 Brain injury is a kind of craniocerebral trauma, in which focal brain tissue is damaged and necrosis occurs.
Brain injury is a kind of craniocerebral trauma, in which focal brain tissue is damaged and necrosis occurs.
It is accompanied by hemorrhages and the formation of hematomas.
Most often, tissue death due to injury occurs in the following areas of the brain:
- temporal;
- frontal;
- occipital;
- parietal.
Contents of the
- Trauma mechanism and its causes
- Shock VS injury
- Degrees of traumatization and classification
- Diagnosis for suspected trauma
- First aid
- Complex of measures
- Serious impact on all body systems
- Relapse prevention
Trauma mechanism and its causes
Trauma can be obtainedas a result of a stroke, an accident, a fall from a high altitude.
Consider the course of a brain contusion on the examples of the existing classification of any craniocereberal trauma:
- primary damage;
- secondary damage.
In the case of primary damage, the kinesthetic effects of a stroke or concussion come to the fore: the damage to the bones of the skull and brain tissues. Formed so-called.foci of injury characterized by vascular ruptures, axonal injuries,
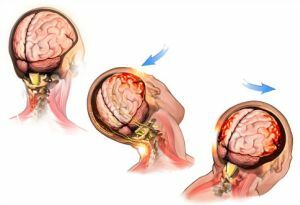 brain stem contusions.
brain stem contusions. There are structural disorders at the micro level: the integrity of neurons, synapses, vessels, cell membranes is affected. As a consequence, a tissue death mechanism is triggered, accompanied by the appearance of edema.
Secondary lesions( ischemia) are a consequence of primary and are expressed in the form of an inflammatory reaction. The process of oxygen supply of the cell, as well as the mechanism of calcium-sodium metabolism in neurons, is disrupted. Cells of the brain are overflowed with calcium, which leads to rupture of their membranes and death.
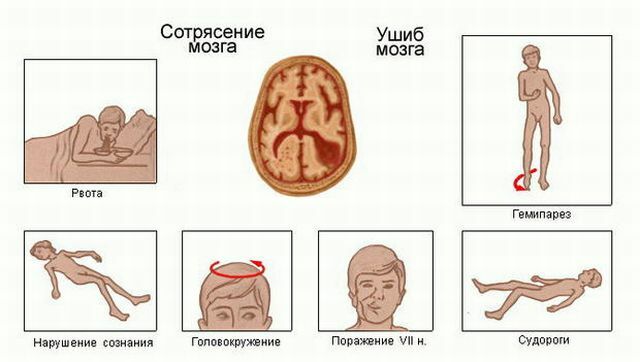
Concussion VS injury
Concussion is always a closed craniocerebral injury, accompanied by mild reversible impairment of consciousness. The bruise of the brain, in contrast to the concussion, is manifested by a prolonged loss of consciousness( up to coma), pronounced symptomatology, serious consequences and difficulties in the restoration of lost abilities, accompanied by fractures of the skull.
Degrees of traumatization and classification of
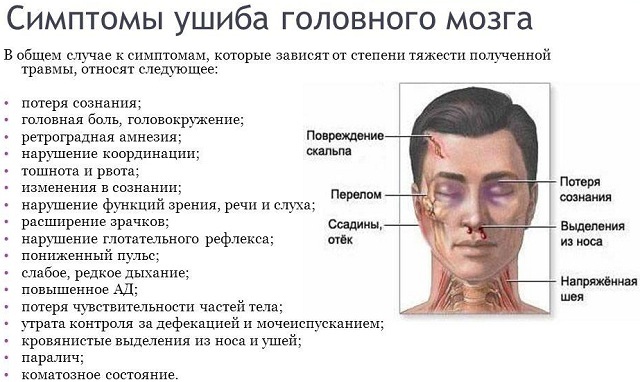
The severity of brain contusions is divided into:
- lungs ( 49% of affected, temporary - 5 to 7 minutes - loss of consciousness with rapid recovery, dizziness, pain, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, subarachnoid hemorrhage,a small area of injury);
- averages ( 33% of the victims, prolonged loss of consciousness, amnesia, severe headache, frequent vomiting, mental disorders, epileptic seizures, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, subarachnoid hemorrhage, affects both the cortex and the white matter of the brain);
- severe ( 18% of affected people, long-term loss of consciousness with coma and coma, coma, excitability, meningeal symptoms, paresis of limbs, neurological disorders, subarachnoid bleeding, brainstem injury, trauma in all departments, including trunk, ICP).
