1 The essence of the problem
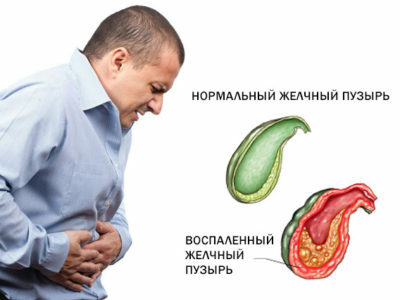
Cholecystitis is a lesion of the gallbladder of an inflammatory type. As is known, this organ plays an important role in the process of digestion, regulating the flow of bile. As a result of the influence of various internal and external factors, the outflow of bile from the gallbladder is disturbed, which leads to its accumulation in the cavity of the organ. As a result of an anomaly with excretion of bile, an inflammatory reaction develops, which is manifested by pain and other signs.
Recommended to consult
- Diet for pancreatitis and cholecystitis
- Hepatic colic
- Treatment of pancreatitis and cholecystitis
- Effective agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer
In general, cholecystitis can develop in any person at different ages. However, women are much more likely to be affected, especially during pregnancy, and also because of hormonal failures. Most often the development of cholecystitis is accompanied by inflammation of the bile ducts - cholangitis.
Pathology can occur in acute and chronic forms. The acute variety, when the signs of cholecystitis have a pronounced character, develops violently against the background of blockage of the ducts and a sharp increase in the volume of the gallbladder. The chronic form, as a rule, is due to the chronicization of acute cholecystitis in the absence of effective treatment. It proceeds in a slow mode - exacerbations alternate with a period of remission.
Given the etiology of cholecystitis, two of its forms are distinguished: calculous and non-calculous varieties. The first form is due to the development of cholelithiasis, and the second is not related to the presence of stones. Both varieties can be both acute and chronic.
2 Etiology of the disease
Several major mechanisms are distinguished in the etiology of cholecystitis. Non-calculous variety is often engendered by various infections: intestinal, typhoid and paratyphoid sticks;streptococci, staphylococci and enterococci. In this case, infection of the gallbladder can occur in several ways:
- Enterogenic, an ascending path from the intestine: the main cause is a violation of the closure function of the sphincter of Oddi, which regulates the lumen of the common bile duct.
- Hematogenous path: penetration of infection from distant foci( tonsils, dental caries, etc.) with blood flow in the barrier dysfunction of the liver elements.
- Lymphatic pathway: infection is caused by the lymphatic flow.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
Infection can not lead to rapid development of the disease. So, after a cure for typhoid fever, it may take several years to develop the pathology. In order to create a pathogenic microflora in the cavity of the gallbladder, you need a fundamental factor - stasis of bile. Most often, stagnant phenomena occur in cholelithiasis, when stones can clog the ducts or cause spasms. Even the movement of stones can damage the mucous membrane, which creates conditions for the introduction of infection.
In addition to the calculous factor, bile congestion occurs for a number of other reasons: compression and inflection of the ducts;dyskinesia of the bladder and ducts under stress;omission of internal organs;starvation, including the observance of a "hungry diet";chronic constipation;hypotension of a way of life;pregnancy in women.
A significant role in the etiology of cholecystitis is played by some diseases. Especially distinguished pathology of the gastrointestinal system, in particular, gastric Achilles. Low acidity of gastric juice increases the infection on the ascending path. Contribute to diseases of enteritis and colitis. Barrier liver functions may be compromised in hepatitis. There is a role in the etiological mechanism of pathogenic microorganisms( lamblia, ascarids) as a result of their injury to the shell. The trigger mechanism is capable of reflux pancreatic juice. Cholecystitis can become a complication of diabetes mellitus.
-
 Gastroenterologist important: "I beg you, if you started to bother abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, gas is not in any way do not make. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist important: "I beg you, if you started to bother abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, gas is not in any way do not make. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
3 Symptomatic manifestations of the disease
By the nature of the course of the inflammatory reaction the disease is divided into the following types: catarrhal, purulent, gangrenous, phlegmonous cholecystitis and a mixed form of reaction. Gangrenous and phlegmonous types combine into one category - destructive cholecystitis. Depending on the type of disease, the symptoms of cholecystitis also differ, and the doctor must clearly differentiate the varieties for successful treatment.
The first symptoms of pathology are associated with the manifestation of pain. The disease begins with a pain syndrome in the side to the right, slightly below the ribs, with pains that are harsh and unexpected. The first pains usually pass quickly enough( spontaneously or after taking pain medications), but then they arise again, with renewed vigor, and become a frequent guest. Increased pain syndrome is accompanied by fever, nausea and vomiting. Significantly deteriorating the general condition of a person, which is associated with a general intoxication of the body.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;

With the development of the disease, the pains become regular( almost constant) and acquire a noisy character. Most characteristic is their appearance and enhancement 1-2 hours after eating, especially when consuming fatty or fried foods. Such pains spread from the right hypochondrium upwards - right up to the right shoulder, neck, scapula, and are given in the left hypochondrium. In the presence of stones, characteristic gallstone stones develop.
In addition to the pain syndrome, dyspeptic symptoms are noted: the taste of bitterness and metal in the mouth;air belching;bloating;alternation of constipation and diarrhea. In addition, there are often signs of a neurogenic nature. The symptoms of jaundice are very rare and are associated with complications that spread to the liver.
Severely destructive cholecystitis with pronounced general intoxication during exacerbation proceeds. Observed are the following symptoms: chills, febrile condition, general weakness, severe pain in the area of the gall bladder, increased liver size, anemia.
WE RECOMMEND!
For prevention and treatment of Digestive Diseases our readers advise Monastic tea. This unique remedy consists of 9 medicinal herbs useful for digestion, which not only supplement, but also strengthen each other's actions. Monastic tea will not only eliminate all symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system, but will also permanently eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
Opinion of doctors. .. »

