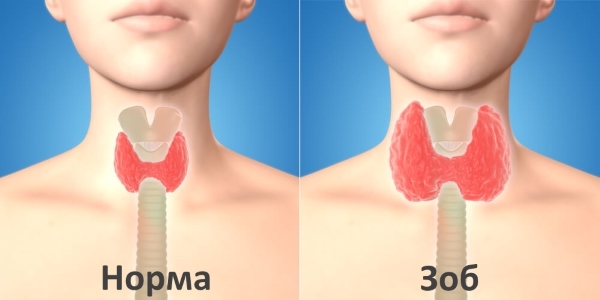
Multi-nodular goiter is more common among endocrine diseases today. According to statistics over the past decade, the prevalence of this disease is approaching diabetes mellitus. Consider the reasons for the appearance, symptoms and treatment of multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland.
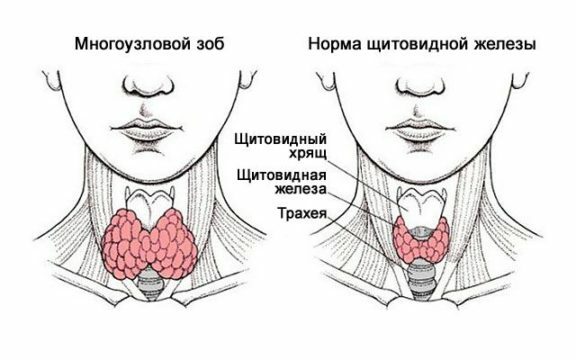
Description of the disease
A multinodal goiter is called a pathology of the thyroid gland, in which increased pathological areas on the surface of the body are formed, not exceeding 10 mm in size.
The nature of the nodes can be different. They can be cystic, colloidal, follicular - these are the most common, although there are more rare types of nodal formations. Sometimes several species occur simultaneously.
Depending on what changes in the gland's body caused the formed nodes, distinguish three types of multinodular goiter:
- Diffuse - uniform proliferation of gland tissues throughout its area, which indicates a reduced activity of the body in terms of hormone secretion.
- Nodal - uneven organ enlargement, which indicates that the thyroid gland works excessively, secreting an excessively high amount of hormones.
- Mixed type is less common and is called endemic goiter in clinical practice. In this case, the gland's body is enlarged unevenly, but there is a certain uniformity in some of its areas.
If ultrasound diagnostics detects more than two nodes with a fixed diameter of more than one centimeter, endocrinologists often recommend puncture of the gland.
But there are practically no reasons for panic: 95% of the detected nodes are benign in nature, and benign nodes point only to euthyroid goiter.
It should be understood that the development of malignant and benign neoplasms varies considerably in their mechanisms. If we talk about the formation of malignant nodes, they appear because of the abnormally rapid division of cells with a damaged genetic code. Such formations do not replace the existing cells of the gland, but grow between them.
This disease occurs in almost a sixth of the population of Russia, moreover, women suffer from multinodular goitre four times more often than men. The average age range of patients with identified goiter is between 45-55 years.
Regardless of the fact that the disease is not considered life threatening, the consequences of ignoring multinodal goiter treatment can be dangerous, since the lack of adequate therapy can lead to the degeneration of some types of nodes into malignant ones.
Symptomatology
For a long time, the goiter of this etiology can not manifest itself at all: the thyroid function remains normal, the patient does not feel any discomfort and any pronounced clinical picture. Visually detect nodes can be when one or several of them in total reach two centimeters in diameter.
Often, the disease is detected during an ultrasound examination as part of planned inspections. If you leave the problem without attention, there is a risk of developing hyperthyroidism.
The clinical picture resembles a picture of toxic goiter with the only exception that nontoxic goiter does not show ophthalmopathy and myxedema.

Patients complain of sweating, emotional instability, decreased performance, especially in the warm season, increased heart rate, especially noticeable symptoms in patients with hypertension.
To non-specific symptoms are:
- Stitching pains of medium intensity in the heart, shoulder blades;
- Increased appetite, and, with the development of complications, the appetite increases against a background of weight loss;
- Thirst;
- Stomach upset;
- Tremor of limbs;
- Anxiety at night;
- Decreased libido.
It should be noted that these symptoms are accompanied by other endocrine diseases, for example, sugar and diabetes insipidus, because the symptomatology is nonspecific.
Sometimes the organ is sufficiently enlarged in size to visually or palpate the conclusion about the presence of nodes. The thyroid gland can squeeze nearby organs, and a person's voice changes, there are difficulties with breathing, a feeling of compression in the neck when lying down.

It is possible to detect the nodes independently, since in a healthy state of iron it is elastic and homogeneous. Dense sites with palpation suggest that it is possible to form nodes, and, when swallowed, their mobility is felt.
Degrees of disease
When a multinodal goiter is detected, treatment is prescribed only after the stage of the disease is discovered. When the clinical picture is expressed, three main degrees of goiter are distinguished:
- Goiter of 1st degree - it is difficult to determine visually and palpation, palpation detection at this stage is almost impossible. To diagnose the disease, you need laboratory and ultrasound diagnostics.
- Second degree - with palpation the doctor discovers a slight increase in the gland in the volume, visually the same changes during the 1 and 2 degrees are not noted.
- The third degree is a proliferation of organ tissue, in which an increase in its volume is noticeable not only on palpation, but also visually.
Non-toxic goiter can occur in several ways. Sometimes it does not provoke visible enlargement of the gland, and sometimes the organ increases so that it comes to the sternum and is visually distinct.
Causes of the disease

It is finally to say what exactly provokes the development of goiter, doctors can not yet. But there are certain risk factors that are likely to lead to the development of the disease. Among these factors, in the first place, there is a lack of iodine in the body. Other provoking factors:
- Pathologies in the CNS;
- Liver diseases;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Psychological shocks;
- Climate change, adaptation of the organism;
- Decreased immunity;
- Inflammatory processes in the organ;
- Infectious Diseases;
- Long-term use of interferon preparations;
- Violation of food culture;
- Genetic factor.
Rational therapy will depend on the cause of the disease. The lack of iodine provokes a decrease in the secretory function of the gland. The pituitary body receives a signal about the lack of hormones and provokes the gland by producing a thyroid-stimulating hormone. As a result, the iron increases in volume.
Treatment of
Endocrinologists tend to believe that not all forms of multinodular goiter need to be treated. Sometimes a doctor can recommend constant monitoring. With properly selected therapy, the patient can live with the disease for dozens of years and the proliferation of nodes will not occur, accordingly, there will be no need for surgical intervention.
Levothyroxine therapy is prescribed for patients with hypothyroidism - a deficiency of thyroid hormones in the blood. Dosage is established depending on the level of TSH.Stifle goiter is usually observed after 5-7 months from the start of therapy.
Thyreostatics is prescribed with excess gland function to suppress its secretory activity. Also prescribe drugs that contain iodine to slow the synthesis of TSH.It slows down and reduces the development of goiter.
Radioactive iodine - iodine 131 isotope is injected into the gland to destroy the cells of the formed node. This procedure affects the node pointwise, leaving the surrounding tissues intact.
The selection of the technique is carried out only after full-fledged laboratory diagnostics, ultrasound examination and the collection of anamnesis. With the correct selection of therapy, the prognosis of the disease is only positive.