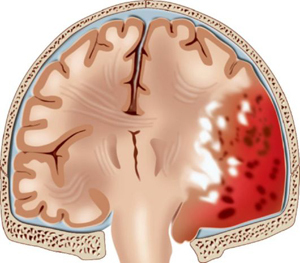
 Epidural brain hematoma is an intracranial accumulation of blood that is located between the inner wall of the skull and the hard shell of the brain, resulting in the squeezing of brain tissue.
Epidural brain hematoma is an intracranial accumulation of blood that is located between the inner wall of the skull and the hard shell of the brain, resulting in the squeezing of brain tissue.
The incidence of this pathology is approximately 1% of all head injuries.
On average, the volume of cerebral hematoma reaches 120 ml, the size of a small hematoma is 30 ml, the size of a large hematoma is 250 ml. The size is approximately 7-8 cm. Epidural hematoma often affects one or two parts of the brain.
The most common lesions occur in the temporal zone and adjacent areas. Such a lesion is characterized by a compacted central part that narrows to the periphery.
Deformation of the dura mater and brain substance is due to the incompressibility of the hematoma. In other words, it exerts pressure on the shell due to its mass, while a dent of a certain size is formed.
The source of bleeding in most cases is an artery with branches, rarely veins and sinuses, and only in exceptional cases - a spongy tissue that is between the inner and outer layers of the skull.
In children who have not reached the age of two, the hard shell of the brain is much more closely fused to the inner surface of the skull than in an adult. That is why such a pathology at this age is practically not found.
Contents
- Main cause - trauma
- Primary cause - trauma
- Differences in epidural and subdural hematomas
- Acute disruption of
- absence of light gap
- Classic version with clear gap
- Acute EG with mild light gap
- Subacute form EG
- Diagnosis of violation
- Approach to therapy
- Prognosis and complications
The main cause is
trauma. Epidural hematoma occurs due to stroke. Thus there is such classification: 
- blow by a small subject on a head;
- header directly on the injured thing.
In addition to the temporal zone, the low-region area is often damaged. When the temporal deformation of the skull is formed, there is a rupture of the vessels, which are directly connected with the hard shell.
This mechanism provokes the development of hematoma and edema of the brain.
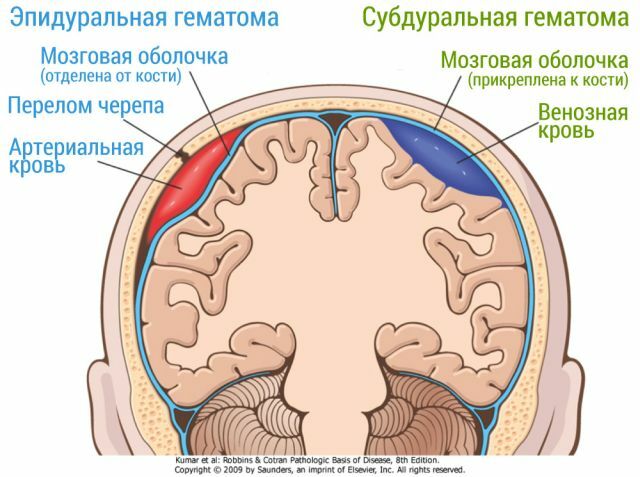
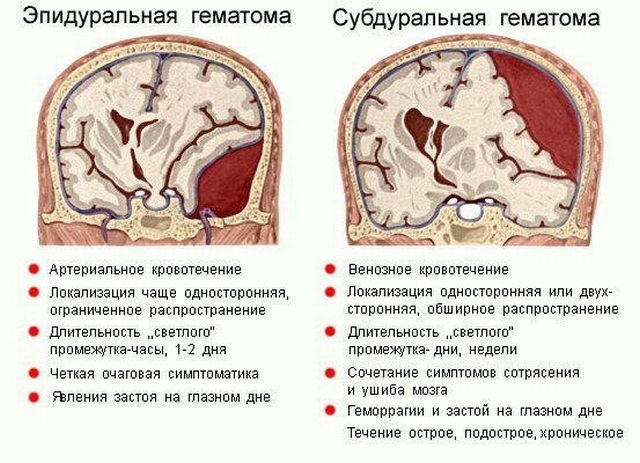
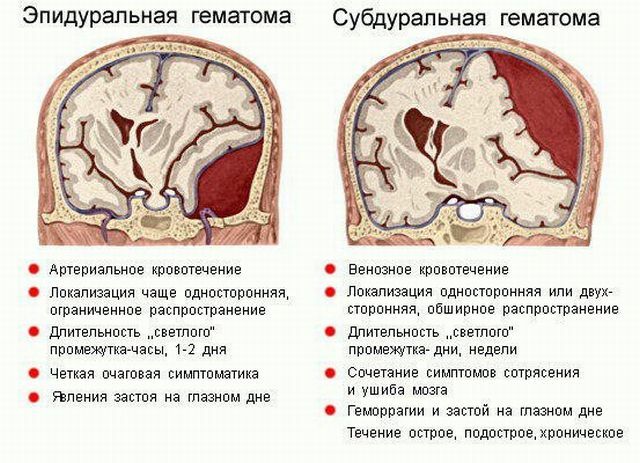
Differences in epidural and subdural hematomas
Subdural hematoma( CG), in contrast to epidural( EG), begins more slowly, this is due to the fact that the rate of venous bleeding is much lower than the rate of arterial bleeding.
Also among other differences can be identified:
- For EG typical of arterial hemorrhage, for SG - venous.
