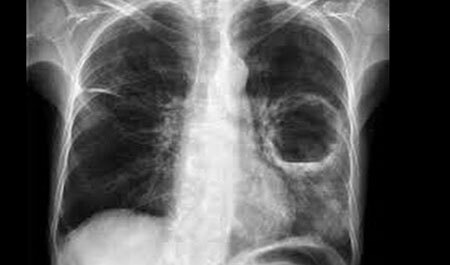
What is it? Atelectasis is a condition of the lung that develops in the absence of air in the lung tissue. Usually the air presses against the walls of the pulmonary vesicles, causing them to acquire a filled form resembling a bunch of grapes.
If there is no air, the lung is "blown off", it loses its fullness and volume. However, if a surfactant is present, the pulmonary alveoli do not stick together. But, in the absence of this substance, there is a collapse and clumping of the pulmonary vesicles - this is called lung atelectasis.
Content
- 1 symptoms of atelectasis by type
- 1.1 obstructive atelectasis
- 1.2 compression atelectasis
- 1.3 Distenzionny atelectasis
- 1.4 Mixed atelectasis
- 2 Diagnostics atelectasis
- 3 Treatment of atelectasis
symptoms of atelectasis by type
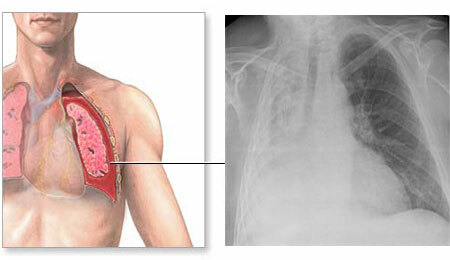
Atelectasis is divided into two fundamentally different groups, depending on thewhether the lungs breathed before it developed or not. If there was no respiratory activity in the lungs - atelectasis would be primary or congenital, if the lungs worked - secondary, or acquired.
Primary atelectasis only develops in newborns. The causes of its occurrence lie in the underdevelopment of pulmonary tissue, in swallowing meconium and amniotic fluid, which after birth interfere with the filling of the lungs with air and their physiological opening, as well as as a result of the depression of the respiratory center during birth traumas of the head.
In some cases, hereditary deficiency of the surfactant can be observed.
Congenital atelectasis can be focal and extensive. In the first case, there is shortness of breath, cyanosis of the skin around the mouth( nasolabial triangle), if the area of the lesion is small, there are no symptoms. Extensive primary atelectasis manifested by severe shortness of breath, a change in the color of the skin, can lead to the development of pneumonia in the child, often results in the death of the newborn.
Especially dangerous aspiration pneumonia against the background of ingress of meconium( first-born feces) into the lungs. This leads to aggressive inflammation, which provokes the development of acute respiratory failure leading to death.
Atelectasis in newborns will be considered secondary if lung decay occurs after initial normal filling with air. The type of secondary atelectasis depends on the prevalence of the process.
The largest is total atelectasis. Then, in decreasing the area of the lesion, the atelectasis of the lung lobe, segmental and lobular atelectasis, occurs. The smallest in size is the discoid lung atelectasis. It practically does not manifest itself with clinical manifestations.
The mechanism of development acquired atelectasis is divided into 4 types.
Obturation atelectasis
Obtuse atelectasis is associated with the occurrence of an obstruction to the flow of air within the lungs, which can be located at different levels. The deeper and closer to the alveoli the block is located, the smaller the area of the lung will be deprived of air, respectively, the less symptomatic will be expressed.
The causes that cover the lumen of the bronchi are:
- Foreign body;
- Mucous plug;
- Very dense phlegm;
- Tumor inside the bronchus. The most common cause is bronchogenic lung cancer;
- Bronchus compression from the outside with a tumor, scar tissue, enlarged lymph node with metastasis of malignant neoplasms.
With obstructive atelectasis, symptoms may be absent or develop gradually. Usually dyspnea appears and builds up, which is supplemented by a dry cough, persistent and not bringing relief. Breathing makes breathing difficult.
