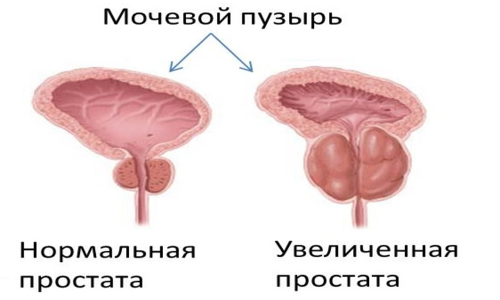
Some male diseases are benign in nature, amenable to successful treatment - drug and surgical. This is hyperplasia of the prostate gland, which is otherwise called prostate adenoma. The disease is quite common, occurs in middle-aged men, and also old age( starting from the age of 40), is formed due to the negative impact on the functioning of the prostate gland of certain factors. During the diagnostic examination, competent detection of these factors is carried out with their further elimination through medication or surgical intervention.

Contributing factors, or etiology of the prostate
During the lifetime of prostatic hyperplasia, as a type of male disease, traditional medicine advocates hypothesized that the main reason lies in the age of the patient. That is, the older the man, the more likely it is to face hyperplasia. Another reason is the impact of the environmental factor on the development of the pathological process.
Speaking about age-related changes, their influence on the development of the disease, it is necessary to imply hormonal imbalances, which subsequently lead to a pathological process. What's happening? Violation of the hormonal background due to the fact that men decrease male hormones androgens due to the increase in estrogen. A small number of male hormones androgen occurs due to the large content of estrogens. This imbalance of hormones is the cause of pronounced disruption of the cells, prostate tissue, their deformation, uncontrolled proliferation.
Hyperplasia of the prostate gland in men is considered in most cases an insidious disease, as it can develop long enough, for several decades, without manifesting or disturbing a person. Brightly expressed symptomatology is observed in the patient in the case when the pathological process becomes chronic. Given this undeniable fact, many leading experts recommend regular medical examinations, face-to-face consultations with the appropriate delivery of the necessary tests in order to timely identify problems of the genitourinary system of man.
With regard to weak or overly active sexual life, sexual orientation, excessive use of tobacco, alcoholic beverages, inflammatory and venereal diseases transferred, their direct effect on prostatic hyperplasia is not fully revealed. Therefore today all opinions of the specialists-urologists are reduced to one factor - the age factor. However, such a statement does not exclude that the use of poor-quality food, various spirits, and the habit of leading a passive life on the development of hyperplasia have a certain effect.
Another important factor is heredity, or a genetic predisposition to this kind of disease. It was revealed that in the risk group are those representatives of the stronger sex, whose previous generation was affected by this pathology. Taking into account this rationale, it is advisable for men who are at greatest risk because of genetic predisposition to undergo an annual preventive examination from the age of 30.This approach will ensure the timely identification of pathology, will prevent or slow its development in a relatively short period of time.
Types and symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia
Prostatic hyperplasia, like all other male pathologies associated with the genitals, does not do without a clinical picture, which is quite pronounced. Speaking about the symptoms, it is expedient to first understand the stages of the disease, which are divided into:
- compensated;
- is subcompensated;
- decompensated.
The compensated stage is considered the initial and most harmless, characterized by a slight delay in the process of urination. There is a sluggish stream of urine, the patient is disturbed by frequent desires, repeated at night. In the diagnostic examination, an enlarged gland is found, with a clearly delineated border. The median furrow is well palpable and painless. There is an absolute devastation of the bladder. This stage covers a period of 1-3 years.
With a subcompensated stage, there is a noticeable compression of the urethra. This state of affairs results in the inability of the bladder to function normally or completely emptying of the urinary fluid. The bladder remains slightly filled, so the patient always feels incomplete full emptying. This stage is also characterized by small portions of urine, which is subsequently involuntarily secreted as soon as the bladder is refilled. In this case, the urine changes color, becomes turbid with the presence of a small amount of blood.
In the third stage, decompensated, the bladder stretches due to the fact that enough urine remains. As the prostate grows too much, reaching a certain size, urine is already released by drop, because of the constant stagnation it becomes too dark, again with the presence of blood. There is a violation of the proper functioning of the kidneys, so it is appropriate to talk about kidney failure.
Given the fact that prostatic hyperplasia passes through three stages of development( each of them has its own symptomatology), it is advisable to consult a specialist for medical help when the first symptoms are observed. This approach to solving the problem will ensure the complete elimination of existing symptoms, allow the patient to get rid of hyperplasia for a short enough period for him.
If you combine the symptoms of all three stages, the overall clinical picture with hyperplasia can be characterized by:
- with a rather weak jet observed in the first stage of the pathological process;
- difficulty with the onset of urination;
- frequent interruptions in the process of urination;
- frequent urge to urinate, especially at night;
- need to regularly strain the lower abdomen when urinating;
- lack of ability to completely empty the bladder;
- additional visit to the toilet after a certain( short) period of time;
- development of chronic diseases on the background of infection of the urinary tract due to the constant stagnation of urine;
- formation of stones in the bladder, as well as the urinary tract;
- a noticeable impairment of kidney function;
- is a chronic urinary retention that occurs due to compression of the urinary tract from the side of the enlarged prostate to a certain size.
