 The pituitary gland( pituitary gland or lower cerebral appendage) is a small gland of internal secretion located in the brain, which coordinates the work of the entire endocrine system in the body. It is performed by the pituitary gland due to the development of its own hormones. Its weight is about 0.5 g.
The pituitary gland( pituitary gland or lower cerebral appendage) is a small gland of internal secretion located in the brain, which coordinates the work of the entire endocrine system in the body. It is performed by the pituitary gland due to the development of its own hormones. Its weight is about 0.5 g.
Changing the functional state affects the parameters of its weight and dimensions. They increase during pregnancy and childbirth in women, and the gland as a result remains more developed than in men.
Contents
- Anatomico-physiological properties of the pituitary gland
- Cystic neoplasm of the pituitary gland
- Pocket cuff Ratke - occurrence and development of
- Causes and symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment of the disease, prognosis for recovery
- Possible complications and their prevention
Anatomico-physiological properties of the pituitarygland
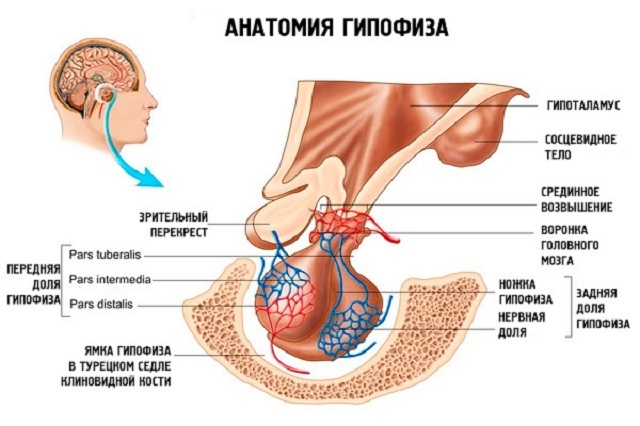
The lower cerebral appendage has an oval or rounded shape. The gland is located at the base of the brain in the Turkish saddle of the sphenoid bone of the skull, produces hormones involved in the metabolic and reproductive processes responsible for the growth and physical development of the body.
The body of the pituitary gland of the brain has two parts and the middle part. They are different in origin, development, structure, functionally. Each of them has its own blood supply, not associated with another lobe.
Anterior part - adenohypophysis several times more massive than the posterior one. It is inserted in utero from the ectoderm. It functions in conjunction with the hypothalamus, which is carried through the leg of the pituitary gland. Posterior part - the neurohypophysis and the leg of the gland are formed later from the protrusion of the wall of the third ventricle.
The majority of hormones are produced by adenohypophysis:
- , the aseptic substances regulate the thyroid gland to synthesize its own hormones;
- adrenocorticotropic substance regulates the production of hormones by the adrenal glands;
- gonadotropic hormones coordinate the reproductive capacity of the body;
- Growth Hormone - Growth hormone promotes protein formation in cells that provides physical development and growth of the body;
- Prolactin stimulates lactation in women during the period of feeding, prevents pregnancy at this time;
- lipidrops of the middle part are involved in the processing of fats in the human body, intermediates are responsible for skin pigmentation from ultraviolet rays, lipotropes for memory function.
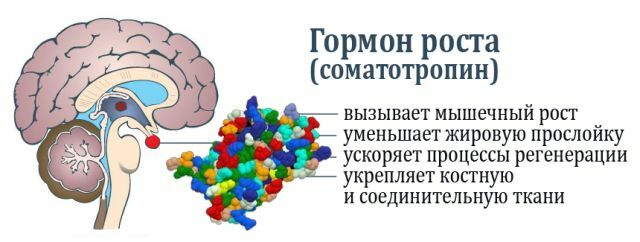
Neurohypophysis, producing hypothalamic hormones, produces:
- Oxytocin , which provides for a multiple increase in the contractility of the uterus musculature in labor, it is also important to participate in the lactation process.
