and persistent treatment, it takes at least six months.
Consequences of an
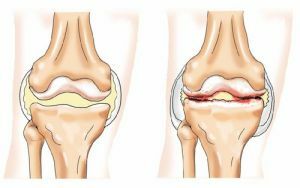 injury The transferred knee ligament injury can cause chronic arthritis with pain, stiffness.
injury The transferred knee ligament injury can cause chronic arthritis with pain, stiffness.
The disrupted composition of the synovial fluid subsequently promotes the development of arthrosis. In any case, athletes are not advised to continue the load.
For knee injuries, see a doctor as soon as possible. Treatment is most effective in the first days after injury. This will help to keep the activity at any age.