The above symptoms of hyperplasia can disturb a patient either alone or in a complex manner. As one or several signs manifest themselves, without consulting a competent specialist, you can not do it, because you need an accurate diagnosis. This is due to the fact that many diseases of the genitals are similar in their symptoms, and incorrect diagnosis can lead to erroneous treatment, which subsequently leads to serious complications.
Are there any complications?
Any disease, if not taken care of in time, leads to a number of serious complications, which are much more difficult to eliminate than at an early stage of pathology development. The prostate gland begins to increase to a certain size, taking various forms: sub-tubular, intravesical, retrotrigonal. With a sub-tubercular form, the tumor grows toward the rectum. Intravesical is characterized by growth towards the bladder. When retrotrigonal, the tumor forms under the triangle of the bladder.
Speaking of possible complications, guided by:
- obstruction of the urinary tract;
- diseases( infectious nature) of the urinary tract;
- with bladder stones;
- by ruptures, diverticula of the bladder;
- with kidney damage;
- acute retention of urine outflow.
Urinary tract obstruction characterized by pain symptoms due to stretching of their upper part. During the examination of the patient, a bladder enlarged to a certain size, renal colic, prostate cancer is observed.
Because of hyperplasia of the gland, the urethra is narrowed considerably, which is the reason for the multiplication of various microorganisms. That is why many patients with hyperplasia suffer from various infectious diseases, although they adhere to the rules of safe sex.
Due to overfulfilment of the bladder, precipitation forms, which subsequently hardens to form various stones.
Diverticula and bladder ruptures are formed due to the fact that it does not completely emptied of urine. The walls of the bladder lose the ability to contract, which leads to their thinning, weakening, the inability to push out urine. In place of thinning and protrusion, diverticula are formed, which are broken at physical stress.
Since the bladder can not repel urine, it exerts a high pressure on the kidneys. With such a prolonged pressure, the process of development of hydronephrosis - expansion in the kidneys of the collecting system - begins.
Acute urinary retention leads to the inability of the bladder to empty. This condition can occur suddenly, leads to severe pain, fraught with rupture of the walls of the bladder. They call for medical help, which will ensure the installation of a catheter aimed at removing the spasm, widening the walls of the urinary tract, and maximizing the emptying of the bladder.
Diagnostic examination
Hyperplasia of the prostate gland requires an obligatory diagnostic examination, which is carried out by experienced specialists. In order not to be mistaken when making a diagnosis, the patient is subjected to a thorough  examination, consisting of a series of activities. These activities are due to:
examination, consisting of a series of activities. These activities are due to:
- palpable rectal examination;
- laboratory research;
- instrumental research;
- uroflowmetry;
- with urethrocystoscopy;
- CT urography.
Palpable( finger) research helps determine the size, consistency of the prostate gland, the degree of soreness, the presence of a groove on the prostate, which should normally be present. Laboratory studies consist of the delivery of a general urine test, a biochemical blood test, the determination of PSA( antibodies in the blood).Instrumental research is carried out using transrectal ultrasound, which allows you to get a visual picture of the size of the prostate gland, respectively.
With uroflowmetry, the volume and speed of urine output are determined. The procedure of urethrocytoscopy provides data on the state of the walls of the bladder, urethra, allowing to reveal diverticula, not allowing their ruptures. CT urography is performed if the doctor suspects the presence of bladder stones.
Control of hyperplasia: medicamentous, operative, non-operative
The medicamentous method of combating prostatic hyperplasia is effective in the early stages of pathology development. Implications of treatment:
- Alpha-1-adrenoblockers. These are: "Terazozin", "Doxazosin", "Tamsulosin".Thanks to the listed products it is possible to relax, remove spasms of the musculature of the prostate gland, the neck of the bladder, to prevent obstruction of the urethra.
- Blockers of 5-alpha-reductase. These are: "Finasteride", "Dutasteride", "Permixon".These drugs block the formation of the hormone dihydrotestosterone, reducing the size of the prostate gland, counteracting the obstruction of the urethra.
The operative method of treatment is used in severe cases, when drug treatment does not give positive results, it is not appropriate to solve the existing problem. Speaking about surgical treatment, it is expedient to consider the following forms:
- open;
- minimally invasive;
- embolization of the arteries of the prostate.
An open surgery is performed on the wall of the bladder, is traumatic, but contributes to the complete cure of the disease. A minimally invasive method of surgery is carried out by the urethra, is non-traumatic, since it does not allow any incisions. The third type of operation( embolization) is carried out through the femoral artery, aimed at occluding the arteries of the prostate gland.
Non-surgical types of wrestling are performed with:
- prosthetic balloon dilatation, which facilitates the expansion of the narrowed section;
- installation of prostatic stents in the constricted area;
- thermotherapy or microwave coagulation of the prostate;
- of transurethral needle ablation;
- cryodestruction.
Today for the treatment of neglected forms of hyperplasia, surgical methods that help to get rid of pathology and prevent its re-education are a great success. However, the scheme, type of treatment determines the specialist, based on the patient's history, the results of the diagnostic examination.