On the "problem" side: the thorax decreases in volume, the intercostal spaces are narrowed, the shoulder is lowered, the spine is shifted to a healthy side. Skin covers are cyanotic. A frequent complication of obturation atelectasis is pneumonia.
The development of pneumonia with atelectasis is due to the fact that an increased negative pressure is created on the side of the lesion, which leads to a violation of lymph and blood circulation;there is a "stretching" of fluid, blood cells, mucus into the lumen of airless bronchi.
In such conditions, microorganisms easily penetrate into the lung tissue, leading to infection. Against this background, the development of the edema of the lungs and the subsequent acute hypoxia of the organism is possible.
Compression atelectasis
Compression atelectasis occurs if a pathological "volume" appears in the pleural cavity, which begins to gradually squeeze the lung tissue. Acceleration of the severity of the primary process leads to an increase in the volume of the squeezing factor and the appearance of atelectasis symptoms.
The factors that put pressure on the lungs from the inside are:
- A large amount of inflammatory fluid, which is a consequence of pleurisy - the inflammation of the lung membranes against pneumonia, tuberculosis, systemic diseases( SLE, rheumatism) and other processes;
- Gidorothax - fluid accumulation around the lungs with poor heart function, when blood stagnation occurs in the pulmonary veins and the liquid part of the blood begins to seep into the pleural cavity;
- Pneumothorax - air that enters the lung cavity from the inside and from the outside with injuries of the chest;
- Hemotorax - blood in the pleural cavity with massive bleeding associated with trauma;
- A large tumor originating from the lungs or bronchi.
Symptoms of compression atelectasis appear against the background of the underlying disease and increase gradually. The main specific clinical signs are shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, both on inhalation and exhalation, cough, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the affected half of the chest.
With compression atelectasis, signs of cyanosis( cyanosis) of the lips and skin are noted. On the side of the development of lung recession, the thorax is enlarged, there is a bulging of the tissues in the intercostal spaces, a noticeable lag of this half when breathing.
Compression atelectasis from obturation is characterized by the character of dyspnea. In the first case, it is mixed, i.e.as indicated above, it is difficult to inhale and exhale. In the second case, it is of an expiratory nature, i.e.it is difficult to exhale only because of the existing obstacle.
Distent atelectasis
Distential atelectasis refers to a functional type that reduces the filling of lungs with air on inspiration due to the limitation of the volume of respiratory movements and spasm of the bronchi.
Occurs because of the limited mechanics of respiratory movements:
- Patients on prolonged bed rest in lower lobes of the lungs;
- When a person deliberately does not take a deep breath because of pain in the chest or abdomen;
- When breathing is impeded by the accumulation of air or fluid in the abdominal cavity( ie, is a consequence of flatulence, ascites);
- Decreased elasticity of bronchi and muscle tone in myasthenia gravis.
Also, atelectasis can occur with the inhibition of the respiratory center of the brain, which leads to a weakening of the respiration and reflex spasm of the bronchi:
- after anesthesia;
- for barbiturate poisoning;
- with stroke - such atelectasis is called spastic, or contractile.
Symptoms of this type of pathology are often absent, due to its small size. With multiple foci may manifest as mild dyspnoea and dry cough. The thorax is not asymmetric, its value, as a rule, is not changed.
When listening to the lungs at a deep entrance you can hear the wheezing that is associated with the opening of the asleep areas of the lungs. Unlike pneumonia, these rales are unstable and disappear after several respiratory movements.
Mixed atelectasis
Mixed atelectasis occurs when two or three types of secondary atelectasis are combined. This is observed when there is an abscess of the lungs, a focus of inflammation in pneumonia, a cavity in tuberculosis.
These states have a less favorable forecast than all the others.
