1 Anatomy of the esophagus
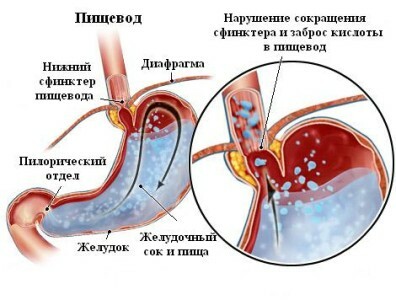
The anatomical structure of the esophagus is due to its function - to serve as an intermediate stage for transporting a comatose coma from the oral cavity to the stomach. The esophagus is an organ consisting of the following tissues:
- Muscular tissue. In the proximal part of the esophagus to the arch of the aorta - transversely striated, in the distal - smooth. Muscular tissue has two layers, the outer has a longitudinal arrangement, and the inner one - circular. The outer layer provides expansion, and the inner layer constricts the esophagus. Thus, peristalsis ensures the progression of a coma.
- Connective tissue, mucosa, submucosa. The mucous membrane lining the esophagus over its entire surface, directly over the mucosa occurs food slipping. The submucosa contains lymphatic and blood vessels, secretion glands and nerve endings. Nervous tissue is represented by vagus nerves.
Recommended to read
- What is DDD
- Signs of bowel cancer
- Radiography of the esophagus
- Effective agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer
Each component of this well-organized anatomical structure under certain conditions can create difficulties for the advancement of a coma. Especially often, problems arise where there are bends and natural anatomical narrowing of the esophagus. How is the tube designed to promote food?
- It is about 25 cm long, starts from the pharynx, ends with the stomach.
- Has 2 sphincters( muscle rings), which can be narrowed by the work of nerve endings. Sphincters are located at the beginning and end of the esophagus. The superior sphincter is formed by the circular muscles, the lower sphincter is longitudinal.
- In a relaxed state, the surface has a relief. When swallowed volumetric food coma, it is smoothed to ensure advancement.
Rapid and painless swallowing is provided by perfectly coordinated operation of all esophagus systems. If this coordination is not fully implemented, it is difficult or impossible to swallow.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
2 Manifestation of narrowing
Regardless of the cause, stenosis of the esophagus leads to the same complaints in patients. How does stricture manifest itself?
Dysphagia. Disturbance of the swallowing function manifests itself more or less intensively, depending on the degree of narrowing of the esophagus. At 3-4 degrees the patient can eat exclusively semi-liquid and liquid dishes, at 1-2 degrees, consumption of soft or semi-solid food is possible. Even 1 degree of stricture does not allow full use of large pieces of hard, solid or dry food.
Odynophagia. Painful sensations during swallowing are localized in the area behind the sternum, but pain can be given to the pharynx, the lower jaw, the left or right part of the chest, under the left or right scapula. Such a spread of pain is due to the proximity of the vagus nerves.
Eating, nausea and vomiting after eating. The stricture of the esophagus leads to the inability to safely deliver the food coma from the pharynx to the stomach. Without getting into the stomach, the food moves upwards due to the reflex reduction of the musculature. As a result, there is a feeling of nausea, and in more serious stages - a full vomiting of all eaten food volume. Mechanical damage to the neoplasm or mucous membrane leads to bleeding, so vomit can contain blood.
-
 Gastroenterologist. VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gas in any way. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gas in any way. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
All this set of symptoms does not have a good appetite for the victim. The stricture of the esophagus, the symptoms of which lead to a restriction of food intake, in most cases is accompanied by weight loss. Even if the patient absorbs food, despite the pain, eructations and vomiting, some of the nutrients are not absorbed because it does not stay in the body. Compliance with diet and proper treatment of esophageal stenosis helps to improve the situation.
So any stricture of the esophagus manifests itself. Private complaints will vary depending on the cause of the violation.
3 Reasons for stenosis
Congenital stenosis is caused by pathologies of intrauterine development. The following causes lead to acquired stenosis:
- Chemical or thermal burn of soft tissues. If only the upper layers of the mucosa are burned, healing without scars and scars is possible. If as a result of exposure to high temperatures and corrosive liquids the submucosal or even layers of muscle tissue have suffered, the healing proceeds with scarring. Chemical burns often occur when attempting suicide by poisoning, for example, acetic acid, gasoline, chlorinated water. Every suicide should think about the fact that a burn of the esophagus often leads not to death, but to prolonged torment and the inability to eat normally.
