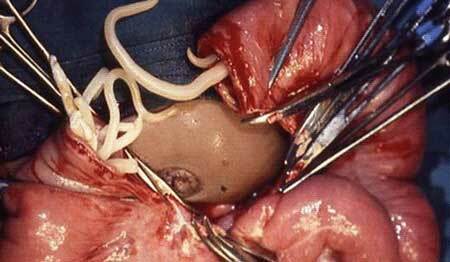
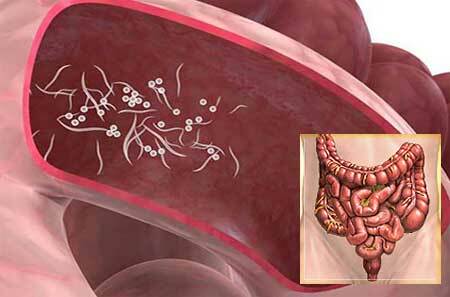
What is it? Echinococcosis is an infectious disease that occurs when the larvae of the ribbon echinococcus worm are parasitized in humans.
The helminth itself lives and multiplies in the body of carnivores. Most often they are infected with dogs and wild dogs - wolves, jackals, foxes. Rarely sick cats. Therefore, owners of pets should be very careful to avoid infection.
When the eggs are ripe, they are isolated with feces out. In this case, they can get on the animal's fur, in the ground, water, plants.
Infection occurs when a mature egg is introduced into the mouth through the hands, contaminated after "communicating" with the animal. Also, the probability of invasion persists due to the ingress of "infected" herbs, forest berries, water( if these factors are used for food consumption).
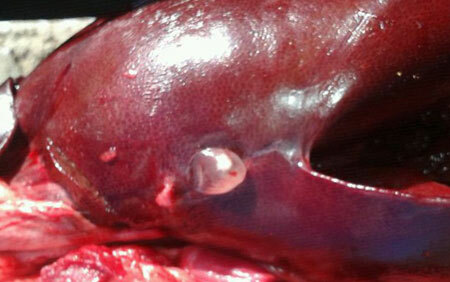
Echinococcosis in the liver
In addition to humans, sheep, cows and goats can be infected through grass on the pasture. This path is more rare, but it is not worth forgetting about it.
Human and herbivores are intermediate hosts in which the larva develops. The further chain of infection is built only with the death of the intermediate host and the eating of its remains infected with larvae. This is done by dogs or wild animals.
Thus, a person becomes a dead-end way for the further development of echinococcus. However, this leads to serious complications developing in the body.
Professions that are dangerous in terms of infection with echinococcus are associated with livestock and hunting. Thus, a high risk of echinococcosis in shepherds, hunters, workers of slaughterhouses, leather workers, as well as members of their families. Therefore, among these populations, vaccination is widespread. Its effectiveness has been proven in a series of clinical studies that were originally conducted on sheep.
Contents
- 1 Symptoms of echinococcosis
- 2 Diagnosis
- 3 Treatment of liver echinococcosis
- 4 Complications of echinococcosis
- 5 Prevention of echinococcosis
Symptoms of echinococcosis
After entering the digestive tract, eggs enter the blood through enterocytes( intestinal cells).With the current of blood, they can enter into any organ, but in 75% of cases oncospheres of echinococcus enter the liver. It is hepatic localization that determines the specificity of the clinical picture for this disease.
The second organ for the frequency of invasion is the lungs - in 20% of cases. Rarely occurs seeding of the brain, spleen, bones, heart, pancreas, approximately in 1-3% of cases.
The minimum frequency of echinococcus parasitism in these organs is associated with a high frequency of diagnostic errors. For its reduction to zero, it is very important to find out the person's contacts with potential sources of infection.
Over time, a specific echinococcal cyst is formed and grows inside the affected organ, initially not having a strong effect on the body. As it grows, there is a squeezing effect on the affected organ, and if the walls are damaged and the fluid is released, an allergic reaction occurs.
Thus, the symptoms of echinococcosis, on the one hand, are composed of signs of mechanical compression and associated atrophy, and on the other - allergic action of the parasite.