Diagnosis of atelectasis
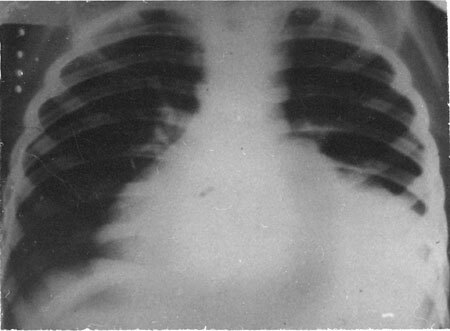
In addition to questioning and objective examination, including percussion and auscultation of the chest, X-ray examination is carried out in two positions of the body( in 2 projections).This is the main method for detecting lung atelectasis.
X-ray images show the following signs indicating a decrease in lung tissue:
- Homogeneous darkening in the affected area. The size of the shadow depends on the type of atelectasis: a large obscuration is revealed in the lobar, in the segmental region, in the form of a wedge or a triangle located at the apex of the lung root, lobular atelectasis is multiple and similar to focal pneumonia. Distential atelectasis is located low, near the diaphragm, has small dimensions and the shape of transverse bands or dark discs.
- Displacement of organs: with compression atelectasis, the displacement is observed in the healthy side, since the pressure on the side of the lesion is greater, with the obturative one, on the contrary - the displacement will be towards the atelectasis, as the attracting negative pressure builds up on the side of the lesion.
- Raise the dome of the diaphragm - this is evident from the location of the liver.
In addition to all of the above, fluoroscopy, that is, a study "live", allows you to see where the organs move depending on the phase of breathing, coughing. This is an additional sign of atelectasis, helping to identify the type of disease.
A preliminary, radiologic diagnosis is the "right-side syndrome", in which the area of the middle lobe of the right lung is obscured.
The frequent occurrence of atelectasis of the right lung is associated with the anatomical features of the right mid-lobe bronchus: it is narrow and long, so it often overlaps with a pathological process.
If the diagnosis is not clear, an X-ray examination is supplemented with a CT scan. When the lumen of the lumen is closed, bronchoscopy is performed - examination along the bronchi by means of a probe with a chamber, which is injected into the respiratory tract.
During the investigation, the cause of the block and the level of its location are detected.
Prolonged atelectasis requires contrast study methods: bronchography and angiopulmonography. The study provides information on the depth of lesions of the left and right lung, reveals the deformation of the bronchi, and also assesses the course of the vessels.
A study of the gas composition of blood reveals a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen to a large extent. This diagnostic test determines the degree of acute respiratory failure leading to total hypoxia.
Treatment of atelectasis
 Treatment of atelectasis in newborns is to purify the respiratory tract by sucking the contents through a catheter, in severe cases, carry out artificial ventilation and pulmonary spreading. When immature lungs are prescribed measures that improve the maturation of the surfactant.
Treatment of atelectasis in newborns is to purify the respiratory tract by sucking the contents through a catheter, in severe cases, carry out artificial ventilation and pulmonary spreading. When immature lungs are prescribed measures that improve the maturation of the surfactant.
First of all, this is the introduction of drugs based on this substance. It is important to take into account that with meconial aspiration immediately remove the original feces from the respiratory tract by means of an electric suction that creates a negative pressure.
The elimination of secondary atelectasis is combined with the treatment of the underlying disease.
- In the treatment of obturation atelectasis, bronchoscopy is performed: a foreign body, a viscous secret, is extracted from the bronchi.
- Atelectasis caused by a tumor is eliminated after surgical treatment of the underlying disease, i.e.surgical intervention, chemotherapy and radiation can be performed.
- Compression atelectasis requires an urgent thoracocentesis - puncturing a special tissue needle in the intercostal space with subsequent removal of air or fluid from the pleural cavity. This eliminates the mechanical compression of the lung tissue.
In the event of postoperative forms of the disease, chest massage is performed by tapping, inhalation with bronchodilators( substances that expand the bronchi), exercise therapy. Important early activation of the patient, if it is a long time in a horizontal position, for example, with a fracture of the femur.
Surgical treatment of atelectasis is indicated with prolonged, chronic lung sagging, which can not be spread by conventional methods. In the operation, the affected part of the lung is removed.
Any kind of this pathology requires the appointment of anti-inflammatory therapy, and when joining the infection - antibiotics.