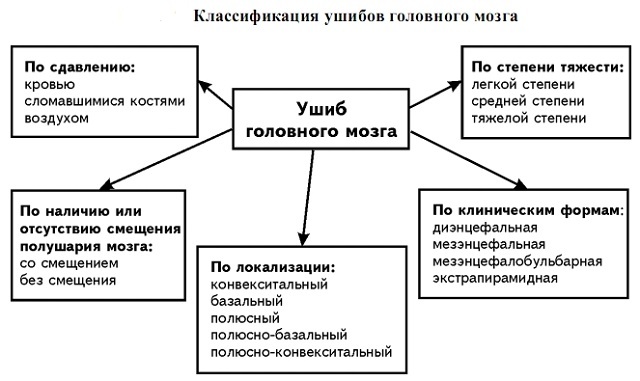
Classification by clinical forms of contusions:
- diencephalic ( trauma of the diencephalic department of the hypothalamic region);
- mesenceptic ( midbrain trauma);
- mesencephalobulbar ( trauma of the medulla oblongata);
- extrapyramidal ( trauma of the subcortical brain structures).
There are types of brain contusions for localization:
- convective;
- basal;
- pole;
- pole-basal;
- pole-convective.
Given the displacement of the hemispheres of the brain, the following differentiation of bruises is distinguished:
- with displacement;
- without bias.
Diagnosis for suspected trauma
In the diagnosis, the specialist pays special attention to the reason for the injury. The patient's behavior, 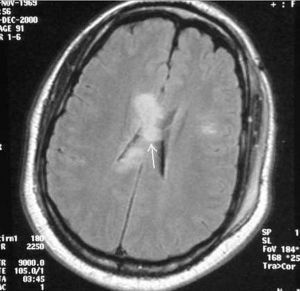 ability to answer questions, ability to perform certain actions, orientation in space, reaction to pain is assessed. To clarify the details, a survey of witnesses, accompanying, relatives of the patient is conducted.
ability to answer questions, ability to perform certain actions, orientation in space, reaction to pain is assessed. To clarify the details, a survey of witnesses, accompanying, relatives of the patient is conducted.
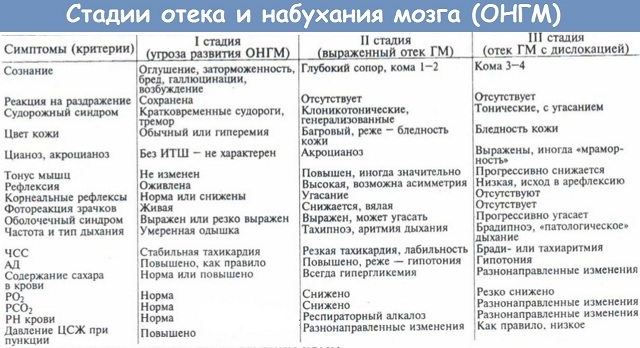
The diagnosis determines the duration of loss of consciousness, the level of wakefulness, the appearance of convulsive syndrome, the behavior of the patient after an injury. The state of consciousness is assessed on the Glasgow scale( 15 points - normal state, 7 and below - severe).
An external inspection is performed. Blood pressure, pulse, and respiration of the patient are measured. There is a neurological anamnesis.
Additional studies based on neuroimaging:
- craniography;
- echoencephaloscopy;
- lumbar puncture;
- angiographic examination;
- MRI;
- CT scan.
First aid
After you have called the doctor, it is necessary to give the victim a horizontal position( preferably on his side, so that the vomit does not enter the respiratory pass).
Place something soft under the patient's head, place it 30-40 ° above the surface, fix in one position. The victim's body should lie on a hard surface.
Remove from a person tight clothes, release his throat, chest, waist. Oxygen should flow freely when breathing. Create for him conditions of complete rest.
Before the arrival of doctors, place a sick ice on your head or a wet towel. Carefully watch for the presence of respiration and pulse in the victim. If necessary, begin an indirect massage of the heart. With cramps, fix the patient's body. Any movement is only in a horizontal position on a stretcher.
Complex of measures
The victim of a brain injury is immediately hospitalized in the intensive care unit. Promptly conducted intensive  pathogenetic therapy. A lumbar puncture is prescribed to clean the CSF.
pathogenetic therapy. A lumbar puncture is prescribed to clean the CSF.
In severe cases, reanimation of the respiratory function of the patient( artificial ventilation of the lungs), maintenance of a normal amount of blood is required. Infusion therapy is performed.
Restoration of a patient after a bruise depends on the severity of the lesion:
- mild degree - 7-10 days;
- medium degree - 3 weeks;
- severe degree - more than a month.
After rendering of the operative help, the patient is transferred on a stationary-rehabilitation mode of treatment.
