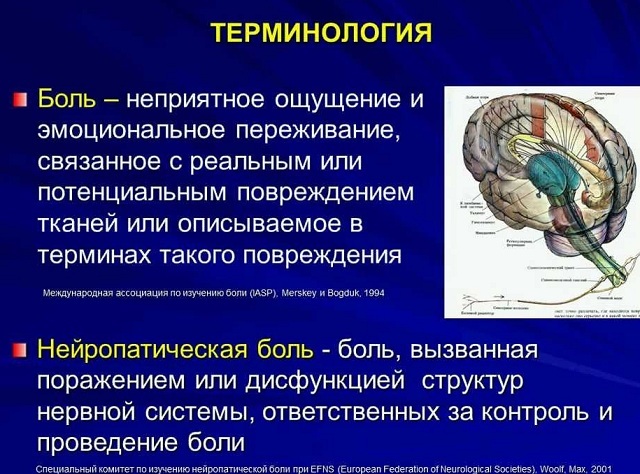
 Neuropathic pain is a type of pain that differs from the usual one in that it is not a reaction to physical damage, but is the result of pathological excitation of neurons of the central or peripheral nervous system, can develop in children and adults, regardless of age.
Neuropathic pain is a type of pain that differs from the usual one in that it is not a reaction to physical damage, but is the result of pathological excitation of neurons of the central or peripheral nervous system, can develop in children and adults, regardless of age.
This pathology today is widespread and for every hundred people, seven suffer from it. Disease can even the most simple actions turn into anguish.
So even the most simple action, such as putting on shoes can become simply impossible due to the presence of severe pain. What is characteristic, often the patient simply can not describe the nature of the pain to the doctor and its features, which does not allow for an adequate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Pain can be permanent or episodic. It manifests as a burning sensation, a feeling of frost in the skin, itching, cutting pain, sometimes stitching, numbness.
Pathology progresses as a result of nerve fiber damage or disruption of its nutrition. So, if the fiber stops functioning normally, a signal is sent to the brain, for example, that the person touched the hot one, although in fact he did not touch anything at all.
In turn, the brain sends a signal and in a healthy place, absolutely without damage, you will feel pain and burning like a burn.
What is pain - a neurological educational program
Pathophysiology of the process
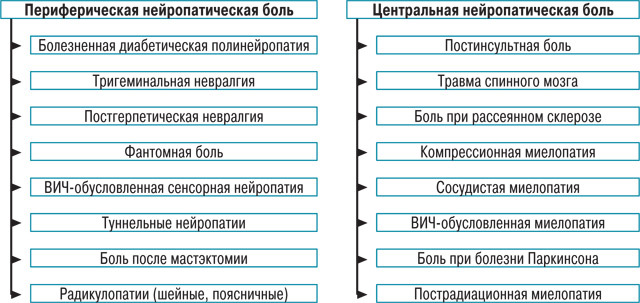
From the point of view of pathophysiology, neuropathic pain is a pain syndrome that occurs when the central and peripheral nervous systems are damaged and disturbed. Depending on the level of the lesion and the provoking disease, the pain syndrome will also vary:
- peripheral nerve : polyneuropathy, mononeuropathy, tunnel syndrome, nerve trauma;
- brainstem : multiple sclerosis, tumor, stroke, syringobulbia, tuberculoma;
- nerve root : postherpetic neuralgia, compression, trigeminal neuralgia;
- spinal cord conductors : myelopathy, compression, funicular myelosis, multiple sclerosis;
- visual hill : swelling, stroke;
- posterior horn of the spinal cord : swelling, syringobulbia;
- bark of the cerebral hemispheres( brain) : craniocerebral trauma, tumor, arterio-venous malformation, stroke.
The mechanism of pain formation is a result of the restructuring of various parts of the nervous system. At the level of the peripheral apparatus, there is a decrease in the level of excitability and activation of the "sleeping" structures, which provide pain perception( nociceptors).
An important role is played by the processes of destruction and restoration of the fiber membrane( myelin) and the development of processes of neurons directed atypically, which form active bonds with other neurons.
The activation of the sympathetic nervous system also affects the process, as a result of which neuropathic pain and its symptoms are supplemented by trophic and vegetative disorders.
Causes and factors-provokers
Neuropathic pain can arise as a result of such reasons:
- Diabetes mellitus : The elevated blood sugar level inherent in this disease affects the state of the nervous system. Such nerve damage in diabetics is called diabetic polyneuropathy. The pain in this case, not too strong, is localized in the area of the feet. If a person with this pathology has to stay on his feet for a long time, the pain may intensify, especially during a night's sleep, greatly interfering with rest.
- Herpes infection : with herpes zoster there is a characteristic rash and after its disappearance, pain may appear. The most susceptible to this pathology are people over 50 years old due to the already fairly faulty nervous system. Sensations of pain are localized at the site of rashes. Unpleasant sensations can cause even a touch of clothing. Spinal Cord Injuries .All the major nerve endings pass through the spinal cord, so after the injury you can experience squeezing, stitching, shooting pains in the trunk, as well as in the lower and upper extremities.
- Post-stroke pain .Stroke is a trauma to the entire nervous system, so it provokes the appearance of neuropathic pains( they can appear even a year and a half after the attack).The patient may feel a burning sensation, tingling in the affected side, and a feeling of cold.