With echinococcosis, a person's symptoms may appear several years after infection, as the cyst grows slowly. This is also due to the fact that the parasite uses adaptive mechanisms to not be detected by the immune system.
So, the larva develops a number of substances that depress the work of human immunity, and is protected by the incorporation into its shell of the protein structures of the host, as a result of which the immune cells perceive it as their own and do not attack. This causes a prolonged persistence of echinococcus in the body.
In case of liver echinococcosis , the signs are common, nonspecific. Patients noted weakness, the appearance of increased fatigue, dyspepsia, that is, nausea, indigestion, eructation, heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
Headaches may occur, as well as allergic skin rash and itching. The growing cyst slowly begins to squeeze the liver tissue, which leads to a gradual disruption of its normal structure and functioning: first there is a degeneration of the cells, that is a violation in them of a normal metabolism, and then atrophy - complete withering away.
Atrophy of a part of the hepatic tissue adversely affects the overall functionality of the entire organ, which is especially noticeable with increasing liver load, for example, poisoning, the intake of large amounts of alcohol. Thus, chronic liver failure is formed.
Squeezing of the bile ducts leads to the appearance of pain in the right hypochondrium, such as colic, nausea, and discolored stool. These all signs are united in the concept of intrahepatic cholestasis. One of its bright signs is intense and painful itching of the skin.
It is caused by the accumulation in the dermis of bile acids, which are a strong irritant for sensitive nerve endings.
Echinococcosis of the lungs manifests itself depending on the location of the cyst, its size and growth rate. If the cyst is located closer to the ribs, then, even if its small size, it will show itself early enough, as it will constantly press on the shell of the lungs - the pleura, and lead to painful sensations.
When the parasite is closer to the bronchi, a persistent dry cough, shortness of breath, pain in breathing, and blood in the sputum may appear. When the pulmonary tissue is compressed, chronic respiratory failure gradually increases. Clinically, this is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Increased respiratory rate;
- Feeling of air shortage;
- Cyanosis of the nose, nasolabial triangle, fingertips, etc.(acrocyanosis);
- Increased fatigue with normal physical activity;
- Involvement of auxiliary muscles in the act of breathing, etc.
Echinococcosis of the brain also manifests itself as the cyst grows. At the onset of symptoms may not be, but with the development of a squeezing effect on brain tissue, the symptoms may resemble manifestations of volumetric processes - tumors.
There is a persistent headache, which is difficult or impossible to eliminate with usual analgesics. There is an increase in intracranial pressure, dizziness may develop, epileptic seizures.
If the cyst of the brain parts responsible for movement is damaged, motor disruptions occur in the limbs, on the side opposite to the location of the parasite.
However, unlike tumors and stroke in cerebral echinococcosis, serological tests to identify this pathogen are positive. In addition, conservative antiparasitic treatment is effective and leads to a regression of clinical symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic search for suspected echinococcosis has several purposes:
- Identification of indirect signs of the presence of parasites in the body;
- Direct identification of the pathogen;
- Determination of the degree of damage to target organs, i.e.degree of their insufficiency.
Therefore, all patients who are expected to have echinococcosis are prescribed the following studies that detect characteristic abnormalities:
- A blood test reveals a high level of eosinophils;
- Immunological methods consist in the detection of specific antibodies in the blood serum. For this purpose, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent reaction or an indirect hemagglutination reaction is performed. At the beginning of the disease, the result may be negative. As the cyst grows, these tests reveal liver echinococcosis in 90% of cases, lung echinococcosis in 60%;
- Biochemical blood test to determine the level of metabolites formed or destroyed in the liver( this analysis allows you to determine the degree of liver failure);
- Liver ultrasound is a very effective method of detecting hepatic echinococcus;
- Radiography of the lungs reveals a parasitic cyst;
- CT, MRI allow you to determine the prevalence of the process and the nature of any organ.
Often, echinococcosis is detected accidentally with ultrasound of the liver, preventive fluorography, as well as some other infections with helminths. This is due to the presence of a phase of asymptomatic disease.