Pharmacological treatment of brain contusion consists in the admission of the following medicinal groups to the patient:
- nootropics;
- diuretics;
- tranquilizers;
- anticonvulsant;
- is sedative;
- vascular drugs;
- antibiotics;
- reparative drugs.
 In the case of a severe degree of injury, as well as fractures and profuse swelling( diameter more than 4 cm) or crushing of brain areas, surgery is performed( up to 15% of patients are required), focused on working with lesions.
In the case of a severe degree of injury, as well as fractures and profuse swelling( diameter more than 4 cm) or crushing of brain areas, surgery is performed( up to 15% of patients are required), focused on working with lesions.
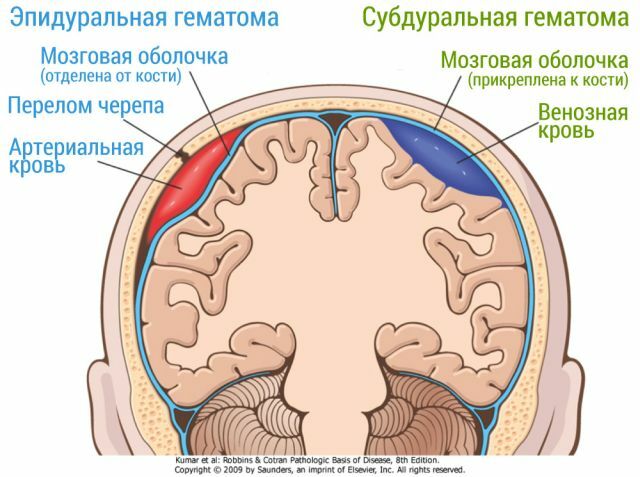
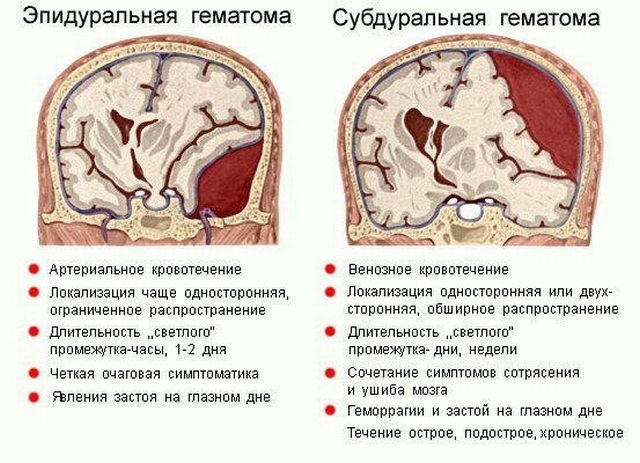
Surgeons remove the hematoma, carry out a number of operations to reduce intracranial pressure. Lethal outcome after surgery is possible in 40% of cases and depends on the degree of wakefulness of the patient.
Serious impact on all body systems
The brain contusion has severe consequences for the victim: from functional and neurological disorders, to confluence with the vegetative state with the syndrome of minimal consciousness. There is a risk of encountering the following violations:
- speech loss;
- hearing loss;
- traffic disturbances.
Brain injury can be a cause and a risk factor for development:
- of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's;
- epileptic seizures;
- ischemia;
- hemorrhage;
- hypertension-dislocation syndrome;
- of the cysts of the brain.
As a rule, after a brain injury( especially severe), the patient is given the status of an invalid.
Prevention of relapse
Prevention in this matter implies a series of measures taken after the injury and medical intervention aimed at strengthening the brain cells and preventing repeated damage and complications.
The entire post-traumatic period( and beyond) the patient is required to monitor and monitor his intracranial pressure. It is important not to allow abundant blood flow to the head. If necessary, take muscle relaxants and sedatives.
The doctor may prescribe additional preventive medicine courses. Neuroprotectors are prescribed to protect and  to strengthen neurons and brain tissue( Erythropoietin, Progesterone, statins, Citicoline).To prevent posttraumatic epileptic processes, specialists prescribe a course of anticonvulsants.
to strengthen neurons and brain tissue( Erythropoietin, Progesterone, statins, Citicoline).To prevent posttraumatic epileptic processes, specialists prescribe a course of anticonvulsants.
In the conditions of modern life rates, development of infrastructure and constant technical progress, craniocerebral traumas in humans have become a common and habitual factor that is increasing day by day. Accidents and incidents in production are at the top of the list of doctors. Often, non-compliance with the rules of technical safety and banal inattention lead to disastrous consequences.
To prevent injury, it is necessary to be vigilant in places of increased danger, to study technical and safety rules when performing work, to observe safety precautions, and to avoid traumatic situations. Working in difficult technical conditions, try to study the problem of craniocerebral injuries and ways of providing first aid in case of bruises of the brain.