- Vasopressin controls the reabsorption of purified fluid in the kidneys after blood filtration. This prevents dehydration, leading to serious consequences. The normal activity of all systems in the body depends to some extent on the availability of the necessary amount of this hormone.
Violation of the production of pituitary hormones provokes the development of many pathologies, one of which is the cyst.
Cystic neoplasm of the pituitary gland
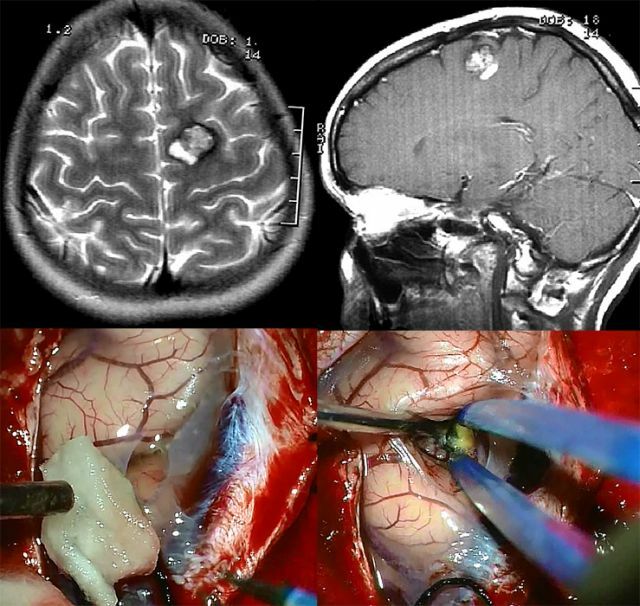
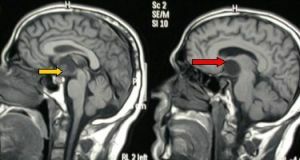
The pituitary cyst is a benign tumor of the brain. This is a small enclosed cavity with liquid contents. Most often, they are detected with an MRI scan of the brain for other reasons. But the glands are always under the close attention of doctors, since the largest number of cysts develops in their tissues. They can be congenital or acquired during life.
Less than 10% of these neoplasms pose a threat to human health. They expand, they press on the pituitary gland and nearby tissues.
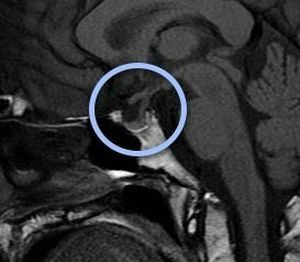
Cyst of pituitary gland on MRI
It is especially dangerous at the same time to increase the production of hormones by the gland, which leads to malfunctions in the work of all organs and systems in the body and the development of pathologies. The remaining cysts exist without manifestations and do not affect the functioning of the body, but require constant monitoring.
The reasons for their appearance in most cases are difficult to determine or impossible. Symptoms of the disease also do not always manifest the same, they are usually individual and not pronounced. In many respects, the symptoms of the pituitary cyst of the brain depend on its location and size.
The disease can occur at any age. More often occurs in women than in men.
The cyst of the Ratke pocket is the emergence and development of
. Among benign neoplasias, the cyst of the Ratke pocket is distinguished, with features in its origin, development and treatment.
This is an epithelial neoplasm whose cavity is expelled by a serous or mucoid epithelium that produces liquid contents filling the cyst. Sometimes in its liquid part, peeled epithelial cells are found. They can be round or oval in shape, not more than 2 cm.
 Ratke pocket is of embryonic origin, as it is formed in the process of bookmarking and development of the pituitary in utero. It is located between the anterior and posterior lobes of the gland.
Ratke pocket is of embryonic origin, as it is formed in the process of bookmarking and development of the pituitary in utero. It is located between the anterior and posterior lobes of the gland.
