 Brain edema is a serious disorder and represents a serious threat to life. Consider this disease in detail.
Brain edema is a serious disorder and represents a serious threat to life. Consider this disease in detail.
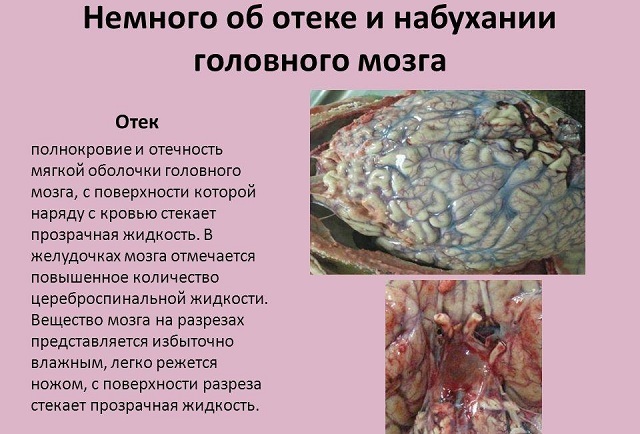
Edema is a pathological process that involves the diffuse impregnation of brain tissue with fluid contained in the vascular space.
The onset of the process is due to the appearance of an irritant, for example infection, intoxication or head trauma. This leads to the formation of excess fluid in the brain cells, resulting in swelling.
If a patient with a brain swelling was not provided with timely medical care, this often leads to severe consequences, often - to death.
This process is a response of the human body to excessive loads, trauma or infectious diseases.
The development of the process takes place quite quickly, excessive fluid accumulates in the cells and in the intercellular space, and the size of the brain begins to increase. This leads to an increase in the rates of intracranial pressure, worsening of blood circulation and death of brain cells.
With the development of this pathological process, it is difficult to make a prediction, it all depends on the timeliness of the provision of medical care. If assistance was provided immediately, this greatly reduces the risk of serious consequences.
Contents
- provocative factors
- provocation First signs
- Clinical features
- First aid for suspected edema
- Diagnosis
- Therapeutic package
- Very dangerous and unpredictable
- Particular attention to infants
- Prevent not to die
Factors provocative
Towards developmentcerebral edema can cause many factors - the most common causes of this condition:
- for infectious diseasesSuch as encephalitis and meningitis;
- due to craniocereberal trauma;
- in pre-insult states and with ischemic stroke;
- during the postoperative period, when brain tissue is damaged during surgery;
- in the presence of brain tumors, regardless of whether they are benign or malignant;
- in the course of intracranial hemorrhages, for example, due to aneurysm rupture;
- as a result of prolonged course of arterial hypertension;
- for epilepsy;
- as a result of severe blood diseases;
- as a result of toxic lesions of brain tissues during alcoholism and drug addiction.
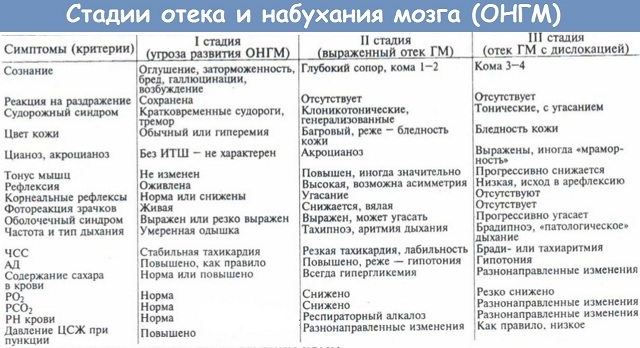
First signs of
The development of cerebral edema occurs in stages, at the beginning of this process you can observe the following symptoms:
- raspiruyuschie headaches, often accompanied by vomiting;
- appearance of persistent nausea;

- is a manifestation of a stunned or restless state, with often disoriented orientation in space and time;
- drowsiness;
- breathing failure;
- narrowed pupils;
- high blood pressure;
- occurrence of arrhythmia.
As the process progresses, more serious symptoms and disorders appear.
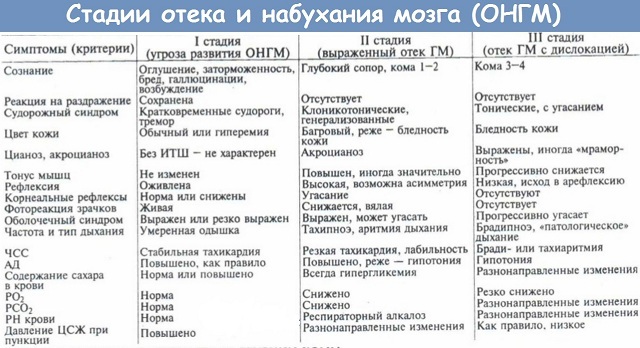
Features of the clinical picture
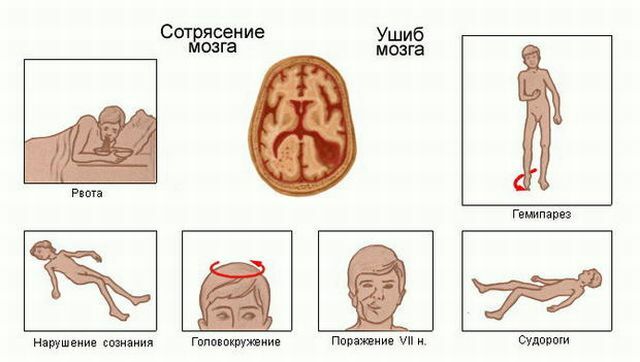
Symptomatology depends on how long the disease lasts and what the localization of lesions of brain structures is. There are three groups of symptoms.
Neurological symptoms caused by edema in the cerebral cortex with penetration into the subcortical region. These include:
- increased intracranial pressure;

