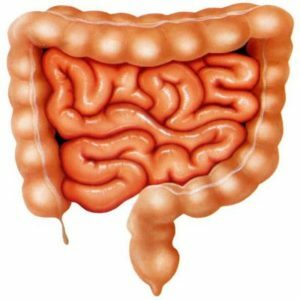
Enzymes of the small intestine, and more than 20, participate in the digestion process. They process food to the state of nutrients, which are then absorbed by the body and enter the bloodstream. The small intestine is a long tube( 2-4 m), which is part of the digestive tract and connects the stomach and the large intestine. In it, the processes of digestion of food are most active. Here, most of the vitamins, minerals, fats and some water are absorbed. Muscle contractions, called peristalsis, cause the food to move to the large intestine.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
Functional and anatomically it is divided into 3 departments:
- duodenum;
- small intestine;
- iliac.
The duodenum is the first and the shortest section, its length is about 25 cm. The food enters it from the stomach through the muscular sphincter. There are ducts from the pancreas and the gallbladder. In this part, iron is absorbed. The lean and ileal gut forms numerous loops. Sugars, amino acids and fatty acids are absorbed here. In the last part of the intestine, vitamin B12 and bile acids are absorbed.
- 1 Internal structure
- 2 Kinds of substances and their action
1 Internal structure
Throughout the length of the organ wall has 3 shells:
- external serous( peritoneal);
- is an average muscular, consisting of 2 layers;
- inner mucosa with submucosal layer.
See also
- Description of the role of the enzyme lipase
- Causes and treatment of bloating in the intestine
- Causes and treatment of unpleasant bitterness in the mouth and throat
- Effective agent for gastritis and stomach ulcer
The inner layer with a sublayer has folds. The mucous membrane is provided with outgrowths( villi), which have close contact with incoming food. Between them are long indentations or crypts that secrete intestinal juice. At their base, there are special cells that produce antibacterial enzyme lysozyme. Special goblet cells secrete mucus, which participates in digestion and helps to promote the liquid contents of the stomach( chyme).
2 Kinds of substances and their action
In the duodenum, an alkaline liquid is produced that neutralizes the acid in the gastric juice, thereby helping to maintain an optimum pH value of 7 to 9. This is a necessary condition for the productive work of enzymes. All enzymes produced in the small intestine are formed in the epithelium of the mucosa or on the fibers of villi and are part of the intestinal juice. They are divided according to the type of substrate, which is affected. The following enzymes are distinguished:
- protease and peptidase cleave proteins to amino acids;
- lipase converts fats into fatty acids;
- carbohydrases break down carbohydrates such as starch and sugar;
- nuclease converts nucleic acids into nucleotides;
- hydrolases split large molecules into smaller ones in the lumen of the intestine.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
Many enzymes enter the intestine from the pancreas and gallbladder. The pancreatic enzymes that it takes are lipase, trypsin, and amylase. Trypsin cleaves proteins into shorter polypeptides, lipase converts fats and oils into fatty acids and glycerol, amylase turns amylose( starch) into maltose. The incoming bile emulsifies fats and allows more efficient work of intestinal lipase, which is less active than lipase of the pancreas.
Under the influence of these compounds, proteins, fats and carbohydrates break down into smaller molecules. But they are not yet fully split. Then they are affected by intestinal enzymes. These include:
- sucrose, which converts sucrose into glucose and fructose;
- maltase, which cleaves maltose to glucose;
- isomaltase, which affects maltose and isomaltose;
- lactase, which breaks down lactose;
- intestinal lipase, which promotes the breakdown of fats;
- peptidase, destroying peptides to simple amino acids.
The formed simple molecules are absorbed into the blood with the help of villi in the jejunum and ileum.