By the time the baby is born, the pituitary gland is completing its formation, and the pocket is overgrown with the glandular tissue of the pituitary gland. In some cases, there is a gap or individual elements of the pocket, from which the cysts develop. That is, a child is born with a benign tumor.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The risk factors for the appearance and development of the cyst of the pocket of Ratke include:
- genetic predisposition;
- viral diseases of a pregnant woman;
- inflammatory diseases during pregnancy;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- hypoxia of the fetal brain;
- radiation exposure of a pregnant woman;
- heavy delivery.
Symptoms of the disease appear only after the cyst of the pituitary gland of the brain begins to grow, develop and exert a pathological effect on the work of other organs and systems. This can happen under certain conditions.
They can be - older age, craniocerebral trauma, neuroinfections, cerebral circulation, heredity, occupational activity associated with poisonous substances, irradiation.
An enlarged cyst, first of all, begins to exert pressure on the pituitary gland, the vessels of the brain and to the right and left optic nerve at the point of their crossing at the base of the skull.
In this regard, there is a violation of cerebral circulation and cerebral functions, a violation of the cerebrospinal fluid movement through the cerebrospinal fluid, hypofunction of the pituitary gland grows. They are manifested by such symptoms:
- severe headaches, dizziness;
- impaired vision, sleep;
- development of ataxia( impaired movement and coordination);

- increased intracranial pressure;
- attacks of nausea, vomiting;
- disorders of the psyche, consciousness;
- syncope;
- epileptic syndrome;
- violation of manual( shallow) motor skills;
- development of endocrine diseases.
With the increase of the cyst, the manifestations of the disease are increasing.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis begins with testing the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands on hormones, ophthalmological examination by a specialist. The condition of the cyst is assessed using MRI without contrast agent and with it.
CT determines the state of the skull's skeletal structure, reveals craniopharyngiomas. In addition, angiography of cerebral vessels, encephalography, and dopplerography is performed.
It is possible to study the tumor for good quality by biopsy.
Treatment of a disease, prognosis for recovery
If the cyst does not grow, the patient is observed and periodically inspected. With a slight increase in the tumor, individual hormone therapy is selected. More often it is used after a significant increase in the cyst and the presence of neurologic symptoms.
Several methods of surgical treatment of the pituitary cyst of the brain are also used:
- excision of education using classic surgery under anesthesia;
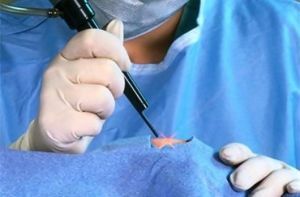
- application of transsphenoidal microscopic operation ( with the use of a microscope) for partial removal of neoplasm;
- endoscopic removal of tumor provides visual control and reduces risks, provides the ability to remove the entire cyst.
After removal of the cyst, especially partial, radiotherapy and antitumor antibiotics( Blenamax, Bleomycin) are prescribed.
An insignificant number of relapses of the disease have been registered after surgical treatment. Timely diagnosis and treatment gives good results. With late detection of the disease, irreversible complications, such as loss of vision, can occur.
Possible complications and their prevention
Compression of adjacent tissues and vessels, a growing cyst, leads to severe complications:
hydrocephalus of the brain;
- intracranial pressure disorder;
- complete loss of vision;
- hemorrhage in the cyst;
- development of pituitary adenoma;
- degeneration into malignant neoplasm.
 To prevent severe consequences of the pituitary cyst, it is necessary to monitor any changes in the hormonal background. Protect the head from mechanical influences and injuries. At least once a year to be examined by a neurologist.
To prevent severe consequences of the pituitary cyst, it is necessary to monitor any changes in the hormonal background. Protect the head from mechanical influences and injuries. At least once a year to be examined by a neurologist.
Exclude professional activity with poisonous substances and under irradiation conditions. It is necessary to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol. Exclude large physical exertion.
Revise food, use more foods with a low carbohydrate content. Thus, it is possible to maintain the health and normal functioning of the brain.