4 Chronic development of pathology
In general, the course of chronic cholecystitis occurs in a slow mode, with alternating exacerbations and soothing. Given the frequency of exacerbations, the chronic variety is conditionally divided into latent and recurrent forms. In a mild form, the exacerbation is observed no more than 2 times a year with a duration of up to 20 days. They are caused by a violation of the diet and physical overexertion.
The pathology of moderate severity proceeds with exacerbation 5-6 times a year, and a small pain syndrome is felt even in the period between exacerbations. In the acute phase, there are signs: dyspeptic symptoms, icteric manifestations, subfebrile temperature, a large risk of complications in the form of hepatitis, cholangitis. In severe form, exacerbations can occur up to 2 times a month with biliary colic and frequent complications.

In addition to typical manifestations, chronic cholecystitis can have atypical forms of manifestation. Among them, the following varieties can be distinguished:
- Cardial type. This cholecystitis is characterized by transient disturbances of the heart rhythm, and the physician should clearly differentiate it, distinguishing it from coronary insufficiency.
- Arthritic type. The main manifestations of the disease are complemented by concomitant arthralgia, as well as clinical signs of infectious-allergic polyarthritis.
- Subfebrile variant. This form of pathology is characterized by a long( up to 20 days) period of having a subfebrile temperature within 37.5-38 degrees. The doctor, as a rule, notes the general intoxication of the body and chills.
- Neurasthenic variety: described by signs of neurasthenia and damage to the vegetative-vascular system: weakness, irritability, sleep disturbance, hypochondria, carcinophobia.
- Hypothalamic form. The doctor may note the presence of a characteristic tremor: high blood pressure, symptoms of angina and muscle weakness.
5 Possible complications of
If a person does not cure the disease, cholecystitis can go into a severe chronic form fraught with serious complications. The most characteristic complications are hepatitis and cholangitis. Since most often before the confluence of the duodenum is the union of the biliary and pancreatic ducts, one should expect a frequent complication in the direction of the development of pancreatitis.

Acute attack of cholecystitis in the absence of measures can cause the following complications: purulent or diffuse peritonitis;rupture of the gallbladder wall;acute form of pancreatitis;mechanical jaundice. Purulent cholecystitis can develop in the following direction: the formation of the empyema of the gallbladder, the perforation of the walls with the development of peritonitis, the entry of pus into the blood and sepsis.
6 Therapeutic measures
The doctor treats cholecystitis taking into account the type of disease, its etiology and the nature of the manifestation, the individual characteristics of the organism.

Treatment is necessarily based on an integrated approach, with exacerbation recommended bed rest.
The most important element of treatment is dietary nutrition. The main method of treatment - a conservative method with the appointment of medications and physiotherapy procedures. Surgical intervention is performed when it is necessary to remove stones and obvious complications in the form of peritonitis, acute biliary obstruction, etc.
Treatment begins with the organization of dietary nutrition. The drinking regime is provided by warm liquids in the volume of up to 1.5 liters per day. The food is often taken( up to 6 times), but in small portions. Such products are eliminated from the diet: canned food, marinades, smoking, salting, fatty foods, products with astringent character, products that can induce indigestion( dairy products, legumes, drinks with gas), products that change the pH of the environment( alcoholic beverages, sorrel,spinach, citrus fruit).Recommended for use: low-fat products of animal origin after grinding and steaming;products of plant life without coarse fiber, but containing vitamins and essential trace elements.
Drug therapy is based on the appointment of such groups of drugs:
- antibiotics: appointed after determining the specific causative agent of infectious disease and are designed to eliminate the inflammatory reaction;
- antispasmodics: to eliminate spasms of ducts and ensure the patency of the small intestine;
- cholagogue preparations: choleretics such as Allahol, Cholenzym, Dehnolin, Holigol, as well as herbal products;cholekinetics such as cholecystokinin, sulphurous magnesia, sorbitol, magnet-xylitol;
- hepatoprotectors: for normalization of hepatic function.
Cholecystitis is considered quite a dangerous disease that can not be started. Treatment of the disease in severe form is accompanied by great difficulties and may require surgical intervention. At the first manifestations of pathology, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
- 1 The essence of the problem
- 2 Etiology of the disease
- 3 Symptomatic manifestations of the disease
- 4 Chronic development of the pathology
- 5 Possible complications
- 6 Therapeutic measures
Cholecystitis is a fairly common pathology of the gallbladder, which can bring a lot of trouble. If in the initial stage the patient has a good chance of a full recovery, then in a neglected state, treatment is much more difficult, and pathology can cause serious complications. All questions related to cholecystitis are resolved by a gastroenterologist. It is the doctor of this specialty who diagnoses the disease, conducts its differentiation from other diseases and develops a treatment regimen.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method is to write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;