- EG has unilateral localization with limited spread, SG can be either one - or two - sided with extended spread.
- With EH, the light interval lasts one or two days, with the SG it can reach several weeks.
- Symptoms of EG are focal. Symptoms of SG are combined with signs of a bruise and concussion of the brain.
The flow of epidural brain hematoma can be classified according to the forms:
- acute;
- subacute;
- is chronic.
The acute course of the
violation It is customary to distinguish three variants:
- classical with a pronounced light gap;
- with a small bright gap;
- with no clear span.
Absence of light gap
 It is observed in case of acute epidural hematomas after extensive severe injuries provoking serious brain damage.
It is observed in case of acute epidural hematomas after extensive severe injuries provoking serious brain damage.
In this case, the condition of the victim will be stun or coma. There will also be a brain edema.
Positive dynamics will be observed only after surgical intervention. In this state, death may occur.
Classic version with a light gap
This is the most common variant of the development of the violation. The course of EG can be considered according to the following scheme:
- trauma,
- light gap,
- deterioration.
Injuries of varying severity lead to a short-term loss of consciousness, after it returns to the person, and the condition stabilizes, residual sopor, headache and physical weakness are noted.
During this period, amnesia, reflex reflex activity and other symptoms of moderate head injury that cause cerebral edema are possible. In this case, the duration of the light period can be several hours with the subsequent deterioration of the state, which is inherent:
- reactive headache increase;

- multiple episodes of vomiting;
- feeling of insuperable drowsiness;
- change the size of the pupils, for example, they can greatly expand, or be of different sizes;
- no pupillary response to a light stimulus;
- repeated syncope;
- arrhythmia;
- increase in blood pressure.
Hematoma and cerebral edema provoke the onset of a coma, which is characterized by loss of consciousness, a disorder of reflex functions. These processes lead to destabilization of the course of physiological processes that are necessary for normal vital activity.
Acute EG with a small clear gap
This form can be detected with head injuries of severe severity. After a primary syncope, coma may occur, and often disorders of vital functions are noted.
A few hours after coma comes the stunning, while the person becomes relatively able to contact with others. In this case, the light period can last for several hours or days. Then comes a violation of consciousness.
Focal and stem symptoms also worsen, and as a result - paralysis. This condition is characterized as extremely difficult.
Subacute form of EG
The hematoma of this form has some similarity with acute, but it should be noted some differences:
- a light interval occurs approximately 20 minutes after injury and may last more than ten days;
- vital functions remain intact;
- may experience arrhythmia and changes in blood pressure, but not always;
- consciousness does not change or there are signs of mild soporus;
- presence of blood stasis on the fundus.
After a light interval, a violation of consciousness occurs instantly, and goes into a state of stunning - a coma.
Diagnosis of a disorder
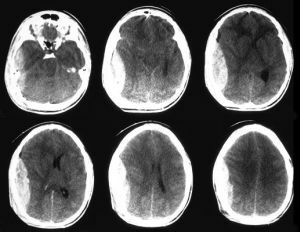 When making a diagnosis, epidural hematoma should be differentiated from subdural. For this, the method of computed tomography is used. In this case, the EG has the form of a biconvex lens, and the SG is a concave crescent shape.
When making a diagnosis, epidural hematoma should be differentiated from subdural. For this, the method of computed tomography is used. In this case, the EG has the form of a biconvex lens, and the SG is a concave crescent shape.
Diagnostics also allows to identify the severity of the process, which is determined by the time interval from the moment of injury, after which the first signs of violation appeared.
Symptomatically EC is diagnosed by the presence of such signs:
- presence of a light gap;
- increased pupil size;
- partial paralysis;
- arrhythmia and high blood pressure;
- pain, localized in a specific place;
- presence of edema of the membrane.
Approach to therapy
After diagnosis, urgent measures are required. Surgery to stop the hematoma is carried out in stages:
- removal of the blood clot by means of an aspirator;
- search for a hemorrhage source and stop bleeding;
- closure of the opening with a flap of skin and stitching.
The effectiveness of surgical intervention directly depends on the time that has passed since the injury and the general well-being of the patient. Sometimes there are cases when the hematoma is formed again, then the operation is performed again.
Conservative treatment is only used when the hematoma is small, does not increase, and there are no signs of compression of the brain tissue. Therapeutic procedures in this case will be conducted in a hospital with strict bed rest and constant medical examination. 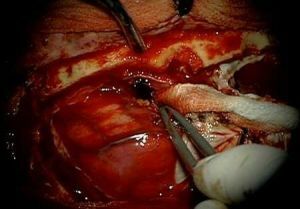
Conservative treatment uses such drugs:
- diuretics;
- haemostatics - to stop bleeding;
- means that promote resorption of the hematoma.
If a person's condition begins to deteriorate, an operation is carried out without delay.
Forecast and complications of
In the case of conservative treatment of small hematomas with minor edema, the percentage of rapid recovery is quite high. With surgical removal of hematomas with moderate decompensation, the prognosis in most cases will be favorable. The percentage of deadly  cases is minimal.
cases is minimal.
However, if epidural hematoma occurs without light gaps, mortality may increase to 25%.If, in addition to the epidural hematoma, a subdural hematoma is found, the prognosis will be much worse, and then the lethality reaches 90%, the same applies to untimely treatment.
In most cases, with adequate and timely initiation of therapy, there are no consequences. Otherwise, a person can die. If the brain is damaged due to a hematoma, complete or partial paralysis can occur.
To preventive measures can be attributed only to the prompt application for medical help immediately after receiving a serious head injury.