Treatment of liver echinococcosis
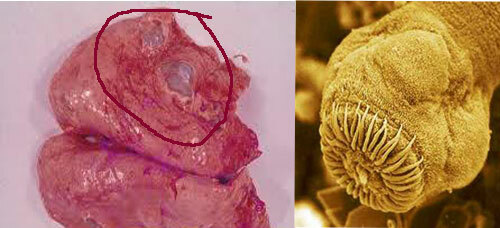
The main method for late detection is surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is urgently performed to remove superficial cysts, with a high probability of rupture when organs and ducts are squeezed, large and infected neoplasms are present.
In the case of the appearance of jaundice symptoms in echinococcosis, treatment also consists in the urgent operation with simultaneous administration of symptomatic therapy. With multiple cysts, the operation is carried out in several stages. Difficult, small cysts, as well as die-off formations subject to calcification, do not operate.
Drug treatment may complement surgical, and may be independent, if surgery is not possible. When echinococcosis treatment with albendazole is prescribed for 1-1,5 years, courses for 28 days with interruptions for 2 weeks.
During treatment every 5-7 days, a blood test( general clinical and biochemical) should be performed, as the drug is toxic and can cause a decrease in leukocytes and toxic hepatitis.
Conservative therapy of echinococcosis is a rather complex task, requiring an individual approach.
Complications of echinococcosis
Often only the development of complications can lead to the diagnosis of echinococcosis - these conditions dramatically change the general condition of a person and force an urgent call for a doctor.
The severity and nature of the negative consequences of the presence of echinococcus in the body can be different. To the greatest extent, it depends on the localization of the cyst.
1. Complications in the liver cyst are as follows:
Larvae death and suppuration of the echinococcal cyst. In this case, there is general weakness, intoxication, fever, pain in the liver.
Cyst rupture due to stroke, fall, lifting of gravity, too active palpation. Characterized by the appearance of severe pain, then there may be a severe allergic reaction - anaphylactic shock.
The danger of rupture of the cyst is also the mass distribution of larvae along the body, as a result, multiple foci in other organs can form.
Manifestation of complication occurs 1-2 years after cyst rupture. Damage to the festering cyst is dangerous for the development of peritonitis.
Squeezing the bile ducts leads to inflammation of the bile ducts - cholangitis, manifested by fever, pain in the hypochondrium, then jaundice develops. Often the end of echinococcosis of the liver can be cirrhosis and amyloidosis( deposition of "harmful" amyloid protein in organs).
Squeezing the portal vein with a large cyst leads to an increase in pressure in the system of vein portal hypertension. It is manifested by the widening of the veins on the anterior wall of the abdomen, weakness and increased risk of bleeding from the esophagus, which can lead to death.
2. The cyst is located in the lungs of the - around it there is an expansion and deformation of the bronchi, septa appear, and pulmonary hemorrhage may occur. There is also a real possibility of developing acute cardiovascular insufficiency.
With the rupture of the cyst located closer to the ribs, there is the development of acute pleurisy, in severe cases anaphylactic shock develops - a deadly allergic reaction.
Breakthrough cyst in the large bronchi leads to a sharp appearance of a strong cough up to choking, allergic reaction. In the future, aspiration pneumonia may develop.
3. Growth of cysts in the bone tissue of results in the gradual destruction of bones and pathological fractures.
4. A small size cyst in the heart muscle of can lead to cardiac weakness, and its breakthrough into the pericardial cavity is the cause of sudden death.
The negative effect of echinococcosis is the rapid, rapid course of the disease. This occurs in people with weakened immunity, when a person is already infected with a serious illness, in pregnant women, as well as those who became infected when they visited an unsuccessful echinococcosis area, not being a native.
Prevention of echinococcosis
The main measures to prevent infection are to wash hands after "communicating" with dogs. Also, when keeping dogs, an important preventive measure is the annual conduct of de-worming with special veterinary drugs. Prevent echinococcosis drugs: Milbimax, Dirofen, Helminthal, Kanikvantel, etc.
People from risk groups need to carefully observe hygiene measures after work, hiking in the forest, hunting. When collecting berries in the forest before consumption, they must be washed.
In regions with a high incidence of echinococcosis, planned prophylactic medical examination is carried out. In addition, not only the nonspecific prevention mentioned above, but also the specific one, has been widespread recently. It involves the introduction of a vaccine against echinococcosis in risk groups.