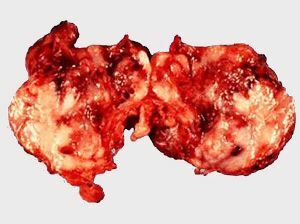
 Ganglioneuroblastoma is a malignant formation containing neuroblasts. It is a tumor node without a coat of grayish pink color, consisting of dead tissue and hemorrhages.
Ganglioneuroblastoma is a malignant formation containing neuroblasts. It is a tumor node without a coat of grayish pink color, consisting of dead tissue and hemorrhages.
Among tumors of the nervous system, every second is ganglioneuroblastoma, most often it occurs in the retroperitoneal space, at the level of the thorax. The reason is the transformation of benign gangleoneuromy into malignant formation.
The extreme form of transformation is neuroblastoma. Explanations of the exact causes of tumor occurrence in neurologists do not. Often it affects children 5-10 years of age.
This disease is accompanied by a sharp weight loss. The tumor is formed in various parts of the body, which is accompanied by squeezing nearby organs. The presence of neoplasm with the help of MRI is determined, ultrasound - biopsy research and analysis.
Possible localization of ganglionioroblastoma:
- is a tumor of the retroperitoneal region;
- malignant neoplasm in the mediastinum region;
- brain tumor.
Stages of development of the tumor process:
- Stage 1 - the tumor is within one organ;
- Stage 2 - the tumor extends beyond the affected organ, but does not reach the lymph nodes;
- Stage 3 - tumor development seizes the lymph nodes on both sides of the spine;
- Stage 4 - metastases penetrate all organs and tissues of the body.
Clinical picture
Symptoms indicating the development of the tumor process:
- fever;
- anorexia;
- anemia;
- elevated blood pressure;
- redness of the face;
- sweating;
- bruises under the eyes;
- diarrhea;
- malfunctioning of the heart.
If ganglioneuroblastoma is formed in the retroperitoneum, then the weight decreases sharply, the skin turns pale, the temperature rises, the person is feverish.
Neuroblasts in the blood
Adrenaline and other cotecolamines in the blood are increasing. This causes increased sweating, increased blood pressure and tachycardia. In the abdomen there is a feeling of heaviness, the presence of foreign education.
Ganglioneuroblastoma of the mediastinum causes shortness of breath, coughing, choking. There are neuropathic disorders in the larynx, when the tumor compresses the vagus nerve and its branches. Symptoms are marked by sudden appearance and rapid development.
The tumor can be small in size and do not affect the lungs. If there is pressure on the upper sections of the chest, then there are changes in the eyes - the lower eyelid, the enlargement or a different size of the pupils.
Tumor of the brain manifests itself in a focal point in accordance with the location of the compaction. Metastases spread through the channels of the nervous system and affect the brain and spinal cord.
Ganglioneuroblastoma in the brain is determined by a disruption in the functioning of the department in which the tumor is present. It can be a decrease in vision, hearing, memory, smell.
If the tumor develops in the abdominal or thoracic region, neighboring organs and tissues are affected by metastases - liver, bones, intestines.
Diagnosis of
To determine or exclude the presence of a tumor, the doctor prescribes a set of studies and analyzes that give a complete and unmistakable picture.
In laboratory studies on ganglionic fibroids, a blood test is used for the level of catecholamines and a urine test for metabolites.
X-rays give indirect assumptions, determining the shape of a possible tumor. If it is located in the retroperitoneal region, then in the picture of the survey radiography you can see unnaturally stretched loops of the intestine. When the seal is localized in the mediastinum, a dense opaque shadow can be seen, an expansion of the space between the ribs, and the place where the tumor adheres to the ribs.
Clearly see a tumor will help:
- MSCT;
- of the abdominal ultrasound;
- CT of thoracic department;
- MRI of the head;
- scintigraphy.
