Hypothyroidism in newborns is one of the varieties of thyroid pathologies. The main danger lies in its influence on the mental and physical development of the child, so it is very important to know which babies are at risk, as well as the main symptoms of the disease.

What is it?
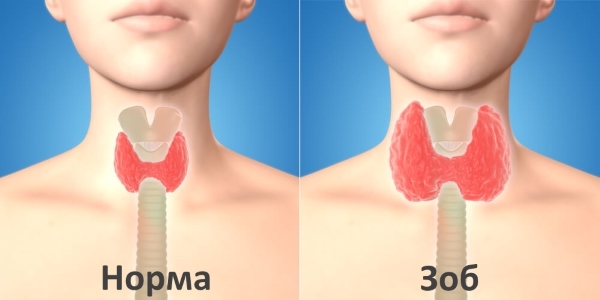
Congenital hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the functions of the thyroid gland decrease. The statistics says that for every 5,000 children, one or two children are born with this pathology. Accordingly, this disease is difficult to attribute to frequent, but to know about it follows every mother. Predominantly susceptible to the diagnosis of a girl, although boys can be sick with it.
The thyroid gland is of great importance in the work of the whole organism, even if newly born. It is responsible for control and temperature exchange, regulation of fat, protein and carbohydrate balance, calcium metabolism and, most importantly, participates in the formation of intelligence.
When a newborn is diagnosed with hypothyroidism, the level of hormones decreases sharply, resulting in the thyroid gland not working at its fullest, leading to unpleasant consequences.
Causes of
 Various causes can contribute to the onset of the disease, as well as their combination. Among them are the following:
Various causes can contribute to the onset of the disease, as well as their combination. Among them are the following:
- Heredity. Often the kid faces the disease precisely because of the genetics - some genetic mutations affect the development of the disease, disrupting the thyroid gland activity even at the stage of intrauterine development.
- Hormonal disorders of - in this case the sensitivity of the cells of the gland to iodine decreases, or iodine metabolism is disturbed.
- Disturbance of the hypothalamus is an important center of the nervous system responsible for the thyroid gland functioning, with any deviations and lesions affecting the endocrine system, disrupting its functioning.
- The decrease in sensitivity to thyroid hormones - similar is observed after taking pregnant antithyroid drugs. This need arises with a disease of the future mother with certain diagnoses, for example, goiter.
- Iodine deficiency in a pregnant - this is usually the case for women living in large industrial cities. If the gynecologist has prescribed additional use of iodine for prophylactic purposes, it means that there are reasons for this and one should not ignore the doctor's recommendations.
Thus, absolutely healthy parents, in whose family there were no problems with endocrinology, and during pregnancy, who did not encounter violations, most likely, will bring up a healthy baby. However, it is worth remembering that this pathology is acquired - that is, the born baby will be healthy, and in a few years he will have signs of the disease.
Symptoms
 The presence of pathology, as a rule, is reported even in the hospital, since its signs are quite pronounced. These include:
The presence of pathology, as a rule, is reported even in the hospital, since its signs are quite pronounced. These include:
- large weight of the child at birth - 4 kg or more, in some cases 3.5 kg or more;
- excessively swollen face and head;
- mouth almost all the time ajar;
- in the supraclavicular fossa there are pronounced edema resembling pads;
- is a jaundice of newborns, not passing even after procedures under the lamps and increasing the intake of water and liquid by a toddler;
- observed cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- baby's crying unnaturally coarse for a baby.
