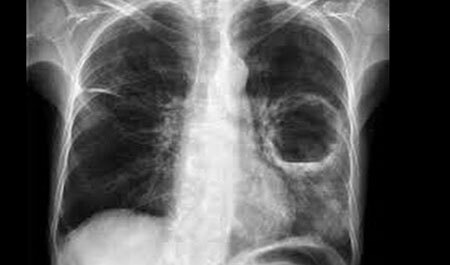
Prolonged pulmonary and bronchial diseases lead to the formation of connective tissue scars. The same changes occur when inhaled dust and toxic substances, congestive pneumonia and heart failure.
This causes sclerosis of the lung tissue and the occurrence of a number of chronic diseases.
Contents of
- 1 Pneumosclerosis of the lungs: what is it?
- 2 Causes of pneumosclerosis of the lungs
- 3 Symptoms of pneumosclerosis of the lung
- 4 Diagnosis of the disease
- 5 Treatment of pneumosclerosis of the lung
- 5.1 Folk methods of treatment
- 6 Consequences and complications
- 7 ICD code 10
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs: what is it?
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs is a pathological process of replacement of normal connective lung tissue.
In this case, respiratory function is impaired, the size of the respiratory surface decreases. The disease occurs at any age, men get sick more often.
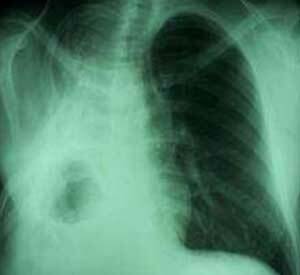
Pneumosclerosis of light photo X-ray
Pneumosclerosis of the lung is classified according to several signs.
In terms of prevalence, the following are isolated:
- Fibrosis. In this case, pulmonary and connective tissue are present simultaneously.
- Sclerosis. Pulmonary tissue passes into the connective tissue.
- Cirrhosis. The heaviest stage, the pleura, vessels are condensed, the respiratory process is disrupted.
This disease is also divided according to the site of the lesion:
- Apical pneumosclerosis - connective tissue grows on the upper part of the organ.
- Basal pneumosclerosis - in this case, tissue proliferation occurs in the basal part of the lung.
- Basal pneumosclerosis - lung tissue is replaced by a connective in the basal parts of the organ.
In addition, there are two degrees of spread of the disease - focal and diffuse .
If the disease spreads to both organs, then we can say that it is diffuse pneumosclerosis of the lungs. As a rule, with this form can occur cystic formations, lung tissue receives less nutrition, and the lungs decrease in size.
Causes of pneumosclerosis of the lungs
This disease in most cases develops as a result of lung diseases or complications after them.
Common causes:
- Infection in which pulmonary tissue, tuberculosis become inflamed;
- Chronic bronchitis and inflammation;
- Long stay in rooms with polluted air, for example, at work;
- Inflammations caused by various allergens;
- Beck's lung disease;
- Pulmonary Injury;
- Heredity.
The frequent cause of the development of such a disease are not completely cured inflammatory processes in the lungs: bronchitis, pneumonia.
Symptoms of pneumosclerosis of the lungs
The clinic depends on the form: diffuse or focal. The latter is characterized by mild dyspnea and a satisfactory condition.
For diffuse pneumosclerosis the following symptoms are typical:
- Shortness of breath. In the diffuse form, it does not appear immediately, at the initial stage it happens only with physical exertion. When the disease progresses, dyspnea is present even in a state of rest.
- Cough, very strong, with excretions similar to phlegm with an admixture of pus.
- Constant weakness, fatigue, head may be dizzy.
- In the chest, constant pain.
- Skin becomes cyanotic.
- A person can lose weight, while not changing their diet.
- The chest is gradually deformed, and the phalanges of the fingers thicken at the ends and become like drumsticks.
- Pulmonary insufficiency.
The presence of bronchiectasis is accompanied by hemoptysis and purulent sputum. Fibrous changes in lung tissue are manifested by superficial, rapid breathing, high diaphragm standing( due to a decrease in lung size), and deformation of the bronchial tree.
Progression of the disease leads to stagnation in the lungs and expansion of the right heart. The development of heart failure is manifested by increased edema and dyspnea.
If the symptoms are not much and are expressed blurred, then we can talk about the mild form of pneumosclerosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
This disease is diagnosed with an X-ray. It clearly shows changes in the tissues of the organ. In the initial stages, changes are visible only in one area.
Functional pulmonary tests are satisfactory, but with diffuse pneumosclerosis, they deviate significantly from the norm and can not be treated therapeutically.
In obstructive type( emphysema, chronic bronchitis) - air conduction is violated, which leads to hypoxemia( decrease of oxygen saturation).
Restructive type( lung reduction) - leads to a decrease in the vital capacity of the lung, conductivity is disturbed insignificantly.
Pulmonologists for diagnosis use external examination of the patient, bronchoscopy, bronchography. If necessary, appoint an MRI.
Treatment of pneumosclerosis of the lung
 Diseases are handled by a physician pulmonologist or therapist. The methods of treatment used depend on the stage of the disease.
Diseases are handled by a physician pulmonologist or therapist. The methods of treatment used depend on the stage of the disease.
There is no specific treatment, the therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause that triggered the development of the disease. With a light form, the main rule is caution and support of the body, to exclude the occurrence of inflammatory foci.
Treatment of diffuse pneumosclerosis includes the following items:
- Antimicrobial medication;
- Bronchodilators and medications with expectorant properties are prescribed;
- Doctors can drain bronchial tubes;
- Cardiac preparations are also used to prevent myocarditis symptoms.
If there is no pulmonary insufficiency, a specialist can prescribe special physiotherapy procedures. In particularly difficult cases, surgical intervention may be required.
Traditional methods of treatment
In unopened cases, use traditional medicine. As a rule, most of them are used to treat bronchitis. Here are some recipes:
- In a thermos you need to brew 1 tablespoon of sowing oats half a liter of boiling water. Leave for the night, drain in the morning and drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Well-washed dried fruits should be soaked overnight. They need to be eaten on an empty stomach in the morning. Due to its diuretic and laxative properties such a tool helps to clear the lungs of stagnation.
- There is another wonderful tool - onions. One thing you need to cook and rub it with sugar. Take this mixture you need one tablespoon every two hours.
There are many recipes, but do not abuse self-medication - use folk methods in addition to drug treatment, and only after consultation / appointment of a doctor.
Consequences and complications of
complications
The person, of course, will have a question: what is dangerous for pneumosclerosis of the lungs? If this disease is not treated, then cardiac and pulmonary insufficiency may occur.
In later stages, the lower part of the lung may gradually become like a porous sponge( the so-called honeycomb lung).As a result, there are problems with breathing, and the infection develops again, which leads to deterioration of the human condition.
Life expectancy with pulmonary pneumosclerosis depends on the stage at which the disease is detected, the timeliness of treatment, compliance with all prescriptions of doctors, prevention. If you do not run the disease, then the probability of a favorable outcome is very high.
All pulmonary diseases must be treated on time and completely cured. It is best to apply for this to specialists, and not engage in self-medication.
If the cause of the disease is contaminated air in the work area, consider changing your professional activities.
ICD Code 10
Section( J84) - Other interstitial lung diseases
- ( J84.0) Alveolar and parieto-alveolar disorders;
- ( J84.1) Other interstitial lung diseases with mention of fibrosis;
- ( J84.8) Other specified interstitial pulmonary diseases;
- ( J84.9) Interstitial pulmonary disease, unspecified.