- convulsions;
- excited state;
- increased muscle tone;
- appearance of pathological reflexes.
In cases where cerebral edema causes a sharp increase in intracranial pressure, this has the following manifestations:
- occurrence of nausea and vomiting;
- frequent change of the oppressed state to psychomotor agitation;
- headaches;
- disorder of eyeball movements;
- appearance of seizures.
Seizures can occur in the facial muscles and limbs, and may also be longer, which is characterized by an unnatural position of the body.
With progressive edema resulting in the displacement and infringement of the brain structures, the following symptoms appear:
- body temperature increase of 40 and more degrees, which can not be reduced;
- , the pupil's response to light is weak or absent;
- appear unilateral paresis( paralysis) and seizures;
- cardiac rhythm is broken;
- there are no pain and tendon reflexes;
- coma.
If the patient is on artificial ventilation, the frequency and depth of breathing first increase, after which the respiratory and cardiac activities terminate.
First aid for suspected edema
If you develop cerebral edema, timely and correct medical care is important. The patient is to be immediately hospitalized, where he will receive the following first aid measures:
- providing the permeability of the lungs by supplying oxygen through a mask or nasal catheters;
- Administration Mannitol intravenously 3-4 times a day;
- after Mannitol, Furosemide is administered;
- with high rates of intracranial pressure use magnesium sulfate.
In cases where edema is accompanied by convulsions and respiratory failure, it is advisable to use:
- of droperidol;

- Diazepam;
- Sodium oxybate;
- Dexamethasone;
- Phenobarbital;
- Hexenal.
To stimulate the brain, Trental can be administered intravenously, and in 2-3 days Piracetam is administered.
Diagnosis of
Neurologists suspected cerebral edema may cause an ever worsening state of a person, accompanied by impaired consciousness and the presence of meningeal symptoms.
Confirm or disprove the preliminary diagnosis with CT or MRI, as well as by evaluating the neurological status, analyzing the blood and examining and identifying possible causes of the condition.
Due to the fact that edema of the brain is a rapidly developing process, the primary diagnosis should be carried out as soon as possible, while the patient should be better placed in a hospital.
A complex of therapeutic measures
In rare cases, the disease passes for several days, for example, if the edema was caused by a slight concussion of the brain. Other cases require immediate medical attention.
The main goal of the treatment is to normalize the metabolic processes of the brain cells, as a result of which the edema decreases. Treatment consists in combining the medicamental and surgical effects on the problem.
 In such cases, it is necessary to ensure sufficient supply of the brain with oxygen, for this purpose, artificial introduction of oxygen through inhalers or other devices is carried out. The result of these measures is the saturation of blood and brain with oxygen, which contributes to a speedy recovery.
In such cases, it is necessary to ensure sufficient supply of the brain with oxygen, for this purpose, artificial introduction of oxygen through inhalers or other devices is carried out. The result of these measures is the saturation of blood and brain with oxygen, which contributes to a speedy recovery.
In order to maintain indicators of intracranial pressure and fight infections, methods of administering medications through a dropper are used.
If the swelling of the brain is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, it is necessary to take measures to reduce it. This helps reduce edema.
The choice of medications in this case depends on the characteristics of the patient's condition, symptoms and causes of edema.
Especially severe cases require the following measures:
- removal of excess fluid in the ventricles of the brain with a catheter, which helps reduce intracranial pressure;
- restoration of damaged blood vessel or removal of neoplasms in case of their detection;
- removal of cranial fragments to reduce intracranial pressure.
Brain edema refers to unpredictable pathologies, so there is no guarantee that the treatment will be effective.
Very dangerous and unpredictable
The swelling of the brain is critical and often results in the death of a person. Damage to the brain tissue caused by this condition leads to serious changes in the state of the body or are completely incompatible with life.
There are only three development options: 
- No consequences and full recovery of the patient .This occurs extremely rarely, in cases when edema occurs in a young and healthy person, for example, with alcohol or other poisoning. If medical care is provided in a timely manner, the violation will not lead to any serious consequences.
- Treatment of edema with partial recovery and disability .This variant is much more common when the cause of edema is meningitis, encephalitis, or craniocerebral trauma. It is not uncommon for cases when defects acquired as a result of a disease are minimal and do not interfere with the full life of the patient.
- The death of the patient caused by the progression of the violation. Such an outcome is possible in about 50 percent of cases. The fluid accumulates in the tissues, which leads to the squeezing of the brain and its deformation, and then to the stopping of breathing and palpitation.
The danger of a violation lies in the fact that it is almost impossible to predict which consequences it will lead in any particular case.
Particular attention to infants
Brain tissue and nervous system in newborns are under development, for this reason, cerebral edema occurs in them differently than in adults. It develops in a matter of minutes and the following factors can serve as reasons:
- consequence of birth injuries;
- presence of intrauterine infections;
- infection with meningitis or meningoencephalitis during labor or later;
- congenital pathology of brain and nervous system development.
Suspicion of edema development may occur on the basis of the following symptoms: 
- occurrence of vomiting;
- inhibited state;
- restless behavior and continuous crying;
- breast failure;
- convulsions;
- swollen a large fontanel even when the child is calm.
Prevent not to die
To prevent the onset of cerebral edema, the following safety measures should be observed: 
- to give up harmful habits: smoking and alcohol abuse;
- to avoid head injuries( to fasten your seat belt in the car, to wear a helmet when riding a bicycle and rollers, etc.);
- to monitor blood pressure;
- to take measures to prevent infectious diseases of the brain;
- normalize weight and eat right;
- timely treat diseases associated with a violation of the circulatory system.
Compliance with these simple rules will help reduce the risk of dangerous pathology.