- Shingles .
- : as a result of it, nerve endings have been affected in a certain area, which now work differently than before, so the patient can feel burning, tingling, "creepy."
- AIDS .
- Back problems with : displacement or damage to the vertebrae can lead to nerve injury, which in turn can lead to neuropathic pain.

- Multiple sclerosis .
- Amputation of : leads to the appearance of so-called "phantom" pain( the limb is no longer present in a person, and the brain signals that it hurts).
- Chemical, Radiation Exposure .
- Neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve leads to the development of this type of pain, which manifests itself when you touch the skin, while chewing, swallowing.
Species of the syndrome
In medical practice, several types of neuropathic pain are considered:
- Constant pain, burning sensation, tingling : most often these sensations are localized in the fingers of the upper and lower extremities. Not bad pain is treated with analgesics, Aspirin, combined drugs. If the pain is unbearable, the use of stronger analgesics, such as Codeine, is necessary. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that pain intensifies during rest, therefore before going to bed, the patient should take a stronger drug to provide a more or less calm and full sleep. It is also important to warn a person that completely the pain may not pass and that even a little relief is already a big plus.
- Short-term attacks of acute pain : the duration of pain is only a couple of seconds and they are localized in the area of the feet, shins, fingers. Treatment of this pathology is done by anticonvulsants. Relief will be palpable and will come in a few days after the start of treatment.
- Pressure, constrictive pain : a kind of pain that is difficult to treat. It covers the legs and feet and can join
 with other types of neuropathic syndrome, significantly worsening the patient's condition. A person should know that even strong analgesics will not help to completely get rid of the pain.
with other types of neuropathic syndrome, significantly worsening the patient's condition. A person should know that even strong analgesics will not help to completely get rid of the pain. - Sensation of painful cold in the fingers of the lower extremities also poorly suits the anesthesia of medicines.
- Supersensitivity to the touch of may be accompanied by painful spontaneous sensations. So even an ordinary touch to the patient's skin can cause him great discomfort. The complexity of the situation is also that at night such a person puts on cotton gloves and socks, wraps his feet in the edge of the sheet, in order not to make unnecessary movements in a dream that can wake and cause pain. To alleviate this condition can be the appointment of tricyclic antidepressants.
Features of the pain syndrome
Symptomatic of neuropathic pain persists long enough and even after the end of treatment may persist for some time:
- dull constant pain;
- dysesthesia;
- hyperalgesia
- hypoesthesia;
- hyperpathy;
- allodynia;
- burning sensation;
- numbness;
- pain syndrome;
- tingling;
- sleep disturbance due to the presence of unpleasant( painful) sensations;
- decreased quality of life;
- anxiety, with a claim to grow into depression.
Method of three "C"
 The diagnosis of neuropathic pain is based on the method of three "C": listen( what the patient says), watch( assess the sensitivity disorders), correlate( analyze the compliance of complaints and results obtained as a result of the examination).
The diagnosis of neuropathic pain is based on the method of three "C": listen( what the patient says), watch( assess the sensitivity disorders), correlate( analyze the compliance of complaints and results obtained as a result of the examination).
To date, there have been developed whole systems and scales for assessing subjective complaints and objective neurological symptoms( diffodiagnosis).
In practice, the confidence in the DN4 questionnaire, where, in response to four or more questions, "neuropathic pain" of ten, justified the diagnosis, the diagnosis takes place.
Following is a clinical study, a neurophysiological examination: electroneuromyography, sensory testing, morphological or neuroimaging confirmation of the lesion.
Features of therapy and prevention
In the treatment of neuropathic pain, the main goal is to get rid of the underlying cause( if possible) and alleviate the symptoms.
Therapy of the underlying cause can significantly reduce pain. For each of the problems, the narrow specialist assigns his specific effective treatment.
To ease the condition, medicinal pain medications( Paracetamol), anti-inflammatory drugs( Ibuprofen) are used, but they will only reduce pain.
Tricyclic antidepressants that can relieve unpleasant symptoms for a period of several  days to several weeks are more effective. In order to reduce drowsiness, it is suggested to prescribe medications from the smallest doses.
days to several weeks are more effective. In order to reduce drowsiness, it is suggested to prescribe medications from the smallest doses.
Opioid analgesics are another option for reducing pain. They are more powerful pain killers. The most popular drugs are Tramadol, Codeine, Morphine.
Anticonvulsants are an alternative to antidepressants. They can stop the nerve impulses, thereby preventing a possible attack of epilepsy.
For greater effectiveness, combinations of drugs can be prescribed: an antidepressant and an anticonvulsant.
Physiotherapy is prescribed to reduce neuropathic pain. The most effective are reflexotherapy, therapeutic massage, magnetotherapy, laser treatment.
It is not bad to achieve a positive effect and apply asanas of Yoga and exercise therapy.
Neuropathic pain is complicated by the fact that everyday life turns into torture: dressing, walking and any movements can become intolerably painful.
For prophylaxis it is necessary:
- performing exercises on all muscle groups;
- a healthy lifestyle;
- foot bath( every other day);
- wearing comfortable shoes;
- examination of limbs for sensitivity( daily);
- refusal from alcohol and tobacco smoking;
- avoidance of back and limb injuries.