If in the first days the child's condition is good, the above signs are not observed, you should carefully consider the first months of life. The disease is not for nothing called insidious, because it is not always manifested in the first days of life. Symptoms to look out for when the baby is 3-4 months old:
- decreased appetite or complete lack of interest in food and fluid, including breast milk;
- weakly expressed sucking reflex;
- umbilical hernia( not in all cases);
- edges of the eyelids seem unnaturally thick;
- a long healing of the umbilical cord or a later fall of the umbilical cord;
- lack of necessary reflexes;
- fatigue, constant whims;
- the child is always cold;
- lag in growth, weight and from the norms of the volume of the head;
- weak pulse;
- reduced pressure;
- constipation and frequent bloating;
- dry skin, peeling;
- pallor of the skin;
- obesity;
- increased face, tongue;
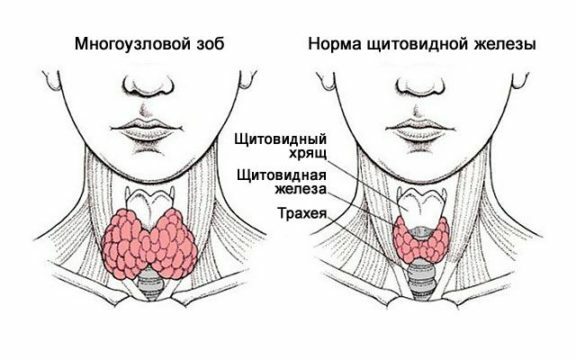
- goiter is a disease of the thyroid gland.
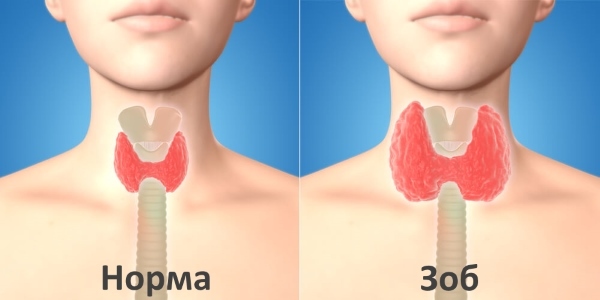
Since the causes of the pathology are different, and the complications lead to serious disorders, the disease is tried, as early as possible, to reveal the appropriate therapy. For this reason, in the maternity hospital and conduct a screening, on the basis of which they make a diagnosis or reject it. Sometimes transient hypothyroidism occurs in newborns, but, as a rule, this is a temporary phenomenon, and it passes by itself, without requiring treatment after eliminating the cause of its occurrence.
Treatment of
Once diagnosed, symptoms are evaluated and an assessment of the patient's condition is made, treatment is started. It consists of hormone replacement therapy. The thyroid gland is designed in such a way that if it ceases to produce the necessary hormones, in most cases it is not possible to resume the natural process. Therefore, only the use of hormonal drugs in a dosage prescribed by a doctor can help a newborn.
Treatment is carried out throughout the life span - maintenance therapy requires constant monitoring, otherwise at any time another disruption in the endocrine system and the body as a whole can occur. In this case, the correctly calculated dosage of drugs will allow the child to calmly develop and learn on an equal footing with peers, to keep up with studies and to be physically fit and strong.
It is necessary to pay attention to the immune system of children with hypothyroidism - because of the constant use of drugs, the body becomes easily susceptible to viral diseases. In the ARVI season, antiviral drugs should be used in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician.

A therapeutic diet is of great importance for patients with hypothyroidism, which is also observed throughout life. Firstly, light carbohydrates are completely excluded from the daily diet - all kinds of buns, cakes, refined flakes, pads, etc.
Foods high in fat( butter, animal fat, pork, fatty fish, etc.), tooare inadmissible. Also, the sick should not abuse salt and consume large amounts of water.
Small patients should undergo annual checkups from an endocrinologist and take tests for hormones. Often, when after the therapy and proper application of the diet, the child's hormones reach the desired level. Doctors in this case reduce the dosage of hormone replacement drugs, and sometimes temporarily exclude, in parallel monitoring the patient. However, even in the case of a prolonged absence of treatment and well-being, it is still necessary to regularly monitor the blood counts and the state of the baby, since at any time the situation can return to its origin.
Summing up
The causes of hypothyroidism are clear, it's also hard not to notice the signs, and this is a big plus - the sooner doctors diagnose and start treatment, the less the child will suffer. The disease is not fatal, taking control of its development and dynamics, you can perfectly live your whole life, almost without infringing yourself in anything. Much more dangerous procrastination and carelessness - the baby will live, but it will be difficult to develop and learn.
If at least several of the signs are found in the baby, it is necessary to consult the endocrinologist and take the appropriate examination. In the future, and in adult children, hypothyroidism can be observed, it is already acquired disease that occurs in most cases due to a lack of iodine intake.