To conduct brain research on the presence or absence of a tumor process, a stereotactic biopsy is performed. Soft tissue of the head is opened and a microscopic opening is made in the skull to insert a thin needle. At the site of the tumor, a tissue sample is captured by a needle. Sew a suture. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Multislice computer diagnosis of internal organs is done on a moving tomograph, which enables the body to be examined from different viewing angles. When X-ray radiographic examination of the mediastinum, nitrous oxide is introduced into the tissue.
Metastases are visible on the X-ray, they are detected with ultrasound of the liver, lymph biopsy. For a more accurate diagnosis, a tumor sample, seized by surgery, is examined under a microscope.
Comprehensive analyzes and studies are conducted to accurately determine the type and composition of the lesion. Combined Ganglioneuroblastoma is similar in structure to other small-cell malignant tumors.
Magnetic resonance imaging accurately determines the presence of the neoplasm and its exact location in the organs.
ultrasound of the liver shows characteristic organ changes and possible screening of gangleoneuroblastoma. A biopsy of the lymph node is prescribed in the event that the compaction and enlargement of the node are palpated.
Scintigraphy is an examination of bone tissue by X-rays that can show an alien bulk formation in the bones.
Complex of measures
The treatment of ganglioneuroblastoma consists in surgical excision of the tumor and removal of its consequences and possible metastases with the help of chemical and radiotherapy.
Surgical treatment: 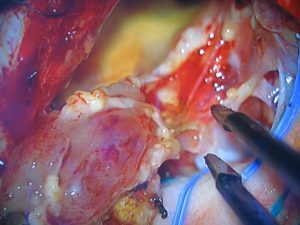
- Gangloneuroblastoma of the brain is removed by a neurosurgeon. The principle of conducting the operation is similar to the type of surgical intervention in diseases of the brain.
- In the retroperitoneal region or in the mediastinum, the thoracic surgeon operates. If the tumor is local, it is removed without touching the proximal organs. But often metastasis affects the surrounding space. Then resection of lymph nodes and adipose tissue is carried out. The tactic of advanced tumor removal allows to remove all affected tissues. In the case where it is not possible to completely remove the tumor, it is partially removed to reduce pressure on the internal organs.
Chemical therapy in the postoperative period:
- monochemotherapy -drugs used to reduce the active proliferation of cancer cells - Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine.
- cytostatic medications are used in the period before bone marrow transplantation.
Chemical therapy gives good results. Therefore, irradiation is used in rare cases. The disease often affects young children who are extremely dangerous exposure to radiation.
In severe cases, when a brain tumor is removed, bone marrow transplantation is required after removal, since metastases also affect it.
When choosing a strategy for the treatment of the disease in each case, doctors take into account the prognosis of the development of the tumor upon detection, and its response to ongoing treatment.
Not only the extent of resection of the affected organ and surrounding tissues depends on the stage of the disease, the size of the tumor, and the location of its localization, but also the choice of chemical preparations, their dosage and the duration of application after the operation.
Forecast for
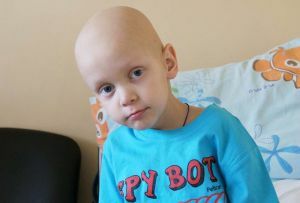 patients 70% of patients after an average treatment live no more than 2 years. The most favorable prognosis for survival is in patients with a tumor in the mediastinum region. It is 80%.Ganglioneuroblastoma in the retroperitoneal region survives 60% of patients.
patients 70% of patients after an average treatment live no more than 2 years. The most favorable prognosis for survival is in patients with a tumor in the mediastinum region. It is 80%.Ganglioneuroblastoma in the retroperitoneal region survives 60% of patients.
In the case of timely detection of a tumor and its radical excision without metastases, the chance of a two-year survival rate is almost 95% of patients.
Only half of patients with escalating ganglionic fibroblasts after all treatment activities have a survival probability.
The most optimistic prognosis in those patients to whom a radical method of tumor removal is applied. In the absence of a regressive process, radiotherapy is used in a tumor after chemical treatment.