- Cicatricial stenosis occurs and for another reason - cutting or piercing the esophagus when swallowing sharp piercing-cutting objects. Wounds in the chest and neck can cause cicatrical stricture of the esophagus. This problem is more relevant for children than for adults. The impact of needles, glass, nails, bones and toys with hard edges leads to damage to the surface or deep tissues. The stronger this damage, the greater the scar.
- One option of a chemically aggressive liquid is gastric juice. The peptic form of stenosis is expressed in the inflammation of the mucosa as a result of regular reflux of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus and pharynx. Weakness of the lower sphincter and spasm of the stomach muscles in the complex give such a picture. Gastroesophageal disease and ulcerative esophagitis lead to pathological changes in the mucosa at the cellular level and repeatedly increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Benign tumors. The degree of narrowing of the esophagus is determined by the size of the neoplasm. A tumor is called benign if it consists of esophagus tissues without degeneration.
- Malignant tumors consisting of a different type of tissue. Esophageal cancer most often develops with the participation of a traumatic factor, the effects of gastric juice or chemically aggressive vapors or fluids.
- Ulcers, swelling and diverticula. Diverticulum is a protrusion of the wall into the lumen of the esophagus, it has a rounded shape.
- Spasm of the muscles of the esophagus. It can be caused by infections, diseases of the nervous system and brain, burns or mucous trauma. With spasm, swallowing is either difficult or completely impossible.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;

Stricture is amenable to elimination by various means, depending on the prerequisites for the appearance of a pathological condition. Folk remedies narrow the esophagus is not treated;The earlier the patient applies for qualified medical care, the more favorable the forecast will be. Especially dangerous is the treatment of folk remedies for esophageal cancer. The loss of precious time can cost the patient life.
4 Methods of treatment
If you have pain and discomfort when swallowing you need to undergo a checkup with a gastroenterologist. What procedures does the doctor prescribe to clarify the cause of the disease?
- general blood tests, urine tests;
- biochemical blood test;
- fecal occult blood test;
- transesophageal ultrasound;
- radiography or computed tomography;
- manometry of the coordination of peristalsis of the esophagus and contractile activity of the musculature;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- study of acidity of gastric juice.
After these examinations, the causes of the stricture of the esophagus become clear. Treatment can be prompt or conservative. Benign tumors should be removed with a gastroscope. The seized material is sent for histological examination to the laboratory for precise determination of the cellular composition. When malignant tumors are detected, removal of the entire esophagus is performed, in its place a part of the intestine is transplanted. If surgery is not possible or as an additional measure to combat metastases, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed. With cicatricial stenosis, the lumen of the esophagus is restored by balloon dilatation or by the method of drilling, surgical parting of the walls under the control of esophagoscopy. With muscle spasms, sedatives may be sufficient, and with reflux of gastric juice and bowel diseases, normalization of acidity and restoration of the lower sphincter are required. The choice of drugs and treatment methods is completely dependent on the disorder that led to stricture.
5 Diet
With any esophageal stricture, a diet is required. Food should be divided, portions - small, and meals - frequent. Anything that can make swallowing difficult and cause choking is excluded. The temperature of the food is moderately warm, the consistency is soft, semi-liquid or liquid. Despite all the restrictions, the food should be high-grade, and optionally supplemented with vitamins and minerals.
- 1 Esophageal device
- 2 Manifestation of constriction
- 3 Reasons for stenosis
- 4 Treatment methods
- 5 Diet
Esophageal stenosis can be congenital or acquired by nature of origin. There are 4 degrees:
- The first degree, in the narrowest place the diameter of the esophagus is 9-11 mm;
- Second degree, the diameter of the bottleneck is 6-8 mm;
- Third degree, diameter 3-5 mm;
- Fourth, the heaviest degree of narrowing of the esophagus, the diameter of the lumen - 1-2 mm.
The narrower the clearance, the heavier the person is given food intake. The term "stricture" refers to the organic or functional narrowing of the esophagus.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
The organic narrowing includes changes in the muscular, epithelial and mucosal tissues( tumors, scars, diverticula), to the functional - the spasms of the muscles surrounding the esophagus.